MariaDB 数据库管理
章节内容:
- 介绍 MariaDB 数据库
- 部署 MariaDB 数据库
- 实践 MariaDB 中 SQL
- 管理 MariaDB 用户
- 备份和恢复 MariaDB
介绍 MariaDB
数据库介绍
**数据库,是一个存放计算机数据的仓库。**这个仓库是按照一定的数据结构来对数据进行组织和存储的,我们可以通过数据库提供的多种方法来管理其中的数据。
数据结构,是指数据的组织形式或数据之间的联系。
数据库种类
按照早期的数据库理论,比较流行的数据库模型有三种,分别为:
- 层次式数据库,以层次模型建立的数据库,例如文件系统。DNS。
- 网状数据库,以网状模型建立的数据库,例如网络通信。
- 关系型数据库,以二维表模型建议的数据库,例如图书馆管理系统。
在当今的互联网企业中,最常用的数据库模式主要有两种:
- 关系型数据库,把复杂的数据结构归结为简单的二维表形式。在关系型数据库中,对数据的操作几乎全部建立在一个或多个关系表格上,通过对这些关联的表格分类、合并、连接或选取等运算来实现数据库的管理。例如:Oracle、MySql和PostgreSQL等。
- 非关系型数据库 ,也被称为 NoSQL 数据库,本意是"Not Only SQL",而非"NO SQL"的意思,因此,NoSQL的产生并不是要彻底否定关系型数据库,而是作为传统数据库的一个有效补充。典型产品有Redis(持久化缓存)、Mongodb、Memcached(纯内存)等。
关系数据库
关系数据库将结构化数据存储在一组相互关联的表中。 这意味着一个表中的信息可以轻松地与另一表中的信息组合在一起,以处理和提供有关该数据的报告。
关系数据库管理系统(RDBMS-relational database management system)是用于管理关系数据库的软件。大多数关系数据库管理系统都允许您使用结构化查询语言(SQL)查找和管理数据库中的数据。
许多组织使用关系数据库存储业务信息,例如:库存,销售和财务。 关系数据库管理系统在许多应用中起着关键作用。 例如,许多需要支持动态生成内容的Web应用程序都是围绕LAMP(LNMP)解决方案构建:
- Linux 操作系统提供了基本的环境。
- Apache HTTPS Server 或Nginx,提供Web服务器。
- MariaDB ,MySQL 或其他关系数据库,例如PostgreSQL,用于存储站点数据。
- 由 Web 服务器运行的编程语言,例如 PHP,Python,Perl,Ruby,Java,服务器端JavaScript或其他,可以更新数据库中的数据并使用它为用户动态构建网页。
由于关系数据库通常与系统管理员管理的应用程序集成在一起,因此即使您不是数据库管理员,也有必要了解这些服务及其数据的安装和管理知识。
MariaDB 介绍
MariaDB数据库管理系统是MySQL数据库的一个分支,主要由开源社区维护,采用GPL授权许可。开发这个MariaDB数据库分支的可能原因之一是:甲骨文公司收购了MySQL后,有将MySQL闭源的潜在风险,因此MySQL开源社区采用分支的方式来避开这个风险。
MariaDB数据库完全兼容MySQL数据库,包括API和命令行,使之能轻松的成为MySQL的代替品。
MariaDB数据库管理系统可以包含多个database,每个database包涵多张表。
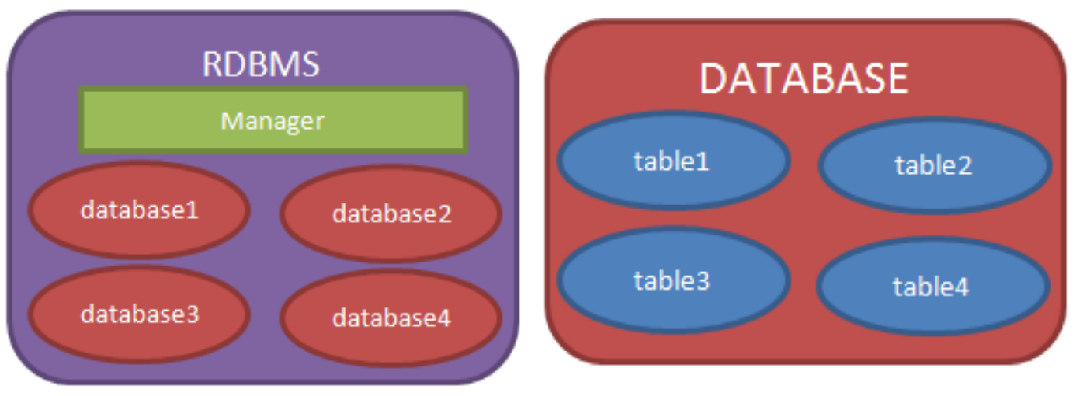
关系数据库的表采用二维表格来存储数据,类似于Excle工作表。
- 表中的一行即为一个元组 ,或称为一条记录。
- 数据表中的每一列称为一个字段(属性),表是由其包含的各种字段定义,每个字段描述了它所含有的数据意义,为每个字段分配一个数据类型,定义它们的数据长度和其他属性。
- 行和列的交叉位置表示某个属性值。
部署 MariaDB
安装 MariaDB
安装
bash
#安装服务端
[root@server ~ 10:12:05]# yum install -y mariadb
#安装客户端
[root@client ~ 10:23:37]# yum install -y mariadb启用并启动服务
bash
systemctl enable -y mariadb --now加固 MariaDB
MariaDB数据库默认具有test 数据库和一些不太安全的配置。运行mysql_secure_installation修改这些配置。
bash
[root@server ~ 10:13:08]# mysql_secure_installation交互式提示您进行更改,包括:
- 为root帐户设置密码。 Y
- 禁止root帐户从本地主机外部访问数据库。Y
- 删除匿名用户帐户。Y
- 删除用于演示的test数据库。 Y
连接 MariaDB
MariaDB客户端可以通过两种方式连接到服务器:
bash
mysql -u root -p 123
mysql -u root -p配置 MariaDB
默认情况下,MariaDB 侦听系统中所有网络地址上3306/TCP端口。
MariaDB 配置文件:
- 主配置文件 /etc/my.cnf
- 辅助配置文件 /etc/my.conf.d/*
/etc/my.cnf.d/server.cnf 文件是数据库服务主要配置。 在该文件的 [mysqld] 块中可以定义以下参数:
- bind-address ,该指令指定MariaDB用来侦听客户端连接的网络地址。 只能输入一个选项。 可能的选项包括:
- 单个IPv4地址。
- 单个IPv6地址。
- ::连接到所有可用地址(IPv6和IPv4)。
- 对于所有IPv4地址,保留为空白(或设置为0.0.0.0)。
- 如果只希望本地客户端访问MariaDB,则可以使用127.0.0.1或**::1**作为网络地址。
- port , 您可以使用此设置指定3306/TCP以外的网络端口。
