目录
一、延迟加载
立即加载
概念: 当查询主对象时,立即执行所关联的sql语句 ,一次性将对象数据全部查询出来。
行为: 执行SELECT * FROM order WHERE id = #{id}后,立马执行SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = #{userId}。
使用场景: 多对一查询
优点: 数据一次性加载完毕,响应速度快。
缺点: 可能查询出不需要的数据,造成数据库资源和网络传输的浪费,降低性能。
使用: 默认使用立即加载。
延迟加载
概念: 当查询主对象时,只查询主对象的数据 。关联对象的数据不会立即查询,只用程序第一次真正访问关联对象时,才会加载关联对象的数据。
行为: 先执行SELECT * FROM order WHERE id = #{id},当调用order.getUser()方法时,才执行SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = #{userId}。
使用场景: 一对多查询
优点: 按需加载,避免了不必要的数据库查询。
缺点: 当第一次访问关联对象时,会有个短暂的查询延迟。后续访问多个关联对象,会产生多次数据库查询。
使用: 需要手动开启延迟加载。
- 在主配置文件中开启延迟加载:
lazyLoadingEnabled为true开启延迟加载,aggressiveLazyLoading控制延迟加载的行为,默认值为false,按需加载 - 在子配置文件中:在
<association>标签或<collection>标签中设置fetchType指定哪个关联查询 使用延迟加载。fetchType属性值:lazy- 延迟加载;eager- 立即加载
实操案例
将一对多查询和多对一查询都进行延迟加载演示:
多对一延迟加载实操案例演示:
-
在AccountMapper接口类中编写方法
javapackage com.tx.mapper; import com.tx.entity.Account; import java.util.List; public interface AccountMapper { // 延迟加载:多对一查询,查询某一个用户的所有账户信息 public List<Account> findAccountAll(); } -
在AccountMapper.xml中进行配置和SQL语句
xml<mapper namespace="com.tx.mapper.AccountMapper"> <!--延迟加载:多对一查询--> <!--内连接查询--> <select id="findAccountAll" resultMap="accountMap"> select * from account </select> <!--通过用户的id查询账户信息--> <select id="findByUid" parameterType="int" resultType="account"> select * from account where uid = #{uid} </select> <!--配置映射--> <resultMap id="accountMap" type="account"> <result property="id" column="id" /> <result property="uid" column="uid" /> <result property="money" column="money" /> <!--在多的一方指定关联查询的延迟加载--> <association property="user" javaType="user" select="com.tx.mapper.UserMapper.findUserById" column="uid" fetchType="lazy"> <id property="id" column="id"/> <result property="username" column="username" /> <result property="birthday" column="birthday"/> <result property="sex" column="sex"/> <result property="address" column="address" /> </association> </resultMap> </mapper> -
在UserMapper接口类中编写方法
javapackage com.tx.mapper; import com.tx.entity.User; import java.util.List; public interface UserMapper { // 延迟加载:多对一查询 public List<User> findUserById(Integer uid); } -
在UserMapper.xml中进行配置文件
xml<mapper namespace="com.tx.mapper.UserMapper"> <!--配置延迟加载:多对一查询--> <select id="findUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="user"> select * from user where id = #{id} </select> </mapper> -
在主配置文件中开启延迟加载
