提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档
文章目录
- 前言
- [1. 实现Index类](#1. 实现Index类)
-
- [1.1 实现索引结构](#1.1 实现索引结构)
- [1.2 实现新增正排](#1.2 实现新增正排)
- [1.3 实现构造倒排](#1.3 实现构造倒排)
- [1.4 如何改进权重公式](#1.4 如何改进权重公式)
- [1.5 实现词频统计](#1.5 实现词频统计)
- [1.6 更新倒排索引](#1.6 更新倒排索引)
- [1.7 保存索引到文件](#1.7 保存索引到文件)
- [1.8 加载索引](#1.8 加载索引)
- [1.9 给保存和加载添加时间](#1.9 给保存和加载添加时间)
- [1.10 在Parser中调用Index](#1.10 在Parser中调用Index)
- [1.11 验证索引制作](#1.11 验证索引制作)
- [1.12 关于索引制作速度](#1.12 关于索引制作速度)
- [1.13 多线程制作索引](#1.13 多线程制作索引)
- 总结
前言
1. 实现Index类
java
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.42</version>
</dependency>
java
@Data
public class DocInfo {
private int docId;
private String title;
private String url;
private String content;
}
java
@Data
//这个类就是把文档id和词的相关性 权值 进行一个包裹
public class Weight {
private int docId;
private int weight;//weight就表示文档和词之间的相关性,词越大,相关性越强
}
java
public class Index {
//实现功能
//1.给定一个docID,在正派索引中查询文档的详细信息
public DocInfo getDocInfo(int docId){
return null;
}
//2. 给点一个词,在倒排索引中,查哪些文档和这个词关联
//注意词和文档之间是有相关性的---》要根据相关性来排序的
public List<Weight> getInverted(String term){
return null;
}
//3. 往索引中新增一个文档
public void addDoc(String title,String url, String content){
}
//4. 把内存中的索引结构保存到磁盘中
public void save(){
}
//5. 把磁盘中索引数据加载到内存中
public void load(){
}
}1.1 实现索引结构
java
//使用数组下标来表示docId
private ArrayList<DocInfo> forwardIndex = new ArrayList<>();
//使用哈希表来表示倒排索引,key就是词,value就是一组文章
private HashMap<String,ArrayList<Weight>> invertedIndex = new HashMap<>();
java
public DocInfo getDocInfo(int docId){
return forwardIndex.get(docId);
}
java
public List<Weight> getInverted(String term){
return invertedIndex.get(term);
}查询的操作都是O(1)的,而且是在内存中进行的,快
1.2 实现新增正排
java
//3. 往索引中新增一个文档
public void addDoc(String title,String url, String content){
//新增文档操作,需要同时给正派索引,和倒排索引添加
DocInfo docInfo = buildForward(title,url,content);
buildInverted(docInfo);
}
private void buildInverted(DocInfo docInfo) {
}
private DocInfo buildForward(String title, String url, String content) {
DocInfo docInfo = new DocInfo();
docInfo.setTitle(title);
docInfo.setUrl(url);
docInfo.setContent(content);
forwardIndex.add(docInfo);//因为是加在最后的,所以下标就是数组长度,就是docId
docInfo.setDocId(forwardIndex.size()-1);
return docInfo;
}1.3 实现构造倒排
词到文档id之间的映射关系
先要知道这个文档有什么词
所以就要先分词
1.针对标题分词
2.针对正文分词
url就不用分词了
然后就可以结果这个分词的结果,就知道这个文档id应该压迫加入到哪个倒排索引的key中了
倒排索引是一个键值对结构,key是分词结果,value是和这个分词结果有关的文档id列表
如何来确定权值的值呢---》权值:词和文档之间的相关性----》用出现词出现的次数来表示
真实搜素引擎:-----》根据文档中提取的特征,训练模型,来衡量相关性,出现次数只是它的一个指标,还有很多指标,比如语义,同义词,近义词等等----》算法工程师,做的算法,搞得是人工智能的算法
所以我们使用词频来衡量
为什么要对标题和正文分别进行分词,因为标题和正文的词的权重是不一样的
java
private void buildInverted(DocInfo docInfo) {
//1,根据文档标题进行分词
//2.遍历分词结果,统计每个词出现的次数
//3,根据文档正文进行分词
//4.遍历分词结果,统计每个词出现的次数
//5.汇总到一个HashMap里面,最终文档的权重,就是标题出现次数*10+正文次数,正常的话,这里计算权重也是很复杂的,要持续调整,反复迭代
