书接上回
上一章,主要介绍了 Spring 通过使用SqlSessionTemplate 这个 SqlSession的门面类,在内部通过动态代理的方式,在创建 真正执行所需的 DefaultSqlSession(Mybatis原生组件) 时,会通过Spring的 事务管理器 *TransactionSynchronizationManager 来获取 ThrealLocal 中 SqlSessionFactory 为key 的 SqlSessionHolder ,同时在 事务环境中 ,会向 Spring 中注册 事务执行的 回调 钩子 SqlSessionSynchronization , 用于管理创建的 SqlSession 的生命周期(在事务完成之后,关闭SqlSession等)
但是这其中也缺失了 关于Spring AOP 以及事务执行管理的介绍 ,以及文章最后提出了问题
像mybatis 这种作为Spring的集成组件,也可以说是下游组件,从代码里也可以看到 相关组件的获取是从TransactionSynchronizationManager中通过ThreadLocal获取的,所以Connection的放入也是Spring先放的,所以 在事务场景下默认情况下,Spring的事务会在 AOP 一开始执行就默认创建好一个 Connection,而不管后续是否真正有使用Connection的需求。这块也会在下面的 源码 解读中会看到源码是怎么处理这块的
最后本文 主要详细梳理下下Spring 事务的执行过程,以及Spring 事务执行过程中,一些关键组件的使用
Spring 事务
Springboot的自动配置
Springboot-autoconfigure 项目中的 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration 配置类如下,可以看到是通过静态类的方式默认引入了 CglibAutoProxyConfiguration 配置,而这个配置又被 @EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = true) 注解标注,所以可以看到Springboot其实还是利用了Spring时期的@EnableXXX注解。下面详细讲解下 @EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = true) 注解
less
@AutoConfiguration
@ConditionalOnClass(PlatformTransactionManager.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(TransactionProperties.class)
public class TransactionAutoConfiguration {
//............ 省略 .................
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnBean(TransactionManager.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration.class)
public static class EnableTransactionManagementConfiguration {
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = false)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop" , name = "proxy-target-class" , havingValue = "false" )
public static class JdkDynamicAutoProxyConfiguration {
}
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = true)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop" , name = "proxy-target-class" , havingValue = "true" ,
matchIfMissing = true)
public static class CglibAutoProxyConfiguration {
}
}
//............ 省略 .................
}@EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = true)
而这个注解最终是通过 @Import (TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector .class) 引入一个实现了
ImportSelector 接口的配置导入类
less
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector.class)
public @interface EnableTransactionManagement {
/**
* Indicate whether subclass-based (CGLIB) proxies are to be created ({ @code true}) as
* opposed to standard Java interface-based proxies ({ @code false}). The default is
* { @code false}. <strong> Applicable only if { @link #mode()} is set to
* { @link AdviceMode#PROXY} </strong> .
* <p> Note that setting this attribute to { @code true} will affect <em> all </em>
* Spring-managed beans requiring proxying, not just those marked with
* { @code @Transactional}. For example, other beans marked with Spring's
* { @code @Async} annotation will be upgraded to subclass proxying at the same
* time. This approach has no negative impact in practice unless one is explicitly
* expecting one type of proxy vs another, e.g. in tests.
*/
boolean proxyTargetClass() default false;
/**
* Indicate how transactional advice should be applied.
* <p><b> The default is { @link AdviceMode#PROXY}. </b>
* Please note that proxy mode allows for interception of calls through the proxy
* only. Local calls within the same class cannot get intercepted that way; an
* { @link Transactional} annotation on such a method within a local call will be
* ignored since Spring's interceptor does not even kick in for such a runtime
* scenario. For a more advanced mode of interception, consider switching this to
* { @link AdviceMode#ASPECTJ}.
*/
AdviceMode mode() default AdviceMode.PROXY;
/**
* Indicate the ordering of the execution of the transaction advisor
* when multiple advices are applied at a specific joinpoint.
* <p> The default is { @link Ordered#LOWEST_PRECEDENCE}.
