openGauss + LangChain Agent实战:从自然语言到SQL的智能数据分析助手
大家好,我是Leo哥~~
上周五下午,销售部的小王又来找我了:"Leo哥,能不能帮我查一下上个月销售额超过10万的客户名单?"我看了看自己手头还没写完的代码,叹了口气:"好的,等我十分钟..."
这已经是这周第5次被打断了。作为公司唯一懂SQL的技术,我成了全公司的"人肉SQL查询工具"。运营要数据找我,财务要报表找我,就连HR要统计入职人数也找我...
我突然想:能不能让AI来帮我干这活?让所有人都能用自然语言查数据库?
于是就有了今天这篇文章------用openGauss + LangChain Agent打造一个智能SQL助手,让不懂技术的同事也能自己查数据!
一、业务痛点:为什么需要SQL Agent?
1.1 真实场景:技术人员的日常
让我先给大家还原一下我们公司的真实情况:
场景1 - 销售部小王:
- 需求:查询本月销售额TOP10的客户
- 现状:不会SQL,要找技术部帮忙
- 等待时间:最快30分钟,慢的话半天
- 频率:每周至少3-5次
场景2 - 财务部老李:
- 需求:统计各部门的费用支出明细
- 现状:Excel导出后手动筛选汇总
- 耗时:每次2-3小时
- 频率:每月至少10次
场景3 - 我(研发部部) :
- 现状:每天被各种查询需求打断
- 影响:正常开发进度严重受影响
- 痛苦指数:⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
1.2 传统解决方案的问题
我之前尝试过几种解决方案:
| 方案 | 优点 | 缺点 | 适用性 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 教他们学SQL | 一劳永逸 | 学习成本高,3个月还没学会 | ❌ |
| 做固定报表 | 操作简单 | 需求多变,做不完 | ❌ |
| BI工具 | 界面友好 | 配置复杂,灵活性差 | ⚠️ |
| SQL Agent | 自然语言交互,灵活性强 | 需要技术积累 | ✅ |
🤔 思考:
如果是你的公司,遇到这种情况会怎么解决?是教同事学SQL,还是做个工具让他们自己查?
1.3 SQL Agent的价值
定义:Text-to-SQL Agent是一种基于大语言模型的智能系统,能够将用户的自然语言查询请求转换为SQL语句,并执行返回结果。
Leo哥说人话:就是让AI当你的SQL翻译官 + 执行助手。你用中文说"我要查XXX",AI自动帮你写SQL、执行查询、返回结果,甚至还能画图表!
核心优势:
- 💬 自然语言交互:不需要懂SQL语法,说人话就行
- 🎯 灵活性强:什么查询都能做,不受固定报表限制
- 🚀 响应快:秒级返回结果,不用等技术人员
- 🧠 越用越聪明:历史查询向量化存储,相似问题直接推荐
- 🔒 安全可控:执行前确认,不怕误操作
二、核心架构设计
2.1 系统架构图
先看整体架构,心里有个数:
2.2 核心组件说明
2.2.1 Agent决策层
-
职责:理解用户意图,选择合适的工具
-
实现:LangChain ReAct Agent
-
关键特性:
- 推理(Reasoning):分析用户问题
- 行动(Acting):调用工具解决问题
- 观察(Observing):根据结果调整策略
2.2.2 工具层(Tools)
| 工具名称 | 功能 | 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SQL生成器 | 自然语言→SQL | 用户问题 + 表结构 | SQL语句 |
| SQL执行器 | 执行SQL查询 | SQL语句 | 查询结果 |
| 历史检索器 | 查找相似历史查询 | 用户问题 | 历史SQL推荐 |
| 图表生成器 | 数据可视化 | 查询结果 | 图表链接 |
2.2.3 数据层
业务表:
customers:客户信息表orders:订单表products:商品表order_items:订单明细表
辅助表:
sql_history:存储历史查询的SQL和元数据(使用全文检索优化查询)
2.3 工作流程
sql
openGauss向量检索工具SQL执行工具SQL生成工具Agent用户openGauss向量检索工具SQL执行工具SQL生成工具Agent用户"查询本月销售额TOP10的客户"分析问题检索相似历史查询向量相似度查询返回历史SQLTOP3相似查询生成SQLSELECT语句显示SQL,请求确认确认执行执行SQL执行查询返回结果查询结果展示结果+可视化💭 Leo哥提问:
看到这个架构,你能想到还可以加哪些工具吗?比如数据导出工具、异常检测工具?
三、环境搭建实战
好了,理论讲完了,开始撸代码!
3.1 openGauss-DataVec安装
3.1.1 系统要求
makefile
# 硬件要求
CPU: 2核心以上
内存: 8GB以上
磁盘: 50GB以上
# 操作系统(以下任选其一)
CentOS 7.6+
Ubuntu 20.04+
openEuler 20.03+我这里的机器配置是2c8g的配置,操作系统是centos 7.6。
3.1.2 安装步骤
方式1:使用Docker(推荐)
bash
# 拉取openGauss官方镜像(使用7.0.0-RC1版本)
docker pull opengauss/opengauss:7.0.0-RC1
# 启动容器(注意:必须加 --privileged=true 参数)
docker run --name opengauss \
--privileged=true \
-p 5432:5432 \
-e GS_PASSWORD=Gauss@123 \
-d opengauss/opengauss:7.0.0-RC1
# 等待30秒让数据库初始化完成
sleep 30
# 验证安装
docker exec -it opengauss su - omm -c "gsql -d postgres -p 5432"执行后的效果:

连接成功后,可以执行以下SQL验证版本:
csharp
-- 查看版本信息
SELECT version();你应该看到类似输出:
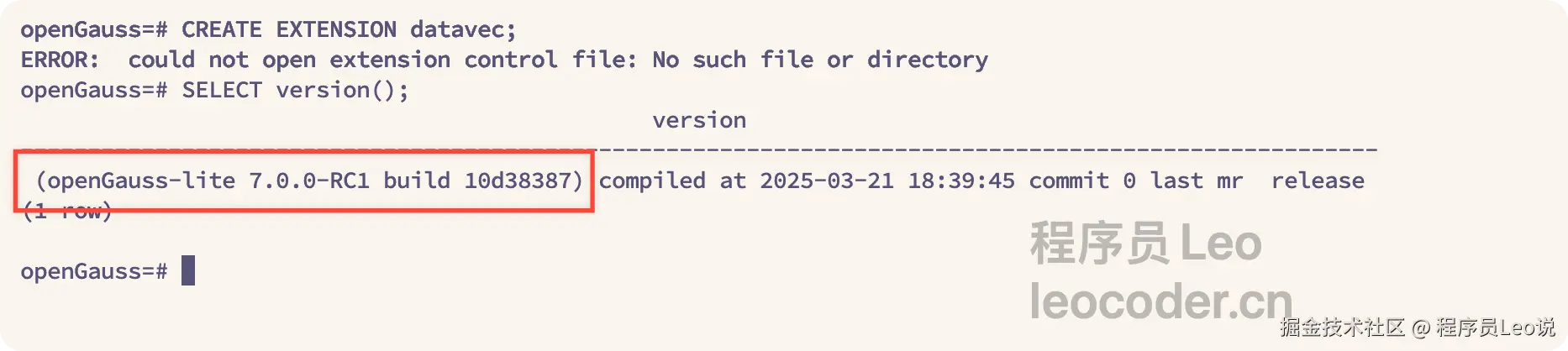
openGauss-lite 7.0.0-RC1 build 10d38387常见问题及解决:
如果遇到连接失败,可以:
- 查看容器日志:
docker logs opengauss --tail 50 - 确认容器正在运行:
docker ps | grep opengauss - 等待更长时间让数据库完成初始化
创建快捷连接别名(可选):
bash
# 在 ~/.bashrc 中添加别名
echo 'alias ogsql="docker exec -it opengauss su - omm -c "gsql -d postgres -p 5432""' >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
# 以后只需输入 ogsql 即可连接
ogsql方式2:二进制安装包
bash
# 下载安装包
wget https://opengauss.org/zh/download/5.0.0/x86_64/openGauss-5.0.0-CentOS-64bit.tar.bz2
# 解压
tar -jxf openGauss-5.0.0-CentOS-64bit.tar.bz2
cd openGauss-5.0.0-CentOS-64bit
# 初始化数据库
gs_initdb -D /opt/gaussdb/data --nodename=single_node -w Gauss@123
# 启动数据库
gs_ctl start -D /opt/gaussdb/data3.1.3 验证数据库功能
sql
-- 查看当前数据库
SELECT current_database();
-- 查看所有数据库
\l
-- 查看版本信息
SELECT version();
-- 测试创建表
CREATE TABLE test_table (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(100)
);
-- 插入测试数据
INSERT INTO test_table (name) VALUES ('测试数据');
-- 查询测试
SELECT * FROM test_table;
-- 删除测试表
DROP TABLE test_table;
3.2 Python环境配置
3.2.1 创建虚拟环境
bash
# 创建虚拟环境
python3 -m venv sql_agent_env
# 激活环境
source sql_agent_env/bin/activate # Linux/Mac
# sql_agent_env\Scripts\activate # Windows
# 升级pip
pip install --upgrade pip3.2.2 安装依赖包
ini
# 核心依赖
pip install langchain==0.1.20
pip install langchain-community==0.0.38
pip install langchain-openai==0.1.7
pip install psycopg2-binary==2.9.9
pip install python-dotenv==1.0.0
pip install pandas==2.1.4
pip install numpy==1.26.4
pip install sentence-transformers==2.5.1
# 可视化相关(可选)
pip install matplotlib==3.8.2
pip install plotly==5.18.0
3.2.3 配置环境变量
创建.env文件:
ini
# .env文件内容
OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
OPENAI_API_BASE=https://api.openai.com/v1 # 如果用其他服务商,修改这里
# 数据库配置
DB_HOST=localhost
DB_PORT=5432
DB_NAME=postgres
DB_USER=omm
DB_PASSWORD=Gauss@123这里我配置的是deepseek的api和秘钥,大家可以选择合适的即可。
目录结构:
bash
sql_agent_project/
├── .env # 环境变量配置
├── requirements.txt # 依赖清单
├── src/
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── database.py # 数据库连接模块
│ ├── text_to_sql.py # SQL生成模块
│ ├── tools.py # Agent工具定义
│ ├── agent.py # Agent主程序
│ └── utils.py # 工具函数