//6.遍历HashMap,依次更新倒排索引中的结构
}1.4 如何改进权重公式
要想进行改进,就需要要有办法来评估好与坏
真实的搜索引擎中,往往是使用点击率来衡量的
点击率 = 点击次数/展示次数
如果流量比较大---》假设服务器每天大概有1亿访问量---》可以分为若干份,30%,30%,30%,10%
每个部分使用不同的权重公式---》分别统计点击率,就选择点击率高的公式-----》进过一定时间迭代------》就会变得越来越好
1.5 实现词频统计
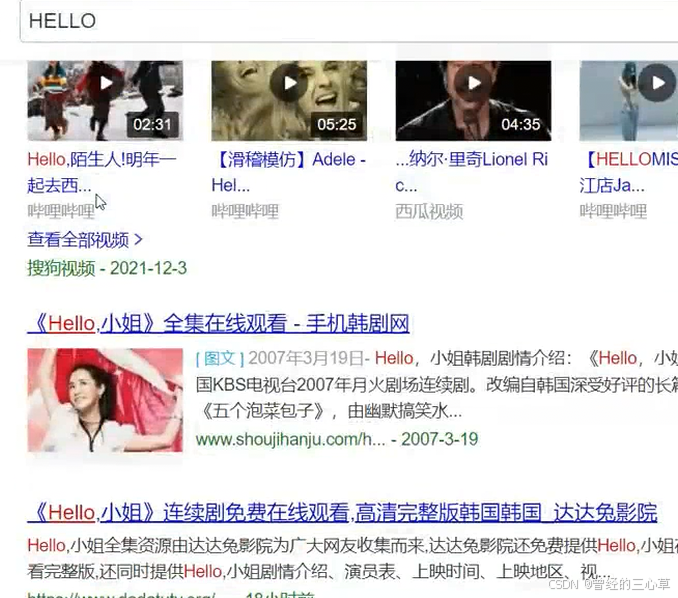
ArrayList和arrayLIst这种词算出现一词,还是两次呢
别人都没区分大小写,所以算两次
java
class WordCnt{
public int titleCount;//这个词在标题中出现次数
public int contentCount;//词在正文中出现次数
}
//统计词频的数据结构
HashMap<String,WordCnt> wordCntHashMap = new HashMap<>();
//1,根据文档标题进行分词
List<Term> terms = ToAnalysis.parse(docInfo.getTitle()).getTerms();
//2.遍历分词结果,统计每个词出现的次数
for (Term term : terms){
String word = term.getName();
WordCnt wordCnt = wordCntHashMap.get(word);
if (wordCnt == null){
//先判断这个term是否存在,如果不存在就创建一个新的键值对,插入进去,titleCount=1
WordCnt newWordCnt = new WordCnt();
newWordCnt.titleCount = 1;
newWordCnt.contentCount = 0;
wordCntHashMap.put(word,newWordCnt);
}else {
//如果存在的话,titleCount+1
wordCnt.titleCount++;
}
}
//3,根据文档正文进行分词
terms = ToAnalysis.parse(docInfo.getContent()).getTerms();
//4.遍历分词结果,统计每个词出现的次数
for (Term term : terms){
String word = term.getName();
WordCnt wordCnt = wordCntHashMap.get(word);
if (wordCnt == null){
//先判断这个term是否存在,如果不存在就创建一个新的键值对,插入进去,titleCount=1
WordCnt newWordCnt = new WordCnt();
newWordCnt.titleCount = 0;
newWordCnt.contentCount = 1;
wordCntHashMap.put(word,newWordCnt);
}else {
//如果存在的话,titleCount+1
wordCnt.contentCount++;
}
}
java
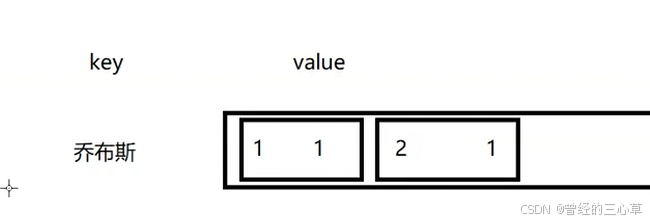
private HashMap<String,ArrayList<Weight>> invertedIndex = new HashMap<>();这个可以实现词---》文档权重的对应
1.6 更新倒排索引
java
//5.汇总到一个HashMap里面,最终文档的权重,就是标题出现次数*10+正文次数,正常的话,这里计算权重也是很复杂的,要持续调整,反复迭代
//6.遍历HashMap,依次更新倒排索引中的结构
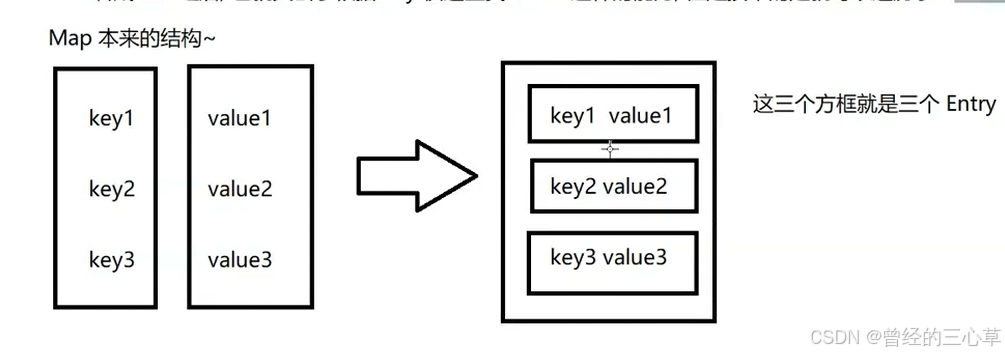
//map没有实现Iterable,所以不能直接foreach,所以可以把map转为set,然后来foreach,set这里存的是把键值对打包在一起的类,称为Entry
for(Map.Entry<String,WordCnt> entry : wordCntHashMap.entrySet()){
//先根据词去倒排索引中查
ArrayList<Weight> invertedList = invertedIndex.get(entry.getKey());
if(invertedList == null){
//插入一个新的键值对
invertedList = new ArrayList<>();
Weight weight = new Weight();
weight.setDocId(docInfo.getDocId());
weight.setWeight(entry.getValue().titleCount*10+entry.getValue().contentCount);
invertedList.add(weight);
invertedIndex.put(entry.getKey(),invertedList);
}else{
Weight weight = new Weight();
weight.setDocId(docInfo.getDocId());
weight.setWeight(entry.getValue().titleCount*10+entry.getValue().contentCount);
invertedList.add(weight);
}
}1.7 保存索引到文件
因为构建索引是比较耗时的,所以就不应该在服务器启动的时候才构建索引,不然服务器就会启动很久
所以这种耗时的操作,先单独执行,执行完之后,在让服务器启动的时候直接加载就可以了
怎么保存呢
把索引结构变成字符串,序列化----》写入文件
把特定结构字符串---》变成对象-----》反序列化
我们这里使用JSON格式来进行序列化,Jackson
java
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.13.0</version>
</dependency>
java
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
