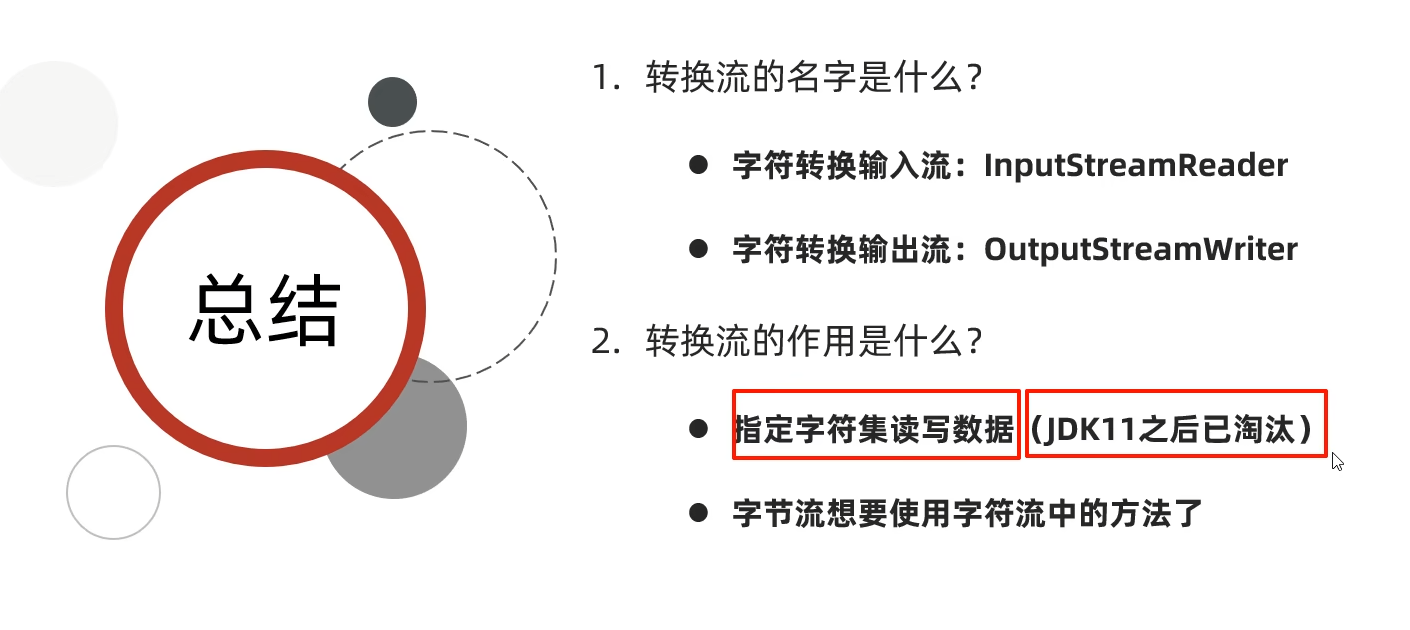
一、转换流
转换流是inputstreamreader 和 outputstreamwriter,把字节流转化为字符流,可以调用字符流的方法,也可以改变idea的编码方式,不过都已经过时,自JDK11后,用基本流filereader和 filewriter 就可以做到转换流的功能。
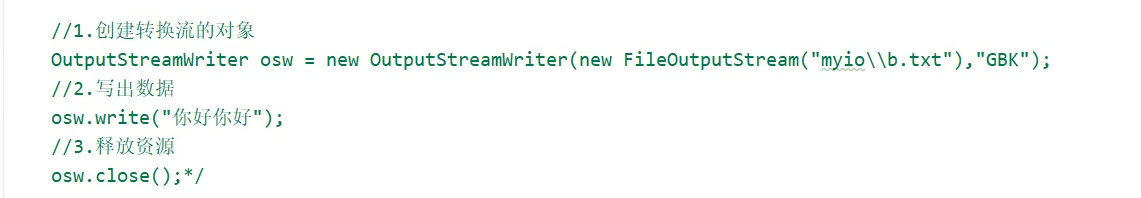
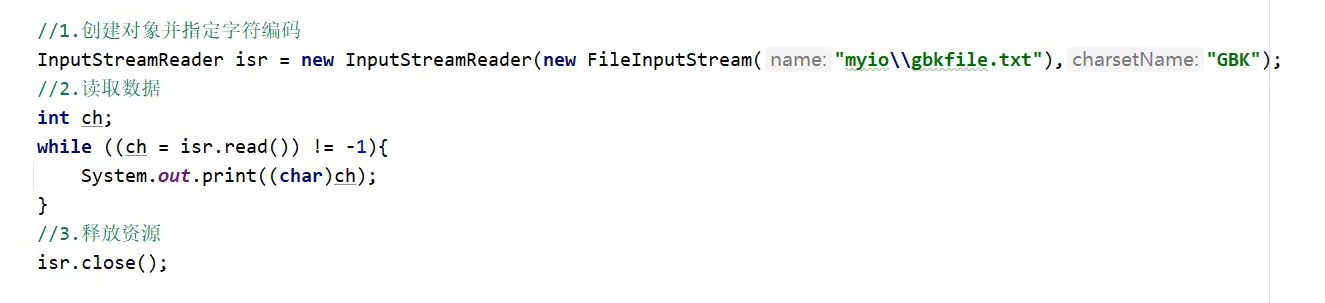
1.1 idea默认编码方式是UTF-8,现在想在idea中读取和写入文本文件时的编码方式是GBK,如何做?