├── data/
│ └── sample_data.sql # 示例数据
└── tests/
└── test_agent.py # 测试用例四、数据库设计实战
4.1 业务表设计
我们以一个电商系统为例,设计几张核心业务表。
🤔 思考时间:
如果让你设计一个电商系统的数据库,你会设计几张表?主要包含哪些字段?
4.1.1 客户表(customers)
sql
-- 创建客户表
CREATE TABLE customers (
customer_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
customer_name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(100) UNIQUE,
phone VARCHAR(20),
city VARCHAR(50),
province VARCHAR(50),
registration_date DATE DEFAULT CURRENT_DATE,
customer_level VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT '普通会员', -- 普通会员、VIP、SVIP
total_purchase_amount DECIMAL(12,2) DEFAULT 0.00,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
-- 创建索引
CREATE INDEX idx_customer_name ON customers(customer_name);
CREATE INDEX idx_city ON customers(city);
CREATE INDEX idx_level ON customers(customer_level);
-- 添加注释
COMMENT ON TABLE customers IS '客户信息表';
COMMENT ON COLUMN customers.customer_level IS '会员等级:普通会员、VIP、SVIP';4.1.2 商品表(products)
sql
-- 创建商品表
CREATE TABLE products (
product_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
product_name VARCHAR(200) NOT NULL,
category VARCHAR(50),
price DECIMAL(10,2) NOT NULL,
stock_quantity INT DEFAULT 0,
supplier VARCHAR(100),
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
updated_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
CREATE INDEX idx_product_name ON products(product_name);
CREATE INDEX idx_category ON products(category);
COMMENT ON TABLE products IS '商品信息表';4.1.3 订单表(orders)
sql
-- 创建订单表
CREATE TABLE orders (
order_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
customer_id INT NOT NULL REFERENCES customers(customer_id),
order_date DATE DEFAULT CURRENT_DATE,
total_amount DECIMAL(12,2) NOT NULL,
status VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT '待付款', -- 待付款、已付款、已发货、已完成、已取消
payment_method VARCHAR(50),
shipping_address TEXT,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
updated_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
CREATE INDEX idx_customer_id ON orders(customer_id);
CREATE INDEX idx_order_date ON orders(order_date);
CREATE INDEX idx_status ON orders(status);
COMMENT ON TABLE orders IS '订单表';
COMMENT ON COLUMN orders.status IS '订单状态:待付款、已付款、已发货、已完成、已取消';4.1.4 订单明细表(order_items)
sql
-- 创建订单明细表
CREATE TABLE order_items (
item_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
order_id INT NOT NULL REFERENCES orders(order_id),
product_id INT NOT NULL REFERENCES products(product_id),
quantity INT NOT NULL,
unit_price DECIMAL(10,2) NOT NULL,
subtotal DECIMAL(12,2) NOT NULL,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
CREATE INDEX idx_order_id ON order_items(order_id);
CREATE INDEX idx_product_id ON order_items(product_id);
COMMENT ON TABLE order_items IS '订单明细表';4.1.5 插入示例数据
sql
-- 插入客户数据
INSERT INTO customers (customer_name, email, phone, city, province, customer_level, total_purchase_amount) VALUES
('张三', 'zhangsan@example.com', '13800138000', '北京', '北京', 'VIP', 150000.00),
('李四', 'lisi@example.com', '13900139000', '上海', '上海', 'SVIP', 280000.00),
('王五', 'wangwu@example.com', '13700137000', '广州', '广东', '普通会员', 35000.00),
('赵六', 'zhaoliu@example.com', '13600136000', '深圳', '广东', 'VIP', 120000.00),
('孙七', 'sunqi@example.com', '13500135000', '杭州', '浙江', '普通会员', 25000.00),
('周八', 'zhouba@example.com', '13400134000', '成都', '四川', 'VIP', 95000.00),
('吴九', 'wujiu@example.com', '13300133000', '武汉', '湖北', '普通会员', 18000.00),
('郑十', 'zhengshi@example.com', '13200132000', '西安', '陕西', 'SVIP', 310000.00);
-- 插入商品数据
INSERT INTO products (product_name, category, price, stock_quantity, supplier) VALUES
('iPhone 15 Pro', '手机', 8999.00, 150, '苹果公司'),
('MacBook Pro 16', '电脑', 19999.00, 80, '苹果公司'),
('小米14 Ultra', '手机', 5999.00, 200, '小米公司'),
('华为Mate 60 Pro', '手机', 6999.00, 180, '华为公司'),
('ThinkPad X1', '电脑', 12999.00, 100, '联想公司'),
('AirPods Pro 2', '耳机', 1899.00, 300, '苹果公司'),
('iPad Air', '平板', 4799.00, 120, '苹果公司'),
('小米手环8', '智能穿戴', 299.00, 500, '小米公司');
-- 插入订单数据(简化版,实际应该更多)
INSERT INTO orders (customer_id, order_date, total_amount, status, payment_method) VALUES
(1, '2024-10-15', 28998.00, '已完成', '支付宝'),
(2, '2024-10-20', 45997.00, '已完成', '微信支付'),
(3, '2024-10-25', 8999.00, '已发货', '支付宝'),
(4, '2024-10-28', 20998.00, '已完成', '信用卡'),
(1, '2024-11-01', 1899.00, '已完成', '支付宝'),
(2, '2024-11-02', 6999.00, '已付款', '微信支付'),
(5, '2024-11-03', 12999.00, '待付款', '支付宝');
-- 插入订单明细
INSERT INTO order_items (order_id, product_id, quantity, unit_price, subtotal) VALUES
(1, 1, 2, 8999.00, 17998.00),
(1, 6, 2, 1899.00, 3798.00),
(2, 2, 1, 19999.00, 19999.00),
(2, 1, 1, 8999.00, 8999.00),
(3, 1, 1, 8999.00, 8999.00),
(4, 4, 2, 6999.00, 13998.00),
(4, 7, 1, 4799.00, 4799.00),
(5, 6, 1, 1899.00, 1899.00),
(6, 4, 1, 6999.00, 6999.00),
(7, 5, 1, 12999.00, 12999.00);4.2 历史查询表设计
这是我们实现智能推荐的关键------存储历史SQL查询,通过全文检索找到相似查询!