xml<configuration> <!--配置延迟加载--> <settings> <!-- 开启延迟加载 --> <setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/> <!-- 将积极加载改为消极加载及按需加载 --> <setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/> </settings> <!--定义类型别名--> <typeAliases> <package name="com.tx.entity" /> </typeAliases> <!--主配置文件--> <!--配置环境们--> <environments default="mysql"> <!--配置环境--> <environment id="mysql"> <!--配置事务的类型,使用本地事务策略--> <transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager> <!--配置是否使用连接池 POOLED表示使用链接池,UNPOOLED表示不使用连接池--> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///mybatis_db"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="root"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <!--加载映射文件--> <mappers> <mapper resource="mapper/UserMapper.xml"></mapper> <mapper resource="mapper/AccountMapper.xml"></mapper> </mappers> </configuration> -
测试代码
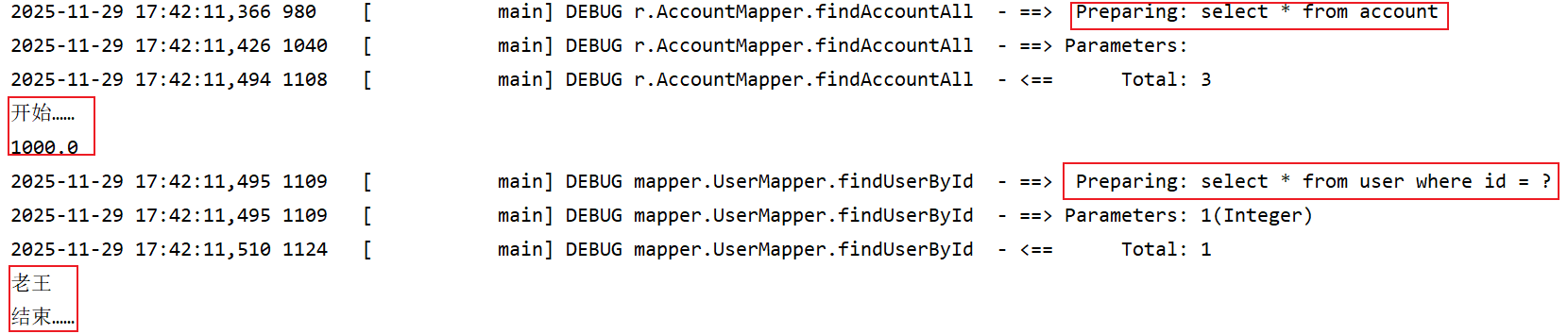
javapackage com.tx.test; import com.tx.entity.Account; import com.tx.entity.User; import com.tx.mapper.AccountMapper; import com.tx.mapper.UserMapper1; import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.List; // 入门程序 public class Test01 { private InputStream in; private SqlSessionFactory factory; private SqlSession session; @Before public void init() throws IOException { // 1. 加载主配置文件,目的是构建SqlSessionFactory对象 in = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml"); // 2. 创建SqlSessionFactory(Sql会话工厂)对象 factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in); // 3. 获取session对象,使用SqlSessionFactory工厂对象创建SqlSession对象 session = factory.openSession(); } @After public void destory() throws IOException { // 5. 释放资源 session.close(); in.close(); } // 4.1 延迟加载:多对一查询 @Test public void testFindAccountAll(){ // 4.1.1 通过session创建Mapper接口的代理对象 AccountMapper mapper = session.getMapper(AccountMapper.class); // 4.1.2 执行方法 List<Account> list = mapper.findAccountAll(); for (Account account:list){ System.out.println("开始......"); System.out.println(account.getMoney()); System.out.println(account.getUser().getUsername()); System.out.println("结束......"); System.out.println(); } } }
一对多延迟加载实操案例演示:
-
在UserMapper接口类中编写方法
javapackage com.tx.mapper; import com.tx.entity.User; import java.util.List; public interface UserMapper1 { // 延迟加载:一对多查询 public List<User> findUserAll(); } -
在UserMapper.xml中进行配置和SQL语句
xml<mapper namespace="com.tx.mapper.UserMapper1"> <!--配置延迟加载:一对多查询--> <select id="findUserAll" resultMap="userMap"> select * from user </select> <!--数据封装--> <resultMap id="userMap" type="user"> <id property="id" column=""/> <result property="username" column="username"/> <result property="birthday" column="birthday"/> <result property="sex" column="sex"/> <result property="address" column="address"/> <!--select="":使用账号的方法查询 column="":使用id值去查询账号 --> <collection property="accounts" ofType="account" select="com.tx.mapper.AccountMapper1.findAccountByUid" column="id" fetchType="lazy"> <id property="id" column="id"/> <result property="uid" column="uid"/> <result property="money" column="money"/> </collection> </resultMap> </mapper> -
