目录
- 1.模式概述
-
- [1.1 模式定义](#1.1 模式定义)
- [1.2 四大设计原则体现](#1.2 四大设计原则体现)
- [2. 模式结构](#2. 模式结构)
-
- [2.1 UML类图](#2.1 UML类图)
- [2.2 核心角色说明](#2.2 核心角色说明)
- 3.代码实现:数据流处理系统
-
- [3.1 核心组件定义](#3.1 核心组件定义)
- [3.2 装饰器体系实现](#3.2 装饰器体系实现)
- [3.3 客户端调用示例](#3.3 客户端调用示例)
- 4.模式优势深度分析
- 5.模式劣势与应对策略
- 6.应用场景
-
- [6.1 典型应用场景](#6.1 典型应用场景)
- [6.2 Java I/O中的装饰器模式](#6.2 Java I/O中的装饰器模式)
- [7. 扩展变体深度剖析](#7. 扩展变体深度剖析)
-
- [7.1 状态感知装饰器](#7.1 状态感知装饰器)
- [7.2 链式装饰器构建](#7.2 链式装饰器构建)
- [7.3 混合装饰器](#7.3 混合装饰器)
- [7.4 响应式装饰器](#7.4 响应式装饰器)
- [7.5 行业应用变体案例](#7.5 行业应用变体案例)
-
- [7.5.1 Web安全装饰器](#7.5.1 Web安全装饰器)
- [7.5.2 缓存装饰器](#7.5.2 缓存装饰器)
- [7.5.3 监控装饰器](#7.5.3 监控装饰器)
- 8.与组合模式对比分析
- 9.总结
-
- [9.1 模式精髓](#9.1 模式精髓)
- [9.2 适用场景决策树](#9.2 适用场景决策树)
- [9.3 未来发展趋势](#9.3 未来发展趋势)
1.模式概述
1.1 模式定义
装饰器模式(Decorator Pattern) 是一种结构型设计模式,允许向一个现有的对象添加新的功能,同时又不改变其结构。它是通过创建一个包装对象(装饰器)来包裹真实对象的方式实现的。
1.2 四大设计原则体现
- 开闭原则:不修改原有代码即可扩展功能
- 单一职责原则:每个装饰器只负责一个功能扩展
- 组合优于继承:使用对象组合替代多重继承
- 松耦合原则:装饰器与核心组件相互独立
核心组件 基础装饰器 装饰器A 装饰器B 装饰器C
2. 模式结构
2.1 UML类图
<<interface>> Component +operation() ConcreteComponent +operation() Decorator -component: Component +Decorator(Component) +operation() ConcreteDecoratorA +addedState +operation() +addedBehavior() ConcreteDecoratorB +operation() +addedBehavior()
2.2 核心角色说明
| 角色 | 职责 | 实现要点 |
|---|---|---|
| Component | 定义对象接口 | 抽象组件或接口 |
| ConcreteComponent | 实现Component接口的具体对象 | 被装饰的核心对象 |
| Decorator | 持有Component引用 | 实现Component接口的抽象装饰器 |
| ConcreteDecorator | 具体的装饰器实现 | 添加额外的功能或职责 |
3.代码实现:数据流处理系统
3.1 核心组件定义
java
// 数据处理器接口
public interface DataProcessor {
String process(String data);
String getDescription();
}
// 基础处理器
public class BasicProcessor implements DataProcessor {
public String process(String data) {
return data; // 原始数据处理
}
public String getDescription() {
return "Basic Processor";
}
}3.2 装饰器体系实现
java
// 抽象装饰器
public abstract class ProcessorDecorator implements DataProcessor {
protected final DataProcessor processor;
public ProcessorDecorator(DataProcessor processor) {
this.processor = processor;
}
public String process(String data) {
return processor.process(data);
}
public String getDescription() {
return processor.getDescription();
}
}
// 加密装饰器
public class EncryptionDecorator extends ProcessorDecorator {
public EncryptionDecorator(DataProcessor processor) {
super(processor);
}
@Override
public String process(String data) {
String encrypted = encrypt(super.process(data));
return encrypted;
}
private String encrypt(String data) {
// 模拟加密逻辑
return "ENCRYPTED(" + data + ")";
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return super.getDescription() + " + Encryption";
}
}
// 压缩装饰器
public class CompressionDecorator extends ProcessorDecorator {
public CompressionDecorator(DataProcessor processor) {
super(processor);
}
@Override
public String process(String data) {
String compressed = compress(super.process(data));
return compressed;
}
private String compress(String data) {
// 模拟压缩逻辑