- skip-networking ,如果在配置文件的[mysqld]部分中设置skip-networking或skip-networking = 1 ,则将禁用网络连接,并且客户端必须使用套接字文件与MariaDB通信。 如果您设置skip-networking = 0(默认值),MariaDB会侦听网络连接。
客户端配置示例:
bash
[root@client ~ 11:34:42]# vim /etc/my.cnf.d/client.cnf
bash
##作用是预设客户端连接参数,避免每次执行 mysql 命令时手动输入主机、端口、用户名和密码
[client-mariadb]
host=10.1.8.10
port=3306
user=ltx
password=123
# database=testMariaDB 中 SQL
描述 SQL
SQL(Structured Query Language),结构化查询语言,是1986年10 月由美国国家标准局颁布的数据库语言。国际标准化组织(ISO)也颁布了SQL国际标准。
结构化查询语言是关系数据库最重要的操作语言,它的影响已经超出数据库领域,得到其他领域的重视和采用,如人工智能领域的数据检索,第四代软件开发工具中嵌入SQL的语言等。
SQL语句可简单分为如下几类:
- 数据查询语言 (DQL:Data Query Language):也称为"数据检索语句",用以从表中获得数据,保留字
SELECTWHERE,ORDER BY,GROUP BY和HAVING。 - 数据操作语言(DML:Data Manipulation Language):其语句包括动词INSERT,UPDATE和DELETE。
- 数据定义语言(DDL):其语句包括动词CREATE和DROP。例如,在数据库中创建新表(CREATE TABLE)、删除表(DROP TABLE),为表添加索引等。
- 事务处理语言(TPL):它的语句能确保被DML语句影响的表的所有行及时得以更新。TPL语句包括BEGIN TRANSACTION,COMMIT和ROLLBACK。
- 数据控制语言(DCL):它的语句通过GRANT或REVOKE获得许可,确定单个用户和用户组对数据库对象的访问。
连接数据库
mariadb 软件包提供了命令mysql,该命令支持对MariaDB数据库的交互式和非交互式访问。
- 交互式执行时,结果以ASCII表的格式显示。
- 非交互执行时,结果以制表符分隔的格式显示。
示例:
bash
[root@mariadb ~ 17:23:11]# mysql -u root -h localhost -p123首次安装时,MariaDB默认设置root用户帐户无需密码即可进行访问。
bash
[root@mariadb ~ 17:23:11]# mysql -uroot执行交互式SQL语句时,MariaDB提示符在方括号中显示您当前选择数据库。
数据库操作
查询数据库列表
bash
MariaDB [(none)]> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| inventory |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
+--------------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)数据库说明:
- mysql 数据库,是一个系统数据库,保存数据库用户及其访问权限等信息。
- INFORMATION_SCHEMA 数据库,保存关于数据库或者数据表的元数据信息。
- **PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA **数据库,保存数据库服务器性能信息。
使用数据库
您可以使用 USE 语句选择数据库之一,例如:USE mysql;,后续默认操作的表属于mysql数据库。
bash
MariaDB [(none)]> use mysql;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
MariaDB [mysql]> SQL语句不区分大小写,但数据库名称区分大小写。 通常的做法是数据库名称全为小写字母,SQL语句全为大写字母,以区分SQL语句与语句的目标或参数。
创建数据库
bash
MariaDB [mysql]> create database ltx;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [mysql]> use ltx;
Database changed
MariaDB [ltx]> 删除数据库
DROP DATABASE 语句删除数据库中的所有表并删除数据库。 这将破坏数据库中的所有数据。 只有对该数据库具有DROP 特权的用户才能运行此语句。 这不会更改数据库的用户特权。 如果重新创建具有该名称的数据库,则为旧数据库设置的用户权限仍然有效。
bash
MariaDB [ltx]> drop database ltx;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)表操作
SQL CRUD操作(create 添加数据 read读取数据 update 修改数据delete删除数据)。
环境准备
bash
# 导入备份
mysql -uroot -predhat -e 'create database inventory;'
mysql -uroot -predhat inventory < inventory.dump查询表
查询表列表
bash
#查询列表
MariaDB [(none)]> USE inventory;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
MariaDB [inventory]> show tables;
