十,进程控制
10.1进程创建
在linux中fork函数是非常重要的函数,它从已存在进程中创建⼀个新进程。新进程为子进程,而原进程为父进程。
写时拷贝
通常,父子代码共享,父子再不写⼊时,数据也是共享的,当任意一方试图写入,便以写时拷贝的方式各自有⼀份副本。具体见下图:
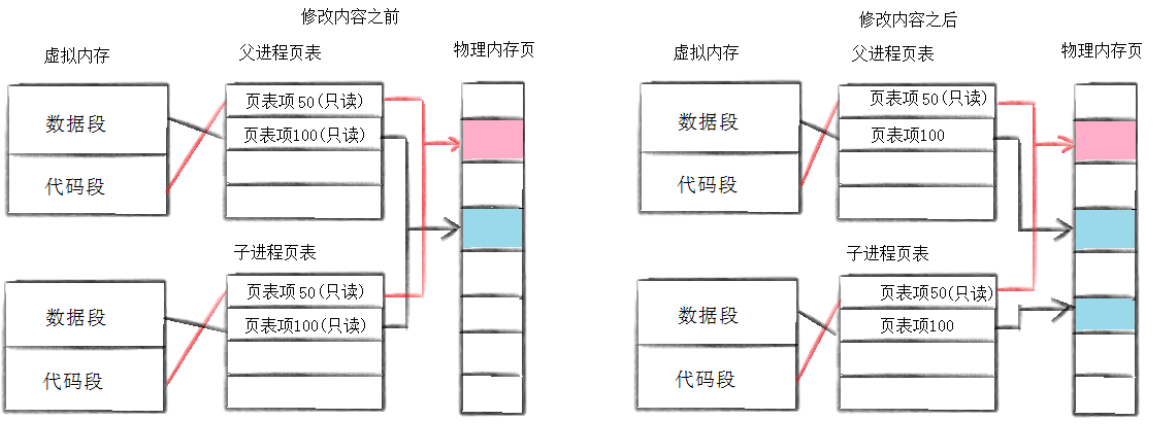
因为有写时拷贝技术的存在,所以父子进程得以彻底分离。完成了进程独里性的技术保证。写时拷贝是⼀种延时申请技术,可以提高整机内存的使用率。
fork
NAME
fork - create a child process
SYNOPSIS
#include <unistd.h>
pid_t fork(void);
RETURN VALUE
On success, the PID of the child process is returned in the parent, and 0 is re‐
turned in the child. On failure, -1 is returned in the parent, no child process
is created, and errno is set to indicate the error.- ⼀个父进程希望复制自己,使父子进程同时执行不同的代码段。例如,⽗进程等待客户端请求,⽣成子进程来处理请求。
- ⼀个进程要执行⼀个不同的程序。例如子进程从fork返回后,调用exec系列函数。
fork调用失败原因
- 系统进程太多
- 实际用户进程数量超过限制
10.2进程终止
进程退出情况
- 代码运行完毕,结果正确。
- 代码运行完毕,结果不正确。
- 代码异常终止。
退出码
++对于运行结果,如何判断其正确性?++
退出码。
退出码(退出状态)可以告诉我们最后⼀次执行的命令的状态。在命令结束以后,我们可以知道命令是成功完成的还是以错误结束的。其基本思想是,程序返回退出代码0时表示执行成功,没有问题。代码1或0以外的任何代码都被视为不成功。
而相似的有:库函数调用失败,返回错误码。
当代码异常终止时,此时退出码是没有意义的,关键是什么原因导致的异常。
exit和_exit
在不考虑异常的情况下,让进程退出一般有以下方法:
- main函数return。注意:非main函数return,函数结束。
- 在任意地方调用exit,非main函数exit,进程结束。
- 在任意地方调用_exit。
| 函数 | exit | _exit |
|---|---|---|
| 终止进程,强制刷新缓冲区? | 会 | 不会 |
| 归属 | C语言库函数 | 系统调用 |
注意:
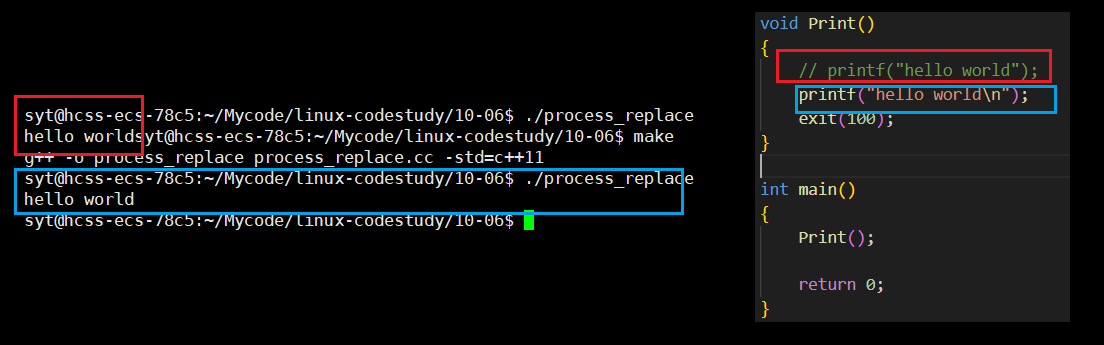
- exit终止进程会强制刷新缓冲区,但是_exit不会。
- 缓冲区和刷新缓冲区的操作一定不在内核中完成,该操作其实是由C++代码维护的。
10.3进程等待
必要性
- 子进程退出,父进程如果不管理回收,就可能造成僵尸进程的问题,进而造成内存泄漏。
- 进程⼀旦变成僵尸状态,就无法被杀死,kill -9 也无能为力,因为谁也没有办法杀死⼀个已经死去的进程。