4.2.1 SQL历史表设计
sql
-- 创建SQL历史表
CREATE TABLE sql_history (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
user_question TEXT NOT NULL, -- 用户的原始问题
generated_sql TEXT NOT NULL, -- 生成的SQL语句
execution_result TEXT, -- 执行结果(JSON格式)
is_successful BOOLEAN DEFAULT true, -- 执行是否成功
execution_time DECIMAL(6,2), -- 执行耗时(毫秒)
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
user_feedback INT CHECK (user_feedback BETWEEN 1 AND 5), -- 用户评分1-5星
usage_count INT DEFAULT 1 -- 使用次数
);
-- 创建全文检索索引(使用GIN索引,适合全文搜索)
CREATE INDEX idx_question_fts ON sql_history
USING gin(to_tsvector('simple', user_question));
-- 创建其他辅助索引
CREATE INDEX idx_created_at ON sql_history(created_at DESC);
CREATE INDEX idx_is_successful ON sql_history(is_successful);
CREATE INDEX idx_usage_count ON sql_history(usage_count DESC);
-- 添加注释
COMMENT ON TABLE sql_history IS 'SQL查询历史表,存储用户问题和对应的SQL';
COMMENT ON COLUMN sql_history.user_feedback IS '用户反馈评分,1-5星';
COMMENT ON COLUMN sql_history.usage_count IS '使用次数,用于推荐热门查询';Leo哥说人话:
这个历史表就像你的"SQL查询小本本"。每次用户问问题,我们把问题和SQL都存起来。下次有人问类似的问题,用全文检索找到最相关的历史查询,把之前的SQL拿过来参考或直接用,是不是很聪明?
4.2.2 历史查询检索示例
sql
-- 方法1:关键词匹配(简单但有效)
-- 查找包含"销售"和"金额"关键词的历史查询
SELECT
id,
user_question,
generated_sql,
usage_count,
user_feedback
FROM sql_history
WHERE is_successful = true
AND user_question LIKE '%销售%'
AND user_question LIKE '%金额%'
ORDER BY usage_count DESC, user_feedback DESC
LIMIT 3;
-- 方法2:全文检索(更智能)
-- 使用PostgreSQL的全文搜索功能
SELECT
id,
user_question,
generated_sql,
ts_rank(to_tsvector('simple', user_question),
to_tsquery('simple', '销售 & 金额')) AS rank,
usage_count
FROM sql_history
WHERE is_successful = true
AND to_tsvector('simple', user_question) @@ to_tsquery('simple', '销售 & 金额')
ORDER BY rank DESC, usage_count DESC
LIMIT 3;
-- 方法3:根据热度推荐(最常用的查询)
SELECT
id,
user_question,
generated_sql,
usage_count,
user_feedback
FROM sql_history
WHERE is_successful = true
ORDER BY usage_count DESC, user_feedback DESC NULLS LAST
LIMIT 10;五、Text-to-SQL核心实现
这是整个系统的核心中的核心!Text-to-SQL就是把用户的自然语言转换成SQL语句。
5.1 Prompt工程
定义:Prompt Engineering是设计和优化输入提示词,以引导大语言模型生成期望输出的技术。
Leo哥说人话:就是"怎么跟AI说话,让它理解你的意思并给出正确答案"。Prompt就是你给AI的指令,写得好,AI就聪明;写得不好,AI就傻。
5.1.1 Prompt模板设计
一个好的Text-to-SQL Prompt需要包含:
- 角色定位:告诉AI它是谁
- 任务描述:要做什么
- 数据库Schema:有哪些表和字段
- Few-shot示例:给几个例子
- 输出格式:要什么格式的结果
diff
# src/text_to_sql.py
TEXT_TO_SQL_TEMPLATE = """
你是一个专业的SQL专家,擅长根据用户的自然语言问题生成准确的SQL查询语句。
### 数据库Schema
**客户表(customers)**:
- customer_id (INT): 客户ID,主键
- customer_name (VARCHAR): 客户姓名
- email (VARCHAR): 邮箱
- phone (VARCHAR): 电话
- city (VARCHAR): 城市
- province (VARCHAR): 省份
- customer_level (VARCHAR): 会员等级(普通会员、VIP、SVIP)
- total_purchase_amount (DECIMAL): 累计消费金额
- registration_date (DATE): 注册日期
- created_at (TIMESTAMP): 创建时间
**商品表(products)**:
- product_id (INT): 商品ID,主键
- product_name (VARCHAR): 商品名称
- category (VARCHAR): 商品类别
- price (DECIMAL): 价格
- stock_quantity (INT): 库存数量
- supplier (VARCHAR): 供应商
- created_at (TIMESTAMP): 创建时间
**订单表(orders)**:
- order_id (INT): 订单ID,主键
- customer_id (INT): 客户ID,外键关联customers
- order_date (DATE): 下单日期
- total_amount (DECIMAL): 订单总金额
- status (VARCHAR): 订单状态(待付款、已付款、已发货、已完成、已取消)
- payment_method (VARCHAR): 支付方式
- created_at (TIMESTAMP): 创建时间
**订单明细表(order_items)**:
- item_id (INT): 明细ID,主键
- order_id (INT): 订单ID,外键关联orders
- product_id (INT): 商品ID,外键关联products
- quantity (INT): 购买数量
- unit_price (DECIMAL): 单价
- subtotal (DECIMAL): 小计金额
- created_at (TIMESTAMP): 创建时间
### Few-shot示例
**示例1**:
用户问题:查询本月销售额TOP10的客户
SQL语句:
```sql
SELECT
c.customer_name,
SUM(o.total_amount) AS total_sales
FROM customers c
JOIN orders o ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id
WHERE o.order_date >= DATE_TRUNC('month', CURRENT_DATE)
AND o.status IN ('已完成', '已发货')
GROUP BY c.customer_id, c.customer_name
ORDER BY total_sales DESC
LIMIT 10;示例2: 用户问题:统计各省份的VIP客户数量 SQL语句:
vbnet
SELECT
province,
COUNT(*) AS vip_count
FROM customers
WHERE customer_level = 'VIP'
GROUP BY province
ORDER BY vip_count DESC;示例3: 用户问题:查询最近7天内购买了iPhone的客户信息 SQL语句:
vbnet
SELECT DISTINCT
c.customer_name,
c.email,
c.phone,
o.order_date,
o.total_amount
FROM customers c
JOIN orders o ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id
JOIN order_items oi ON o.order_id = oi.order_id
JOIN products p ON oi.product_id = p.product_id
WHERE p.product_name LIKE '%iPhone%'
AND o.order_date >= CURRENT_DATE - INTERVAL '7 days'
ORDER BY o.order_date DESC;生成规则
- 只返回SQL语句,不要有任何解释或额外文字
- SQL语句必须可执行,语法正确
- 考虑性能,尽量使用索引字段
- JOIN时必须指定连接条件
- 日期查询使用DATE_TRUNC或INTERVAL
- 聚合查询必须使用GROUP BY
- 如果不确定,倾向于保守查询(添加更多过滤条件)
- 金额相关查询注意状态过滤(排除已取消订单)
用户问题
{user_question}
历史相似查询(参考)
{similar_queries}
生成的SQL语句(直接输出,不要有其他内容):
"""
python
### 6.2 Few-shot示例构建
Few-shot就是给AI几个例子,让它模仿着生成。
**为什么需要Few-shot?**
- ❌ **Zero-shot**(不给例子):AI可能生成错误的表名、字段名
- ✅ **Few-shot**(给2-5个例子):AI知道你的表结构和查询风格
**如何选择Few-shot示例?**
| 类型 | 示例 | 为什么选它 |
|------|------|-----------|
| 简单查询 | 查询所有VIP客户 | 让AI知道基本的SELECT语法 |
| JOIN查询 | 客户和订单关联 | 展示表之间的关系 |
| 聚合查询 | 统计各省份客户数 | 展示GROUP BY用法 |
| 日期查询 | 查询本月订单 | 展示日期函数用法 |
| 复杂查询 | 多表JOIN+过滤 | 展示综合应用 |
### 6.3 完整代码实现
```python
