1、Thymeleaf模板引擎
1.1、模板引擎
前端交给我们的页面,是html页面。如果是我们以前开发,我们需要把他们转成jsp页面,jsp好处就是当我们查出一些数据转发到JSP页面以后,我们可以用jsp轻松实现数据的显示,及交互等。
jsp支持非常强大的功能,包括能写Java代码,但是呢,我们现在的这种情况,SpringBoot这个项目首先是以jar的方式,不是war,像第二,我们用的还是嵌入式的Tomcat,所以呢,他现在默认是不支持jsp的。
那不支持jsp,如果我们直接用纯静态页面的方式,那给我们开发会带来非常大的麻烦,那怎么办呢?
SpringBoot推荐你可以来使用模板引擎:
模板引擎,我们其实大家听到很多,其实jsp就是一个模板引擎,还有用的比较多的freemarker,包括SpringBoot给我们推荐的Thymeleaf,模板引擎有非常多,但再多的模板引擎,他们的思想都是一样的,什么样一个思想呢我们来看一下这张图:
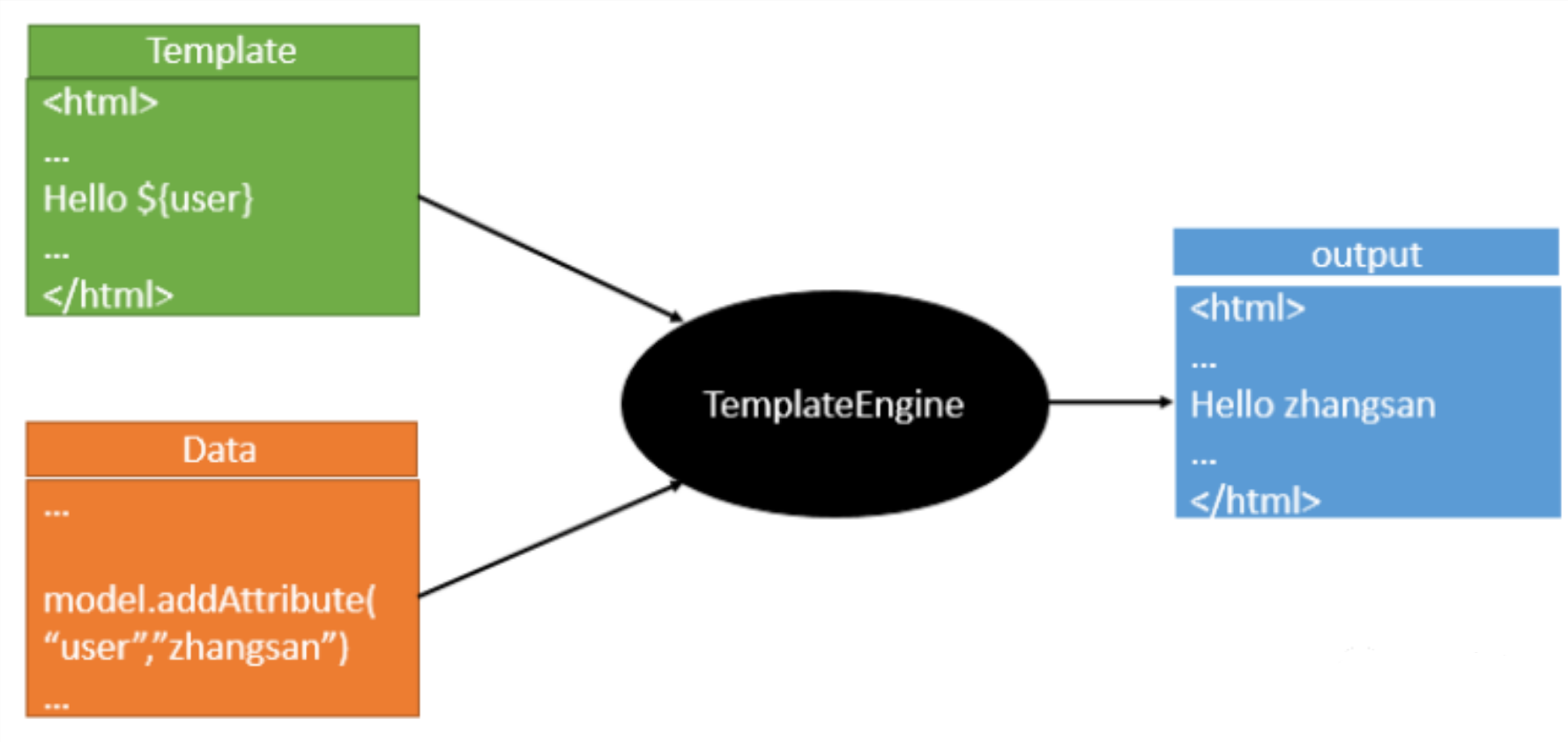
模板引擎的作用就是我们来写一个页面模板,比如有些值呢,是动态的,我们写一些表达式。而这些值,从哪来呢,就是我们在后台封装一些数据。然后把这个模板和这个数据交给我们模板引擎,模板引擎按照我们这个数据帮你把这表达式解析、填充到我们指定的位置,然后把这个数据最终生成一个我们想要的内容给我们写出去,这就是我们这个模板引擎,不管是jsp还是其他模板引擎,都是这个思想。只不过,不同模板引擎之间,他们可能这个语法有些许不同。
主要来介绍一下SpringBoot给我们推荐的Thymeleaf模板引擎,这模板引擎呢,是一个高级语言的模板引擎,语法更简单,功能更强大。
首先,我们来看SpringBoot里边怎么用。
1.2、引入Thymeleaf
对于springboot来说,我们去在项目中引入一下starter。给大家三个网址:
Thymeleaf 官网:https://www.thymeleaf.org/
Thymeleaf 在Github 的主页:https://github.com/thymeleaf/thymeleaf
Spring官方文档:找到我们对应的版本
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.2.5.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#using-boot-starter
找到对应的pom依赖:可以适当点进源码看下本来的包!
xml
<!--thymeleaf-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>Maven会自动下载jar包,我们可以去看下下载的东西;
1.3、Thymeleaf分析
我们已经引入了Thymeleaf,那这个要怎么使用呢?
我们首先得按照SpringBoot的自动配置原理看一下我们这个Thymeleaf的自动配置规则,在按照那个规则,我们进行使用。
我们去找一下Thymeleaf的自动配置类:ThymeleafProperties
java
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.thymeleaf")
public class ThymeleafProperties {