- 最后,我们需要知道父进程派给子进程的任务完成的如何。如:子进程运行完成,结果对还是不对,或者是否正常退出。
- 父进程通过进程等待 的方式,回收子进程资源,获取子进程退出信息。
wait
NAME
wait, waitpid, waitid - wait for process to change state
SYNOPSIS
#include <sys/wait.h>
pid_t wait(int *_Nullable wstatus);
pid_t waitpid(pid_t pid, int *_Nullable wstatus, int options);
RETURN VALUE
wait(): on success, returns the process ID of the terminated child; on failure, -1
is returned.
waitpid(): on success, returns the process ID of the child whose state has
changed; if WNOHANG was specified and one or more child(ren) specified by pid ex‐
ist, but have not yet changed state, then 0 is returned. On failure, -1 is re‐
turned.
返回值:
成功返回被等待进程pid,失败返回-1。
参数:
输出型参数,获取⼦进程退出状态,不关⼼则可以设置成为NULL如果父进程wait子进程 ,但是子进程就是没有退出 ,那么父进程会阻塞在wait函数中。
补充一点,了解即可:<sys/types.h> 是系统编程中的基础头文件,它定义了与操作系统底层交互所需的各种数据类型。虽然现代编译环境中很多其他头文件已经包含了它,但显式包含可以确保代码在不同平台和编译器之间的可移植性
waitpid
waitpid:获取子进程的退出信息,包括退出码和退出信号。
情况及结果(退出码:exit_code,退出信号:exit_sig):
-
代码运行结束(运行期间没有收到信号)&& return 0
即
exit_code = 0,exit_sig = 0; -
exit_code != 0,exit_sig = 0; -
此时exit_code无意义,
exit_sig != 0;
获取子进程status
wait和waitpid,都有⼀个status参数,该参数是⼀个输出型参数,由操作系统填充。
如果传递NULL,表⽰不关⼼⼦进程的退出状态信息。
否则,操作系统会根据该参数,将⼦进程的退出信息反馈给⽗进程。
status不能简单的当作整形来看待,可以当作位图来看待,具体细节如下图(只研究status低16⽐特位):
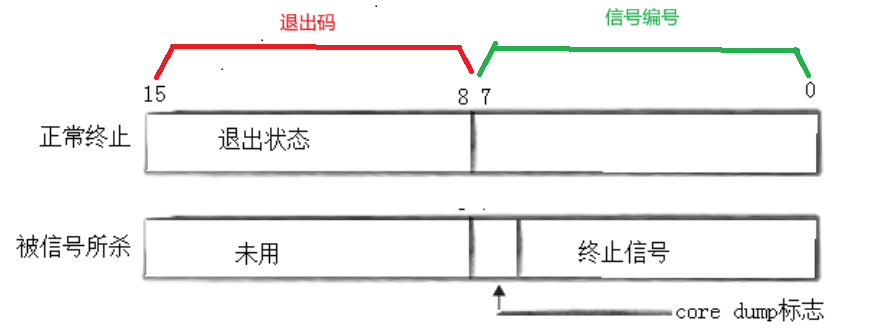
根据以上的位图,可以推断出:
int exit_code = ((status >> 8) & 0xFF); // 1111 1111
int exit_sig = status & 0x7F; // 0111 1111(只有7位有效)示例