在AccountMapper接口类中编写方法
javapackage com.tx.mapper; import com.tx.entity.Account; import java.util.List; public interface AccountMapper1 { // 延迟加载:一对多查询 public List<Account> findAccountByUid(Integer uid); } -
在AccountMapper.xml中进行配置和SQL语句
xml<mapper namespace="com.tx.mapper.AccountMapper1"> <!--延迟加载:一对多查询--> <!--通过用户的id查询账户信息--> <select id="findAccountByUid" parameterType="int" resultType="account"> select * from account where uid = #{uid} </select> </mapper> -
在主配置文件中开启延迟加载
xml<configuration> <!--配置延迟加载--> <settings> <!-- 开启延迟加载 --> <setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/> <!-- 将积极加载改为消极加载及按需加载 --> <setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/> </settings> <!--定义类型别名--> <typeAliases> <package name="com.tx.entity" /> </typeAliases> <!--主配置文件--> <!--配置环境们--> <environments default="mysql"> <!--配置环境--> <environment id="mysql"> <!--配置事务的类型,使用本地事务策略--> <transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager> <!--配置是否使用连接池 POOLED表示使用链接池,UNPOOLED表示不使用连接池--> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///mybatis_db"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="root"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <!--加载映射文件--> <mappers> <mapper resource="mapper/UserMapper1.xml"></mapper> <mapper resource="mapper/AccountMapper1.xml"></mapper> <mapper resource="mapper/UserMapper2.xml"></mapper> </mappers> </configuration> -
测试代码
java// 4.2 延迟加载:一对多查询 @Test public void testFindUserAll(){ // 4.2.1 通过session创建Mapper接口的代理对象 UserMapper1 mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper1.class); // 4.2.2 执行方法 List<User> list = mapper.findUserAll(); for (User user:list){ System.out.println("开始......"); System.out.println(user.getUsername()); System.out.println(user.getAccounts()); System.out.println("结束......"); System.out.println(); } }
二、缓存
MySQL使用sql语句缓存。例如,select * from user和select * from user,看起来时同一个表,但是,在MySQL缓存中,用第二表查询不到User表中的数据
MyBtais将数据进行缓存。
一级缓存
级别: SqlSession级别
- SqlSession对象使用Map集合(Key存储执行的SQL语句,value存放查询的对象)存储相互的缓存数据。
- 查询时,先从SqlSession的缓存中查找,如果有,直接返回;如果没有,查询数据库。
- 一级缓存的生命周期和SqlSession的生命周期相同,SqlSession对象关闭,一级缓存也关闭。
session.clearCache();:清除缓存- 调用调用SqlSession的update、insert、delete、commit和close等方法的时候也会清空缓存。
实操案例:
-
在UserMapper2接口类中编写方法