private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING = StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html";
private boolean checkTemplate = true;
private boolean checkTemplateLocation = true;
private String prefix = DEFAULT_PREFIX;
private String suffix = DEFAULT_SUFFIX;
private String mode = "HTML";
private Charset encoding = DEFAULT_ENCODING;
//...
}我们可以在其中看到默认的前缀classpath:/templates/和后缀.html!
我们只需要把我们的html页面放在类路径下的templates下,thymeleaf就可以帮我们自动渲染了。
使用thymeleaf什么都不需要配置,只需要将他放在指定的文件夹下即可!
测试
1、编写一个TestController
java
@Controller
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/t1")
public String t1(){
//classpath:/templates/test.html
return "test";
}
}2、编写一个测试页面 test.html 放在 templates 目录下
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>测试页面</h1>
</body>
</html>3、启动项目请求测试
1.4、Thymeleaf语法学习
要学习语法,还是参考官网文档最为准确,我们找到对应的版本看一下;
Thymeleaf 官网:https://www.thymeleaf.org/ , 简单看一下官网!我们去下载Thymeleaf的官方文档!
我们做个最简单的练习 :我们需要查出一些数据,在页面中展示
1、修改测试请求,增加数据传输;
java
@Controller
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/t2")
public String t2(Model model){
//存入数据
model.addAttribute("msg","Hello, Thymeleaf");
//classpath:/templates/test.html
return "test2";
}
}2、我们要使用thymeleaf,需要在html文件中导入命名空间的约束,方便提示。
我们可以去官方文档的#3中看一下命名空间拿来过来:
html
xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"3、编写前端页面
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
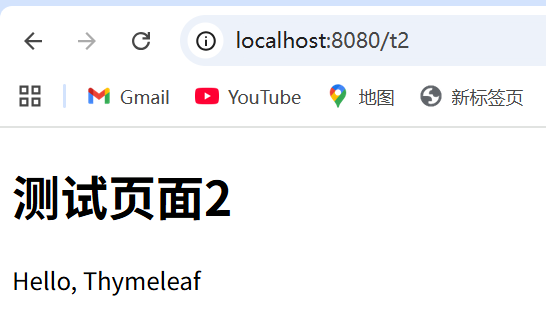
<h1>测试页面2</h1>
<!--th:text就是将div中的内容与它指定的值绑定,和之前学习的Vue一样-->
<div th:text="${msg}"></div>
</body>
</html>4、启动测试!
