MongoDB 中,索引的叶子节点不存储数据。普通索引的叶子节点不直接存储完整的文档数据,而是存储:
- 索引键的值:即创建索引时指定的字段(或复合字段组合)的值。
- 指向对应文档的位置信息(Record ID):通过这个位置信息,MongoDB 可以快速定位到磁盘上存储的完整文档数据。
例如,对name字段创建单字段索引后,索引的叶子节点会存储类似{"age": 30}和对应的 Record ID,通过 Record ID 才能找到30的完整文档(包含name、address等其他字段)。
cpp
> db.user.find().showRecordId();
{ "_id" : ObjectId("67ed4bc76e8444c140bf255c"), "name" : "张三", "age" : 2, "$recordId" : NumberLong(1) }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("67ed4c026e8444c140bf255d"), "name" : "esther", "age" : 3, "$recordId" : NumberLong(2) }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("67ed4c0a6e8444c140bf255e"), "name" : "eric", "age" : 30, "$recordId" : NumberLong(3) }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("67ed4c116e8444c140bf255f"), "name" : "conca", "age" : 5, "$recordId" : NumberLong(4) }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("67f8ad60a871025470df58cd"), "name" : "masike", "age" : 348, "$recordId" : NumberLong(6) }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("68073c78121462affd1ee0c9"), "name" : "kebi", "age" : 2, "$recordId" : NumberLong(7) }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("681dc7ef24a18a334118bc28"), "name" : "chengxuyuan", "age" : 28, "wages" : 18900, "$recordId" : NumberLong(10) }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6835bd1d860a471c8fd32091"), "name" : "alice", "age" : 28, "$recordId" : NumberLong(12) }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6835bd27860a471c8fd32092"), "name" : "aalice", "age" : 238, "$recordId" : NumberLong(13) }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6835c016860a471c8fd32094"), "name" : "aaice", "age" : 238, "$recordId" : NumberLong(14) }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6835c01b860a471c8fd32095"), "name" : "aaie", "age" : 238, "$recordId" : NumberLong(15) }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6835c29d860a471c8fd32097"), "name" : "aie", "age" : 238, "$recordId" : NumberLong(16) }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6835c2a1860a471c8fd32098"), "name" : "ae", "age" : 238, "$recordId" : NumberLong(17) }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("683863086dcfba9023648241"), "name" : "alice", "age" : 28, "$recordId" : NumberLong(18) }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6846e147740390777600de73"), "name" : "alice", "age" : 28, "$recordId" : NumberLong(20) }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("68498eb5233dd9e7a7031244"), "name" : "alice", "age" : 28, "$recordId" : NumberLong(21) }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6852c35e13d076967b719f22"), "name" : "alice", "age" : 28, "$recordId" : NumberLong(22) }