+---------------------+
| Tables_in_inventory |
+---------------------+
| category |
| manufacturer |
+---------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)查询表结构
bash
MariaDB [inventory]> DESCRIBE product;
+-----------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-----------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(100) | NO | | NULL | |
| price | double | NO | | NULL | |
| stock | int(11) | NO | | NULL | |
| id_category | int(11) | NO | | NULL | |
| id_manufacturer | int(11) | NO | | NULL | |
+-----------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
6 rows in set (0.008 sec)
MariaDB [inventory]> 输出显示,表格中有六列(属性):
- Field 列,显示该属性名称。
- Type 列,显示该属性的数据必须采用的格式。例如,stock属性必须是最多11位数字的整数。
- Null 列,指示此属性是否可以为null。
- Default 列,指示如果未指定该属性,则是否设置了默认值。
- Key 列 ,显示属性ID是primary key。 主键是表中一行的唯一标识符。 该属性的任何其他行都不能具有相同的值。
- Extra列,提供该列额外信息,对于id字段标记为auto_increment。 这意味着每次将新项目插入表中时,该条目的属性值都会增加。 这样可以更轻松地使数字主键保持唯一。
查询表中数据
查询表中所有记录所有字段
bash
MariaDB [inventory]> SELECT * FROM product;
+----+-------------------+---------+-------+-------------+-----------------+
| id | name | price | stock | id_category | id_manufacturer |
+----+-------------------+---------+-------+-------------+-----------------+
| 1 | ThinkServer TS140 | 539.88 | 20 | 2 | 4 |
| 2 | ThinkServer RD630 | 2379.14 | 20 | 2 | 4 |
| 3 | RT-AC68U | 219.99 | 10 | 1 | 3 |
| 4 | X110 64GB | 73.84 | 100 | 3 | 1 |
+----+-------------------+---------+-------+-------------+-----------------+
4 rows in set (0.004 sec)
MariaDB [inventory]> SELECT * FROM category;
+----+------------+
| id | name |
+----+------------+
| 1 | Networking |
| 2 | Servers |
| 3 | Ssd |
+----+------------+
3 rows in set (0.001 sec)
MariaDB [inventory]> SELECT * FROM manufacturer;
+----+----------+----------------+-------------------+
| id | name | seller | phone_number |
+----+----------+----------------+-------------------+
| 1 | SanDisk | John Miller | +1 (941) 329-8855 |
| 2 | Kingston | Mike Taylor | +1 (341) 375-9999 |
| 3 | Asus | Wilson Jackson | +1 (432) 367-8899 |
| 4 | Lenovo | Allen Scott | +1 (876) 213-4439 |
+----+----------+----------------+-------------------+
4 rows in set (0.001 sec)
MariaDB [inventory]>查询表中所有记录特定字段
bash
MariaDB [inventory]> SELECT name,price,stock FROM product;
+-------------------+---------+-------+
| name | price | stock |
+-------------------+---------+-------+
| ThinkServer TS140 | 539.88 | 20 |
| ThinkServer RD630 | 2379.14 | 20 |
| RT-AC68U | 219.99 | 10 |
| X110 64GB | 73.84 | 100 |
+-------------------+---------+-------+