# src/text_to_sql.py
import os
from typing import List, Dict, Optional
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain.schema import HumanMessage
import psycopg2
from psycopg2.extras import RealDictCursor
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
class TextToSQLGenerator:
"""Text-to-SQL生成器"""
def __init__(self):
"""初始化生成器"""
# 初始化LLM
self.llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-4",
temperature=0, # 设为0,让输出更确定
openai_api_key=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"),
openai_api_base=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_BASE")
)
# 数据库连接
self.db_config = {
'host': os.getenv('DB_HOST', 'localhost'),
'port': int(os.getenv('DB_PORT', 5432)),
'database': os.getenv('DB_NAME', 'postgres'),
'user': os.getenv('DB_USER', 'gaussdb'),
'password': os.getenv('DB_PASSWORD')
}
# Prompt模板
self.prompt_template = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["user_question", "similar_queries"],
template=TEXT_TO_SQL_TEMPLATE
)
def get_similar_queries(self, question: str, top_k: int = 3) -> List[Dict]:
"""
使用全文检索从历史记录中检索相似的查询
Args:
question: 用户问题
top_k: 返回TOP K个最相似的查询
Returns:
相似查询列表
"""
conn = psycopg2.connect(**self.db_config)
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor_factory=RealDictCursor)
try:
# 提取问题中的关键词(简单分词)
# 实际应用中可以使用jieba等分词工具
keywords = question.replace('查询', '').replace('统计', '').replace('的', ' ').strip()
# 方法1:使用全文检索(ts_rank)
query = """
SELECT
user_question,
generated_sql,
ts_rank(
to_tsvector('simple', user_question),
plainto_tsquery('simple', %s)
) AS rank,
usage_count,
user_feedback
FROM sql_history
WHERE is_successful = true
AND to_tsvector('simple', user_question) @@ plainto_tsquery('simple', %s)
ORDER BY rank DESC, usage_count DESC, user_feedback DESC NULLS LAST
LIMIT %s;
"""
cursor.execute(query, (keywords, keywords, top_k))
results = cursor.fetchall()
# 如果全文检索没有结果,使用关键词LIKE模糊匹配
if not results:
# 提取核心关键词(取前3个字符作为关键词)
core_keywords = keywords.split()[:3]
like_conditions = " OR ".join(["user_question LIKE %s" for _ in core_keywords])
fallback_query = f"""
SELECT
user_question,
generated_sql,
0 AS rank,
usage_count,
user_feedback
FROM sql_history
WHERE is_successful = true
AND ({like_conditions})
ORDER BY usage_count DESC, user_feedback DESC NULLS LAST
LIMIT %s;
"""
like_params = [f'%{kw}%' for kw in core_keywords] + [top_k]
cursor.execute(fallback_query, like_params)
results = cursor.fetchall()
return [dict(row) for row in results]
finally:
cursor.close()
conn.close()
def generate_sql(self, user_question: str) -> str:
"""
根据用户问题生成SQL语句
Args:
user_question: 用户的自然语言问题
Returns:
生成的SQL语句
"""
# 1. 检索相似的历史查询
similar_queries = self.get_similar_queries(user_question)
# 2. 构建similar_queries字符串
similar_str = ""
if similar_queries:
similar_str = "\n".join([
f"问题:{q['user_question']}\nSQL:{q['generated_sql']}\n使用次数:{q['usage_count']}"
for q in similar_queries
])
else:
similar_str = "暂无相似历史查询"
# 3. 填充Prompt
prompt = self.prompt_template.format(
user_question=user_question,
similar_queries=similar_str
)
# 4. 调用LLM生成SQL
messages = [HumanMessage(content=prompt)]
response = self.llm(messages)
# 5. 提取SQL(去除markdown代码块标记)
sql = response.content.strip()
if sql.startswith("```sql"):
sql = sql[6:]
if sql.startswith("```"):
sql = sql[3:]
if sql.endswith("```"):
sql = sql[:-3]
return sql.strip()
def save_to_history(
self,
user_question: str,
generated_sql: str,
execution_result: Optional[str] = None,
is_successful: bool = True,
execution_time: Optional[float] = None
):
"""
保存SQL到历史记录
Args:
user_question: 用户问题
generated_sql: 生成的SQL
execution_result: 执行结果
is_successful: 是否执行成功
execution_time: 执行耗时(毫秒)
"""
# 保存到数据库(不再需要生成embedding)
conn = psycopg2.connect(**self.db_config)
cursor = conn.cursor()
try:
# 先检查是否已存在完全相同的问题和SQL
check_query = """
SELECT id, usage_count FROM sql_history
WHERE user_question = %s AND generated_sql = %s;
"""
cursor.execute(check_query, (user_question, generated_sql))
existing = cursor.fetchone()
if existing:
# 如果存在,更新使用次数
update_query = """
UPDATE sql_history
SET usage_count = usage_count + 1,
execution_result = %s,
execution_time = %s
WHERE id = %s;
"""
cursor.execute(update_query, (execution_result, execution_time, existing[0]))
else:
# 如果不存在,插入新记录
insert_query = """
INSERT INTO sql_history
(user_question, generated_sql, execution_result, is_successful, execution_time)
VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s, %s);
"""
cursor.execute(insert_query, (
user_question,
generated_sql,
execution_result,
is_successful,
execution_time
))
conn.commit()
finally:
cursor.close()
conn.close()
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
generator = TextToSQLGenerator()
# 测试生成SQL
question = "查询本月销售额超过5万元的VIP客户"
sql = generator.generate_sql(question)
print(f"用户问题:{question}")
print(f"生成SQL:\n{sql}")💥 Leo哥踩坑:Prompt太简单导致SQL错误
我第一次做Text-to-SQL的时候,Prompt写得特别简单,就是:"根据用户问题生成SQL"。结果AI生成的SQL各种错误:
- 表名写错(users vs customers)
- JOIN条件遗漏
- 日期格式不对
- 聚合函数用错
后来我发现,必须在Prompt里明确告诉AI:
- 数据库有哪些表
- 每个表有哪些字段
- 表之间的关系是什么
- 给几个标准示例
这样AI才能生成正确的SQL。记住:AI不是万能的,需要你给它足够的信息!