OK,入门搞定,我们来认真研习一下Thymeleaf的使用语法!
1、我们可以使用任意的 th:attr 来替换Html中原生属性的值!

2、我们能写哪些表达式呢?
yaml
Simple expressions:(表达式语法)
Variable Expressions: ${...}:获取变量值;OGNL;
1)、获取对象的属性、调用方法
2)、使用内置的基本对象:#18
#ctx : the context object.
#vars: the context variables.
#locale : the context locale.
#request : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletRequest object.
#response : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletResponse object.
#session : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpSession object.
#servletContext : (only in Web Contexts) the ServletContext object.
3)、内置的一些工具对象:
#execInfo : information about the template being processed.
#uris : methods for escaping parts of URLs/URIs
#conversions : methods for executing the configured conversion service (if any).
#dates : methods for java.util.Date objects: formatting, component extraction, etc.
#calendars : analogous to #dates , but for java.util.Calendar objects.
#numbers : methods for formatting numeric objects.
#strings : methods for String objects: contains, startsWith, prepending/appending, etc.
#objects : methods for objects in general.
#bools : methods for boolean evaluation.
#arrays : methods for arrays.
#lists : methods for lists.
#sets : methods for sets.
#maps : methods for maps.
#aggregates : methods for creating aggregates on arrays or collections.
==================================================================================
Selection Variable Expressions: *{...}:选择表达式:和${}在功能上是一样;
Message Expressions: #{...}:获取国际化内容
Link URL Expressions: @{...}:定义URL;
Fragment Expressions: ~{...}:片段引用表达式
Literals(字面量)
Text literals: 'one text' , 'Another one!' ,...
Number literals: 0 , 34 , 3.0 , 12.3 ,...
Boolean literals: true , false
Null literal: null
Literal tokens: one , sometext , main ,...
Text operations:(文本操作)
String concatenation: +
Literal substitutions: |The name is ${name}|
Arithmetic operations:(数学运算)
Binary operators: + , - , * , / , %
Minus sign (unary operator): -
Boolean operations:(布尔运算)
Binary operators: and , or
Boolean negation (unary operator): ! , not
Comparisons and equality:(比较运算)
Comparators: > , < , >= , <= ( gt , lt , ge , le )
Equality operators: == , != ( eq , ne )
Conditional operators:条件运算(三元运算符)
If-then: (if) ? (then)
If-then-else: (if) ? (then) : (else)
Default: (value) ?: (defaultvalue)
Special tokens:
No-Operation: _练习测试:
1、 我们编写一个Controller,放一些数据
java
@Controller
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/t3")
public String t3(Map<String,Object> map){
//存入数据
map.put("msg","<h1>Hello, Thymeleaf</h1>");
map.put("users", Arrays.asList("lingbo","mikasa"));
//classpath:/templates/test3.html
return "test3";
}
}2、测试页面取出数据
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>绫波粒</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>测试页面</h1>
<!--不转义-->
<div th:text="${msg}"></div>
<div th:utext="${msg}"></div>
<!--遍历数据-->
<!--th:each每次遍历都会生成当前这个标签:官网#9-->
<h4 th:each="user :${users}" th:text="${user}"></h4>
<!--行内写法:官网#12-->
<h4>
<span th:each="user:${users}">[[${user} ]]</span>
</h4>
</body>
</html>3、启动项目测试!
2、MVC自动装配原理
2.1、官网阅读
在进行项目编写前,我们还需要知道一个东西,就是SpringBoot对我们的SpringMVC还做了哪些配置,包括如何扩展,如何定制。
只有把这些都搞清楚了,我们在之后使用才会更加得心应手。
途径一:源码分析,途径二:官方文档!