4 rows in set (0.001 sec)WHERE子句
bash
MariaDB [inventory]> select * from product where price >100;
+----+-------------------+---------+-------+-------------+-----------------+
| id | name | price | stock | id_category | id_manufacturer |
+----+-------------------+---------+-------+-------------+-----------------+
| 1 | ThinkServer TS140 | 539.88 | 20 | 2 | 4 |
| 2 | ThinkServer RD630 | 2379.14 | 20 | 2 | 4 |
| 3 | RT-AC68U | 219.99 | 10 | 1 | 3 |
+----+-------------------+---------+-------+-------------+-----------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)条件操作数
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| = | Equal |
| <> | Not equal. Note: In some versions of SQL, this operator may be written as != |
| > | Greater than |
| < | Less than |
| >= | Greater than or equal |
| <= | Less than or equal |
| BETWEEN | Between an inclusive range |
| LIKE | Search for a pattern |
| IN | Specify multiple possible values for a column |
bash
# 条件操作符包括:=、<>、>、<、>=、<=
MariaDB [inventory]> SELECT * FROM product WHERE price > 100;
# BETWEEN,匹配2个数字之间(包括数字本身)的记录。
MariaDB [inventory]> SELECT * FROM product WHERE id BETWEEN 1 AND 3;
# IN,匹配列表中记录。
MariaDB [inventory]> SELECT * FROM product WHERE id IN (1,3);
MariaDB [inventory]> SELECT * FROM category WHERE name IN ('Servers','Ssd');
# LIKE,用于匹配字符串。%表示一个或多个字符,_表示一个字符,[charlist]表示字符列中的任何单一字符,[^charlist]或者[!charlist]不在字符列中的任何单一字符。
MariaDB [inventory]> SELECT * FROM product WHERE name like '%Server%';
# 逻辑与AND
MariaDB [inventory]> SELECT * FROM product WHERE name like '%RD%' AND price>1000;
# 逻辑或or
MariaDB [inventory]> SELECT * FROM product WHERE name like '%RD%' OR price>500;
# ORDER BY 关键字用于对结果集进行排序。
MariaDB [inventory]> SELECT * FROM product ORDER BY price;
MariaDB [inventory]> SELECT * FROM product ORDER BY price desc;多表查询
bash
# 示例1:产品类型是Servers的产品名称和价格
MariaDB [inventory]> SELECT product.name,product.price
FROM product,category
WHERE product.id_category = category.id
AND category.name='Servers';
# 示例2:查询厂商是Lenovo的产品名称和价格
MariaDB [inventory]> SELECT product.name,product.price
FROM product,manufacturer
WHERE product.id_manufacturer = manufacturer.id
AND manufacturer.name='Lenovo';函数
bash
# 示例1:查询产品价格平均值
MariaDB [inventory]> SELECT avg(price) FROM product;
# 示例2:查询产品价格最大值
MariaDB [inventory]> SELECT max(price) FROM product;
# 示例3:查询产品价格最小值
MariaDB [inventory]> SELECT min(price) FROM product;
# 示例4:查询产品存量
MariaDB [inventory]> SELECT sum(stock) FROM product;
# 示例5:查询产品价格最小值的那个产品信息
MariaDB [inventory]> SELECT min(price) FROM product;
MariaDB [inventory]> SELECT * FROM product WHERE price=73.84;