*/
int order() default Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
}TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector
typescript
@Override
protected String[] selectImports(AdviceMode adviceMode) {
switch (adviceMode) {
case PROXY:
return new String[] {AutoProxyRegistrar.class.getName(),
ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration.class.getName()};
case ASPECTJ:
return new String[] {determineTransactionAspectClass()};
default:
return null;
}
}可以看到注入了两个bean ,
一个是 AutoProxyRegistrar , 这个类主要向容器中注入 InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 这个用于处理 AOP 的BeanPostProcesser ,而一般情况下由于我们系统会添加 AspectJ 风格的注解 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy ,所以系统中最终用于处理AOP的BeanPostProcessor最终是 AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator ,而这个类也是一个BeanPostProcessor,它会在Bean创建时的初始化阶段对Bean的实例进行切面逻辑,这个类也非常重要,会在下面的解析中再次出现
二是向容器中注入配置类 ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration, 这个配置类如下
java
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public class ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration extends AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration {
@Bean(name = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor transactionAdvisor(
TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource, TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor) {
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor advisor = new BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor();
advisor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource);
advisor.setAdvice(transactionInterceptor);
if (this.enableTx != null) {
advisor.setOrder(this.enableTx.<Integer>getNumber( "order" ));
}
return advisor;
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource() {
return new AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource();
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor(TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource) {
TransactionInterceptor interceptor = new TransactionInterceptor();
interceptor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource);
if (this.txManager != null) {
interceptor.setTransactionManager(this.txManager);
}
return interceptor;
}
}可以看到其实主要是向容器中注入了一个 Advisor (一个Advice+PointCut) :
Advisor: BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor
可以看到向这个Advisor中设置了 transactionAttributeSource- 这个类用于解析方法上或者类上关于@Transactional注解原信息,稍微看下注入的这个类的实现类
AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource
csharp
public AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource(boolean publicMethodsOnly) {
this.publicMethodsOnly = publicMethodsOnly;
if (jta12Present || ejb3Present) {
this.annotationParsers = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
this.annotationParsers.add(new SpringTransactionAnnotationParser());
if (jta12Present) {
this.annotationParsers.add(new JtaTransactionAnnotationParser());
}
if (ejb3Present) {
this.annotationParsers.add(new Ejb3TransactionAnnotationParser());
}
}
else {
this.annotationParsers = Collections.singleton(new SpringTransactionAnnotationParser());
}
}可以看到这个类主要是集成了一个 SpringTransactionAnnotationParser 注解解析器,用于处理 @Transactional 注解