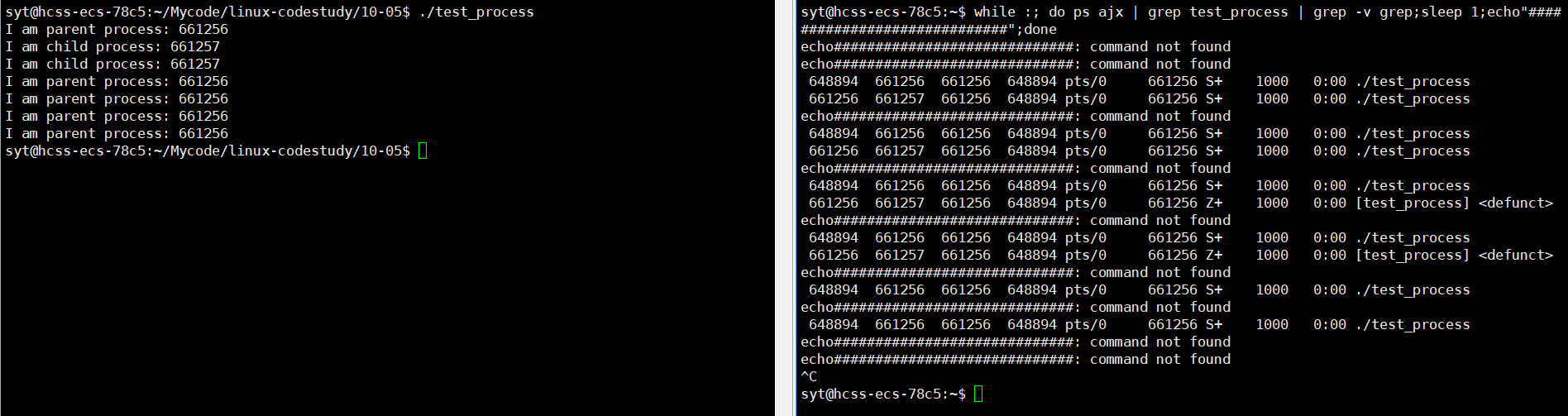
// // 查看指令
// // while :; do ps ajx | grep test_process | grep -v grep;sleep 1;echo"#############################";done
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
int main()
{
pid_t id = fork();
if (id < 0)
{
perror("fork");
exit(2);
}
else if (id == 0)
{
// child process
int cnt = 2;
while (cnt--)
{
std::cout << "I am child process: " << getpid() << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
exit(0);
}
else
{
// parent process
int cnt = 5;
while (cnt--)
{
std::cout << "I am parent process: " << getpid() << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
// 回收子进程,等待僵尸
pid_t rid = wait(NULL);
sleep(2);
// int status = 0;
// pid_t rid = waitpid(id, &status, 0);
// if (rid == id)
// {
// int exit_code = ((status >> 8) & 0xFF);
// int exit_sig = status & 0x7F; // 0111 1111
// printf("pid: %d, wait success!, status: %d, exit_code: %d, exit_sig: %d\n", getpid(), status, exit_code, exit_sig);
// }
}
}
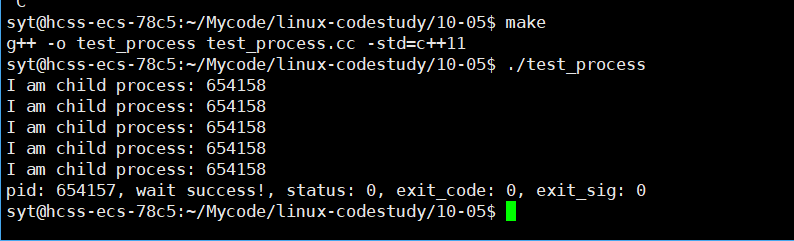
阻塞与非阻塞
简单理解:
阻塞状态:你在一个只能现场点餐、现场取餐的餐厅。
非阻塞状态:想象你在一个现代化的餐厅。你点了一份复杂的菜品。服务员给你一个震动取餐器。你不需要站在出餐口等待。你可以回到座位上和朋友聊天、玩手机、甚至处理一些工作。当你的餐准备好时,取餐器会震动提醒你,你再去取餐。
也就是说阻塞 vs 非阻塞 :核心是等待时能不能干别的事 。是"等"还是"不等"。
非阻塞轮询(同步非阻塞):你不停地跑去出餐口问"好了没?",中间回去玩手机。
| 特性 | 阻塞 | 非阻塞 |
|---|---|---|
| 行为 | 等待直到操作完成 | 立即返回,不等待 |
| 线程状态 | 线程被挂起,不消耗CPU | 线程继续运行,可执行其他任务 |
| 编程复杂度 | 低 | 高 |
| 资源利用率 | 低(线程在等待上浪费时间) | 高(一个线程处理多个I/O) |