private static final String INDEX_PATH = "D:\\spring-project2\\java_doc_sercher";
java
//4. 把内存中的索引结构保存到磁盘中
public void save(){
//使用两个文件分别保存正排索引和倒排索引
File indexPathFile = new File(INDEX_PATH);
if (!indexPathFile.exists()){
indexPathFile.mkdirs();
}
File forwardIndexFile = new File(INDEX_PATH+"/"+"forward.txt");
File invertedIndexFile = new File(INDEX_PATH+"/"+"inverted.txt");
try {
objectMapper.writeValue(forwardIndexFile,forwardIndex);//保存索引,先转为字符串,然后在写入
objectMapper.writeValue(invertedIndexFile,invertedIndex);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}1.8 加载索引
java
//5. 把磁盘中索引数据加载到内存中
public void load() {
System.out.println("加载索引开始");
File forwardIndexFile = new File(INDEX_PATH+"/"+"forward.txt");
File invertedIndexFile = new File(INDEX_PATH+"/"+"inverted.txt");
try {
forwardIndex = objectMapper.readValue(forwardIndexFile, new TypeReference<ArrayList<DocInfo>>() {
});
//第一个参数表示从哪里读取,第二个表示以什么方式来进行解析,转成什么类型
//ArrayList<DocInfo>,,,,这个类型怎么表示呢,,,TypeReference<>可以转成
//new TypeReference<ArrayList<DocInfo>>() {}就是创建了匿名内部类,实现了TypeReference
invertedIndex = objectMapper.readValue(invertedIndexFile, new TypeReference<HashMap<String,ArrayList<Weight>>>() {
});
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("加载索引结束");
}1.9 给保存和加载添加时间
java
//4. 把内存中的索引结构保存到磁盘中
public void save(){
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
//使用两个文件分别保存正排索引和倒排索引
File indexPathFile = new File(INDEX_PATH);
if (!indexPathFile.exists()){
indexPathFile.mkdirs();
}
File forwardIndexFile = new File(INDEX_PATH+"/"+"forward.txt");
File invertedIndexFile = new File(INDEX_PATH+"/"+"inverted.txt");
try {
objectMapper.writeValue(forwardIndexFile,forwardIndex);//保存索引,先转为字符串,然后在写入
objectMapper.writeValue(invertedIndexFile,invertedIndex);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("保存索引成功:"+(end-begin)+"ms");
}
java
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("加载索引结束:"+(end-begin)+"ms");比较快的方法我们就不统计时间了
1.10 在Parser中调用Index
Parser是制作索引的入口,是一个可执行的程序,Index相当于实现了索引的数据结构,提供了一些api
所以INdex要给Parser调用
java
private Index index = new Index();
java
private void parseHTML(File file) {
//1.解析出标题
String title = parseTitle(file);
System.out.println(title);
//2.解析出html对应url
String url = parseUrl(file);
//3.解析出html正文
String content = parseContent(file);
System.out.println(content);
index.addDoc(title,url,content);
}
java
public void run(){
//入口
//1.根据上面指定路径,枚举出所有的文件(html),包括所有的子目录
ArrayList<File> fileList = new ArrayList<>();
enumFile(INPUT_PATH,fileList);
// System.out.println(fileList);
// System.out.println(fileList.size());
//2. 针对上面罗列出的文件路径,打开文件,读取文件内容,解析,构建索引
for (File file : fileList) {
System.out.println("开始解析:"+file.getAbsolutePath());
parseHTML(file);//解析html文件
}
//3.在内存中构造好的索引数据结果,保存到指定的文件中
index.save();
}1.11 验证索引制作
java