另一个就是Advice - TransactionInterceptor 而这个 interceptor 其实就是一个Advice , 而且是一个环绕通知,其实也可以理解,事务本身就是要在一个被包裹的方法中执行,在事务开始前,获取Connection, 并设置commit=false,在事务结束的时候调用commit 或者 rollback. 而这个类也将 使 后面分析的重点,几乎所有的关于事务的逻辑都在这个Advice中。看下这个类的签名,是一个Advice也是一个MethodInterceptor

事务AOP的处理
众所周知,Spring容器在启动的后期,也就是BeanDefinition全都加载完成之后,会进行单例Bean的创建。而Bean的创建会经历 "实例化" ,"属性注入" ,"初始化" 阶段,而众多的 BeanPostProcesser 就会在这个阶段对创建好的Bean做最后的加工,而作为处理 AspectJ 风格的(使用 @Aspect 的切面),以及 @Transactional 注解的方法和类的 BeanPostProcessor 的实现 AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator ,则在其中发挥着重要的作用
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
其继承关系图如下:其中比较重要的 AbstractAutoProxyCreator ,这个类是一个抽象模板类,实现了切面扫描注册, 以及后置的Bean的动态代理生成的逻辑,下面详细分析下这个类
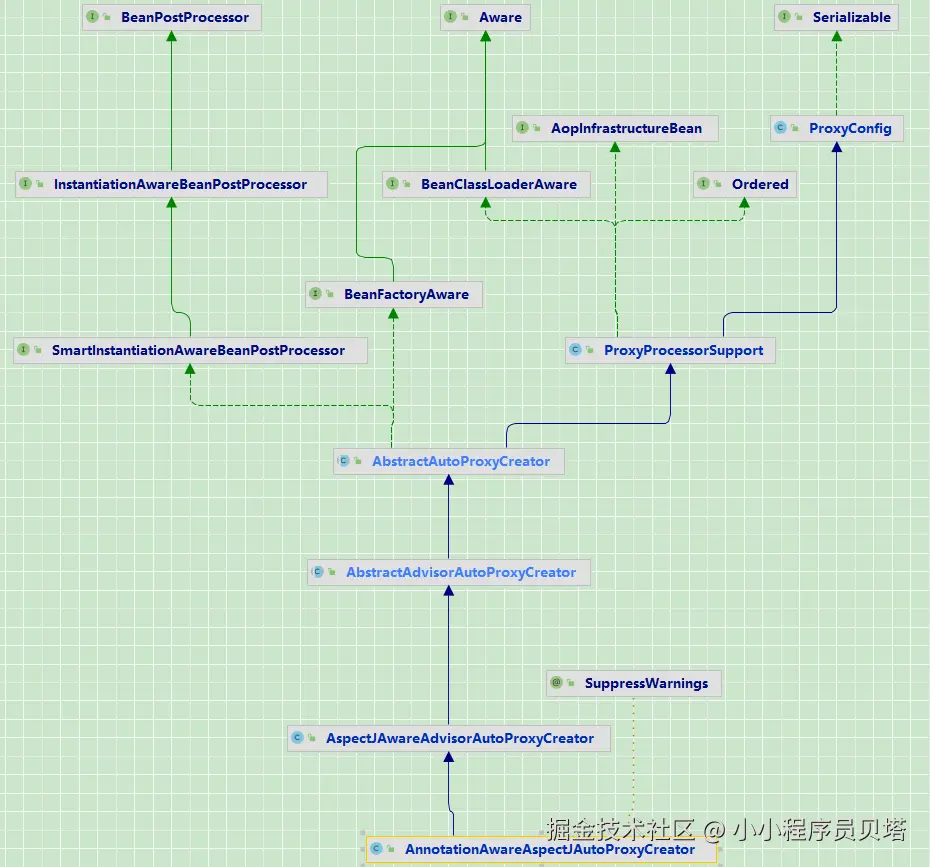
由于其BeanPostProcessor的身份,所以在 org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean
ini
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
//............. 省略若干行代码...............
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
//在这里会进行Bean的初始化,初始化流程中会执行BeanPostProcessor的前置逻辑和后置逻辑处理
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed" , ex);
}
}
//............. 省略若干行代码...............
return exposedObject;
}initializeBean
而在 initializeBean 方法中会执行BeanPostProcessor的前置处理逻辑和后置处理逻辑,而 Advisor的扫描与识别以及组装加载则都是在这个前置处理逻辑中进行的。而后置方法则主要是根据
scss
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed" , ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization
会走到 org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessBeforeInstantiation中
kotlin
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(beanClass, beanName);
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) || !this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
if (this.advisedBeans.containsKey(cacheKey)) {
return null;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return null;
}
}
// Create proxy here if we have a custom TargetSource.
// Suppresses unnecessary default instantiation of the target bean:
// The TargetSource will handle target instances in a custom fashion.
TargetSource targetSource = getCustomTargetSource(beanClass, beanName);
if (targetSource != null) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName)) {
this.targetSourcedBeans.add(beanName);
}
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(beanClass, beanName, targetSource);
Object proxy = createProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource);
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
return null;
}并最终在shouldSkip方法中完成了 Advisor 的扫描 。 一个Advisor = Advice + PointCut . 下面在详细介绍下是如何进行扫描的
typescript
@Override
protected boolean shouldSkip(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
// TODO: Consider optimization by caching the list of the aspect names
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
for (Advisor advisor : candidateAdvisors) {
if (advisor instanceof AspectJPointcutAdvisor &&
((AspectJPointcutAdvisor) advisor).getAspectName().equals(beanName)) {
return true;
}
}
return super.shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName);
}接着在 findCandidateAdvisors() 方法中真正进行Advisor的查找
kotlin
@Override
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {
// Add all the Spring advisors found according to superclass rules.