Spring MVC Auto-configuration
Spring Boot provides auto-configuration for Spring MVC that works well with most applications.
Spring Boot为Spring MVC提供了自动配置,它可以很好地与大多数应用程序一起工作。
The auto-configuration adds the following features on top of Spring's defaults:
自动配置在Spring默认设置的基础上添加了以下功能:
-
Inclusion of
ContentNegotiatingViewResolverandBeanNameViewResolverbeans.包含视图解析器
-
Support for serving static resources, including support for WebJars (covered later in this document)).
支持静态资源文件夹的路径,以及webjars
-
Automatic registration of
Converter,GenericConverter, andFormatterbeans.自动注册的
Converter和FormatterConverter:转换器,这就是我们网页提交数据到后台自动封装成为对象的东西,比如把"1"字符串自动转换为int类型
Formatter:格式化器,比如页面给我们了一个2025-8-24,它会给我们自动格式化为Date对象
-
Support for
HttpMessageConverters(covered later in this document).HttpMessageConverters:SpringMVC用来转换Http请求和响应的的,比如我们要把一个User对象转换为JSON字符串,可以去看官网文档解释;
-
Automatic registration of
MessageCodesResolver(covered later in this document).自动注册用于定义错误代码生成规则的
-
Static
index.htmlsupport.首页定制
-
Custom
Faviconsupport (covered later in this document).图标定制
-
Automatic use of a
ConfigurableWebBindingInitializerbean (covered later in this document).初始化数据绑定器:帮我们把请求数据绑定到JavaBean中!
If you want to keep those Spring Boot MVC customizations and make more MVC customizations (interceptors, formatters, view controllers, and other features), you can add your own @Configuration class of type WebMvcConfigurer but without @EnableWebMvc.
如果您希望保留Spring Boot MVC功能,并且希望添加其他MVC配置(拦截器、格式化器、视图控制器和其他功能),则可以添加自己的
@Configuration类,类型为WebMvcConfiguer,但不添加@EnableWebMvc。
If you want to provide custom instances of RequestMappingHandlerMapping, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter, or ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver, and still keep the Spring Boot MVC customizations, you can declare a bean of type WebMvcRegistrations and use it to provide custom instances of those components.
如果希望提供
RequestMappingHandlerMapping、RequestMappingHandlerAdapter或ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver的自定义实例,并保留Spring Boot MVC的定制化,则可以声明WebMvcRegistrations实例来提供定制化组件实例。
If you want to take complete control of Spring MVC, you can add your own @Configuration annotated with @EnableWebMvc.
如果您想完全控制Spring MVC,可以添加自己的
@Configuration,并使用@EnableWebMvc注解。
我们来仔细对照,看一下它怎么实现的,它告诉我们SpringBoot已经帮我们自动配置好了SpringMVC,然后自动配置了哪些东西呢?
2.2、ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 内容协商视图解析器
自动配置了ViewResolver,就是我们之前学习的SpringMVC的视图解析器;
即根据方法的返回值取得视图对象(View),然后由视图对象决定如何渲染(转发,重定向)。
我们去看看这里的源码:我们找到 WebMvcAutoConfiguration , 然后搜索ContentNegotiatingViewResolver。找到如下方法!
java
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(ViewResolver.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "viewResolver", value = ContentNegotiatingViewResolver.class)
public ContentNegotiatingViewResolver viewResolver(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver resolver = new ContentNegotiatingViewResolver();
resolver.setContentNegotiationManager(beanFactory.getBean(ContentNegotiationManager.class));
// ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 使用所有其他视图解析器来定位视图,因此它应该具有较高的优先级
resolver.setOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
return resolver;
}我们可以点进这类看看!找到对应的解析视图的代码;
java
@Override // 注解说明:@Nullable 即参数可为null
@Nullable
public View resolveViewName(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception {
RequestAttributes attrs = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
Assert.state(attrs instanceof ServletRequestAttributes, "No current ServletRequestAttributes");
List<MediaType> requestedMediaTypes = getMediaTypes(((ServletRequestAttributes) attrs).getRequest());
if (requestedMediaTypes != null) {
// 获取候选的视图对象
List<View> candidateViews = getCandidateViews(viewName, locale, requestedMediaTypes);
// 选择一个最适合的视图对象,然后把这个对象返回
View bestView = getBestView(candidateViews, requestedMediaTypes, attrs);
if (bestView != null) {
return bestView;
}
}
//...