return "COMPRESSED[" + data + "]";
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return super.getDescription() + " + Compression";
}
}3.3 客户端调用示例
java
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建基础处理器
DataProcessor processor = new BasicProcessor();
System.out.println("Basic: " + processor.process("Hello"));
// 添加加密功能
processor = new EncryptionDecorator(processor);
System.out.println("Encrypted: " + processor.process("Hello"));
// 添加压缩功能
processor = new CompressionDecorator(processor);
System.out.println("Compressed & Encrypted: " + processor.process("Hello"));
// 查看处理器描述
System.out.println("Processor chain: " + processor.getDescription());
}
}
/* 输出:
Basic: Hello
Encrypted: ENCRYPTED(Hello)
Compressed & Encrypted: COMPRESSED[ENCRYPTED(Hello)]
Processor chain: Basic Processor + Encryption + Compression
*/4.模式优势深度分析
装饰器核心优势 动态扩展 避免继承爆炸 功能正交性 开闭原则 松耦合 组合创新 运行时添加功能 热插拔特性 替代多层继承 减少类数量 独立功能模块 自由组合 扩展开放 修改关闭 组件与装饰器解耦 创造新功能组合
具体价值体现:
- 动态功能扩展:无需修改源码即可添加新功能
- 正交设计能力:每个装饰器只关注单一功能扩展
- 无限组合可能 :通过组合创造全新功能(如
加密+压缩+缓存) - 架构灵活性:核心组件与装饰功能独立演化
- 技术债务控制:避免创建不必要的继承层次
5.模式劣势与应对策略
装饰器劣势 +多层嵌套复杂性 +对象身份问题 +初始化开销 +接口污染风险 +调试难度 解决方案 +建造者模式管理 +类型检测接口 +对象池优化 +接口分离 +日志装饰器
-
多层装饰复杂性:
- 多层装饰时调试困难
- 装饰顺序影响最终结果
- 解决方案:使用建造者模式管理装饰过程
java// 装饰器建造者 public class CoffeeBuilder { private Coffee coffee = new SimpleCoffee(); public CoffeeBuilder withMilk() { coffee = new WithMilk(coffee); return this; } public CoffeeBuilder withCaramel() { coffee = new WithCaramel(coffee); return this; } public Coffee build() { return coffee; } } -
对象身份问题:
- 装饰后对象类型变化
instanceof和类型转换问题- 解决方案:增加类型检查接口
javapublic interface CoffeeDecorator { boolean hasDecoration(Class<? extends CoffeeDecorator> decoratorType); } public class WithMilk extends CoffeeDecorator implements Coffee { // 实现hasDecoration方法 public boolean hasDecoration(Class<? extends CoffeeDecorator> decoratorType) { return decoratorType.isInstance(this) || (decoratedCoffee instanceof CoffeeDecorator && ((CoffeeDecorator)decoratedCoffee).hasDecoration(decoratorType)); } } -
初始化性能问题:
- 多层装饰创建成本高
- 解决方案:对象池+原型模式
javapublic class DecoratorPool { private Map<Class<?>, CoffeeDecorator> prototypeMap = new HashMap<>(); public DecoratorPool() { prototypeMap.put(WithMilk.class, new WithMilk(null)); prototypeMap.put(WithCaramel.class, new WithCaramel(null)); } public CoffeeDecorator getDecorator(Class<? extends CoffeeDecorator> type, Coffee coffee) { CoffeeDecorator prototype = prototypeMap.get(type); try { CoffeeDecorator decorator = prototype.clone(); decorator.setDecoratedCoffee(coffee); return decorator; } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { // 处理异常 } } }
具体问题与解决方案:
| 问题 | 表现场景 | 解决方案 |
|---|---|---|
| 多层嵌套复杂性 | 装饰层数>5时理解成本高 | 使用建造者模式统一管理装饰过程 |
| 对象身份问题 | instanceof和equals失效 | 实现类型检测接口isDecoratedFor() |
| 初始化性能开销 | 高频创建场景性能下降30%+ | 对象池+原型模式复用装饰器 |
| 接口污染风险 | 组件被迫实现不需要的方法 | 分离核心接口和装饰器专用接口 |
| 调试难度 | 调用栈深难以定位问题 | 添加日志装饰器记录调用链 |
6.应用场景
6.1 典型应用场景