List<Advisor> advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors();
// Build Advisors for all AspectJ aspects in the bean factory.
if (this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder != null) {
advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors());
}
return advisors;
}说明一下:List <Advisor > advisors = super .findCandidateAdvisors(); 这个类的职责主要是查找spring 内部实现的Advisor . 而 this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors() 主要是查找AspectJ风格的Advisor,下面详细看下
两个方法
super .findCandidateAdvisors() ,最终来到org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelper#findAdvisorBeans 方法,可以看到其实是先从容器中获取Advisor类型的Bean的名称 - org.springframework.transaction.config.internalTransactionAdvisor , 而这个正是前面ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration 配置中的BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor , 剩下的就是通过beanFactory.getBean(name, Advisor.class) 获取Bean实例了
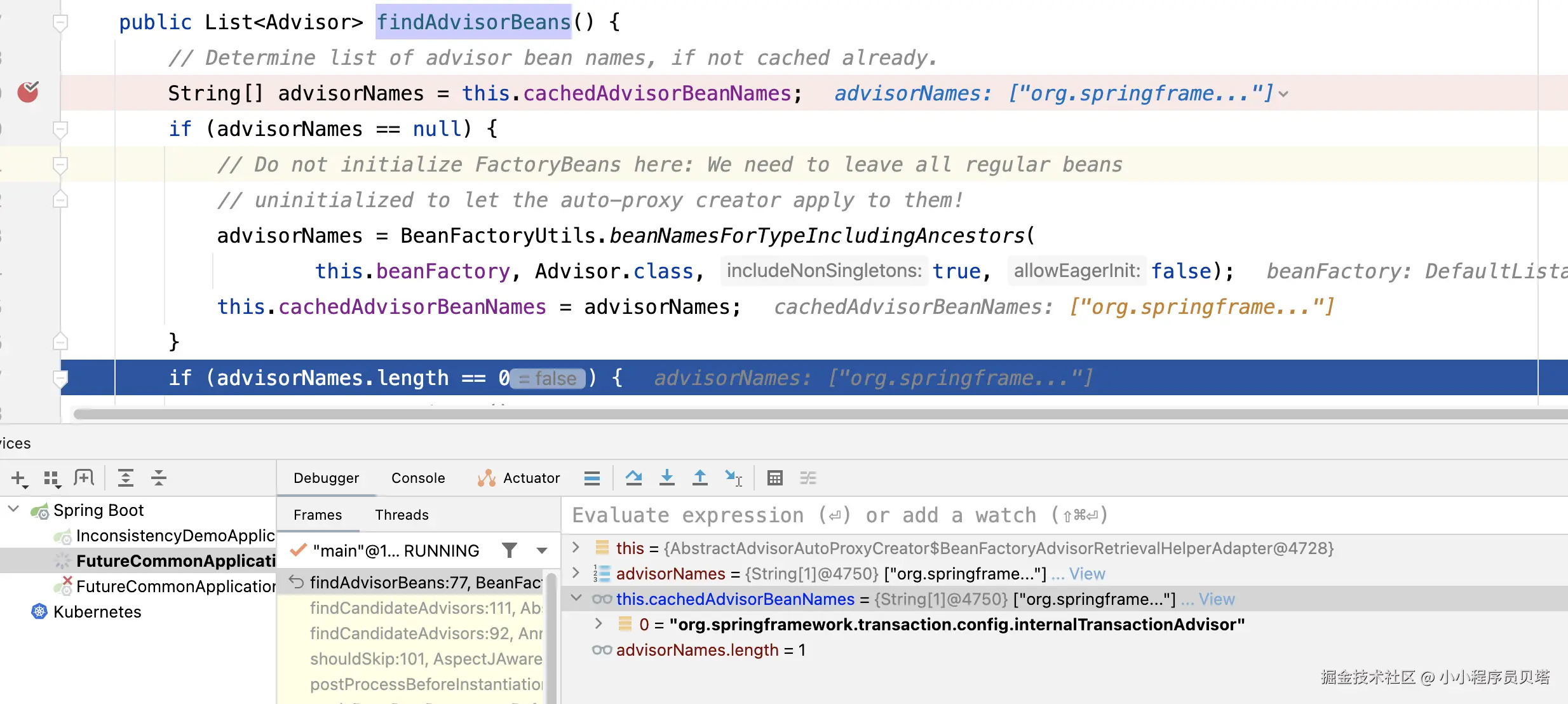
kotlin
public List<Advisor> findAdvisorBeans() {
// Determine list of advisor bean names, if not cached already.