或者
MariaDB [inventory]> SELECT * FROM product WHERE price=(SELECT min(price) FROM product);
# 示例6:查询Lenovo厂商提供了几种产品
MariaDB [inventory]> SELECT count(product.name)
FROM product,manufacturer
WHERE product.id_manufacturer = manufacturer.id
AND manufacturer.name='Lenovo';
# GROUP BY 语句用于结合聚合函数,根据一个或多个列对结果集进行分组。
MariaDB [inventory]> SELECT id_category,sum(stock) FROM product GROUP BY id_category;创建表
bash
MariaDB [inventory]> CREATE TABLE staff(
id INT(11) NOT NULL,
name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
age INT(11) DEFAULT 10,
id_department INT(11)
);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.017 sec)
MariaDB [inventory]> SHOW TABLES;插入记录
bash
MariaDB [inventory]> INSERT INTO staff (id,name,age,id_department)
VALUES (1,'ltx1',28,10);
MariaDB [inventory]> INSERT INTO staff (id,name,age) VALUES (2,'ltx2',20);
MariaDB [inventory]> INSERT INTO staff (id,name) VALUES (3,'ltx3');更新记录
bash
MariaDB [inventory]> UPDATE staff SET age=20 WHERE id=3;
MariaDB [inventory]> UPDATE staff SET age=111如果使用不带WHERE子句的UPDATE,则表中的所有记录都会更新。
删除记录
bash
MariaDB [inventory]> DELETE FROM staff WHERE id=3 ;
MariaDB [inventory]> DELETE FROM staff ;如果使用不带WHERE子句的DELETE子句,则表中的所有记录都会删除。
删除表
bash
MariaDB [inventory]> DROP TABLE staff ;管理 MariaDB 用户
创建用户账户
默认情况下,MariaDB有自己的用户和密码,与本地系统的用户和密码分开。这意味着MariaDB数据库用户与服务器的Linux用户不同, 即使用户帐户具有相同的名称。
为了控制用户对数据库服务器的访问级别,必须在MariaDB中设置数据库用户并授予他们在服务器及其数据上执行操作的权限。
您可以配置MariaDB使用
pam身份验证插件将系统用户帐户和密码集成为MariaDB数据库用户,本课程不介绍该配置。 在大多数情况下,最好分开管理数据库和系统用户账户。
要创建新用户,您需要以下权限级别之一:
- MariaDB的root用户。
- 被授予全局CREATE USER特权的用户。
- 被授予对mysql数据库的INSERT特权的用户。
我们可以使用CREATE USER语句,在mysql数据库的user表中创建一条新记。
用户名格式:user_name@host_name。 这样就可以根据主机源,创建具有相同名称但具有不同特权的多个用户帐户。
bash
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE USER laoma@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '123';当前,laoma 帐户只能使用密码redhat从**%**连接。
用户的密码,会被加密存在在mysql.user表:
bash
MariaDB [mysql]> SELECT host,user,password FROM user WHERE user = 'laoma';
+-----------+--------+-------------------------------------------+
| host | user | password |
+-----------+--------+-------------------------------------------+
| % | laoma | *84BB5DF4823DA319BBF86C99624479A198E6EEE9 |
+-----------+--------+-------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.000 sec)用户帐户定义示例
| Account | Description |
|---|---|
| laoma或者laoma@'%' | User laoma can connect from any host. |
| laoma@'localhost' | User laoma can only connect from localhost. |
| laoma@'192.168.1.5' | User laoma can only connect from the IP address192.168.1.5. |