| 立即返回 | 不会,必须等到有结果 | 总是立即返回 |
| 返回结果 | 操作的实际结果(如数据) | 结果或一个代表"未完成"的状态/错误码 |
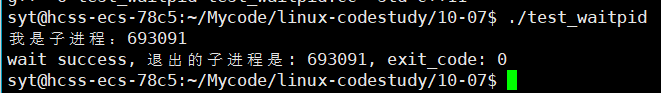
阻塞示例
pid_t id = fork();
if (id < 0)
{
perror("fork");
exit(123);
}
else if (id == 0)
{
// child process
std::cout << "我是子进程:" << getpid() << std::endl;
sleep(5);
exit(0);
}
else
{
// parent process
int status = 0;
pid_t rid = waitpid(id, &status, 0);
if (rid > 0)
{
if (WIFEXITED(status))
{
int exit_code = ((status >> 8) & 0xFF);
printf("wait success, 退出的子进程是: %d, exit_code: %d\n", rid, WEXITSTATUS(status));
}
else
{
printf("子进程是异常退出的!\n");
}
}
else
{
printf("ret: %d\n", rid);
perror("waitpid");
}
}
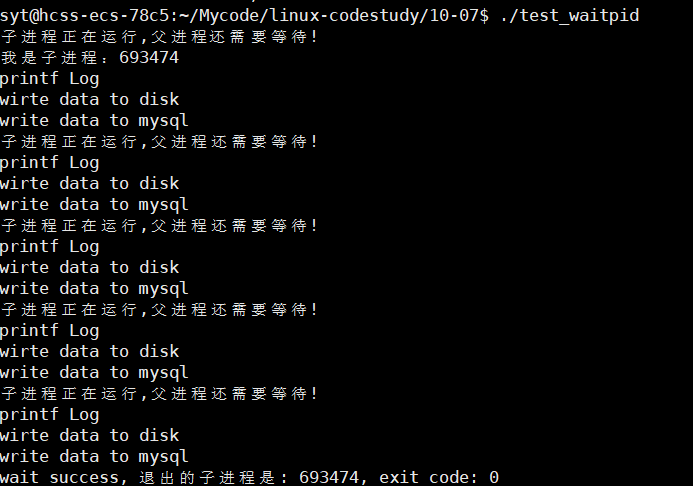
非阻塞示例
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <vector>
//函数指针类型
typedef void (*callback_t)();
void PrintLog()
{
std::cout << "printf Log" << std::endl;
}
void SyncDisk()
{
std::cout << "wirte data to disk" << std::endl;
}
void WriteDataToMysql()
{
std::cout << "write data to mysql" << std::endl;
}
int main()
{
std::vector<callback_t> tasks;
tasks.push_back(PrintLog);
tasks.push_back(SyncDisk);
tasks.push_back(WriteDataToMysql);
pid_t id = fork();
if (id < 0)
{
perror("fork");
exit(123);
}
else if (id == 0)
{
// child process
std::cout << "我是子进程:" << getpid() << std::endl;
sleep(5);
exit(0);
}
else
{
// father
while (1)
{
int status = 0;
// 非阻塞检测&&回收
pid_t rid = waitpid(id, &status, WNOHANG);