}我们继续点进去看,他是怎么获得候选的视图的呢?
getCandidateViews中看到他是把所有的视图解析器拿来,进行for循环,挨个解析!
java
private List<View> getCandidateViews(String viewName, Locale locale, List<MediaType> requestedMediaTypes)
throws Exception {
List<View> candidateViews = new ArrayList<>();
if (this.viewResolvers != null) {
Assert.state(this.contentNegotiationManager != null, "No ContentNegotiationManager set");
//在for循环中挨个解析
for (ViewResolver viewResolver : this.viewResolvers) {
View view = viewResolver.resolveViewName(viewName, locale);
//若非空则添加进候选视图列表
if (view != null) {
candidateViews.add(view);
}
for (MediaType requestedMediaType : requestedMediaTypes) {
List<String> extensions = this.contentNegotiationManager.resolveFileExtensions(requestedMediaType);
for (String extension : extensions) {
String viewNameWithExtension = viewName + '.' + extension;
view = viewResolver.resolveViewName(viewNameWithExtension, locale);
if (view != null) {
candidateViews.add(view);
}
}
}
}
}
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.defaultViews)) {
candidateViews.addAll(this.defaultViews);
}
return candidateViews;
}所以得出结论:ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 这个视图解析器就是用来组合所有的视图解析器的
我们再去研究下他的组合逻辑,看到有个属性viewResolvers,看看它是在哪里进行赋值的!
java
@Override
protected void initServletContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
// 这里它是从beanFactory工具中获取容器中的所有视图解析器
// ViewRescolver.class 把所有的视图解析器来组合的
Collection<ViewResolver> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(obtainApplicationContext(), ViewResolver.class).values();
if (this.viewResolvers == null) {
this.viewResolvers = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.size());
for (ViewResolver viewResolver : matchingBeans) {
if (this != viewResolver) {
this.viewResolvers.add(viewResolver);
}
}
}
//...
}既然它是在容器中去找视图解析器,我们是否可以猜想,我们就可以去实现一个视图解析器了呢?
我们可以自己给容器中去添加一个视图解析器;这个类就会帮我们自动的将它组合进来;
1、在我们的主程序中去写一个视图解析器来试试;
java
public class MyMvcConfig {
@Bean //放入容器
public ViewResolver myViewResolver() {
return new MyViewResolver();
}
//我们写一个静态内部类,视图解析器就需要实现ViewResolver接口
private static class MyViewResolver implements ViewResolver {
@Override
public View resolveViewName(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception {
return null;
}
}
}2、怎么看我们自己写的视图解析器有没有起作用呢?
我们给 DispatcherServlet 中的 doDispatch方法 加个断点进行调试一下,因为所有的请求都会走到这个方法中
3、我们启动我们的项目,然后随便访问一个页面,看一下Debug信息;
找到this
找到视图解析器,我们看到我们自己定义的就在这里了;
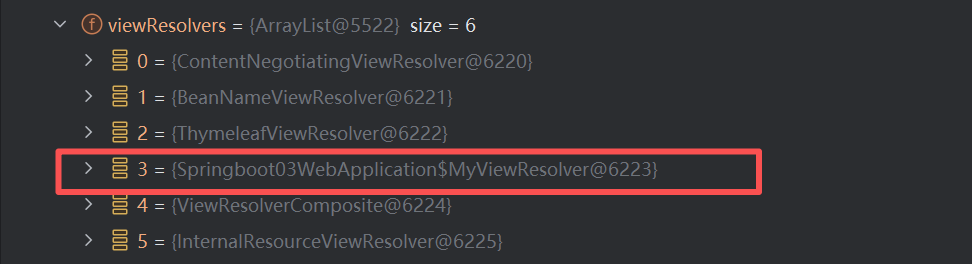
所以说,我们如果想要使用自己定制化的东西,我们只需要给容器中添加这个组件就好了!剩下的事情SpringBoot就会帮我们做了!