思路:原本用转换流,但是现在JDK11之后,filereader和filewriter都有新的构造方法可以在创建对象的时候指明编码方式。文本文件默认编码方式是GBK,而idea是utf-8,所以要想在程序中正确看到文件中的数据,就要以GBK方式读取。程序写入文本时的方式也必须是GBK,才能在文件中看到正确的数据。
**代码:**读取:
java
package com.convertStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class covertStream02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader fr=new FileReader("D:\\桌面\\a.txt", Charset.forName("GBK"));
int b;
while((b= fr.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char)b);
}
fr.close();
}
}输出:与GBK本地文件一样
或用转换流:
代码:写入
java
package com.convertStream;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class covertStream03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
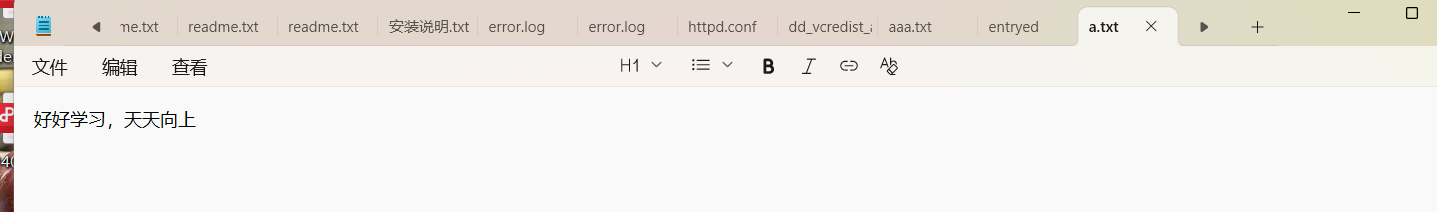
FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("D:\\桌面\\a.txt", Charset.forName("GBK"));
fw.write("好好学习,天天向上");
fw.close();
}
}输出结果:
1.2 将本地文件中的GBK文件,转成UTF-8,如何做?
思路:GBK方式读取本地文件,同时,以UTF-8方式写入另一个文件中
代码:
java
package com.convertStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class convertStream01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("heheh.txt"); //idea默认是UTF-8
FileReader fr=new FileReader("D:\\桌面\\a.txt", Charset.forName("GBK"));
int b;
while ((b=fr.read())!=-1) {
fw.write(b);
}
fr.close();
fw.close();
}
}或用转换流:
1.3 转换流练习

所以用转换流:先把字节流变成 字符流(里用转换流),之后再转换成字符缓冲流,利用它的readline方法读一整行。
java
package com.convertStream;
import java.io.*;
public class test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*//先创建字节流
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("AAA");
//再创建字符流,用转换流
InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(fis);//现在是字符流了
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(isr);*/
//一气呵成:
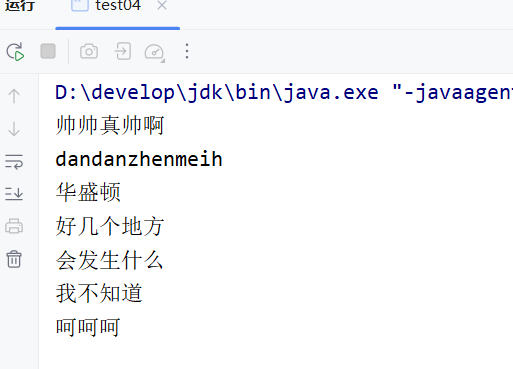