>> db.user.find({"age": 30)});查询结果
cpp
> db.user.find({"age":30});
{ "_id" : ObjectId("67ed4c0a6e8444c140bf255e"), "name" : "eric", "age" : 30 }
>db.user.find({"age": 30)})是怎么从mongodb数据库找到对应的记录的啊?分析这个sql语句,分析执行计划。
> db.user.find({"age": 30)}).explain();
根据索引字段"age": 30查询数据执行步骤explain()分析结果:
cpp
> db.user.find({"age":30}).explain();
{
"queryPlanner" : {
"plannerVersion" : 1,
"namespace" : "db.user",
"indexFilterSet" : false,
"parsedQuery" : {
"age" : {
"$eq" : 30
}
},
"queryHash" : "3838C5F3",
"planCacheKey" : "041C5DE3",
"winningPlan" : {
"stage" : "FETCH",
"inputStage" : {
"stage" : "IXSCAN",
"keyPattern" : {
"age" : 1
},
"indexName" : "age_1",
"isMultiKey" : false,
"multiKeyPaths" : {
"age" : [ ]
},
"isUnique" : false,
"isSparse" : false,
"isPartial" : false,
"indexVersion" : 2,
"direction" : "forward",
"indexBounds" : {
"age" : [
"[30.0, 30.0]"
]
}
}
},
"rejectedPlans" : [ ]
},
"serverInfo" : {
"host" : "LAPTOP-78C0012V",
"port" : 27018,
"version" : "4.0.7",
"gitVersion" : "nogitversion"
},
"ok" : 1
}> db.user.find({"age": 30)})执行计划是FETCH > IXSCAN。IXSCAN根据索引字段age查找索引,然后再根据索引结果$recordId值FETCH读取整条记录。
IXSCAN为什么快?mongodb默认存储引擎wiredtiger,wiredtiger使用的是B+树存储。索引字段age按照B+树逻辑存储,字段age和$recordId对应关系如下图
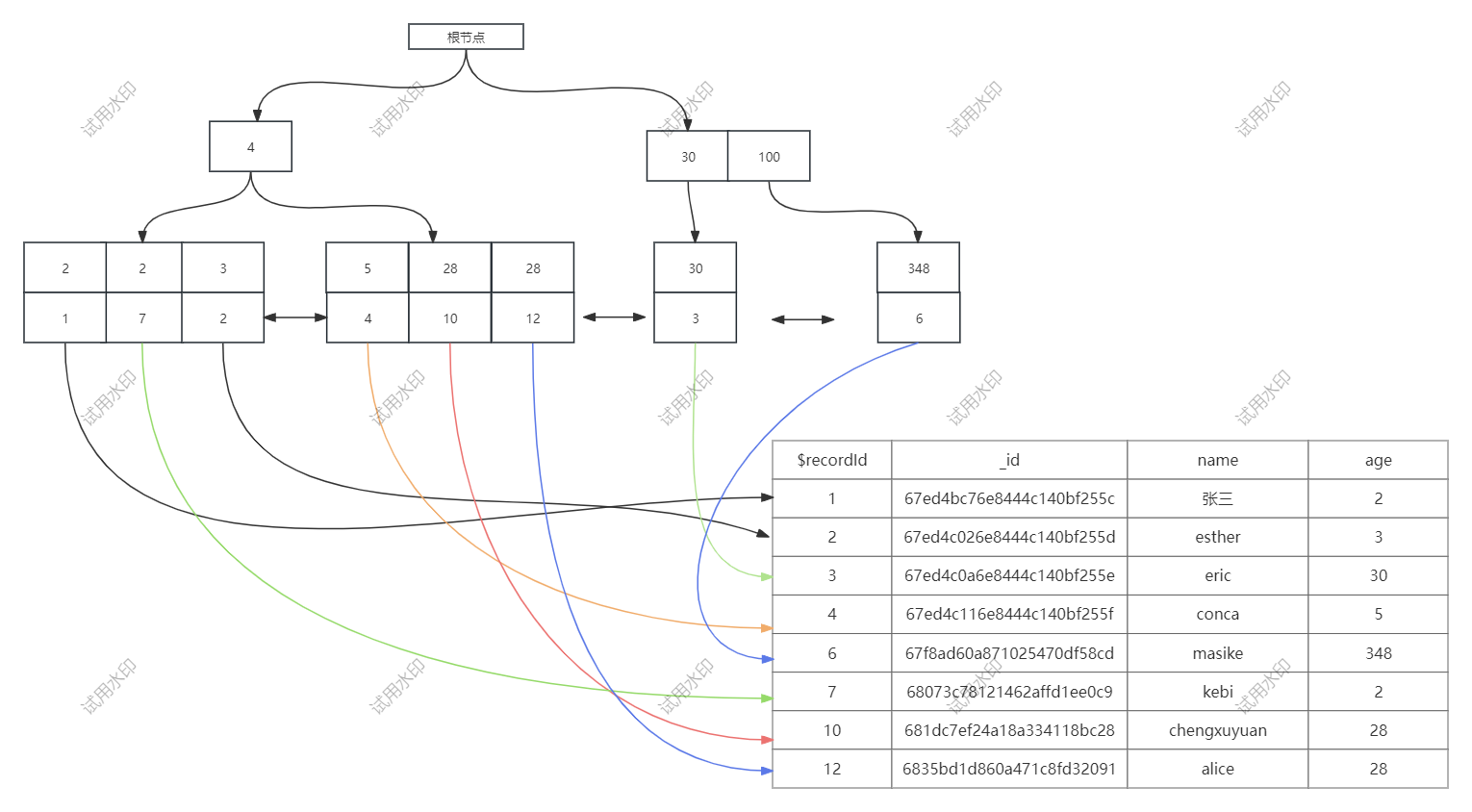
FETCH策略源代码位于mongo/db/exec/fetch.cpp
IXSCAN策略源代码位于mongo/db/exec/index_scan.cpp
> db.user.find({"age": 30)})执行计划是FETCH > IXSCAN,mongo/db/exec/index_scan.cpp根据索引信息获取到age=30对应的recordId值,mongo/db/exec/fetch.cpp再根据recordId获取整体记录内容。
mongo/db/exec/index_scan.cpp这段代码实现了 MongoDB 查询计划中的IXSCAN(索引扫描)执行阶段。它负责与底层索引交互,按照指定的索引范围和过滤条件遍历索引条目,并将符合条件的结果以工作集(WorkingSet)的形式返回给上层查询处理器,源代码如下:
cpp
namespace mongo {
// static
const char* IndexScan::kStageType = "IXSCAN";
IndexScan::IndexScan(OperationContext* opCtx,
IndexScanParams params,
WorkingSet* workingSet,
const MatchExpression* filter)
: RequiresIndexStage(kStageType, opCtx, params.indexDescriptor, workingSet),
_workingSet(workingSet),
_keyPattern(params.keyPattern.getOwned()),
_bounds(std::move(params.bounds)),
_filter(filter),
_direction(params.direction),
_forward(params.direction == 1),
_shouldDedup(params.shouldDedup),
_addKeyMetadata(params.addKeyMetadata),
_startKeyInclusive(IndexBounds::isStartIncludedInBound(params.bounds.boundInclusion)),
_endKeyInclusive(IndexBounds::isEndIncludedInBound(params.bounds.boundInclusion)) {
_specificStats.indexName = params.name;
_specificStats.keyPattern = _keyPattern;