| laoma@'192.168.1.%' | User laoma can connect from any address that belongs to the network 192.168.1.0/24. |
| laoma@'2001:db8:18:b51:c32:a21' | User laoma can connect from the IP address 2001:db8:18:b51:c32:a21. |
控制用户权限
默认情况下,新帐户被授予最小特权。 在不授予其他特权的情况下,laoma用户只能访问最少的帐户信息,大多数其他操作均被拒绝。
示例:
bash
[root@mariadb ~ 18:08:14]# mysql -u ltx -p123
MariaDB [(none)]> select user();
+---------------+
| user() |
+---------------+
| ltx@localhost |
+---------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| inventory |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
+--------------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> USE mysql;
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE inventory;privileges是用户在MariaDB中拥有的能力,确定用户可以做什么以及用户在MariaDB中可以做什么。特权按范围进行组织:
-
全局特权 ,用于管理MariaDB数据库服务器本身,例如CREATE USER。
-
数据库特权 ,用于在MariaDB服务器上创建数据库和使用数据库,例如CREATE DATABASE。
-
表特权 ,用于在特定数据库中创建表和处理数据,例如CRUD命令。
CRUD 是指在做计算处理时的增加(Create)、查询(Retrieve)(重新得到数据)、更新(Update)和删除(Delete)几个单词的首字母简写。
-
列特权,用于授予类似表的命令用法,但用于特定的列(通常很少见)。
详情参考本节末尾引用的MariaDB文档。
查询用户权限
bash
MariaDB [(none)]> show grants for root@localhost;
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Grants for root@localhost |
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY PASSWORD '*23AE809DDACAF96AF0FD78ED04B6A265E05AA257' WITH GRANT OPTION |
| GRANT PROXY ON ''@'' TO 'root'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION |
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)授予用户权限
GRANT 语句可用于向帐户授予特权。 要授予GRANT特权,连接的用户必须具有GRANT OPTION 且必须具有他们所授予的特定特权。
例如,laoma用户无法授予数据库表SELECT特权,除非他们已经具有SELECT特权和GRANT OPTION表特权。
在此示例中,MariaDB根用户向清单数据库中类别表上的laoma用户授予CRUD特权。
bash
[root@mariadb ~ 18:11:37]# mysql -uroot -p123
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MariaDB connection id is 20
Server version: 5.5.68-MariaDB MariaDB Server
Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
MariaDB [(none)]> grant select,update,delete,insert
-> on inventory.category
-> to ltx@'%';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
exit验证权限
bash
[root@mariadb ~ 18:14:17]# mysql -u ltx -p123
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MariaDB connection id is 24
Server version: 5.5.68-MariaDB MariaDB Server
Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.授权示例
| Grant | Description |
|---|---|
| GRANT SELECT ON database.table TO username@hostname | Grant SELECT privilege for a specific table in a specific database to a specific user. |
| GRANT SELECT ON database. TO username@hostname* | Grant SELECT privilege for all tables in a specific database to a specific user. |