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("AAA")));
String line;
while ((line=br.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(line);
}
br.close();
}
}输出成果
1.4 转换流总结
二、序列化流/对象操作输出流write
就是将Java中的对象写到文件中的IO流,所以序列化流也叫做:对象操作输出流
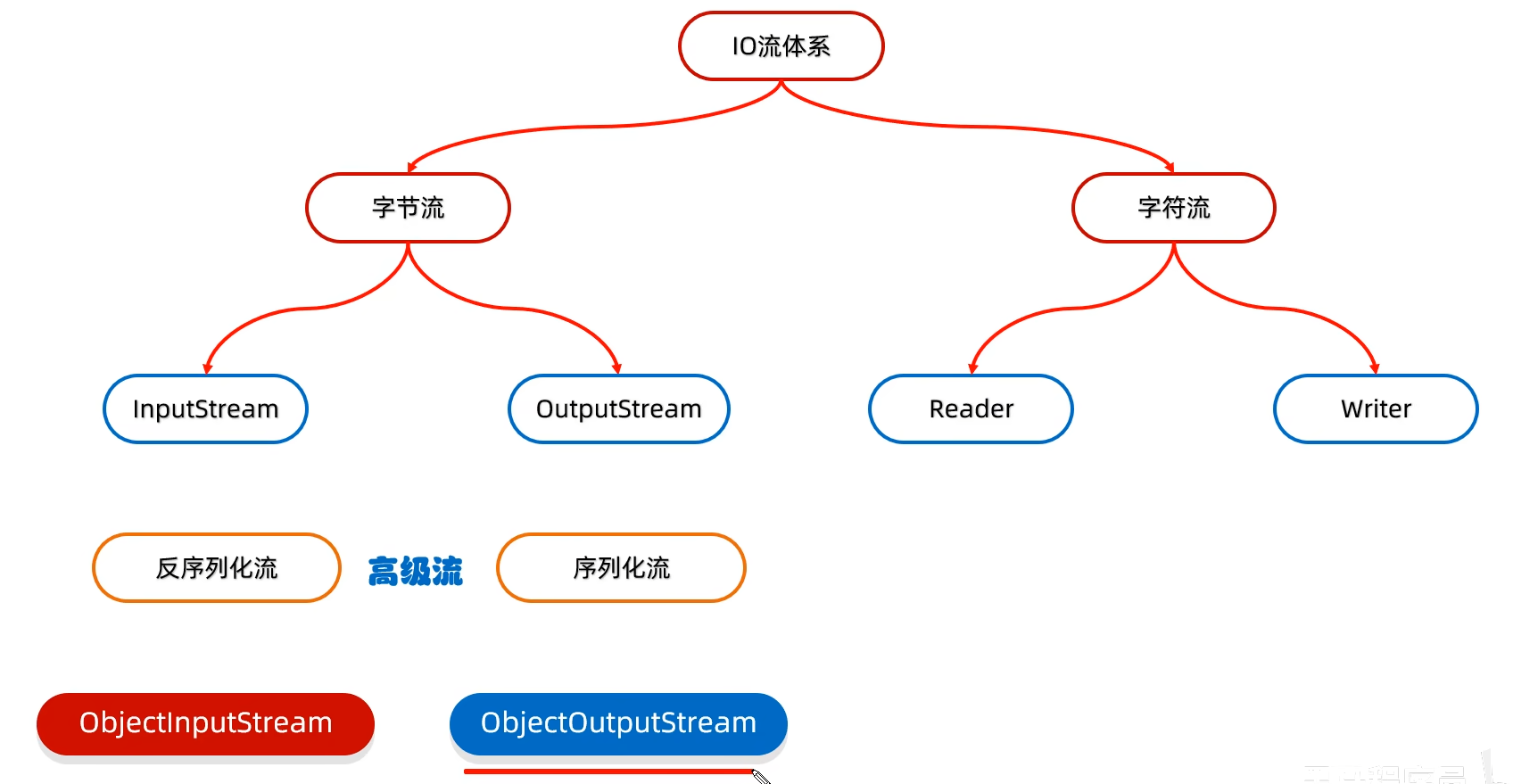

这种方式写到本地用户看不懂,防止用户更改,之后用反序列化流再读取到程序中即可看到原样。

代码实例
java
package com.objectStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class ObjectStream01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("AAA"));
Student stu=new Student("zhangsan",15);
oos.writeObject(stu);
oos.close();
}
}报错,
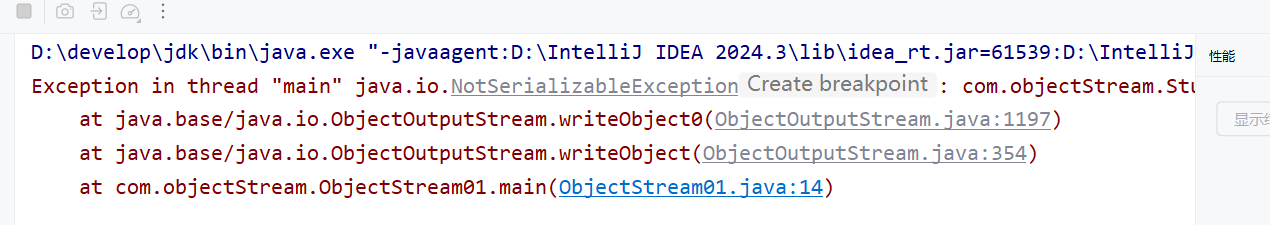
原因是

如何改正:
在javabean类的后面加一个接口就行了
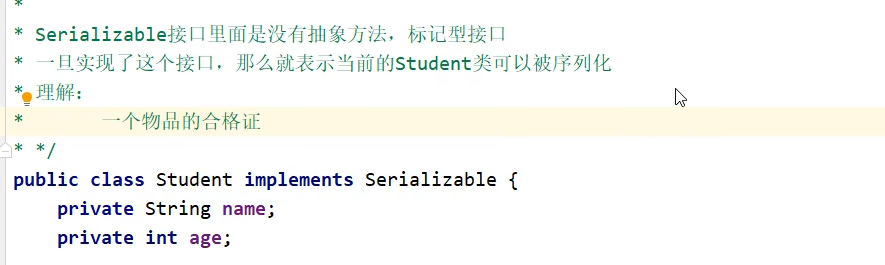
AAA文件内容
三、反序列化流/对象操作输入流read

java
package com.objectStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
public class ObjectStream02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("AAA"));