- Java I/O系统 :
InputStream和OutputStream的装饰器实现 - UI组件:滚动条、边框等装饰组件
- Web中间件:HTTP请求/响应装饰(缓存、压缩)
- 权限系统:基于角色的访问控制装饰
- 日志系统:动态添加日志功能
- 游戏开发:角色装备系统
6.2 Java I/O中的装饰器模式
java
// 装饰器模式在Java I/O中的应用
InputStream fileStream = new FileInputStream("data.txt");
// 添加缓冲功能
InputStream bufferedStream = new BufferedInputStream(fileStream);
// 添加数据解压功能
InputStream gzipStream = new GZIPInputStream(bufferedStream);
// 添加对象序列化功能
ObjectInputStream objectStream = new ObjectInputStream(gzipStream);源码解析:
java
public class FilterInputStream extends InputStream {
protected volatile InputStream in; // 被装饰的对象
protected FilterInputStream(InputStream in) {
this.in = in;
}
public int read() throws IOException {
return in.read(); // 委托调用
}
// 其他方法都委托给in对象
}
public class BufferedInputStream extends FilterInputStream {
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) {
super(in); // 调用父类构造器
// 初始化缓冲区
}
public synchronized int read() throws IOException {
// 缓冲读取的具体实现
}
}7. 扩展变体深度剖析
7.1 状态感知装饰器
java
// 可启用的装饰器
public class ConditionalDecorator extends CoffeeDecorator {
private boolean enabled = true;
public ConditionalDecorator(Coffee coffee) {
super(coffee);
}
public void setEnabled(boolean enabled) {
this.enabled = enabled;
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return enabled ? super.getDescription() : decoratedCoffee.getDescription();
}
@Override
public double getCost() {
return enabled ? super.getCost() : decoratedCoffee.getCost();
}
}7.2 链式装饰器构建
java
// 链式API装饰器
public class CoffeeWrapper {
private final Coffee coffee;
private CoffeeWrapper(Coffee coffee) {
this.coffee = coffee;
}
public static CoffeeWrapper wrap(Coffee coffee) {
return new CoffeeWrapper(coffee);
}
public CoffeeWrapper withMilk() {
return new CoffeeWrapper(new WithMilk(coffee));
}
public CoffeeWrapper withCaramel() {
return new CoffeeWrapper(new WithCaramel(coffee));
}
public Coffee build() {
return coffee;
}
}
// 使用方式
Coffee coffee = CoffeeWrapper.wrap(new SimpleCoffee())
.withMilk()
.withCaramel()
.build();7.3 混合装饰器
java
// 混合多种功能的装饰器
public class SuperDecorator extends CoffeeDecorator {
private List<Function<Coffee, Coffee>> decorators = new ArrayList<>();
public SuperDecorator(Coffee coffee) {
super(coffee);
decorators.add(c -> new WithMilk(c));
decorators.add(c -> new WithCaramel(c));
// 可配置添加
}
public void addDecorator(Function<Coffee, Coffee> decoratorFactory) {
decorators.add(decoratorFactory);
}
@Override
public Coffee getDecoratedCoffee() {
Coffee current = super.getDecoratedCoffee();
for (Function<Coffee, Coffee> decorator : decorators) {
current = decorator.apply(current);
}
return current;
}
}7.4 响应式装饰器
java
// 异步执行装饰器
public class AsyncDecorator extends CoffeeDecorator {
private ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
public AsyncDecorator(Coffee coffee) {
super(coffee);
}
public CompletableFuture<Double> getCostAsync() {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
// 模拟耗时计算