String[] advisorNames = this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames;
if (advisorNames == null) {
// 这里查找所有Advisor类型的Bean的名称
advisorNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Advisor.class, true, false);
this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames = advisorNames;
}
if (advisorNames.length == 0) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String name : advisorNames) {
//这里isEligibleBean 默认返回 True
if (isEligibleBean(name)) {
if (this.beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(name)) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace( "Skipping currently created advisor '" + name + "'" );
}
}
else {
try {
//这里是主要逻辑, 通过BeanFactory.getBean的方式获取指定name的bean实例
advisors.add(this.beanFactory.getBean(name, Advisor.class));
}
// ........ 省略一些异常处理......
}
}
}
return advisors;
}解析完 Spring 内置的 Advisor 之后,开始解析用户自定义 AspectJ 风格的Advisor,也就是我们经常在代码中使用@Aspect 编写的切面逻辑了,这块的主要解析代码在 this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors() 中,下面简单看下这个方法实现 , 在关键处添加了相关注释,并且省略了一些不相干的代码
kotlin
public List<Advisor> buildAspectJAdvisors() {
List<String> aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
synchronized (this) {
aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
aspectNames = new ArrayList<>();
//获取所有的Bean,然后逐个遍历解析是否是 @Aspect 标注的类
String[] beanNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Object.class, true, false);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (!isEligibleBean(beanName)) {
continue;
}
//然后获取这个Bean的Class类型
Class<?> beanType = this.beanFactory.getType(beanName, false);
if (beanType == null) {
continue;
}
//这里判断Class上是否有 @Aspect 注解且不是compiledByAj编译的类
if (this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)) {
aspectNames.add(beanName);
AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName);
if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON) {
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
//这里进行真正解析的地方
List<Advisor> classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors);
}
else {
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
}
advisors.addAll(classAdvisors);
}
else {
//........ 省略若干代码............
}
}
}
this.aspectBeanNames = aspectNames;
return advisors;
}
}
}
//........ 省略若干代码............
return advisors;
}主要看下真正进行解析的地方
List classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);
scss
@Override
public List<Advisor> getAdvisors(MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory) {
Class<?> aspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
String aspectName = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectName();
validate(aspectClass);
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory =
new LazySingletonAspectInstanceFactoryDecorator(aspectInstanceFactory);
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
//这里通过 getAdvisorMethods 方法获取Class中所有非 @PointCut注解标注的方法,
//同时这里方法里指定了切面中通知的顺序, Around->before->after->afterReturn->afterThrowing,以及相同类型的字典的排序
for (Method method : getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass)) {
//这里就是根据方法组装成Advisor的地方
Advisor advisor = getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, 0, aspectName);
if (advisor != null) {
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
//...........................省略若干代码.............