GRANT SELECT ON *.* TO username@hostname |
Grant SELECT privilege for all tables in all databases to a specific user. |
| GRANT CREATE, ALTER, DROP ON database. to username@hostname* | Grant CREATE, ALTER, and DROP TABLES privileges in a specific database to a specific user. |
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* to username@hostname |
Grant all available privileges for all databases to a specific user, effectively creating a superuser, similar toroot. |
回收用户权限
REVOKE 语句从帐户中删除特权。 连接的用户必须具有GRANT OPTION特权,并且必须具有被撤消的特定特权。
bash
MariaDB [(none)]> REVOKE SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, INSERT
-> ON inventory.category FROM ltx;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.011 sec)删除用户
当不再需要特定的用户帐户时,可以使用DROP USER将其从数据库中删除。
用户名使用**'user'@'host'**格式。
bash
MariaDB [(none)]> drop user ltx;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)如果删除了当前连接的帐户,则在关闭连接之前不会删除该帐户,关闭连接之后才会删除该帐户。
更改用户密码
bash
# root用户修改普通用户账户密码
MariaDB [(none)]> USE mysql;
MariaDB [(mysql)]> UPDATE user SET password=PASSWORD('mypass') WHERE user='laoma' and host='localhost';
# 或者
MariaDB [(none)]> SET PASSWORD FOR 'laoma'@'localhost' = PASSWORD('mypass');
# 普通用户修改自己账户密码
MariaDB [(none)]> SET PASSWORD = PASSWORD('mypass');
MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
#root 与 普通用户对比
#UPDATE user SET password=PASSWORD('mypass') WHERE user='laoma' and host='localhost';
#SET PASSWORD = PASSWORD('mypass');排故数据库访问
下表总结了用户在身份验证和访问方面可能遇到的一些问题,以及可能的原因。
| 问题 | 解决方法 |
|---|---|
| 已授予用户从任何主机进行连接的访问权限,但只能使用数据库服务器本地mysql命令进行连接。 | 如果在配置文件/etc/my.cnf.d/server.cnf中设置了skip-networking,请删除该指令并重新启动服务。 |
| 用户可以与localhost上的任何应用程序连接,但不能远程连接。 | 确保/etc/my.cnf.d/server.cnf中的bind-address配置正确。 确保用户表中包含用户要尝试与其连接的主机的条目。 |
| 用户可以连接,但看不到除information_schema以外的任何数据库。 | 确保已授予用户访问其数据库的权限。 刚创建的用户具有最小权限,会遇到这个问题。 |
| 用户可以连接,但不能创建任何数据库。 | 考虑向用户授予全局CREATE特权(这也授予DROP特权)。 |
| 用户可以连接,但不能读取或写入任何数据。 | 向用户授予他们打算使用的数据库的CRUD特权。 |
忘记 root 用户密码
-
编辑**/etc/my.cnf.d/server.cnf**配置文件,在[mysqld]下添加
skip-grant-tables=1。 -
重启 mariadb 服务。
-
执行
mysql -u root命令进入mysql命令行,修改root用户密码。bash[root@mariadb ~ 18:19:17]# mysql -u root MariaDB [(none)]> UPDATE mysql.user SET password=PASSWORD('新密码') where USER='root'; MariaDB [(none)]> exit -
把**/etc/my.cnf.d/server.cnf配置文件中的
skip-grant-tables=1注释掉,然后重启mariadb**服务。
备份和恢复
备份方式
逻辑备份
逻辑备份,将数据库导出为包含重新创建数据库所需的SQL命令的文本文件。
- 通过查询数据库,检索数据库结构。
- 备份速度较慢,因为服务器必须访问数据库信息并将其转换为逻辑格式。
- 逻辑备份具有高度的可移植性,在某些情况下可以还原到其他数据库提供程序(例如PostgreSQL)。
- 在服务器联机时执行。
- 备份不包括日志或配置文件。
物理备份特征
物理备份,复制原始数据库目录和包含数据库内容的文件。
- 备份可以包括日志和配置文件。