2.3、转换器和格式化器
在WebMvcAutoConfiguration中找到格式化转换器FormattingConversionService:
java
@Bean
@Override
public FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService() {
Format format = this.mvcProperties.getFormat();
// 拿到配置文件中的格式化规则
WebConversionService conversionService = new WebConversionService(new DateTimeFormatters()
.dateFormat(format.getDate()).timeFormat(format.getTime()).dateTimeFormat(format.getDateTime()));
addFormatters(conversionService);
return conversionService;
}点进去:
java
public Format getFormat() {
return this.format;
}
public static class Format {
/**
* Date format to use, for example `dd/MM/yyyy`.
*/
private String date;
}可以看到在我们的Properties文件中,我们可以进行自动配置它!
如果配置了自己的格式化方式,就会注册到Bean中生效,我们可以在配置文件中配置日期格式化的规则:
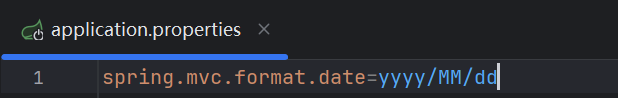
2.4、修改SpringBoot的默认配置
SpringBoot在自动配置很多组件的时候,先看容器中有没有用户自己配置的(如果用户自己配置@bean),如果有就用用户配置的,如果没有就用自动配置的;
如果有些组件可以存在多个,比如我们的视图解析器,就将用户配置的和自己默认的组合起来!
扩展使用SpringMVC
回顾上文提到的官方文档如下:
If you want to keep those Spring Boot MVC customizations and make more MVC customizations (interceptors, formatters, view controllers, and other features), you can add your own @Configuration class of type WebMvcConfigurer but without @EnableWebMvc.
如果您希望保留Spring Boot MVC功能,并且希望添加其他MVC配置(拦截器、格式化器、视图控制器和其他功能),则可以添加自己的
@Configuration类,类型为WebMvcConfiguer,但不添加@EnableWebMvc。
If you want to provide custom instances of RequestMappingHandlerMapping, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter, or ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver, and still keep the Spring Boot MVC customizations, you can declare a bean of type WebMvcRegistrations and use it to provide custom instances of those components.
如果希望提供
RequestMappingHandlerMapping、RequestMappingHandlerAdapter或ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver的自定义实例,并保留Spring Boot MVC的定制化,则可以声明WebMvcRegistrations实例来提供定制化组件实例。
我们要做的就是编写一个@Configuration注解类,并且类型要为WebMvcConfigurer,还不能标注@EnableWebMvc注解;我们去自己写一个;我们新建一个包叫config,写一个类MyMvcConfig;
java
// 因为类型要求为WebMvcConfigurer,所以我们实现其接口
// 可以使用自定义类扩展MVC的功能
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
// 浏览器发送/lingbo,就会跳转到test页面;
registry.addViewController("/lingbo").setViewName("test");
}
}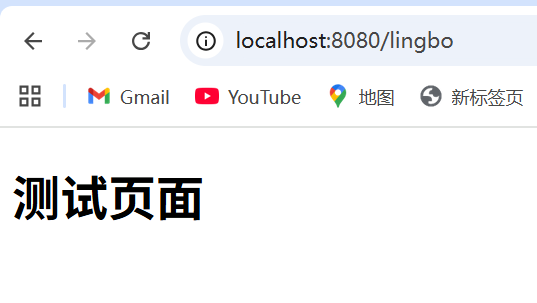
确实也跳转过来了!所以说,我们要扩展SpringMVC,官方就推荐我们这么去使用,既保SpringBoot留所有的自动配置,也能用我们扩展的配置!
我们可以去分析一下原理:
1、WebMvcAutoConfiguration 是 SpringMVC的自动配置类,里面有一个类WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter
2、这个类上有一个注解,在做其他自动配置时会导入:@Import(EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class)
java
@Import(EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class)
public static class WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer {
private final WebMvcProperties mvcProperties;
private final ListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
//...
}3、我们点进EnableWebMvcConfiguration这个类看一下,它继承了一个父类:DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration
这个父类中有这样一段代码:
java
public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
private final WebMvcConfigurerComposite configurers = new WebMvcConfigurerComposite();
// 从容器中获取所有的WebMvcConfigurer
@Autowired(required = false)
public void setConfigurers(List<WebMvcConfigurer> configurers) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {
this.configurers.addWebMvcConfigurers(configurers);
}
}
//...