return advisors;
}下面详细看下Advisor advisor = getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, 0, aspectName);是如何解析并组装成Advisor的,可以看到最终是构造了一个InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl实例返回了,所以也可以看到切面中每一个通知方法都是一个Advisor。 下面进入InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl构造函数中详细看下做了什么
kotlin
public Advisor getAdvisor(Method candidateAdviceMethod, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory,
int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName) {
AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut = getPointcut(
candidateAdviceMethod, aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
if (expressionPointcut == null) {
return null;
}
return new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(expressionPointcut, candidateAdviceMethod,
this, aspectInstanceFactory, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName);
}
public InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(AspectJExpressionPointcut declaredPointcut,
Method aspectJAdviceMethod, AspectJAdvisorFactory aspectJAdvisorFactory,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) {
this.declaredPointcut = declaredPointcut;
this.declaringClass = aspectJAdviceMethod.getDeclaringClass();
this.methodName = aspectJAdviceMethod.getName();
this.parameterTypes = aspectJAdviceMethod.getParameterTypes();
this.aspectJAdviceMethod = aspectJAdviceMethod;
this.aspectJAdvisorFactory = aspectJAdvisorFactory;
this.aspectInstanceFactory = aspectInstanceFactory;
this.declarationOrder = declarationOrder;
this.aspectName = aspectName;
if (aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated()) {
// Static part of the pointcut is a lazy type.
Pointcut preInstantiationPointcut = Pointcuts.union(
aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getPerClausePointcut(), this.declaredPointcut);
// Make it dynamic: must mutate from pre-instantiation to post-instantiation state.
// If it's not a dynamic pointcut, it may be optimized out
// by the Spring AOP infrastructure after the first evaluation.
this.pointcut = new PerTargetInstantiationModelPointcut(
this.declaredPointcut, preInstantiationPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
this.lazy = true;
}
else {
// A singleton aspect.
this.pointcut = this.declaredPointcut;
this.lazy = false;
this.instantiatedAdvice = instantiateAdvice(this.declaredPointcut);
}
}其中比较重要的方法是 this.instantiatedAdvice = instantiateAdvice(this.declaredPointcut); 并且最终会走到如下的方法里,可以看到构造了各种Advice.
ini
public Advice getAdvice(Method candidateAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) {
Class<?> candidateAspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
validate(candidateAspectClass);
AspectJAnnotation<?> aspectJAnnotation =
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (aspectJAnnotation == null) {
return null;
}
// If we get here, we know we have an AspectJ method.
// Check that it's an AspectJ-annotated class
if (!isAspect(candidateAspectClass)) {
throw new AopConfigException("Advice must be declared inside an aspect type: " +
"Offending method '" + candidateAdviceMethod + "' in class [" +
candidateAspectClass.getName() + "]");
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Found AspectJ method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);
}
AbstractAspectJAdvice springAdvice;
switch (aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotationType()) {
case AtPointcut:
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Processing pointcut '" + candidateAdviceMethod.getName() + "'");
}
return null;
case AtAround:
springAdvice = new AspectJAroundAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtBefore:
springAdvice = new AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfter:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfterReturning:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterReturningAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterReturning afterReturningAnnotation = (AfterReturning) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterReturningAnnotation.returning())) {
springAdvice.setReturningName(afterReturningAnnotation.returning());
}
break;
case AtAfterThrowing:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterThrowing afterThrowingAnnotation = (AfterThrowing) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing())) {
springAdvice.setThrowingName(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing());
}
break;
default:
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"Unsupported advice type on method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);
}
// Now to configure the advice...
springAdvice.setAspectName(aspectName);
springAdvice.setDeclarationOrder(declarationOrder);
String[] argNames = this.parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (argNames != null) {
springAdvice.setArgumentNamesFromStringArray(argNames);
}
springAdvice.calculateArgumentBindings();
return springAdvice;
}小总结
这样就把 Spring内置Advosor 和 自定义实现的Aspect 切面中的各种通知方法解析成了并缓存起来了
applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization
在before方法中完成了Advisor的识别以及组装工作之后,在after方法中开始对Bean在需要的时候生成代理了

kotlin
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// Create proxy if we have advice.
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}上面的方法思路也很清晰,再次校验一些基础设施Bean和需要跳过的Bean不需要代理,之后就是通过getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean方法获取能用于当前Bean的Advisor , 如果获取到Advisor不为空,则进行创建代理,否则返回原bean
getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean 内部调用了 findEligibleAdvisors 方法,下面详细看下这个方法,思路还是很清晰的,先查找所有的候选Advisor,然后过滤能应用在当前Bean上的Advisor,之后排序,最后返回。逐个来看
ini
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}findCandidateAdvisors 方法 ,可以看到之前在before方法中已经分析过了,就是查找Spring内置的Advisor 和 解析 Aspect 切面方法为Advisor
kotlin
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {
// Add all the Spring advisors found according to superclass rules.