Student o = (Student)ois.readObject();
ois.close();
System.out.println(o);
}
}输出
java
Student{name = zhangsan, age = 15}四、序列化流和非序列化流的使用细节
当生成一个对象并写入文件中之后,改动JavaBean类(无法避免,随着时间会想着要更新信息),再读取文件中保存的对象,就会报错。因为生成一个JavaBean类后就会自动生成一个序列号(该序列号是根据JavaBean在当时的属性、成员方法、构造方法、静态方法生成的,所以如果属性成员变动,序列号就会随之变化),这个序列号会伴随着创建的对象,所以存入文件的对象的序列号还是改之前的,就会造成当前javabean和对象的序列号不一致错误,如图:
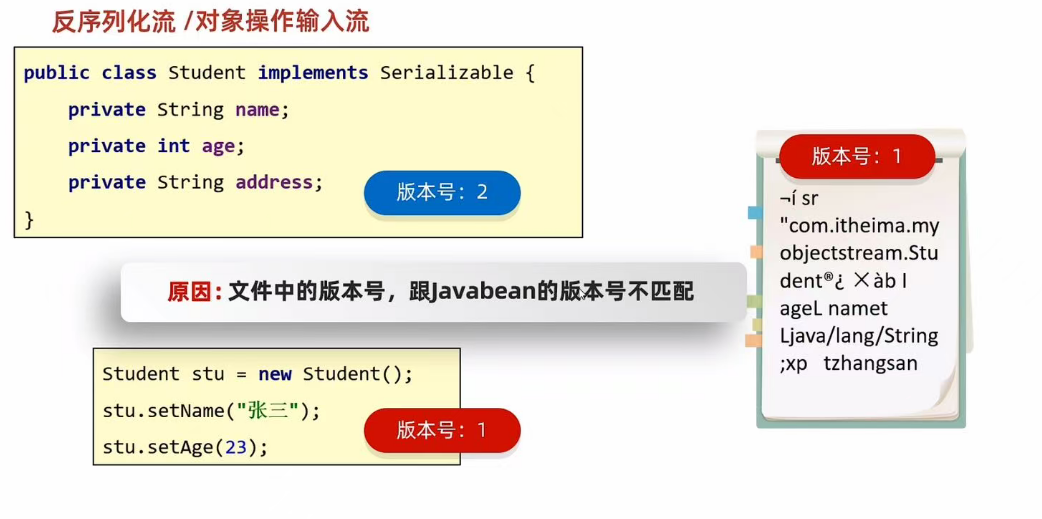
4.1 解决办法:采用静态常量作为属性,这样序列号就不可更改了
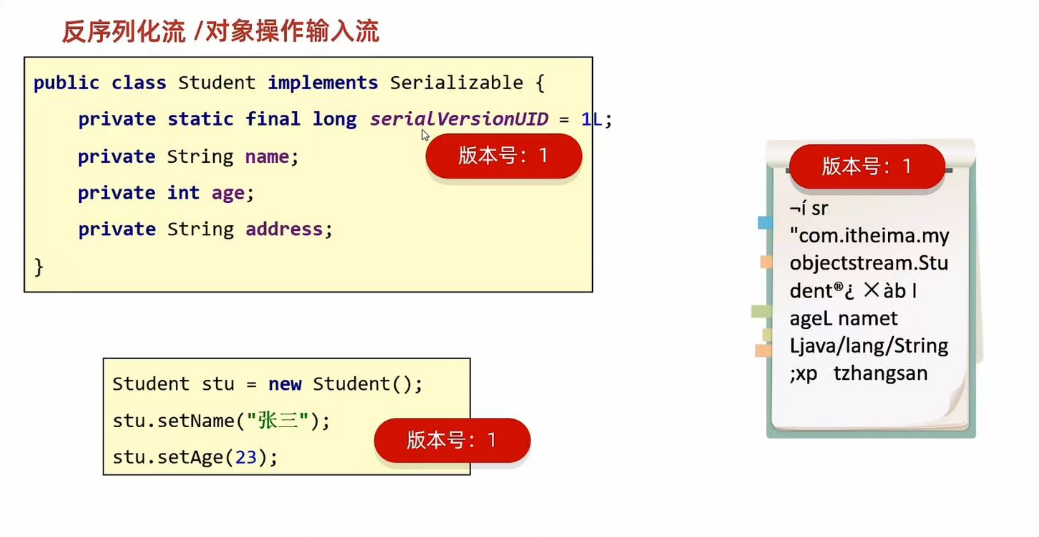
该serialversionUID可以自动设置:
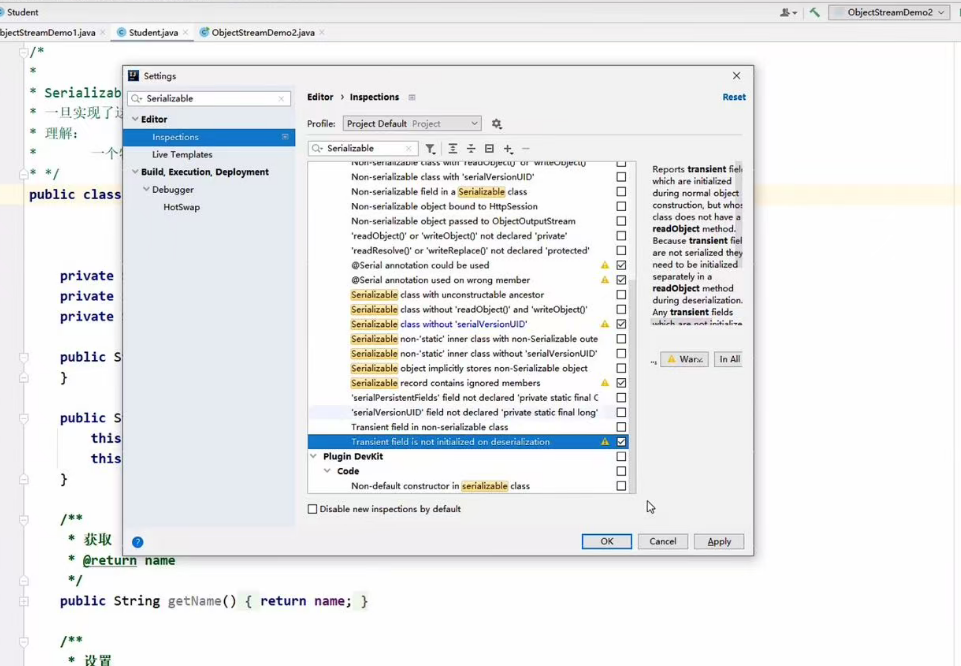
对最后两个勾的地方勾上,之后写javabean会报错,还是alt+enter键解决。
如果无法设置,最简单的方法就是记住 serialVersionUID这个变量名称,并设置一个值如1l。
就像这样:
4.2 瞬态关键字transient
**作用:**不会把当前属性序列化到本地文件当中。
代码:
java
package com.objectStream;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Student implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID=1L;