- 仅可移植到具有类似硬件和软件的其他计算机上。
- 比逻辑备份更快。
- 在服务器脱机或数据库中的所有表均已锁定时执行,以防止在备份期间进行更改。
执行备份
执行逻辑备份和还原
您在运行mysqldump 时所连接的MariaDB用户至少需要对转储表具有SELECT 特权,对转储视图至少需要SHOW VIEW ,对于转储触发器至少需要TRIGGER特权。
使用mysqldump命令执行逻辑备份。
语法:
bash
Usage: mysqldump [OPTIONS] database [tables]
OR mysqldump [OPTIONS] --databases [OPTIONS] DB1 [DB2 DB3...]
OR mysqldump [OPTIONS] --all-databases [OPTIONS]
For more options, use mysqldump --help常用选项:
bash
-A, --all-databases Dump all the databases. This will be same as --databases
with all databases selected.
--ignore-database=name
Do not dump the specified database. To specify more than
one database to ignore, use the directive multiple times,
once for each database. Only takes effect when used
together with --all-databases|-A
-B, --databases Dump several databases. Note the difference in usage; in
this case no tables are given. All name arguments are
regarded as database names. 'USE db_name;' will be
included in the output.
-Y, --all-tablespaces
Dump all the tablespaces.
--ignore-table=name Do not dump the specified table. To specify more than one
table to ignore, use the directive multiple times, once
for each table. Each table must be specified with both
database and table names, e.g.,
--ignore-table=database.table.
-y, --no-tablespaces
Do not dump any tablespace information.
--add-drop-database Add a DROP DATABASE before each create.
--add-drop-table Add a DROP TABLE before each create.
-x, --lock-all-tables
Locks all tables across all databases. This is achieved
by taking a global read lock for the duration of the
whole dump. Automatically turns --single-transaction and
--lock-tables off.示例:
bash
#备份
mysqldump -uroot -p123 inventory > inventory.1124.qsl
#删除产品表
mysql
drop table inventory.product;
*********************************************
#恢复
[root@mariadb ~ 18:00:59]# mysql inventory < inventory.1124.sql
#验证
[root@mariadb ~ 18:00:59]# mysql
MariaDB [(none)]> use c;
MariaDB [(MariaDB [(none)]> )]> show tables;
#备份
[root@mariadb ~ 18:19:17]# mysqldump --database mysql inventory > mysql-inentory.sql执行物理备份
mariabackup 工具由AppStream存储库中的mariadb-backup包提供。 mariabackup工具执行MariaDB服务器的完整物理备份。
bash
#停止服务
[root@mariadb ~ 18:22:36]# systemctl stop mariadb
#复制到backup/
[root@mariadb ~ 18:25:30]# cp -a /var/lib/mysql/ /backup/
#模拟/var/lib/mysql/丢失
[root@mariadb ~ 18:25:55]# rm -fr /var/lib/mysql/
#复制回来
[root@mariadb ~ 18:26:20]# cp -a /backup/ /var/lib/mysql
#查询权限
[root@mariadb ~ 18:26:31]# ls -ld /var/lib/mysql
drwxr-xr-x 4 mysql mysql 39 Nov 24 18:25 /var/lib/mysql
#启动服务
[root@mariadb ~ 18:22:36]# systemctl start mariadb