Rust Slint实现颜色选择器源码分享
一、源码分享
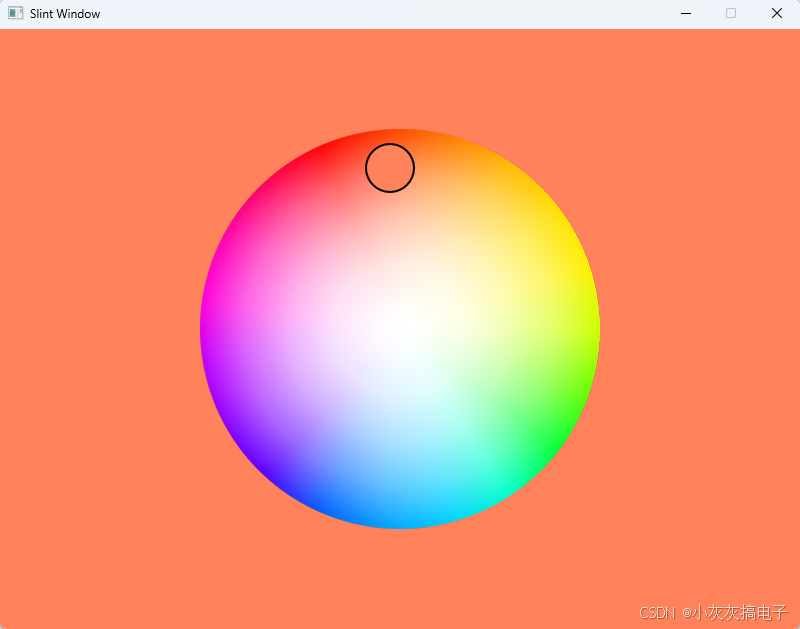
1、效果展示
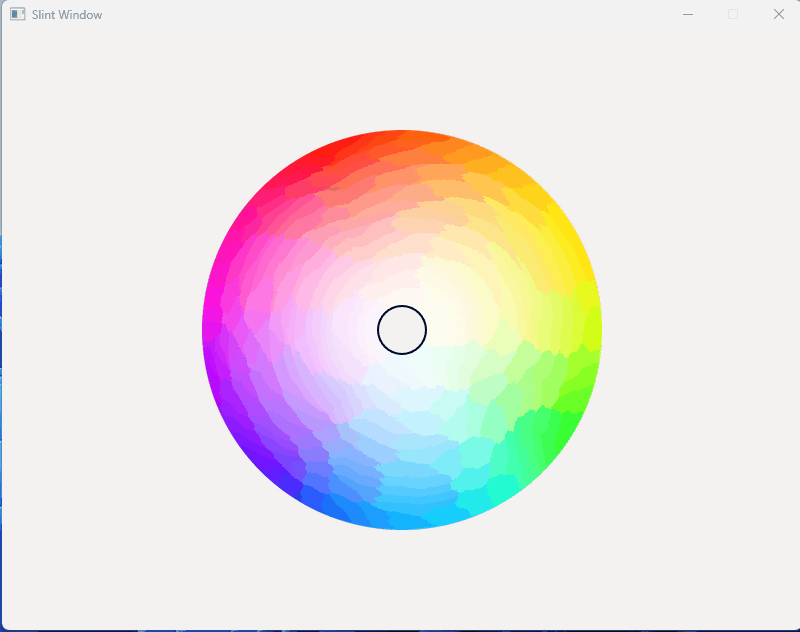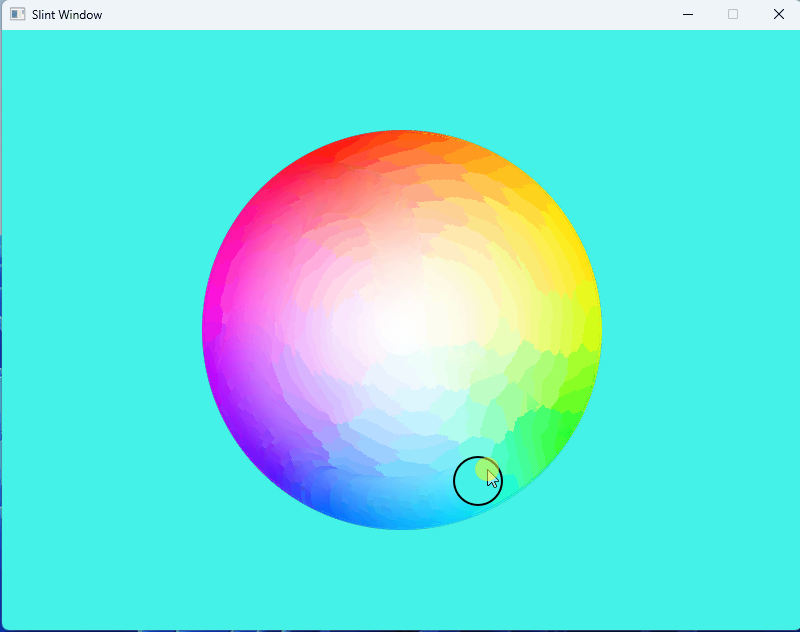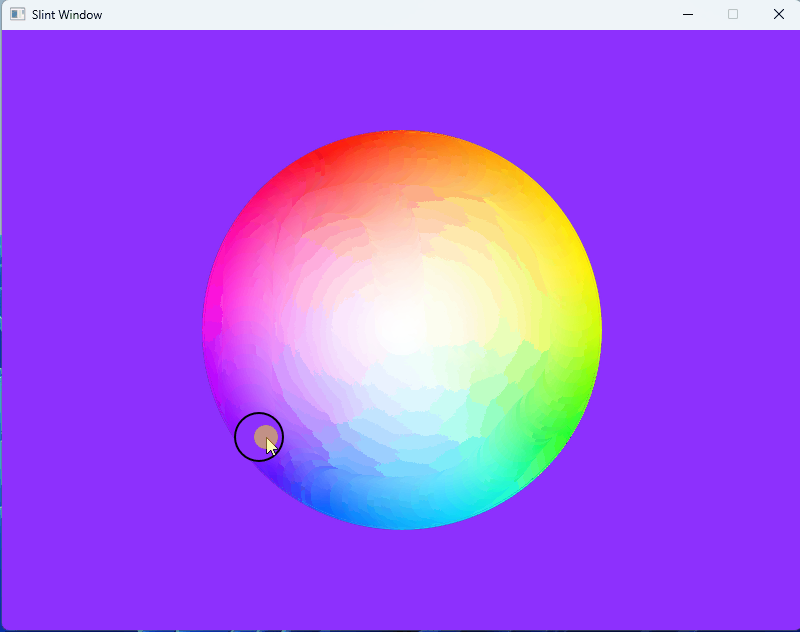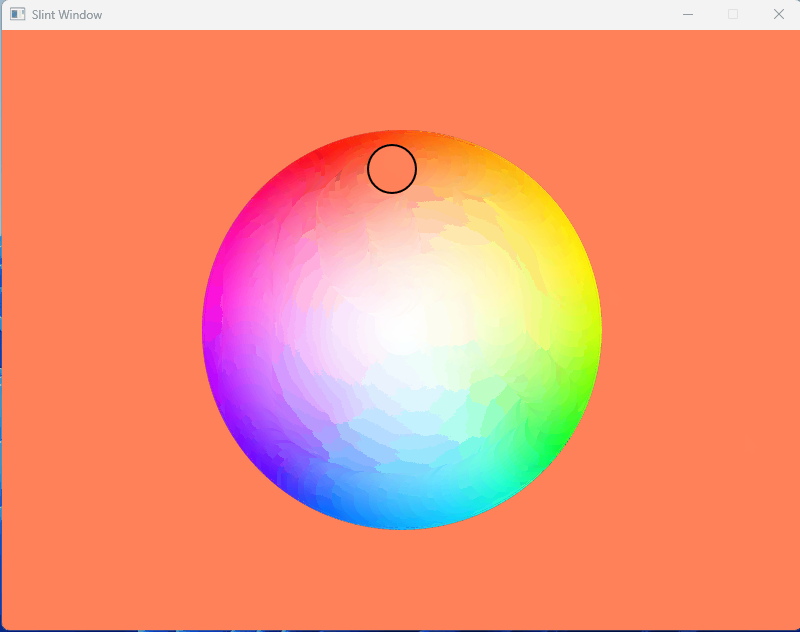
2、源码分享
2.1、工程搭建
参考我这篇博文【Rust 使用Slint库开发UI界面工程搭建详细教程】
2.2、工程结构
2.3、main.rs
rust
use slint::{PlatformError};
use std::rc::Rc;
slint::include_modules!();
fn main() ->Result<(), PlatformError>{
let app: MainWindow = MainWindow::new()?;
let weak: slint::Weak<MainWindow> = app.as_weak();
let image_width = app.get_image_width() as u32;
let image_height = app.get_image_height() as u32;
println!("image_width: {}, image_height: {}",image_width, image_height);
let path = "ui/image/color.png";
let source_image: image::ImageBuffer<image::Rgba<u8>, Vec<u8>> = {
let mut cat_path = std::path::PathBuf::from(env!("CARGO_MANIFEST_DIR"));
cat_path.push(path);
image::open(&cat_path).expect("Error loading cat image").into_rgba8()
};
let resized = image::imageops::resize(
&source_image,
image_width,
image_height,
image::imageops::FilterType::Lanczos3
);
app.set_source_image(slint::Image::from_rgba8(
slint::SharedPixelBuffer::clone_from_slice(
resized.as_raw(),
image_width,
image_height,
),
));
app.on_indictor_moved({
let app = app.clone_strong();
move |x: i32,y|{
// println!("{},{}",x,y);
let color = resized.get_pixel_checked(x as u32, y as u32);
if let Some(color) = color {
app.set_indictor_color(slint::Brush::from(slint::Color::from_argb_u8(
color[3],
color[0],
color[1],
color[2]
)));
}
}
});
let _ = app.run();
Ok(())
} 2.4、main.slint
rust
import { AboutSlint, VerticalBox, LineEdit, HorizontalBox, Button, GroupBox, GridBox,
ComboBox, Spinner, Slider, ListView, Palette, ProgressIndicator, CheckBox, Switch } from "std-widgets.slint";
import { DataAdapter} from "models.slint";
export { DataAdapter}
export component MainWindow inherits Window {