六、Agent工具开发
现在我们有了Text-to-SQL功能,接下来要把它封装成Agent的工具。
6.1 SQL执行工具
python
# src/tools.py
from langchain.tools import Tool
from langchain.pydantic_v1 import BaseModel, Field
import psycopg2
from psycopg2.extras import RealDictCursor
import json
import time
from typing import Dict, Any, List
class SQLExecutorInput(BaseModel):
"""SQL执行工具的输入Schema"""
sql: str = Field(description="要执行的SQL语句")
confirm: bool = Field(
default=False,
description="是否已经过用户确认,默认False需要确认"
)
class SQLExecutorTool:
"""SQL执行工具"""
def __init__(self, db_config: Dict[str, Any]):
"""
初始化SQL执行工具
Args:
db_config: 数据库配置
"""
self.db_config = db_config
self.pending_sql = None # 待确认的SQL
def execute_sql(self, sql: str, confirm: bool = False) -> str:
"""
执行SQL语句
Args:
sql: SQL语句
confirm: 是否已确认
Returns:
执行结果的JSON字符串
"""
# 安全检查:禁止执行危险操作
dangerous_keywords = ['DROP', 'DELETE', 'TRUNCATE', 'UPDATE', 'INSERT', 'ALTER']
sql_upper = sql.upper()
for keyword in dangerous_keywords:
if keyword in sql_upper:
return json.dumps({
"success": False,
"error": f"检测到危险操作关键字:{keyword},禁止执行!",
"sql": sql
}, ensure_ascii=False)
# 如果没有确认,先返回SQL让用户确认
if not confirm:
self.pending_sql = sql
return json.dumps({
"success": False,
"need_confirm": True,
"sql": sql,
"message": "请确认是否执行此SQL语句"
}, ensure_ascii=False)
# 执行SQL
start_time = time.time()
conn = psycopg2.connect(**self.db_config)
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor_factory=RealDictCursor)
try:
cursor.execute(sql)
results = cursor.fetchall()
# 计算执行时间
execution_time = (time.time() - start_time) * 1000 # 转换为毫秒
# 转换结果为可序列化格式
results_list = [dict(row) for row in results]
return json.dumps({
"success": True,
"data": results_list,
"row_count": len(results_list),
"execution_time_ms": round(execution_time, 2),
"sql": sql
}, ensure_ascii=False, default=str)
except Exception as e:
return json.dumps({
"success": False,
"error": str(e),
"sql": sql
}, ensure_ascii=False)
finally:
cursor.close()
conn.close()
def as_tool(self) -> Tool:
"""转换为LangChain Tool"""
return Tool(
name="SQL执行器",
description="""
执行SQL查询语句并返回结果。
注意:
1. 只能执行SELECT查询,不能执行增删改操作
2. 执行前需要用户确认
3. 返回结果为JSON格式
输入参数:
- sql: SQL语句(字符串)
- confirm: 是否已确认(布尔值,默认False)
""",
func=lambda x: self.execute_sql(x.get('sql', ''), x.get('confirm', False))
)
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
load_dotenv()
db_config = {
'host': os.getenv('DB_HOST'),
'port': int(os.getenv('DB_PORT')),
'database': os.getenv('DB_NAME'),
'user': os.getenv('DB_USER'),
'password': os.getenv('DB_PASSWORD')
}
executor = SQLExecutorTool(db_config)
# 测试执行SQL
sql = "SELECT * FROM customers LIMIT 5;"
result = executor.execute_sql(sql, confirm=True)
print(result)6.2 历史查询检索工具
python
# src/tools.py (继续)
from langchain.tools import Tool
import psycopg2
from psycopg2.extras import RealDictCursor
import json
from typing import List, Dict
class HistorySearchTool:
"""历史SQL查询检索工具(使用全文检索)"""
def __init__(self, db_config: Dict[str, Any]):
"""
初始化历史检索工具
Args:
db_config: 数据库配置
"""
self.db_config = db_config
def search_similar_queries(self, question: str, top_k: int = 5) -> str:
"""
使用全文检索查找相似的历史查询
Args:
question: 用户问题
top_k: 返回TOP K个结果
Returns:
相似查询的JSON字符串
"""
conn = psycopg2.connect(**self.db_config)
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor_factory=RealDictCursor)
try:
# 提取关键词(简单分词)
keywords = question.replace('查询', '').replace('统计', '').replace('的', ' ').strip()
# 使用全文检索查询
query = """
SELECT
user_question,
generated_sql,
ts_rank(
to_tsvector('simple', user_question),
plainto_tsquery('simple', %s)
) AS rank,
usage_count,
user_feedback,
execution_time,
created_at
FROM sql_history
WHERE is_successful = true
AND to_tsvector('simple', user_question) @@ plainto_tsquery('simple', %s)
ORDER BY rank DESC, usage_count DESC, user_feedback DESC NULLS LAST
LIMIT %s;
"""
cursor.execute(query, (keywords, keywords, top_k))
results = cursor.fetchall()
# 如果全文检索没有结果,使用LIKE模糊匹配
if not results:
core_keywords = keywords.split()[:3]
like_conditions = " OR ".join(["user_question LIKE %s" for _ in core_keywords])
fallback_query = f"""
SELECT
user_question,
generated_sql,
0 AS rank,
usage_count,
user_feedback,
execution_time,
created_at
FROM sql_history
WHERE is_successful = true
AND ({like_conditions})
ORDER BY usage_count DESC, user_feedback DESC NULLS LAST
LIMIT %s;
"""
like_params = [f'%{kw}%' for kw in core_keywords] + [top_k]
cursor.execute(fallback_query, like_params)
results = cursor.fetchall()
# 格式化结果
formatted_results = []
for row in results:
formatted_results.append({
"question": row['user_question'],
"sql": row['generated_sql'],
"relevance_score": float(row['rank']) if row['rank'] else 0, # 相关性分数
"usage_count": row['usage_count'],
"feedback": row['user_feedback'],
"execution_time_ms": float(row['execution_time']) if row['execution_time'] else None
})
return json.dumps({
"success": True,
"results": formatted_results,
"count": len(formatted_results)
}, ensure_ascii=False, default=str)
except Exception as e:
return json.dumps({
"success": False,
"error": str(e)
}, ensure_ascii=False)
finally:
cursor.close()
conn.close()
def as_tool(self) -> Tool:
"""转换为LangChain Tool"""
return Tool(
name="历史查询检索",
description="""
从历史记录中检索相似的SQL查询(使用全文检索)。
可以帮助找到类似问题的解决方案,提高查询准确性。
输入参数:
- question: 用户问题(字符串)
- top_k: 返回结果数量(整数,默认5)
返回:相似查询列表(JSON格式)
""",
func=self.search_similar_queries
)6.3 数据可视化工具
python
# src/tools.py
from langchain.tools import Tool
import json
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
from typing import Dict, Any, List
import os
from datetime import datetime
class DataVisualizationTool:
"""数据可视化工具"""
def __init__(self, output_dir: str = "./charts"):
"""
初始化可视化工具
Args:
output_dir: 图表输出目录
"""
self.output_dir = output_dir
os.makedirs(output_dir, exist_ok=True)
# 设置matplotlib中文字体
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['Arial Unicode MS', 'SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
def create_chart(self, data: List[Dict], chart_type: str = "bar") -> str:
"""
创建图表
Args:
data: 查询结果数据
chart_type: 图表类型(bar/line/pie)
Returns:
图表文件路径
"""
try:
# 转换为DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
if len(df) == 0:
return json.dumps({
"success": False,
"error": "数据为空,无法生成图表"
}, ensure_ascii=False)
# 生成图表文件名
timestamp = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
filename = f"{chart_type}_{timestamp}.png"
filepath = os.path.join(self.output_dir, filename)
# 创建图表
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
if chart_type == "bar":
# 柱状图
x_col = df.columns[0]
y_col = df.columns[1]
plt.bar(df[x_col], df[y_col])
plt.xlabel(x_col)
plt.ylabel(y_col)
plt.title(f"{y_col} by {x_col}")
plt.xticks(rotation=45, ha='right')
elif chart_type == "line":
# 折线图
x_col = df.columns[0]
y_col = df.columns[1]
plt.plot(df[x_col], df[y_col], marker='o')
plt.xlabel(x_col)
plt.ylabel(y_col)
plt.title(f"{y_col} Trend")
plt.xticks(rotation=45, ha='right')
elif chart_type == "pie":
# 饼图
label_col = df.columns[0]
value_col = df.columns[1]
plt.pie(df[value_col], labels=df[label_col], autopct='%1.1f%%')
plt.title(f"{value_col} Distribution")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig(filepath, dpi=100, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close()
return json.dumps({
"success": True,
"chart_path": filepath,
"chart_type": chart_type,
"data_rows": len(df)
}, ensure_ascii=False)
except Exception as e:
return json.dumps({
"success": False,
"error": str(e)
}, ensure_ascii=False)
def as_tool(self) -> Tool:
"""转换为LangChain Tool"""
return Tool(
name="数据可视化",
description="""
将查询结果可视化为图表。
支持柱状图(bar)、折线图(line)、饼图(pie)。
输入参数:
- data: 查询结果数据(字典列表)
- chart_type: 图表类型(bar/line/pie,默认bar)
返回:图表文件路径(JSON格式)
""",
func=lambda x: self.create_chart(x.get('data', []), x.get('chart_type', 'bar'))
)七、完整Agent搭建
有了工具,接下来就是组装成一个完整的Agent!