javapackage com.tx.mapper; import com.tx.entity.User; public interface UserMapper2 { // 一/二级缓存 public User findById(Integer id); } -
在UserMapper2.xml中配置Sql语句
xml<select id="findById" parameterType="int" resultType="user"> select * from user where id = #{id} </select> -
测试代码
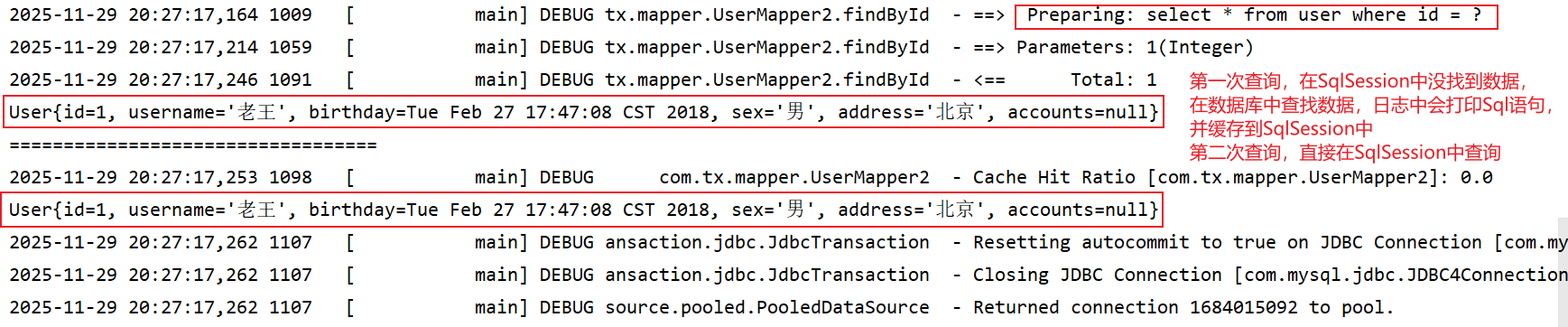
javapackage com.tx.test; import com.tx.entity.User; import com.tx.mapper.UserMapper2; import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; public class Test02 { private InputStream in; private SqlSessionFactory factory; private SqlSession session; @Before public void init() throws IOException { // 1. 加载主配置文件,目的是构建SqlSessionFactory对象 in = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml"); // 2. 创建SqlSessionFactory(Sql会话工厂)对象 factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in); // 3. 获取session对象,使用SqlSessionFactory工厂对象创建SqlSession对象 session = factory.openSession(); } @After public void destory() throws IOException { // 5. 释放资源 session.close(); in.close(); } // 4.1 一级缓存:会话级别 @Test public void testFindById(){ // 获取代理对象 UserMapper2 mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper2.class); // 调用方法,通过主键查询 // 先查询一级缓存,没有数据。 // 会查数据库,都会有sql语句,把查询出来的数据存储到一级缓存中 User user = mapper.findById(1); System.out.println(user); System.out.println("=================================="); // 清除缓存 // session.clearCache(); // 在查询一次 // 先查询一级缓存,存在数据。 // 从缓存中把数据返回,就没有sql语句 User user1 = mapper.findById(1); // 这两个user对象地址一样 System.out.println(user1); } }
二级缓存
级别: SqlSessionFactory级别
需要手动开启二级缓存:
-
在主配置文件开启二级缓存
xml<!--配置延迟加载--> <settings> <!-- 开启延迟加载 --> <setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/> <!-- 将积极加载改为消极加载及按需加载 --> <setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/> <!--开启二级缓存--> <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> </settings> -
在子配置文件开启二级缓存
xml<!--开启二级缓存--> <cache/>
除此之外,还有一个重要的条件:
- 实体类一定要继承
Serializable对象流
实操案例:
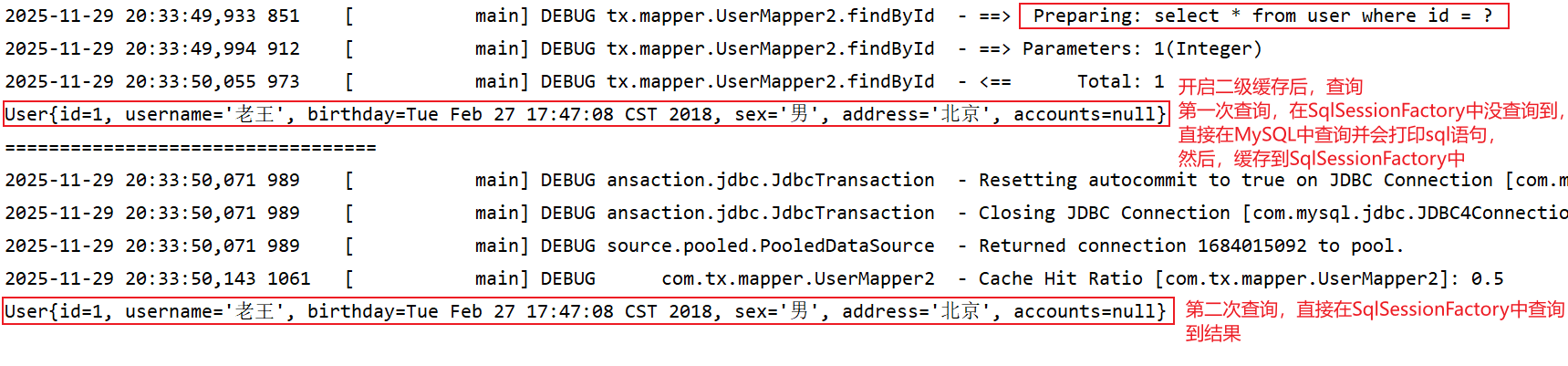
- 测试代码
java
// 4.2 二级缓存:会话工厂级别
// 二级缓存的使用对象地址不同,但是也是从缓存加载。原因是二级缓存存储的是零散数据,组装出来的对象
@Test
public void testFindById2(){
// 获取代理对象
UserMapper2 mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper2.class);
// 调用方法,通过主键查询
// 先查询一级缓存,没有数据。
// 会查数据库,都会有sql语句,把查询出来的数据存储到一级缓存中
User user = mapper.findById(1);
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println("==================================");
// 关闭会话
session.close();
// 获取session对象 和 获取代理对象
session = factory.openSession();
UserMapper2 mapper1 = session.getMapper(UserMapper2.class);
// 在查询一次
// 先查询一级缓存,存在数据。
// 从缓存中把数据返回,就没有sql语句
User user1 = mapper1.findById(1);
// 这两个user对象地址一样
System.out.println(user1);
}