width: 800px;
height: 600px;
background: indictor-color;
callback indictor_moved(int,int);
in property <image> source-image <=> image.source;
out property <length> image-width <=> image.width;
out property <length> image-height <=> image.height;
in property <brush> indictor-color <=> indictor.background;
private property <Point> pressed_point;
private property <bool> is_pressed: false;
private property <float> indictor-center-x: 0;
private property <float> indictor-center-y: 0;
private property <float> distance: 0;
private property <float> dx;
private property <float> dy;
private property <angle> angle;
private property <length> limit-x;
private property <length> limit-y;
image := Image {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
//source: @image-url("image/color.png");
image-fit: fill;
indictor := Rectangle {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
border-radius: self.height/2;
background: #f5f1f1;
border-color: #000000;
border-width: 2px;
TouchArea {
pointer-event(event) => {
if event.kind == PointerEventKind.down && event.button == PointerEventButton.left {
root.is_pressed = true;
root.pressed_point.x = self.mouse-x;
root.pressed_point.y = self.mouse-y
} else if event.kind == PointerEventKind.up && event.button == PointerEventButton.left {
root.is_pressed = false;
}
}
moved => {
if(root.is_pressed){
parent.x += self.mouse-x - root.pressed_point.x;
parent.y += self.mouse-y - root.pressed_point.y;
// 计算当前位置相对于圆心的距离
root.indictor-center-x = (indictor.x + indictor.width/2)/1px;
root.indictor-center-y = (indictor.y + indictor.height/2)/1px;
root.dx = indictor-center-x - image.width/2/1px;
root.dy = indictor-center-y - image.height/2/1px;
root.distance = Math.sqrt(dx*dx + dy*dy);
if (root.distance > image.width/2/1px) {
root.angle = Math.atan2(dy, dx);
root.limit-x = ((image.width/2/1px + Math.cos(angle) * image.width/2/1px - indictor.width/2/1px)*1px);