_specificStats.isMultiKey = params.isMultiKey;
_specificStats.multiKeyPaths = params.multikeyPaths;
_specificStats.isUnique = params.indexDescriptor->unique();
_specificStats.isSparse = params.indexDescriptor->isSparse();
_specificStats.isPartial = params.indexDescriptor->isPartial();
_specificStats.indexVersion = static_cast<int>(params.indexDescriptor->version());
_specificStats.collation = params.indexDescriptor->infoObj()
.getObjectField(IndexDescriptor::kCollationFieldName)
.getOwned();
}
boost::optional<IndexKeyEntry> IndexScan::initIndexScan() {
// Perform the possibly heavy-duty initialization of the underlying index cursor.
_indexCursor = indexAccessMethod()->newCursor(getOpCtx(), _forward);
// We always seek once to establish the cursor position.
++_specificStats.seeks;
if (_bounds.isSimpleRange) {
// Start at one key, end at another.
_startKey = _bounds.startKey;
_endKey = _bounds.endKey;
_indexCursor->setEndPosition(_endKey, _endKeyInclusive);
KeyString::Value keyStringForSeek = IndexEntryComparison::makeKeyStringFromBSONKeyForSeek(
_startKey,
indexAccessMethod()->getSortedDataInterface()->getKeyStringVersion(),
indexAccessMethod()->getSortedDataInterface()->getOrdering(),
_forward,
_startKeyInclusive);
return _indexCursor->seek(keyStringForSeek);
} else {
// For single intervals, we can use an optimized scan which checks against the position
// of an end cursor. For all other index scans, we fall back on using
// IndexBoundsChecker to determine when we've finished the scan.
if (IndexBoundsBuilder::isSingleInterval(
_bounds, &_startKey, &_startKeyInclusive, &_endKey, &_endKeyInclusive)) {
_indexCursor->setEndPosition(_endKey, _endKeyInclusive);
auto keyStringForSeek = IndexEntryComparison::makeKeyStringFromBSONKeyForSeek(
_startKey,
indexAccessMethod()->getSortedDataInterface()->getKeyStringVersion(),
indexAccessMethod()->getSortedDataInterface()->getOrdering(),
_forward,
_startKeyInclusive);
return _indexCursor->seek(keyStringForSeek);
} else {
_checker.reset(new IndexBoundsChecker(&_bounds, _keyPattern, _direction));
if (!_checker->getStartSeekPoint(&_seekPoint))
return boost::none;
return _indexCursor->seek(IndexEntryComparison::makeKeyStringFromSeekPointForSeek(
_seekPoint,
indexAccessMethod()->getSortedDataInterface()->getKeyStringVersion(),
indexAccessMethod()->getSortedDataInterface()->getOrdering(),
_forward));
}
}
}
PlanStage::StageState IndexScan::doWork(WorkingSetID* out) {
std::cout << "conca " << " IndexScan doWork..." << std::endl;
// Get the next kv pair from the index, if any.