}4、我们可以在这个类中去寻找一个我们刚才设置的viewController当做参考,发现它调用了一个addViewControllers方法
java
protected void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
this.configurers.addViewControllers(registry);
}5、我们点进去看一下
java
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
// 将所有的WebMvcConfigurer相关配置来一起调用!包括我们自己配置的和Spring给我们配置的
for (WebMvcConfigurer delegate : this.delegates) {
delegate.addViewControllers(registry);
}
}所以得出结论:所有的WebMvcConfiguration都会被作用,不止Spring自己的配置类,我们自己的配置类当然也会被调用;
2.5、全面接管SpringMVC
官方文档:
If you want to take complete control of Spring MVC you can add your own @Configuration annotated with @EnableWebMvc
全面接管即:SpringBoot对SpringMVC的自动配置不需要了,所有都是我们自己去配置!
只需在我们的配置类中要加一个@EnableWebMvc。
我们看下如果我们全面接管了SpringMVC了,我们之前SpringBoot给我们配置的静态资源映射一定会无效,我们可以去测试一下;
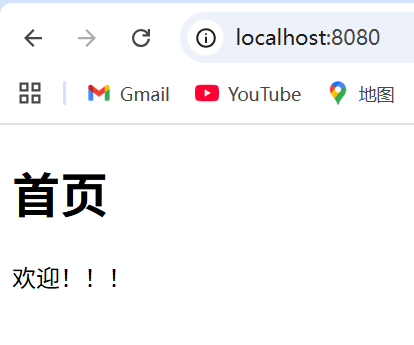
不加注解之前,访问首页:
给配置类MyMvcConfig加上注解:@EnableWebMvc
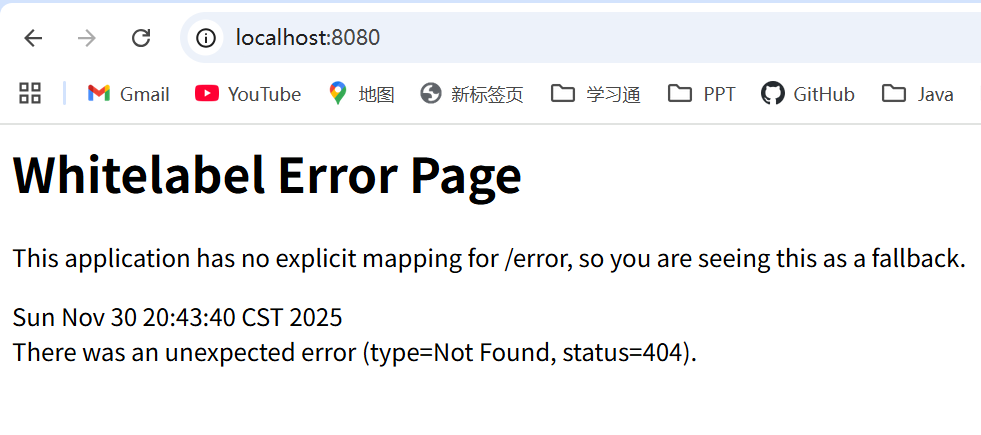
我们发现所有的SpringMVC自动配置都失效了!回归到了最初的样子;
当然,我们开发中,不推荐使用全面接管SpringMVC
思考问题?为什么加了一个注解,自动配置就失效了!我们看下源码:
1、这里发现它是导入了一个类,我们可以继续进去看
java
@Import(DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration.class)
public @interface EnableWebMvc {
}2、它继承了一个父类 WebMvcConfigurationSupport
java
public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
//...
}3、我们来回顾一下WebMvc自动配置类
java
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class })
// @ConditionalOnMissingBean,这个注解的意思就是:容器中没有这个组件的时候,这个自动配置类才生效
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)
@AutoConfigureAfter({ DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class,
ValidationAutoConfiguration.class })
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
//...
}总结一句话:@EnableWebMvc将WebMvcConfigurationSupport组件导入进来了;
而导入的WebMvcConfigurationSupport只是SpringMVC最基本的功能!