root.limit-y = ((image.height/2/1px + Math.sin(angle) * image.height/2/1px - indictor.height/2/1px)*1px);
indictor.x = root.limit-x;
indictor.y = root.limit-y;
}
indictor_moved(indictor.x/1px + indictor.width/2/1px, indictor.y/1px + indictor.height/2/1px);
}
}
}
}
}
show := Rectangle {
y:root.height - self.height;
width: parent.width;
height: 50px;
background: indictor-color;
}
}2.5、Cargo.toml
rust
[package]
name = "ttt"
version = "0.1.0"
edition = "2024"
author = "<peng.xu@sf-express.com>"
[dependencies]
image = "0.25.9"
slint = "1.14.1"
[build-dependencies]
slint-build = "1.14.1"2.6、资源文件
二、实现原理
通过Rust image库来实现。
image库是Rust语言中一个强大且流行的图像处理库,主要用于读取、写入和处理各种图像格式。它提供了丰富的API,支持从基本图像操作到高级处理功能。
1、库概述
image库是一个纯Rust实现的图像处理工具,它支持多种常见图像格式(如JPEG、PNG、BMP、GIF等),并提供了高效的图像数据表示和处理能力。主要优势包括:
- 高性能:利用Rust的内存安全特性,优化了图像解码和编码过程。
- 易用性:API设计简洁,易于集成到Rust项目中。
- 功能丰富:涵盖图像加载、保存、转换和处理等常见任务。
版本0.25.9是该库的一个稳定版本,修复了之前版本的bug并增加了新特性。使用时,需在Cargo.toml中添加依赖:
toml
[dependencies]
image = "0.25.9"2、核心功能
image库的核心功能包括图像解码、编码、转换和基本处理。以下是主要功能的详细说明:
-
图像解码(读取):
- 支持从文件或字节流中读取图像数据。
- 自动检测格式:如JPEG、PNG、WebP等。
- 返回
DynamicImage类型,这是一个枚举,表示不同颜色空间的图像(如RGB、灰度)。
-
图像编码(保存):
- 支持将图像保存为多种格式。
- 可指定质量参数,例如JPEG的压缩级别。
-
图像转换:
- 颜色空间转换:如RGB到灰度、RGBA到RGB等。
- 图像格式转换:将一种格式的图像转换为另一种格式的字节流。
-
图像处理:
- 基本操作:调整大小、裁剪、旋转。
- 高级处理:应用滤镜(如高斯模糊)、边缘检测、直方图计算。
- 数学基础:一些处理函数基于图像处理算法,例如卷积操作可以用公式表示:卷积核 K K K作用于图像 I I I,输出像素 O ( x , y ) = ∑ i , j K ( i , j ) ⋅ I ( x + i , y + j ) O(x,y) = \sum_{i,j} K(i,j) \cdot I(x+i,y+j) O(x,y)=∑i,jK(i,j)⋅I(x+i,y+j)。
-
其他功能:
- 元数据访问:读取图像的EXIF信息等。
- 错误处理:使用Rust的Result类型,提供详细的错误信息。
3、主要模块和类型
image库的核心模块包括image模块,定义了关键类型和函数。以下是重要类型:
DynamicImage:一个枚举,表示不同格式的图像数据,如Luma8(8位灰度)、Rgb8(8位RGB)等。它提供了统一接口处理各种图像。ImageBuffer:一个泛型结构,表示图像缓冲区,如ImageBuffer<Rgb<u8>, Vec<u8>>用于RGB图像。RgbImage和GrayImage:特定颜色空间的图像类型别名,简化使用。- 工具模块 :如
imageops提供图像操作函数(例如resize、crop),codecs处理格式编解码。