boost::optional<IndexKeyEntry> kv;
try {
switch (_scanState) {
case INITIALIZING:
kv = initIndexScan();
break;
case GETTING_NEXT:
kv = _indexCursor->next();
break;
case NEED_SEEK:
++_specificStats.seeks;
kv = _indexCursor->seek(IndexEntryComparison::makeKeyStringFromSeekPointForSeek(
_seekPoint,
indexAccessMethod()->getSortedDataInterface()->getKeyStringVersion(),
indexAccessMethod()->getSortedDataInterface()->getOrdering(),
_forward));
break;
case HIT_END:
return PlanStage::IS_EOF;
}
} catch (const WriteConflictException&) {
*out = WorkingSet::INVALID_ID;
return PlanStage::NEED_YIELD;
}
if (kv) {
// In debug mode, check that the cursor isn't lying to us.
if (kDebugBuild && !_startKey.isEmpty()) {
int cmp = kv->key.woCompare(_startKey,
Ordering::make(_keyPattern),
/*compareFieldNames*/ false);
if (cmp == 0)
dassert(_startKeyInclusive);
dassert(_forward ? cmp >= 0 : cmp <= 0);
}
if (kDebugBuild && !_endKey.isEmpty()) {
int cmp = kv->key.woCompare(_endKey,
Ordering::make(_keyPattern),
/*compareFieldNames*/ false);
if (cmp == 0)
dassert(_endKeyInclusive);
dassert(_forward ? cmp <= 0 : cmp >= 0);
}
++_specificStats.keysExamined;
}
if (kv && _checker) {
switch (_checker->checkKey(kv->key, &_seekPoint)) {
case IndexBoundsChecker::VALID:
break;
case IndexBoundsChecker::DONE:
kv = boost::none;
break;
case IndexBoundsChecker::MUST_ADVANCE:
_scanState = NEED_SEEK;
return PlanStage::NEED_TIME;
}
}
if (!kv) {
_scanState = HIT_END;
_commonStats.isEOF = true;
_indexCursor.reset();
return PlanStage::IS_EOF;
}
_scanState = GETTING_NEXT;
if (_shouldDedup) {
++_specificStats.dupsTested;
if (!_returned.insert(kv->loc).second) {
// We've seen this RecordId before. Skip it this time.
++_specificStats.dupsDropped;
return PlanStage::NEED_TIME;
}
}
if (_filter) {
if (!Filter::passes(kv->key, _keyPattern, _filter)) {
return PlanStage::NEED_TIME;
}
}
if (!kv->key.isOwned())
kv->key = kv->key.getOwned();
// We found something to return, so fill out the WSM.
WorkingSetID id = _workingSet->allocate();
WorkingSetMember* member = _workingSet->get(id);
member->recordId = kv->loc;
member->keyData.push_back(IndexKeyDatum(
_keyPattern, kv->key, workingSetIndexId(), getOpCtx()->recoveryUnit()->getSnapshotId()));
_workingSet->transitionToRecordIdAndIdx(id);
if (_addKeyMetadata) {
member->metadata().setIndexKey(IndexKeyEntry::rehydrateKey(_keyPattern, kv->key));
}
*out = id;
return PlanStage::ADVANCED;
}
bool IndexScan::isEOF() {
return _commonStats.isEOF;
}
void IndexScan::doSaveStateRequiresIndex() {
if (!_indexCursor)
return;
if (_scanState == NEED_SEEK) {
_indexCursor->saveUnpositioned();
return;
}
_indexCursor->save();
}
void IndexScan::doRestoreStateRequiresIndex() {
if (_indexCursor)
_indexCursor->restore();
}
void IndexScan::doDetachFromOperationContext() {
if (_indexCursor)
_indexCursor->detachFromOperationContext();
}
void IndexScan::doReattachToOperationContext() {
if (_indexCursor)
_indexCursor->reattachToOperationContext(getOpCtx());
}
std::unique_ptr<PlanStageStats> IndexScan::getStats() {
// WARNING: this could be called even if the collection was dropped. Do not access any
// catalog information here.