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parser p = new Parser();
p.run();
}

几十MB和GB都是小数据,TB才是大数据
这里的url也可以在浏览器中打开的
1.12 关于索引制作速度
java
public void run(){
//
System.out.println("索引制作开始");
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
//入口
//1.根据上面指定路径,枚举出所有的文件(html),包括所有的子目录
ArrayList<File> fileList = new ArrayList<>();
enumFile(INPUT_PATH,fileList);
// System.out.println(fileList);
// System.out.println(fileList.size());
//2. 针对上面罗列出的文件路径,打开文件,读取文件内容,解析,构建索引
for (File file : fileList) {
System.out.println("开始解析:"+file.getAbsolutePath());
parseHTML(file);//解析html文件
}
//3.在内存中构造好的索引数据结果,保存到指定的文件中
index.save();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("索引制作完毕:"+(end-begin)+"ms");
}
发现12秒多
发现保存索引也没花费多少时间
枚举文件也不花时间
java
for (File file : fileList) {
System.out.println("开始解析:"+file.getAbsolutePath());
parseHTML(file);//解析html文件
}这个最花时间
优化性能---》先用测试的手段,找到其中的性能瓶颈--》所以不能光是说
我们给每个步骤加上时间,看看谁最耗时间
java
public void run(){
//
System.out.println("索引制作开始");
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
//入口
//1.根据上面指定路径,枚举出所有的文件(html),包括所有的子目录
ArrayList<File> fileList = new ArrayList<>();
enumFile(INPUT_PATH,fileList);
long enumFileEnd = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("枚举文件完毕:"+(enumFileEnd-begin)+"ms");
// System.out.println(fileList);
// System.out.println(fileList.size());
//2. 针对上面罗列出的文件路径,打开文件,读取文件内容,解析,构建索引
for (File file : fileList) {
// System.out.println("开始解析:"+file.getAbsolutePath());
parseHTML(file);//解析html文件
}
long parseHTMLEnd = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("循环遍历文件完毕:"+(parseHTMLEnd-enumFileEnd)+"ms");
//3.在内存中构造好的索引数据结果,保存到指定的文件中
index.save();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("索引制作完毕:"+(end-begin)+"ms");
}
发现就是循环遍历文件最花时间
每次循环都是针对一个文件进行解析:读文件,分词,解析内容----》都是CPU的运算
读文件:没办法减少
主要是解析内容,就是parseHTML这个方法,比较耗时间,我们可以使用多线程
1.13 多线程制作索引
java
public void runByThread() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("索引制作开始");
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
ArrayList<File> fileList = new ArrayList<>();
//1.根据上面指定路径,枚举出所有的文件(html),包括所有的子目录
enumFile(INPUT_PATH,fileList);
//2.循环遍历文件,线程池
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(fileList.size());
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
for (File file : fileList) {
executorService.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("解析"+file.getAbsolutePath());
parseHTML(file);//解析html文件
countDownLatch.countDown();//解析完成之后,资源数减一
}
});
}
//3.保存索引,要等线程池执行完成之后才可以,submit只是把任务放入阻塞队列中,执行完毕还要等等
//怎么等待呢,使用CountDownLatch,先指定任务个数,每完成一个任务parseHTML就减一,用await来等待CountDownLatch所有任务数都没有
countDownLatch.await();//会阻塞,直到所有的任务都完成
index.save();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("索引制作完毕:"+(end-begin)+"ms");
}注意我们还要保证是线程安全的