4、方法介绍
该库非常庞大,此表仅涵盖最常用和核心的部分。完整的API请务必参考官方文档。
核心类型
| 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
ImageBuffer<P, Container> |
通用的图像缓冲区,存储像素数据。P是像素类型,Container是底层存储(如Vec<u8>)。 |
DynamicImage |
枚举类型,代表不同像素格式(如Luma8, Rgb8, Rgba8等)的图像,提供了统一的接口。 |
RgbImage |
ImageBuffer的别名,代表Rgb<u8>格式的图像。 |
RgbaImage |
ImageBuffer的别名,代表Rgba<u8>格式的图像。 |
GrayImage |
ImageBuffer的别名,代表Luma<u8>格式的图像(灰度图)。 |
GenericImage |
Trait,定义了图像类型的基本操作(获取像素、设置像素、获取尺寸等)。ImageBuffer和DynamicImage都实现了它。 |
ImageFormat |
枚举类型,表示图像文件格式(如PNG, JPEG, GIF, BMP等)。 |
核心方法 (主要围绕 ImageBuffer 和 DynamicImage)
1. 创建与加载
| 方法/函数 | 描述 | 常用类型/参数 |
|---|---|---|
ImageBuffer::new(width, height) |
创建一个指定宽度和高度的新图像缓冲区,像素初始化为0。 | u32, u32 -> ImageBuffer<P, Vec<P::Subpixel>> |
ImageBuffer::from_pixel(width, height, pixel) |
创建一个指定宽度和高度的新图像缓冲区,所有像素初始化为给定值。 | u32, u32, P -> ImageBuffer<P, Vec<P::Subpixel>> |
ImageBuffer::from_raw(width, height, data) |
从已有的像素数据创建一个图像缓冲区。数据必须匹配像素类型和尺寸。 | u32, u32, Vec<u8> 或其他容器 -> Option<ImageBuffer<P, Container>> |
open(path) |
从文件路径加载图像。返回Result<DynamicImage>。 |
&Path 或 &str -> Result<DynamicImage> |
load_from_memory(buffer) |
从内存中的字节数据加载图像。返回Result<DynamicImage>。 |
&[u8] -> Result<DynamicImage> |
load_from_memory_with_format(buf, format) |
指定格式从内存加载图像。返回Result<DynamicImage>。 |
&[u8], ImageFormat -> Result<DynamicImage> |
2. 基本信息获取
| 方法 | 描述 | 返回值 |
|---|---|---|
.width() |
获取图像的宽度(像素)。 | u32 |
.height() |
获取图像的高度(像素)。 | u32 |
.dimensions() |
获取图像的尺寸 (width, height)。 | (u32, u32) |
.in_bounds(x, y) |
检查坐标(x, y)是否在图像范围内。 | bool |
.get_pixel(x, y) |
获取指定坐标的像素值(只读)。 | &P |
.get_pixel_mut(x, y) |
获取指定坐标的像素值的可变引用(用于修改)。 | &mut P |
.pixels() |
返回一个迭代器,遍历图像中的所有像素 (坐标 + 值)。 | Pixels<...> |
.enumerate_pixels() |
同上,包含像素坐标。 | EnumeratePixels<...> |
.enumerate_pixels_mut() |
同上,提供像素值的可变引用(用于修改)。 | EnumeratePixelsMut<...> |
.as_raw() / .as_bytes() |
获取底层像素数据的字节切片视图。 | &[u8] |