// Add a BSON representation of the filter to the stats tree, if there is one.
if (nullptr != _filter) {
BSONObjBuilder bob;
_filter->serialize(&bob);
_commonStats.filter = bob.obj();
}
// These specific stats fields never change.
if (_specificStats.indexType.empty()) {
_specificStats.indexType = "BtreeCursor"; // TODO amName;
_specificStats.indexBounds = _bounds.toBSON();
_specificStats.direction = _direction;
}
std::unique_ptr<PlanStageStats> ret =
std::make_unique<PlanStageStats>(_commonStats, STAGE_IXSCAN);
ret->specific = std::make_unique<IndexScanStats>(_specificStats);
return ret;
}
const SpecificStats* IndexScan::getSpecificStats() const {
return &_specificStats;
}
} mongo/db/exec/index_scan.cpp中IndexScan构造函数,需要指定关键信息:
_indexCursor:底层索引游标,用于实际遍历索引
_bounds:索引扫描的范围边界
_filter:索引键的过滤条件
_direction:扫描方向(正向 / 反向)
_specificStats:存储索引扫描的详细统计信息
mongo/db/exec/index_scan.cpp中IndexScan::initIndexScan()初始化索引,设置索引开始值和结束值,主要是获取_indexCursor游标。创建底层索引游标;根据索引边界类型(简单范围 / 单区间 / 多区间)进行不同的初始化;将游标定位到扫描起始位置;返回第一个匹配的索引条目。
IndexScan::doWork核心方法, 获取索引条目;检查是否在合法边界内;处理重复记录(如果是多键索引);应用过滤条件;构建工作集并返回结果。
根据当前状态获取下一个索引条目:
switch (_scanState) {
case INITIALIZING: kv = initIndexScan(); break;
case GETTING_NEXT: kv = _indexCursor->next(); break;
case NEED_SEEK: kv = _indexCursor->seek(...); break;
case HIT_END: return PlanStage::IS_EOF;
}。
构建并返回工作集成员:
WorkingSetID id = _workingSet->allocate();
WorkingSetMember* member = _workingSet->get(id);
member->recordId = kv->loc;赋值$recordId。
member->keyData.push_back(...);
_workingSet->transitionToRecordIdAndIdx(id);
mongo/db/exec/fetch.cpp这段代码实现了 MongoDB 查询计划中的FETCH(文档获取)执行阶段。它负责接收来自子阶段(通常是索引扫描阶段)的记录 ID(RecordId),从集合中加载完整的文档,并应用最终的过滤条件,最后将符合条件的文档返回给上层处理器,源代码:
cpp
namespace mongo {
using std::unique_ptr;
using std::vector;
// static
const char* FetchStage::kStageType = "FETCH";
FetchStage::FetchStage(OperationContext* opCtx,
WorkingSet* ws,
std::unique_ptr<PlanStage> child,
const MatchExpression* filter,
const Collection* collection)
: RequiresCollectionStage(kStageType, opCtx, collection),
_ws(ws),
_filter(filter),
_idRetrying(WorkingSet::INVALID_ID) {
_children.emplace_back(std::move(child));
}
FetchStage::~FetchStage() {}
bool FetchStage::isEOF() {
if (WorkingSet::INVALID_ID != _idRetrying) {
// We have a working set member that we need to retry.
return false;
}
return child()->isEOF();
}
PlanStage::StageState FetchStage::doWork(WorkingSetID* out) {
std::cout << "conca " << " FetchStage doWork..." << std::endl;
if (isEOF()) {
return PlanStage::IS_EOF;
}
// Either retry the last WSM we worked on or get a new one from our child.
WorkingSetID id;
StageState status;
if (_idRetrying == WorkingSet::INVALID_ID) {
status = child()->work(&id);
} else {
status = ADVANCED;
id = _idRetrying;
_idRetrying = WorkingSet::INVALID_ID;
}
std::cout << "conca " << " FetchStage doWork...id="<< id << std::endl;
if (PlanStage::ADVANCED == status) {
WorkingSetMember* member = _ws->get(id);
// If there's an obj there, there is no fetching to perform.
if (member->hasObj()) {
++_specificStats.alreadyHasObj;
} else {
// We need a valid RecordId to fetch from and this is the only state that has one.
verify(WorkingSetMember::RID_AND_IDX == member->getState());
verify(member->hasRecordId());
std::cout << "conca " << " FetchStage doWork...$RecordId="<< member->recordId<< std::endl;
try {
if (!_cursor)
_cursor = collection()->getCursor(getOpCtx());
if (!WorkingSetCommon::fetch(getOpCtx(), _ws, id, _cursor)) {
_ws->free(id);
return NEED_TIME;
}
} catch (const WriteConflictException&) {
// Ensure that the BSONObj underlying the WorkingSetMember is owned because it may
// be freed when we yield.