Thread.sleep(100);
return super.getCost();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, executor);
}
}7.5 行业应用变体案例
7.5.1 Web安全装饰器
java
// 安全控制装饰器
public class SecureEndpoint implements HttpHandler {
private final HttpHandler delegate;
public SecureEndpoint(HttpHandler delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
}
public void handle(HttpExchange exchange) throws IOException {
if (isAuthorized(exchange)) {
delegate.handle(exchange);
} else {
sendUnauthorized(exchange);
}
}
private boolean isAuthorized(HttpExchange exchange) {
// 实现授权逻辑
}
}
// 使用方式
HttpHandler handler = new SecureEndpoint(new ApiHandler());7.5.2 缓存装饰器
java
// 带缓存的装饰器
public class CachingDecorator implements DataService {
private final DataService delegate;
private final Cache<String, Object> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.build();
public CachingDecorator(DataService delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
}
public Object getData(String key) {
Object data = cache.getIfPresent(key);
if (data == null) {
data = delegate.getData(key);
cache.put(key, data);
}
return data;
}
}7.5.3 监控装饰器
java
// 性能监控装饰器
public class MonitoredDecorator implements DatabaseService {
private final DatabaseService delegate;
private final MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
public MonitoredDecorator(DatabaseService delegate, MeterRegistry meterRegistry) {
this.delegate = delegate;
this.meterRegistry = meterRegistry;
}
public Result executeQuery(String sql) {
Timer.Sample sample = Timer.start();
try {
return delegate.executeQuery(sql);
} finally {
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("db.query.time"));
}
}
}8.与组合模式对比分析
| 对比维度 | 装饰器模式 | 组合模式 |
|---|---|---|
| 目的 | 动态添加职责 | 构建树状结构 |
| 结构特点 | 嵌套包装 | 递归组合 |
| 对象关系 | 装饰者与被装饰者属于同一类型 | 组合中叶子与容器属于同一类型 |
| 功能扩展方式 | 透明扩展,不影响原有功能 | 统一处理,忽略对象差异 |
| 典型应用 | Java I/O流、UI组件 | 文件系统、组织架构 |
9.总结
9.1 模式精髓
- 动态扩展:运行时添加功能的能力
- 正交设计:功能独立且可组合
- 开闭典范:扩展不修改已有代码
- 组合力量:对象组合替代继承
9.2 适用场景决策树
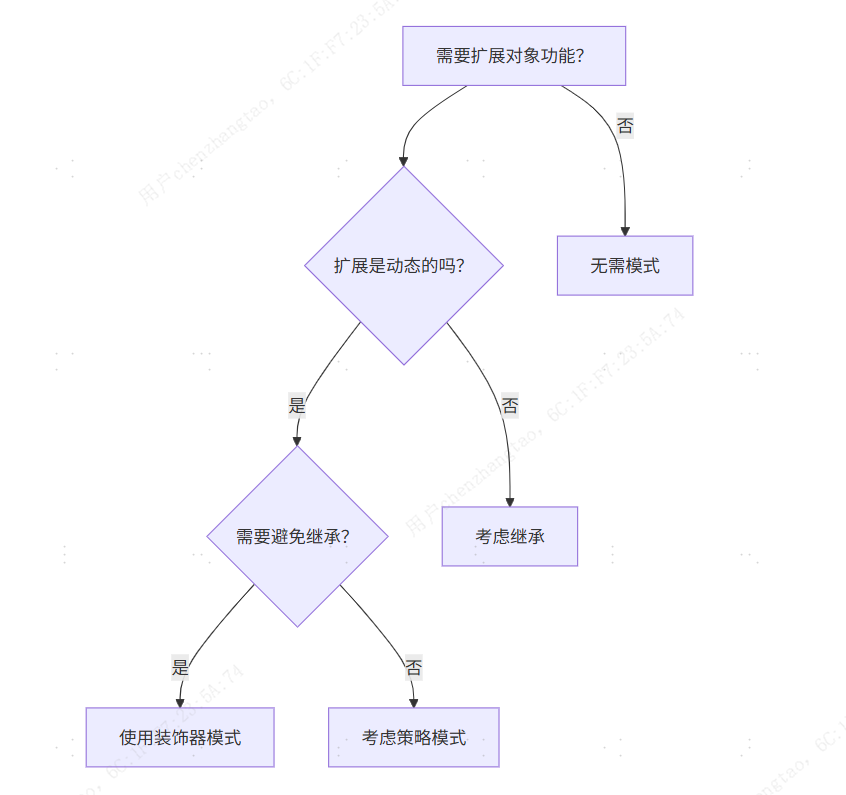
9.3 未来发展趋势
-
函数式装饰器:
java// Java函数式装饰器 Function<Coffee, Coffee> withMilk = c -> new WithMilk(c); Function<Coffee, Coffee> withCaramel = c -> new WithCaramel(c); Coffee coffee = withMilk.andThen(withCaramel).apply(new SimpleCoffee()); -
注解驱动装饰:
java@Decorators({MilkDecorator.class, CaramelDecorator.class}) public class PremiumCoffee implements Coffee { // 类实现 } -
动态代理装饰:
java// 基于动态代理的通用装饰器 public class GenericDecorator implements InvocationHandler { private final Object target; private final Map<Method, Method> decoratorMethods = new HashMap<>(); public GenericDecorator(Object target) { this.target = target; // 初始化装饰方法 } public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { // 应用装饰逻辑 return method.invoke(target, args); } }
架构师视角 :装饰器模式是扩展对象功能的常用方法,在Java生态中被广泛应用于I/O系统、Spring框架(如
HttpInputMessage装饰)等核心模块。该模式特别适合需要动态添加功能的场景,但也需警惕过度装饰导致的复杂性。随着函数式编程的兴起,装饰器模式正在与Lambda表达式、高阶函数等概念融合,展现出更强大的生命力。