.to_vec() |
将像素数据复制到一个新的Vec<u8>中。 |
Vec<u8> |
3. 像素操作与修改
| 方法 | 描述 | 常用参数 |
|---|---|---|
.put_pixel(x, y, pixel) |
在指定坐标设置像素值。 | u32, u32, P |
.fill(color) |
用指定颜色填充整个图像。 | P |
.fill_with_color(&mut self, color) |
同上。 | P |
.blend_pixel(&mut self, x, y, pixel) |
在指定坐标混合一个像素(考虑Alpha通道)。 | u32, u32, P |
.copy_from(&mut self, src, x, y) |
将另一个图像(src)的内容复制到当前图像的指定位置(x, y)。 |
&GenericImageView, u32, u32 |
.sub_image(x, y, width, height) |
获取图像的一个子区域视图(只读)。 | u32, u32, u32, u32 -> SubImage<...> |
.crop_imm(x, y, width, height) |
获取图像的一个子区域视图(只读)。 | u32, u32, u32, u32 -> DynamicImage |
.crop(x, y, width, height) |
获取图像的一个子区域视图(可变)。 | u32, u32, u32, u32 -> DynamicImage |
.resize(width, height, filter) |
调整图像尺寸,返回一个新图像。 | u32, u32, FilterType -> DynamicImage |
.resize_exact(..) |
精确调整到指定尺寸(可能拉伸)。 | u32, u32, FilterType -> DynamicImage |
.resize_to_fill(..) |
调整尺寸以填充目标区域,保持宽高比,居中放置。 | u32, u32, FilterType -> DynamicImage |
.rotate90() |
将图像顺时针旋转90度,返回新图像。 | -> DynamicImage |
.rotate180() |
将图像旋转180度,返回新图像。 | -> DynamicImage |
.rotate270() |
将图像顺时针旋转270度(或逆时针90度),返回新图像。 | -> DynamicImage |
.fliph() |
水平翻转图像,返回新图像。 | -> DynamicImage |
.flipv() |
垂直翻转图像,返回新图像。 | -> DynamicImage |
.brighten(amount) |
调整图像亮度(正数变亮,负数变暗),返回新图像。 | i32 -> DynamicImage |
.adjust_contrast(c) |
调整图像对比度,返回新图像。 | f32 -> DynamicImage |
.unsharpen(sigma, threshold) |
应用反锐化掩蔽滤镜,返回新图像。 | f32, i32 -> DynamicImage |
.blur(sigma) |
应用高斯模糊,返回新图像。 | f32 -> DynamicImage |
.filter(&mut self, kernel) |
使用给定的卷积核(kernel)对图像进行滤波(原地修改)。 | &mut self, Kernel |
4. 保存与编码
| 方法/函数 | 描述 | 常用参数 |
|---|---|---|
.save(path) |
将图像保存到文件路径。自动根据扩展名推断格式。 | &Path 或 &str -> Result<()> |
.save_with_format(path, format) |
将图像以指定格式保存到文件路径。 | &Path 或 &str, ImageFormat -> Result<()> |
DynamicImage::write_to(&self, writer, format) |
将图像以指定格式写入到实现了Write Trait的对象(如文件、内存缓冲区)。 |
&mut dyn Write, ImageFormat -> Result<()> |