private String name;
private int age;
private transient String adress;
public Student() {
}
public Student( String name, int age, String adress) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.adress = adress;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", adress='" + adress + '\'' +
'}';
}
/**
* 获取
* @return name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param name
*/
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return age
*/
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param age
*/
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return adress
*/
public String getAdress() {
return adress;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param adress
*/
public void setAdress(String adress) {
this.adress = adress;
}
}transient修饰的成员变量不会被序列化到文件当中,所以读取出来的是初始化值。如图:
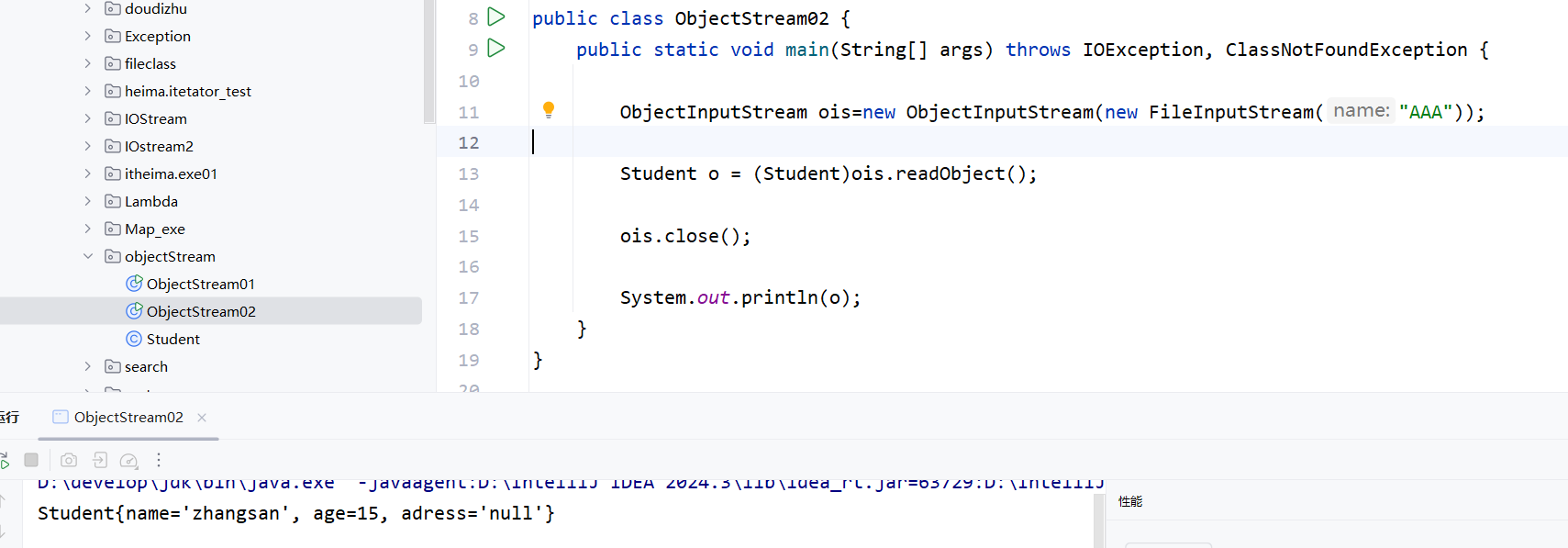
4.3 总结

序列化到文件中的对象是没有办法修改的,修改就不能用了,就会报错。
4.4 练习题

因为不知道对象的个数,所以无法判定读取多少个,而且如果没有数据了还继续读取,不会读取出-1,而是出现异常。所以就想到了写入对象的时候,写入列表,列表类是可序列化的,如图。
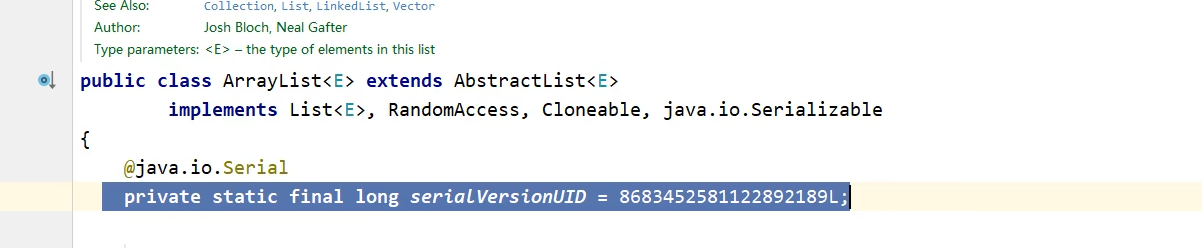
代码如下:
1)写入代码
java
package com.objectStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Student s1=new Student("zhangsan",15,"nanjing");
Student s2=new Student("lisi",16,"beijing");
Student s3=new Student("wangwu",17,"chongqing");
ArrayList<Student> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add(s1);
list.add(s2);
list.add(s3);
ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("AAA"));
oos.writeObject(list);
oos.close();
}
}读取代码
java
package com.objectStream;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//读取
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("AAA"));
ArrayList<Student> list = (ArrayList<Student>)ois.readObject();