if (rid > 0)
{
printf("wait success, 退出的子进程是: %d, exit_code: %d\n", rid, ((status >> 8) & 0xFF));
break;
}
else if (rid == 0)
{
printf("子进程正在运行,父进程还需要等待!\n");
usleep(100000);
for (auto &task : tasks)
{
task();
}
}
else
{
perror("waitpid");
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
10.4进程程序替换
概念
程序替换是通过特定的接口 ,加载磁盘上的⼀个全新的程序(代码和数据) ,加载到调用进程的地址空间中。
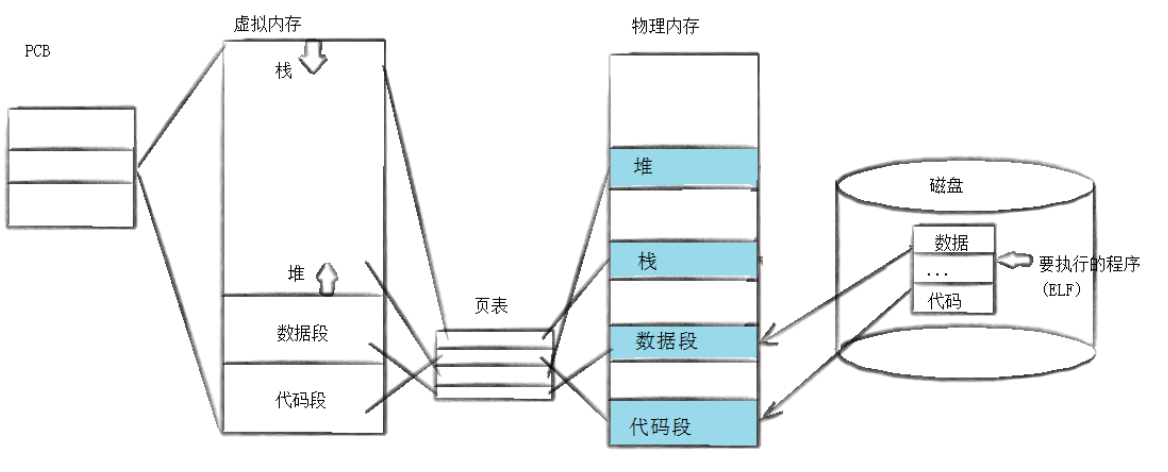
程序替换的本质:把代码和数据拷贝到内存 中,整个过程没有创建新的进程。
程序运行之前,OS必须将其加载到内存中,所有OS必须提供对应的系统调用,即exec*系列函数。
程序替换之后,exec*的后续代码也不会执行,因为代码和数据被替换了。
还有一点,exec*系列的函数,执行成功之后,没有返回值。
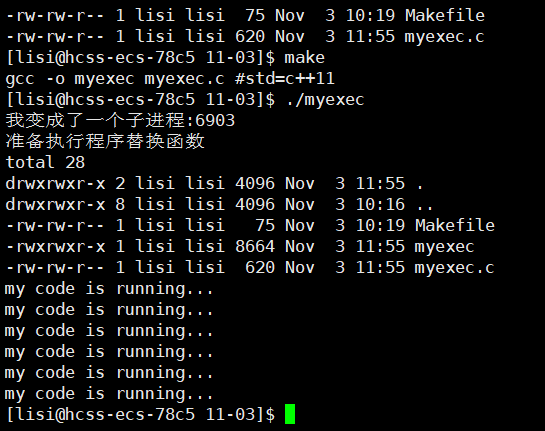
实例
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
int main()
{
printf("我变成了一个子进程:%d\n",getpid());
pid_t id = fork();
if(id == 0)
{
printf("准备执行程序替换函数\n");
execl("/usr/bin/ls","ls","-a","-l",NULL);
printf("程序替换函数执行完成\n"); //正常运行时,该语句会被替换,从而不会执行。
exit(0);
}
wait(NULL);
printf("my code is running...\n");
printf("my code is running...\n");
printf("my code is running...\n");
printf("my code is running...\n");
printf("my code is running...\n");
printf("my code is running...\n");
return 0;
}预期结果
- 父进程创建子进程
- 子进程执行
ls -a -l(程序替换) - 子进程退出
- 父进程从 wait() 返回,继续执行后面的 printf 语句
执行结果
替换函数
库函数:
NAME
execl, execlp, execle, execv, execvp, execvpe - execute a file
LIBRARY
Standard C library (libc, -lc)
SYNOPSIS
#include <unistd.h>
extern char **environ;
int execl(const char *pathname, const char *arg, ...