ImageBuffer::save(path) |
ImageBuffer的保存方法(同上)。 |
&Path 或 &str -> Result<()> |
ImageBuffer::save_with_format(path, format) |
ImageBuffer的保存方法(同上)。 |
&Path 或 &str, ImageFormat -> Result<()> |
5. 格式转换与处理 (DynamicImage特有)
| 方法 | 描述 | 返回值 |
|---|---|---|
DynamicImage::to_rgb8() |
转换为RgbImage。 |
RgbImage |
DynamicImage::to_rgba8() |
转换为RgbaImage。 |
RgbaImage |
DynamicImage::to_luma8() |
转换为GrayImage(灰度图)。 |
GrayImage |
DynamicImage::to_luma_alpha8() |
转换为GrayAlphaImage(带Alpha的灰度图)。 |
ImageBuffer<LumaA<u8>, Vec<u8>> |
DynamicImage::to_bgr8() |
转换为BgrImage。 |
ImageBuffer<Bgr<u8>, Vec<u8>> |
DynamicImage::to_bgra8() |
转换为BgraImage。 |
ImageBuffer<Bgra<u8>, Vec<u8>> |
DynamicImage::grayscale() |
转换为灰度图(Luma8),返回新的DynamicImage。 |
DynamicImage |
DynamicImage::invert() |
反转图像颜色(取反),原地修改DynamicImage。 |
() |
6. 色彩空间转换 (位于 image::imageops::colorops 模块)
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
grayscale(image: &DynamicImage) |
将图像转换为灰度(返回新图)。 |
brighten(image: &DynamicImage, value: i32) |
调整亮度(返回新图)。 |
contrast(image: &DynamicImage, contrast: f32) |
调整对比度(返回新图)。 |
huerotate(image: &DynamicImage, value: i32) |
调整色调(色相旋转)(返回新图)。 |
colorops::dither(image: &mut GrayImage, ...) |
对灰度图应用抖动(dithering)算法(原地修改)。 |
重要说明:
- 泛型参数: 很多
ImageBuffer的方法依赖于像素类型P(如Rgb<u8>,Luma<u16>,Rgba<f32>等)。表格中省略了泛型细节以保持简洁。 GenericImageTrait:get_pixel,put_pixel,width,height,in_bounds,copy_from等方法是通过GenericImageTrait 定义的,因此适用于ImageBuffer和DynamicImage。DynamicImage的便利性:DynamicImage封装了不同格式的图像,并提供了统一的转换(to_*)和处理(grayscale,invert等)方法,使用起来更方便。- 图像处理操作: 许多图像处理操作(如调整大小、旋转、滤镜等)在
imageops模块中有更丰富的实现,它们通常接受&GenericImageView或&mut GenericImage作为输入,并返回新的DynamicImage或在原图上修改。 - 编解码器: 图像的加载(
open,load_*)和保存(save,write_to)功能依赖于对应格式的编解码器实现。
强烈建议: 此表仅作为入门概览。要充分利用image库,请务必查阅其详尽的官方文档和代码示例。
5、使用示例
以下是一个完整的Rust代码示例,展示如何使用image库加载图像、调整大小并保存。代码结构清晰,便于理解。
rust
use image::{ImageFormat, io::Reader};