List<Advisor> advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors();
// Build Advisors for all AspectJ aspects in the bean factory.
if (this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder != null) {
advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors());
}
return advisors;
}接着看下 findAdvisorsThatCanApply 方法,最终走到 canApply 方法中, 可以看到逻辑还是比较清晰的,根据Pointcut 的ClassFilter校验是否匹配目标class,之后再根据PointCut的方法匹配器去匹配目标class中所有的方法,看是否匹配,只要有一个方法满足就可以
ini
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null");
if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {
return false;
}
MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher();
if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE) {
// No need to iterate the methods if we're matching any method anyway...
return true;
}
IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null;
if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) {
introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher;
}
Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<>();
if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
classes.add(ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetClass));
}
classes.addAll(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass));
for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz);
for (Method method : methods) {
if (introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null ?
introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions) :
methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}那么接下来来看下对于Spring 内置的Advisor(BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor)来说,Pointcut的实现是TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut,而TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut的实现中,其实不管是ClassFilter 还是MethodMatcher ,最终都是通过TransactionAttributeSource解析类或者方法上有没有
typescript
public class BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor extends AbstractBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor {
@Nullable
private TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource;
private final TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut pointcut = new TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut() {
@Override
@Nullable
protected TransactionAttributeSource getTransactionAttributeSource() {
return transactionAttributeSource;
}
};
/**
* Set the transaction attribute source which is used to find transaction
* attributes. This should usually be identical to the source reference
* set on the transaction interceptor itself.
* @see TransactionInterceptor#setTransactionAttributeSource
*/
public void setTransactionAttributeSource(TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource) {
this.transactionAttributeSource = transactionAttributeSource;
}
/**
* Set the { @link ClassFilter} to use for this pointcut.
* Default is { @link ClassFilter#TRUE}.
*/
public void setClassFilter(ClassFilter classFilter) {
this.pointcut.setClassFilter(classFilter);
}
@Override
public Pointcut getPointcut() {
return this.pointcut;
}
}
java
abstract class TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut extends StaticMethodMatcherPointcut implements Serializable {
protected TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut() {
setClassFilter(new TransactionAttributeSourceClassFilter());
}
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
return (tas == null || tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) != null);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(@Nullable Object other) {
if (this == other) {
return true;
}
if (!(other instanceof TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut)) {
return false;
}
TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut otherPc = (TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut) other;
return ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(getTransactionAttributeSource(), otherPc.getTransactionAttributeSource());
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut.class.hashCode();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return getClass().getName() + ": " + getTransactionAttributeSource();
}
/**
* Obtain the underlying TransactionAttributeSource (may be { @code null}).
* To be implemented by subclasses.
*/
@Nullable
protected abstract TransactionAttributeSource getTransactionAttributeSource();
/**
* { @link ClassFilter} that delegates to { @link TransactionAttributeSource#isCandidateClass}
* for filtering classes whose methods are not worth searching to begin with.