/*, (char *) NULL */);
int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg, ...
/*, (char *) NULL */);
int execle(const char *pathname, const char *arg, ...
/*, (char *) NULL, char *const envp[] */);
int execv(const char *pathname, char *const argv[]);
int execvp(const char *file, char *const argv[]);
int execvpe(const char *file, char *const argv[], char *const envp[]);系统调用:
NAME
execve - execute program
LIBRARY
Standard C library (libc, -lc)
SYNOPSIS
#include <unistd.h>
int execve(const char *pathname, char *const _Nullable argv[],
char *const _Nullable envp[]);库函数 vs 系统调用
| 特性 | 系统调用 | 库函数 |
|---|---|---|
| 执行环境 | 内核态 | 用户态 |
| 性能开销 | 较大(需要上下文切换) | 较小 |
| 实现位置 | 操作系统内核 | 用户空间库 |
| 可移植性 | 与操作系统相关 | 相对较好 |
| 调用方式 | 通过软中断/陷阱 | 普通函数调用 |
覆盖式:直接指定全新的环境变量表,是对默认的environ的覆盖。
新增式:指既有默认和新的同时存在。putenv
小结:命令行参数表和环境变量表,都是父进程通过exec*系列库函数传递的。
10.5自主shell命令行解释器
0,从配置文件中获取环境变量填充环境变量表,这种方式太复杂,此处从父进程拷贝。
(shell其实是一个死循环。)
1,输出命令行字符串,包含用户名,主机名,当前路径
模拟一下即可,此处使用环境变量获取。
2,获取用户输入,从键盘获取字符串,使用fgets(从指定文件流里获取字符串)。
注意:用户在输入时,至少会输入一次回车。
#include <stdio.h>
char *fgets(char *s, int size, FILE *stream);3,解析字符串("ls -a -l" -> "ls" "-a" "-l")
#include <string.h>
char *strtok(char *str, const char *delim);4,执行命令
-
建立⼀个子进程(fork)
-
替换子进程(execvp)
- 选择execvp原因:
- 传递参数表,所以选择带v的exec*。
- 执行命令是没有路径的,需要系统去环境变量去找,所以需要带p的exec*。(当然execvpe也可以)
- 选择execvp原因:
-
父进程等待子进程退出(wait)
cd ..:路径切换,切换的是当前父进程bash的路径 。而bash的所有子进程会继承父进程的当前工作路径 ,也就是说,更改了bash的工作路径,就是更改了后续执行的所以指令(进程)的工作路径。
所以需要判断这个命令是让父进程bash自己执行(内建命令) ,还是让子进程执行。
其实内建命令就是bash自己调用函数完成命令工作。
内建命令例如:cd,echo,pwd,export等
chdir(change working directory)
#include <unistd.h>
int chdir(const char *path);除此之外还要注意环境变量获取工作路径,因为环境变量没有变化,所以工作路径也不会改变,于是可以使用getcwd系统调用获取工作路径,当然通过更改环境变量也可以。
snprintf将内容以指定格式打印到指定缓冲区中。
| 特性 | const char* |
std::string |
|---|---|---|
| 类型 | C风格字符串,指针 | C++标准库字符串类 |
| 内存管理 | 手动/静态分配 | 自动管理 |
| 可变性 | 指向的内容不可变 | 内容可变 |
| 长度 | 需要strlen()获取 |
.length()或.size()直接获取 |
| 安全性 | 容易缓冲区溢出 | 相对安全 |
代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#define MAX_SIZE 128
#define MAX_ARGS 32
// shell维护的命令行参数表
char *gargv[MAX_ARGS];
int gargc = 0;
const char *gsep = " "; //分隔符
// 环境变量表
char *genv[MAX_ARGS];
int genvc = 0;
// 工作路径
char cwd[MAX_SIZE];
// 最后一次命令退出码
int lastcode = 0;
void LoadEnv()
{
extern char **environ;
for(;environ[genvc];genvc++)
{
genv[genvc] = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char)*4096);
strcpy(genv[genvc], environ[genvc]);
}
genv[genvc] = NULL;
// printf("Load env : \n");