member->makeObjOwnedIfNeeded();
_idRetrying = id;
*out = WorkingSet::INVALID_ID;
return NEED_YIELD;
}
}
return returnIfMatches(member, id, out);
} else if (PlanStage::FAILURE == status) {
// The stage which produces a failure is responsible for allocating a working set member
// with error details.
invariant(WorkingSet::INVALID_ID != id);
*out = id;
return status;
} else if (PlanStage::NEED_YIELD == status) {
*out = id;
}
return status;
}
void FetchStage::doSaveStateRequiresCollection() {
if (_cursor) {
_cursor->saveUnpositioned();
}
}
void FetchStage::doRestoreStateRequiresCollection() {
if (_cursor) {
const bool couldRestore = _cursor->restore();
uassert(50982, "could not restore cursor for FETCH stage", couldRestore);
}
}
void FetchStage::doDetachFromOperationContext() {
if (_cursor)
_cursor->detachFromOperationContext();
}
void FetchStage::doReattachToOperationContext() {
if (_cursor)
_cursor->reattachToOperationContext(getOpCtx());
}
PlanStage::StageState FetchStage::returnIfMatches(WorkingSetMember* member,
WorkingSetID memberID,
WorkingSetID* out) {
// We consider "examining a document" to be every time that we pass a document through
// a filter by calling Filter::passes(...) below. Therefore, the 'docsExamined' metric
// is not always equal to the number of documents that were fetched from the collection.
// In particular, we can sometimes generate plans which have two fetch stages. The first
// one actually grabs the document from the collection, and the second passes the
// document through a second filter.
//
// One common example of this is geoNear. Suppose that a geoNear plan is searching an
// annulus to find 2dsphere-indexed documents near some point (x, y) on the globe.
// After fetching documents within geo hashes that intersect this annulus, the docs are
// fetched and filtered to make sure that they really do fall into this annulus. However,
// the user might also want to find only those documents for which accommodationType==
// "restaurant". The planner will add a second fetch stage to filter by this non-geo
// predicate.
++_specificStats.docsExamined;
std::cout << "conca " << " FetchStage returnIfMatches..._specificStats.docsExamined="<< _specificStats.docsExamined << std::endl;
if (Filter::passes(member, _filter)) {
*out = memberID;
return PlanStage::ADVANCED;
} else {
_ws->free(memberID);
return PlanStage::NEED_TIME;
}
}
unique_ptr<PlanStageStats> FetchStage::getStats() {
_commonStats.isEOF = isEOF();
// Add a BSON representation of the filter to the stats tree, if there is one.
if (nullptr != _filter) {
BSONObjBuilder bob;
_filter->serialize(&bob);
_commonStats.filter = bob.obj();
}
unique_ptr<PlanStageStats> ret = std::make_unique<PlanStageStats>(_commonStats, STAGE_FETCH);
ret->specific = std::make_unique<FetchStats>(_specificStats);
ret->children.emplace_back(child()->getStats());
return ret;
}
const SpecificStats* FetchStage::getSpecificStats() const {
return &_specificStats;
}
} // namespace mongomongo/db/exec/fetch.cpp的doWork()核心流程:
检查是否需要重试之前失败的操作;
从子阶段获取记录 ID(RecordId);status = child()->work(&id); // 从子阶段(如IXSCAN)获取RecordId
如果文档尚未加载,则通过游标从集合中获取完整文档;
verify(member->hasRecordId());
if (!WorkingSetCommon::fetch(getOpCtx(), _ws, id, _cursor)) {
_ws->free(id);
return NEED_TIME;
}
调用returnIfMatches应用过滤条件;return returnIfMatches(member, id, out);
总结:
MongoDB 在执行db.user.find({"age": 30})这类索引查询时,并非直接扫描全集合文档,而是通过 **IXSCAN(索引扫描)+ FETCH(文档获取)** 的组合模式高效完成查询。这一过程就像图书馆找书:先通过索引目录(IXSCAN)定位到书籍位置,再到书架上取书(FETCH),而非逐本翻阅。
- B + 树结构:有序存储 + 平衡树特性,查询时间复杂度 O (log n)
- 覆盖索引优化:仅扫描索引数据,避免全文档加载
- 职责分离:IXSCAN 专注索引处理,FETCH 专注文档获取,单一职责原则的典范
- 效率优先:先通过索引筛选缩小范围,再获取必要数据,避免无效 IO