use image::imageops::resize;
use image::DynamicImage;
fn main() -> Result<(), Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
// 步骤1: 加载图像
let mut reader = Reader::open("input.jpg")?;
reader.no_limits(); // 禁用大小限制(可选)
let img: DynamicImage = reader.decode()?; // 解码图像
// 步骤2: 调整图像大小(例如缩放到宽度300像素)
let resized_img = resize(
&img.to_rgb8(), // 转换为RGB格式
300, // 新宽度
(img.height() as f32 * (300.0 / img.width() as f32)) as u32, // 计算新高度
image::imageops::FilterType::Lanczos3, // 使用Lanczos3滤波器
);
// 步骤3: 保存图像
resized_img.save_with_format("output.jpg", ImageFormat::Jpeg)?;
Ok(())
}代码解释:
- 加载图像 :使用
Reader从文件读取,decode方法解码为DynamicImage。 - 调整大小 :
resize函数应用Lanczos3滤波器进行高质量缩放,新高度通过比例计算: h new = h × w new w h_{\text{new}} = h \times \frac{w_{\text{new}}}{w} hnew=h×wwnew。 - 保存图像 :使用
save_with_format指定格式保存。
6、高级处理示例
如果需要更复杂的操作,如应用滤镜,可以使用imageproc库(image的扩展)。以下是应用高斯模糊的示例:
rust
use image::{DynamicImage, ImageBuffer};
use imageproc::filter::gaussian_blur;
fn apply_gaussian_blur(img: &DynamicImage) -> ImageBuffer<image::Rgb<u8>, Vec<u8>> {
let rgb_img = img.to_rgb8();
gaussian_blur(&rgb_img, 2.0) // 标准差为2.0的高斯模糊
}这里,高斯模糊的数学基础是高斯函数: G ( x , y ) = 1 2 π σ 2 e − x 2 + y 2 2 σ 2 G(x,y) = \frac{1}{2\pi\sigma^2} e^{-\frac{x^2+y^2}{2\sigma^2}} G(x,y)=2πσ21e−2σ2x2+y2,其中 σ \sigma σ是标准差。
7、注意事项
- 版本兼容性:版本0.25.9与旧版本API兼容,但升级时需检查破坏性变更。
- 性能优化 :处理大图像时,使用
ImageBuffer避免不必要的拷贝。 - 错误处理 :总是处理
Result类型,例如使用?运算符传播错误。 - 依赖管理 :image库依赖其他crate如
num-traits,确保Cargo.toml配置正确。 - 数学相关 :图像处理算法常涉及数学公式,如滤波器的卷积操作。独立公式用 . . . ... ...格式,例如卷积的定义:
( f ∗ g ) ( x , y ) = ∑ i = − ∞ ∞ ∑ j = − ∞ ∞ f ( i , j ) ⋅ g ( x − i , y − j ) (f * g)(x,y) = \sum_{i=-\infty}^{\infty} \sum_{j=-\infty}^{\infty} f(i,j) \cdot g(x-i,y-j) (f∗g)(x,y)=i=−∞∑∞j=−∞∑∞f(i,j)⋅g(x−i,y−j)
8、总结
image库是Rust生态中图像处理的强大工具,版本0.25.9提供了稳定且功能丰富的API。通过学习核心功能和使用示例,您可以轻松集成图像处理到Rust项目中。如果需要更高级功能,可结合imageproc等扩展库。参考官方文档(链接)获取最新信息和详细API。如果您有具体问题,欢迎进一步讨论!