7.1 Agent核心代码
python
# src/agent.py
import os
from typing import List, Optional
from langchain.agents import AgentExecutor, create_react_agent
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from text_to_sql import TextToSQLGenerator
from tools import SQLExecutorTool, HistorySearchTool, DataVisualizationTool
load_dotenv()
class SQLAgent:
"""SQL Agent主类"""
def __init__(self):
"""初始化Agent"""
# 数据库配置
self.db_config = {
'host': os.getenv('DB_HOST', 'localhost'),
'port': int(os.getenv('DB_PORT', 5432)),
'database': os.getenv('DB_NAME', 'postgres'),
'user': os.getenv('DB_USER', 'gaussdb'),
'password': os.getenv('DB_PASSWORD')
}
# 初始化Text-to-SQL生成器
self.sql_generator = TextToSQLGenerator()
# 初始化工具
self.sql_executor = SQLExecutorTool(self.db_config)
self.history_searcher = HistorySearchTool(self.db_config) # 不再需要embedding函数
self.visualizer = DataVisualizationTool()
# 构建工具列表
self.tools = [
self.sql_executor.as_tool(),
self.history_searcher.as_tool(),
self.visualizer.as_tool()
]
# 初始化LLM
self.llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-4",
temperature=0.1,
openai_api_key=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"),
openai_api_base=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_BASE")
)
# 创建Agent Prompt
self.agent_prompt = self._create_agent_prompt()
# 创建Agent
self.agent = create_react_agent(
llm=self.llm,
tools=self.tools,
prompt=self.agent_prompt
)
# 创建对话记忆
self.memory = ConversationBufferMemory(
memory_key="chat_history",
return_messages=True
)
# 创建Agent执行器
self.agent_executor = AgentExecutor(
agent=self.agent,
tools=self.tools,
memory=self.memory,
verbose=True, # 显示详细执行过程
max_iterations=10, # 最大迭代次数
handle_parsing_errors=True # 处理解析错误
)
def _create_agent_prompt(self) -> PromptTemplate:
"""创建Agent提示词模板"""
template = """
你是一个专业的SQL助手Agent,帮助用户通过自然语言查询数据库。
## 你的能力
1. **理解自然语言**:理解用户用中文或英文提出的数据查询需求
2. **生成SQL**:根据数据库结构生成准确的SQL查询语句
3. **执行查询**:安全地执行SQL并返回结果
4. **数据可视化**:将查询结果转化为直观的图表
5. **历史推荐**:从历史查询中找到相似的问题和解决方案
## 工作流程
1. **理解问题**:仔细理解用户想要查询什么数据
2. **检索历史**:先查看是否有类似的历史查询可以参考
3. **生成SQL**:如果没有现成的,就生成新的SQL语句
4. **用户确认**:展示SQL给用户确认
5. **执行查询**:用户确认后执行SQL
6. **展示结果**:格式化展示查询结果
7. **可视化(可选)**:如果数据适合可视化,询问用户是否需要生成图表
## 可用工具
{tools}
## 工具说明
- SQL执行器:执行SELECT查询,返回JSON格式结果
- 历史查询检索:查找相似的历史查询记录
- 数据可视化:生成柱状图、折线图、饼图
## 注意事项
1. **安全第一**:只执行SELECT查询,禁止DELETE/DROP等危险操作
2. **用户确认**:执行SQL前必须让用户确认
3. **错误处理**:如果SQL执行失败,分析原因并重新生成
4. **清晰沟通**:用中文和用户交流,解释每一步在做什么
## 对话历史
{chat_history}
## 用户问题
{input}
## 思考过程(Thought/Action/Observation循环)
{agent_scratchpad}
"""
return PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["input", "chat_history", "agent_scratchpad", "tools"],
template=template
)
def chat(self, user_input: str) -> str:
"""
与Agent对话
Args:
user_input: 用户输入
Returns:
Agent回复
"""
try:
# Step 1: 检索历史查询(可选)
similar_queries_result = self.history_searcher.search_similar_queries(user_input)
# Step 2: 生成SQL
sql = self.sql_generator.generate_sql(user_input)
# Step 3: 显示SQL并请求确认
print(f"\n📝 生成的SQL语句:\n{sql}\n")
confirm = input("是否执行此SQL?(y/n): ").strip().lower()
if confirm != 'y':
return "❌ 已取消执行"
# Step 4: 执行SQL
result = self.sql_executor.execute_sql(sql, confirm=True)
# Step 5: 保存到历史
self.sql_generator.save_to_history(
user_question=user_input,
generated_sql=sql,
execution_result=result,
is_successful=True
)
# Step 6: 格式化返回结果
import json
result_dict = json.loads(result)
if result_dict.get("success"):
data = result_dict.get("data", [])
row_count = result_dict.get("row_count", 0)
execution_time = result_dict.get("execution_time_ms", 0)
response = f"\n✅ 查询成功!\n"
response += f"📊 返回 {row_count} 条记录\n"
response += f"⏱️ 执行耗时:{execution_time}ms\n\n"
response += f"结果:\n{json.dumps(data, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)}\n"
# Step 7: 询问是否需要可视化
if row_count > 0 and row_count <= 100:
viz = input("\n是否生成可视化图表?(y/n): ").strip().lower()
if viz == 'y':
chart_result = self.visualizer.create_chart(data, "bar")
chart_dict = json.loads(chart_result)
if chart_dict.get("success"):
response += f"\n📈 图表已生成:{chart_dict.get('chart_path')}"
return response
else:
return f"\n❌ 查询失败:{result_dict.get('error')}"
except Exception as e:
return f"\n❌ 发生错误:{str(e)}"
def run_interactive(self):
"""交互式运行"""
print("\n" + "="*60)
print("🤖 openGauss SQL Agent 启动成功!")
print("="*60)
print("\n💡 使用提示:")
print("- 直接输入自然语言问题,比如:查询本月销售额TOP10的客户")
print("- 输入 'quit' 或 'exit' 退出")
print("- 输入 'help' 查看帮助\n")
while True:
try:
user_input = input("\n👤 你:").strip()
if not user_input:
continue
if user_input.lower() in ['quit', 'exit', '退出']:
print("\n👋 再见!")
break
if user_input.lower() == 'help':
print("\n📖 帮助信息:")
print("1. 查询示例:查询本月销售额超过5万的客户")
print("2. 统计示例:统计各省份的VIP客户数量")
print("3. 分析示例:分析最近30天的销售趋势")
continue
# 执行查询
response = self.chat(user_input)
print(f"\n🤖 Agent:{response}")
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("\n\n👋 再见!")
break
except Exception as e:
print(f"\n❌ 错误:{str(e)}")
# 主程序入口
if __name__ == "__main__":
agent = SQLAgent()
agent.run_interactive()7.2 简化版:直接对话接口
如果你不需要复杂的Agent框架,也可以用简化版:
python
# src/simple_chat.py
from text_to_sql import TextToSQLGenerator
from tools import SQLExecutorTool
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import json
load_dotenv()
def simple_chat():
"""简化版的SQL对话接口"""
# 初始化
db_config = {
'host': os.getenv('DB_HOST'),
'port': int(os.getenv('DB_PORT')),
'database': os.getenv('DB_NAME'),
'user': os.getenv('DB_USER'),
'password': os.getenv('DB_PASSWORD')
}
generator = TextToSQLGenerator()
executor = SQLExecutorTool(db_config)
print("\n🤖 简易SQL Agent启动!\n")
while True:
question = input("你的问题(输入quit退出):").strip()
if question.lower() in ['quit', 'exit']:
break
try:
# 生成SQL
sql = generator.generate_sql(question)
print(f"\n生成SQL:\n{sql}\n")
# 执行
confirm = input("执行?(y/n): ").strip().lower()
if confirm == 'y':
result = executor.execute_sql(sql, confirm=True)
result_dict = json.loads(result)
if result_dict.get("success"):
print(f"\n✅ 成功!返回{result_dict.get('row_count')}条记录")
print(json.dumps(result_dict.get('data'), ensure_ascii=False, indent=2))
# 保存历史
generator.save_to_history(question, sql, result, True)
else:
print(f"\n❌ 失败:{result_dict.get('error')}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"\n❌ 错误:{str(e)}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
simple_chat()八、实战演示
好了,代码都写完了,让我们来测试一下效果!