// for(int i = 0; genv[i]; i++)
// {
// printf("genv[%d]: %s\n", i, genv[i]);
// }
}
static std::string rfindDir(const std::string &p)
{
if(p == "/")
{
return 0;
}
const std::string psep = "/";
auto pos = p.rfind(psep);
if(pos == std::string::npos)
{
return std::string();
}
return p.substr(pos + 1);
}
const char *GetUserName()
{
char *username = getenv("USER");
if(username == NULL)
return "None";
return username;
}
const char *GetHostName()
{
char *hostname = getenv("HOSTNAME");
if(hostname == NULL)
return "None";
return hostname;
}
const char *GetPwd()
{
char *pwd = getenv("PWD");
if(pwd == NULL)
return "None";
return pwd;
}
void PrintCommandLine()
{
printf("%s@%s %s# ",GetUserName(), GetHostName(), rfindDir(GetPwd()).c_str());
fflush(stdout);
}
int GetCommand(char commandline[], int size)
{
if(NULL == fgets(commandline, size, stdin))
{
return 0;
}
// 用户输入的时候,至少会摁一下回车\n abcd\n ,\n '\0'
commandline[strlen(commandline) - 1] = '\0';
return strlen(commandline);
}
int ParseCommand(char commandline[])
{
gargc = 0;
memset(gargv, 0, sizeof(gargv));
gargv[0] = strtok(commandline, gsep);
while((gargv[++gargc] = strtok(NULL, gsep)));
return gargc;
}
int CheckBuiltinExecute()
{
if(strcmp(gargv[0], "cd") == 0)
{
// 内建命令
if(gargc == 2)
{
// 更改内核中的路径
chdir(gargv[1]);
// 更改环境变量
char pwd[1024];
getcwd(pwd, sizeof(pwd));
snprintf(cwd, sizeof(cwd), "PWD=%s",pwd);
putenv(cwd);
}
return 1;
}
else if(strcmp(gargv[0], "echo") == 0)
{
if(gargc == 2)
{
if(gargv[1][0] == '$')
{
// $?看作一个变量名
if(strcmp(gargv[1]+1, "?") == 0)
{
printf("lastcode: %d\n",lastcode);
}
else if(strcmp(gargv[1]+1, "PATH") == 0)
{
printf("%s\n",getenv("PATH"));
}
lastcode = 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int ExecuteCommand()
{
pid_t id = fork();
if(id < 0)
{
return -1;
}
else if(id == 0)
{
// 替换
execvpe(gargv[0], gargv, genv);
exit(1);
}
else
{
// 回收
int status = 0;
pid_t rid = waitpid(id, &status, 0);
if(rid > 0)
{
;// lastcode = WEXITSTATUS(status);
}
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
// 0,从配置文件中获取环境变量填充环境变量表,这种方式太复杂,此处从父进程拷贝
LoadEnv();
char command_line[MAX_SIZE] = { 0 };
// 0,shell是一个死循环
while(1)
{
// 1,打印命令行参数:用户名 主机名 当前路径
PrintCommandLine();
// 2,获取输入字符串,使用`fgets`(从指定文件流里获取字符串)
if(0 == GetCommand(command_line, sizeof(command_line)))
{
continue;
}
// 3,解析字符串"ls -a -l"->"ls""-a""-l"
ParseCommand(command_line);
// 4,内建命令?
if(CheckBuiltinExecute()) // >0
{
continue;
}
// 5,执行命令
ExecuteCommand();
}
return 0;
}