*/
private class TransactionAttributeSourceClassFilter implements ClassFilter {
@Override
public boolean matches(Class<?> clazz) {
if (TransactionalProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz) ||
TransactionManager.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz) ||
PersistenceExceptionTranslator.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
return false;
}
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
return (tas == null || tas.isCandidateClass(clazz));
}
}
}由于我们自定义的Bean(UserService) 上是有事务的注解的,以及有被自定义的aspect切面拦截,所以这里会返回4个Advosir, 见下图,第一个是Spring添加的Interceptor,第二个是用于处理事务的Interceptor ,后面两个是Aspect切面的两个前置通知方法解析而成的Advisor
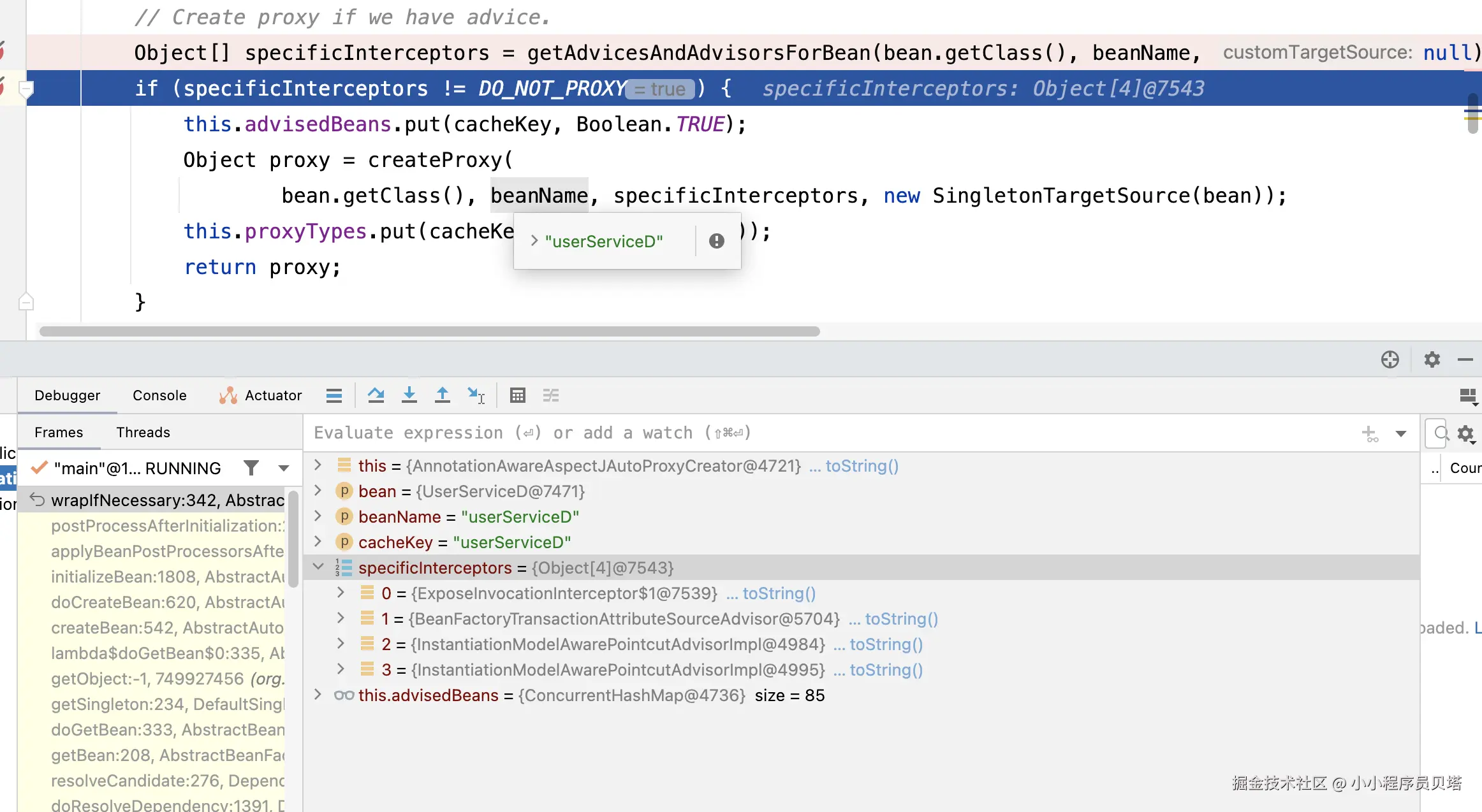
小总结:
从上面的代码中可以看到,spring其实做的事情也没那么复杂,也就是找到容器中所有的候选Advosor,解析工作其实在before方法中也已经处理过一遍了。之后根据这个Advisor中的Pointcut的规则看能否应用在当前的bean上,最终把所有符合的Advisor收集成一个数组,之后就是根据这个Advisor数组来创建代理对象了。
鉴于篇幅,创建代理以及事务Interceptor的执行过程放在下篇中讲解