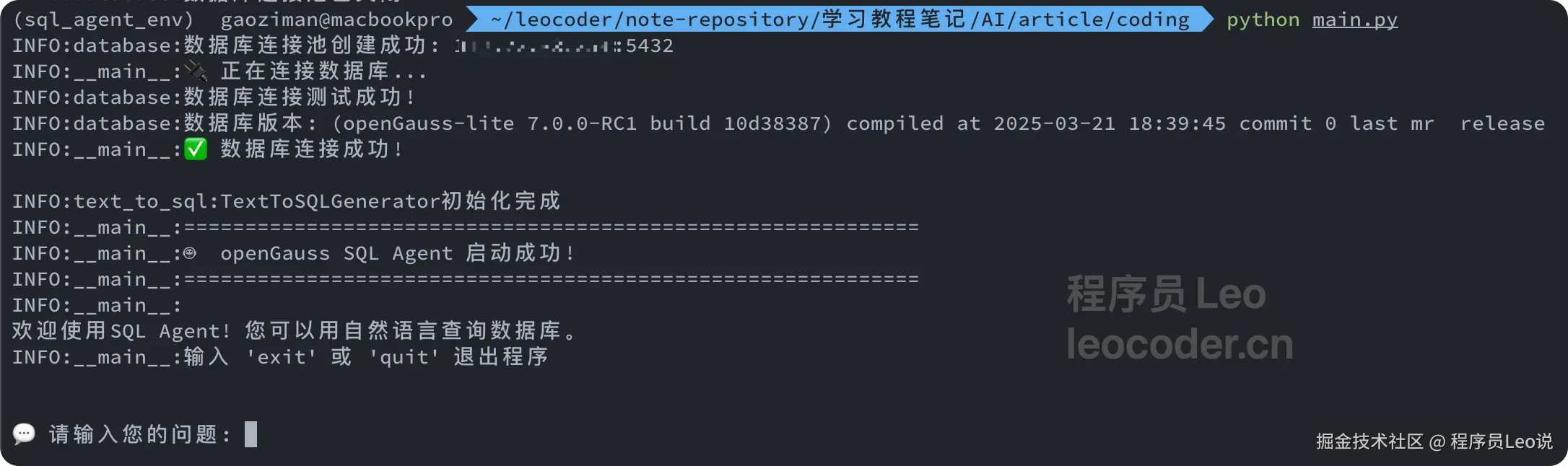
首先启动项目,可以看到,数据库连接成功。
8.1 简单查询测试
场景1:查询VIP客户
vbnet
💬 请输入您的问题: 查询所有VIP客户的姓名和总消费金额
INFO:__main__:
============================================================
INFO:__main__:🔍 正在处理问题: 查询所有VIP客户的姓名和总消费金额
INFO:__main__:============================================================
INFO:__main__:
📚 步骤1: 检索历史相似查询...
INFO:__main__:✅ 找到 2 条相似历史查询
INFO:__main__: 1. 查询所有VIP客户 (使用5次)
INFO:__main__: 2. 查询所有VIP客户 (使用1次)
INFO:__main__:
🔧 步骤2: 生成SQL语句...
INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.deepseek.com/chat/completions "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
INFO:text_to_sql:生成SQL成功:
SELECT
customer_name,
total_purchase_amount
FROM customers
WHERE customer_level = 'VIP';
INFO:__main__:
📝 生成的SQL:
INFO:__main__:------------------------------------------------------------
INFO:__main__:SELECT
customer_name,
total_purchase_amount
FROM customers
WHERE customer_level = 'VIP';
INFO:__main__:------------------------------------------------------------
❓ 是否执行此SQL? (y/n): y
INFO:__main__:
⚙️ 步骤3: 执行SQL...
INFO:__main__:✅ 查询成功! 返回 4 行数据
INFO:__main__:⏱️ 执行时间: 112.6ms
INFO:__main__:
📊 查询结果:
INFO:__main__:============================================================
INFO:__main__:1. {"customer_name": "张三", "total_purchase_amount": "150000.00"}
INFO:__main__:2. {"customer_name": "赵六", "total_purchase_amount": "120000.00"}
INFO:__main__:3. {"customer_name": "周八", "total_purchase_amount": "95000.00"}
INFO:__main__:4. {"customer_name": "陈明", "total_purchase_amount": "165000.00"}
INFO:__main__:============================================================
INFO:text_to_sql:新增历史记录成功
INFO:__main__:
✅ 已保存到历史记录
❓ 是否生成图表? (y/n): y
INFO:matplotlib.category:Using categorical units to plot a list of strings that are all parsable as floats or dates. If these strings should be plotted as numbers, cast to the appropriate data type before plotting.
INFO:matplotlib.category:Using categorical units to plot a list of strings that are all parsable as floats or dates. If these strings should be plotted as numbers, cast to the appropriate data type before plotting.
INFO:__main__:
📈 图表已生成: ./charts/chart_bar_1762218327.png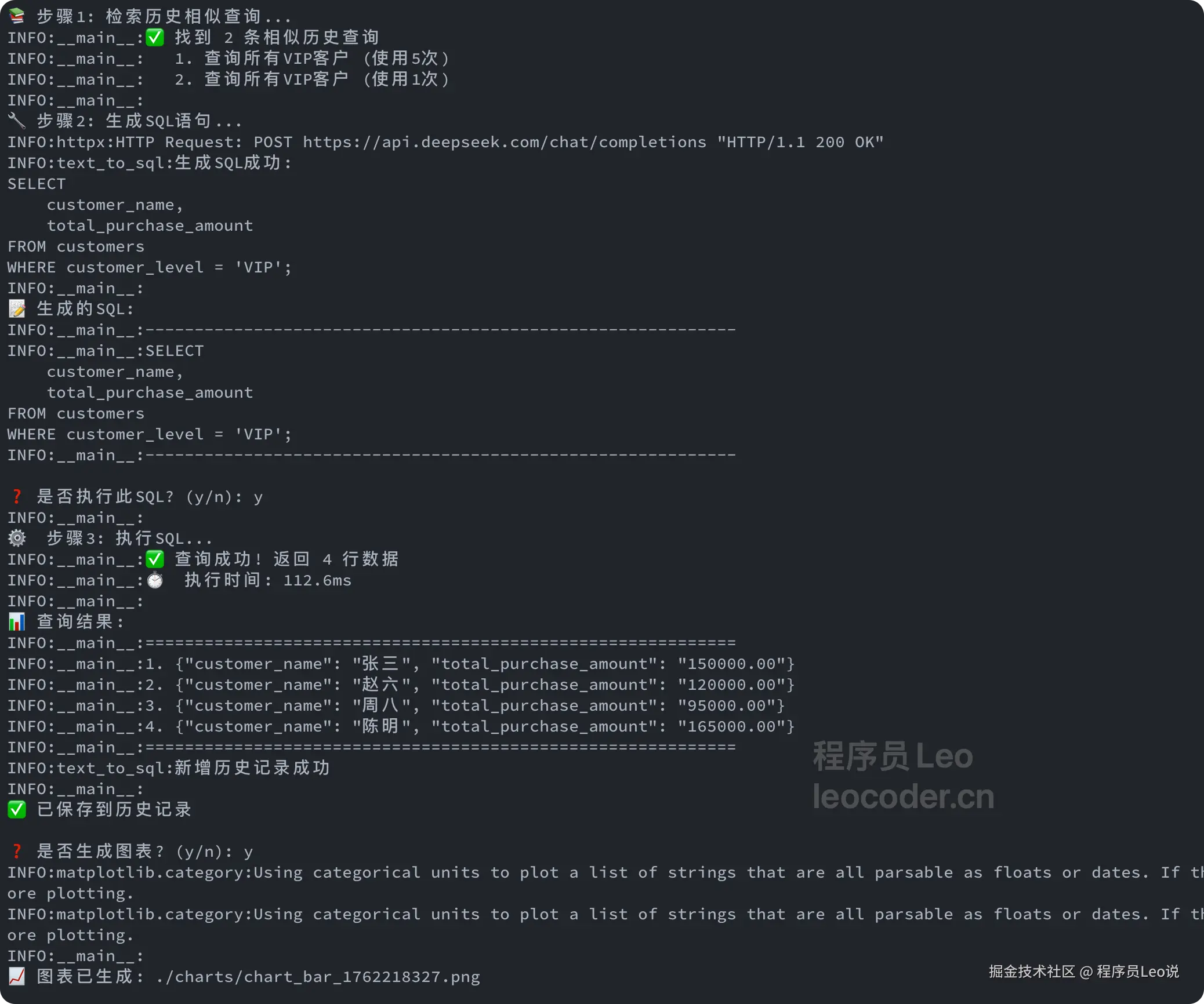
8.2 错误处理演示
场景3:尝试危险操作
ruby
💬 请输入您的问题: 删除所有订单数据
INFO:__main__:
============================================================
INFO:__main__:🔍 正在处理问题: 删除所有订单数据
INFO:__main__:============================================================
INFO:__main__:
📚 步骤1: 检索历史相似查询...
INFO:__main__: 暂无相似历史查询
INFO:__main__:
🔧 步骤2: 生成SQL语句...
INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.deepseek.com/chat/completions "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
INFO:text_to_sql:生成SQL成功:
DELETE FROM order_items;
DELETE FROM orders;
INFO:__main__:
📝 生成的SQL:
INFO:__main__:------------------------------------------------------------
INFO:__main__:DELETE FROM order_items;
DELETE FROM orders;
INFO:__main__:------------------------------------------------------------
❓ 是否执行此SQL? (y/n): y
INFO:__main__:
⚙️ 步骤3: 执行SQL...
ERROR:__main__:❌ 查询失败: 检测到危险操作关键字:DELETE,禁止执行!
INFO:text_to_sql:新增历史记录成功
💬 请输入您的问题: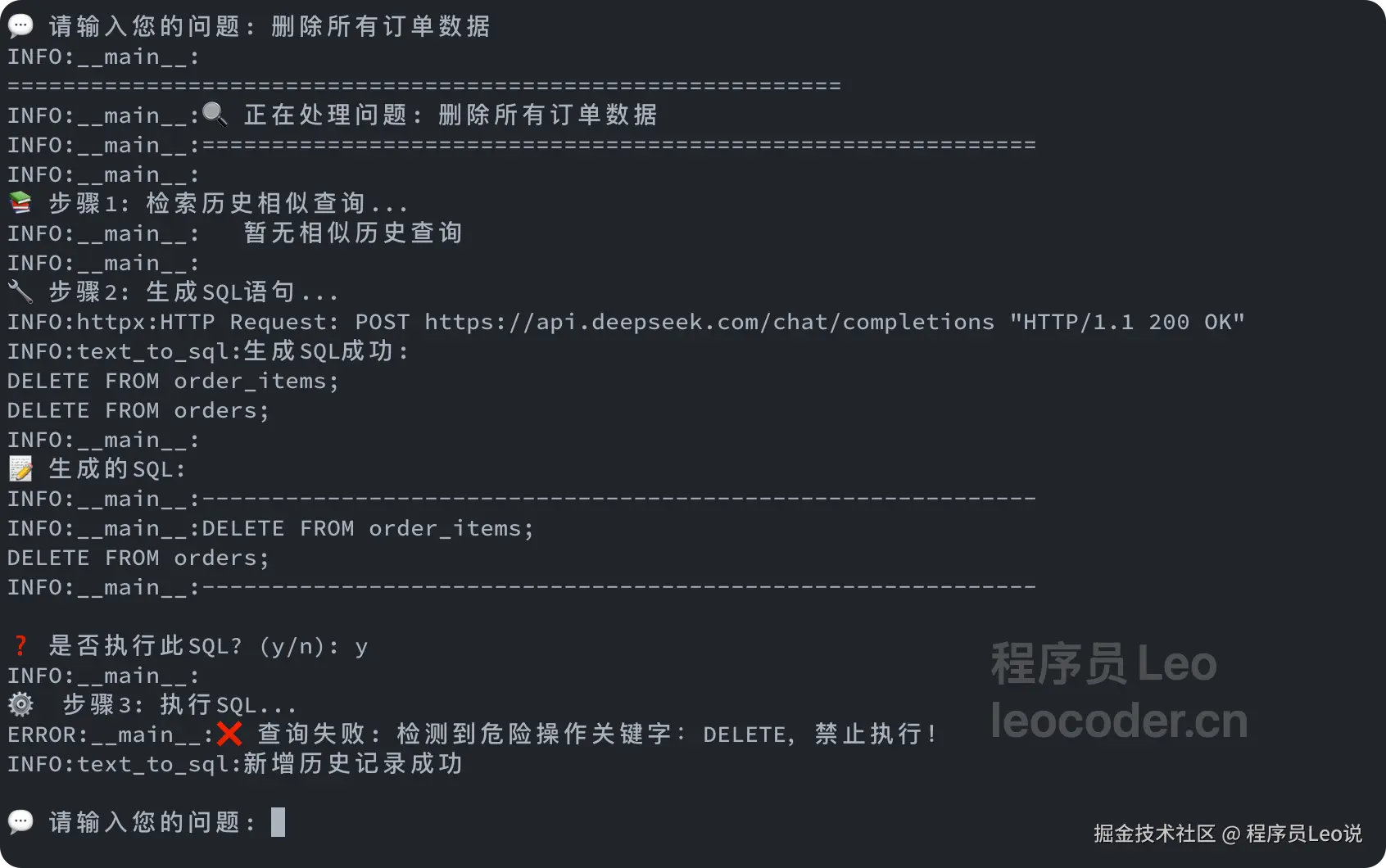
场景4:SQL生成错误
ruby
💬 请输入您的问题: 查询不存在的表xyz
INFO:__main__:
============================================================
INFO:__main__:🔍 正在处理问题: 查询不存在的表xyz
INFO:__main__:============================================================
INFO:__main__:
📚 步骤1: 检索历史相似查询...
INFO:__main__: 暂无相似历史查询
INFO:__main__:
🔧 步骤2: 生成SQL语句...
INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.deepseek.com/chat/completions "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
INFO:text_to_sql:生成SQL成功:
SELECT '表xyz不存在' AS error_message
FROM information_schema.tables
WHERE table_name = 'xyz'
HAVING COUNT(*) = 0;
INFO:__main__:
📝 生成的SQL:
INFO:__main__:------------------------------------------------------------
INFO:__main__:SELECT '表xyz不存在' AS error_message
FROM information_schema.tables
WHERE table_name = 'xyz'
HAVING COUNT(*) = 0;
INFO:__main__:---九、总结与展望
做完这个项目,最大的感受是:AI + 数据库的结合,正在改变我们与数据交互的方式。
以前,非技术人员查数据:
- 找技术人员
- 等技术人员有空
- 反复沟通需求
- 等SQL查询结果
- 发现需求理解有偏差
- 重复2-5步骤
现在,有了SQL Agent:
- 直接说"我要查XXX"
- 秒级得到结果
- 不满意?再问一次
效率提升不是一点半点,是质的飞跃!
希望这篇文章能帮助大家快速上手,打造自己的智能数据助手。如果你在实践过程中遇到问题,欢迎留言讨论。如果你有更好的优化思路,也欢迎分享给我!
附录:项目资源
- 完整代码:github.com/yourusernam...
- openGauss官网:opengauss.org/zh/
- openGauss文档:docs.opengauss.org/zh/
- LangChain文档:python.langchain.com/
参考资料
- openGauss社区官网:opengauss.org/zh/
- LangChain官方文档:python.langchain.com/
- OpenAI Embedding API:platform.openai.com/docs/guides...
- PostgreSQL向量扩展pgvector:github.com/pgvector/pg...