ois.close();
System.out.println(list);
}
}输出结果
java
[Student{name='zhangsan', age=15, adress='null'}, Student{name='lisi', age=16, adress='null'}, Student{name='wangwu', age=17, adress='null'}]五、打印流
打印流不能读,只能写
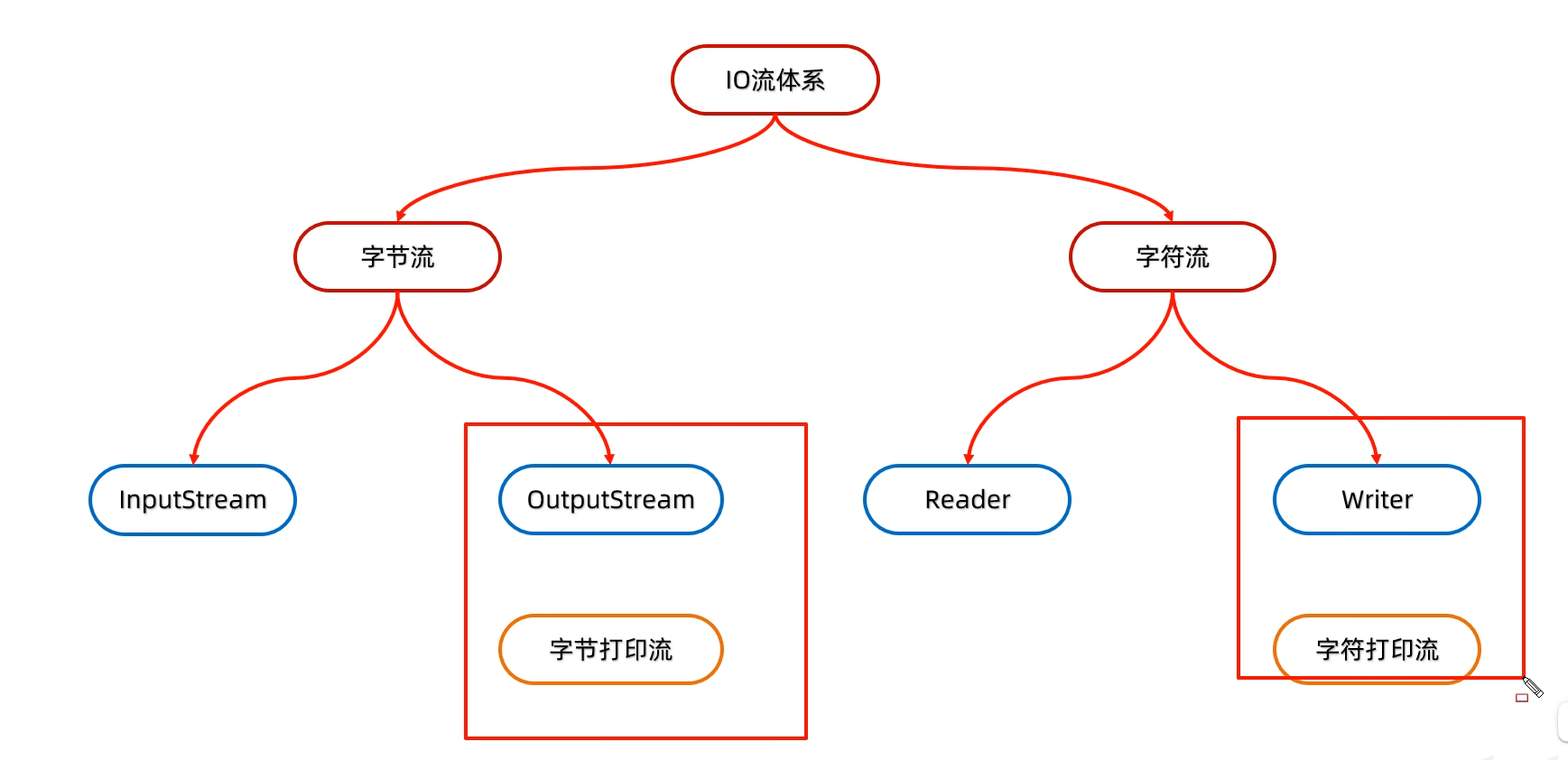

5.1 字节打印流构造方法

5.2 字节打印流成员方法
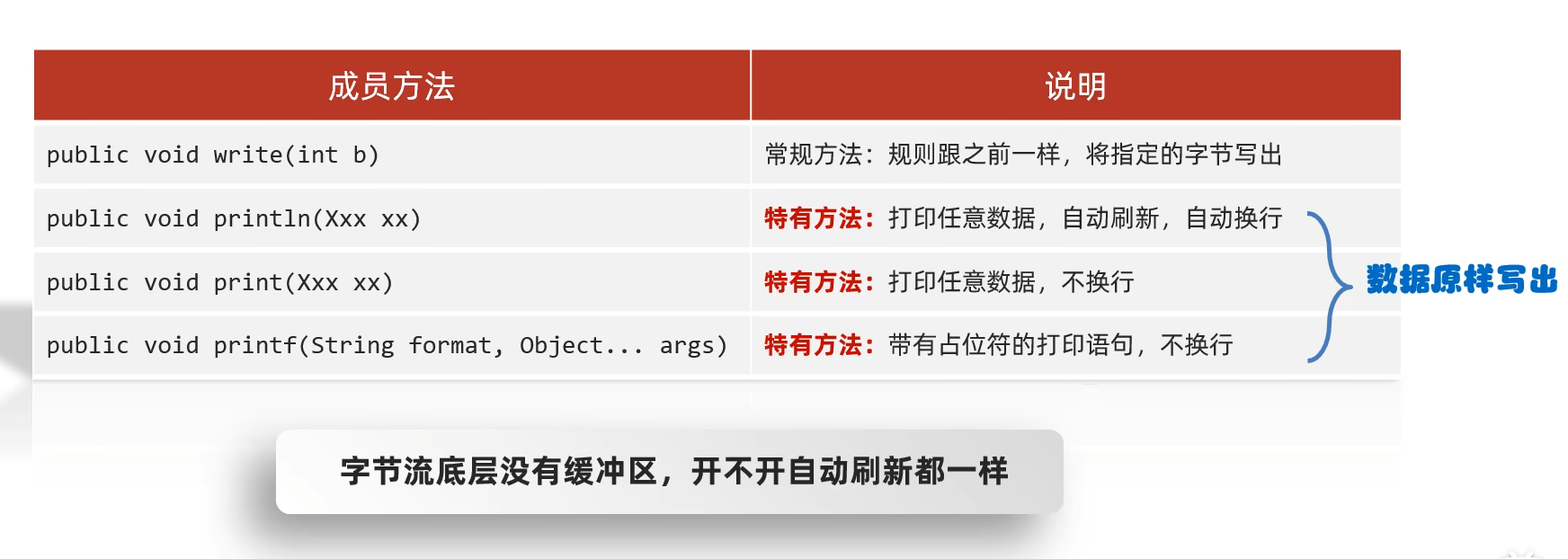
代码:
java
package com.PrintStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.sql.SQLOutput;
public class printstream01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
PrintStream ps=new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("a.txt"),true, Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
ps.write(97);
ps.print(97);
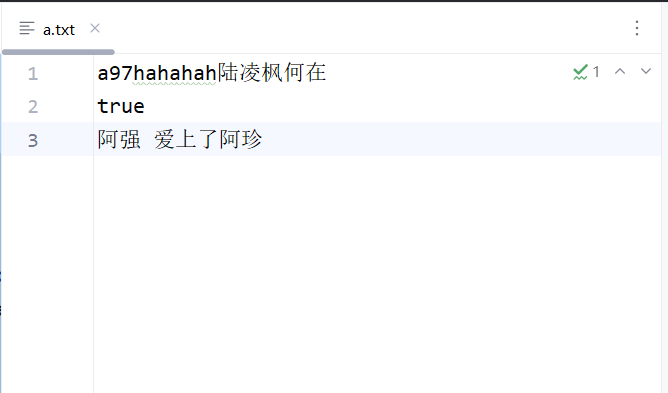
ps.println("hahahah陆凌枫何在");
ps.println(true);
ps.printf("%s 爱上了%s","阿强","阿珍");
ps.close();
}
}输出结果
5.3 字符打印流构造方法

5.4 字符打印流成员方法

代码:
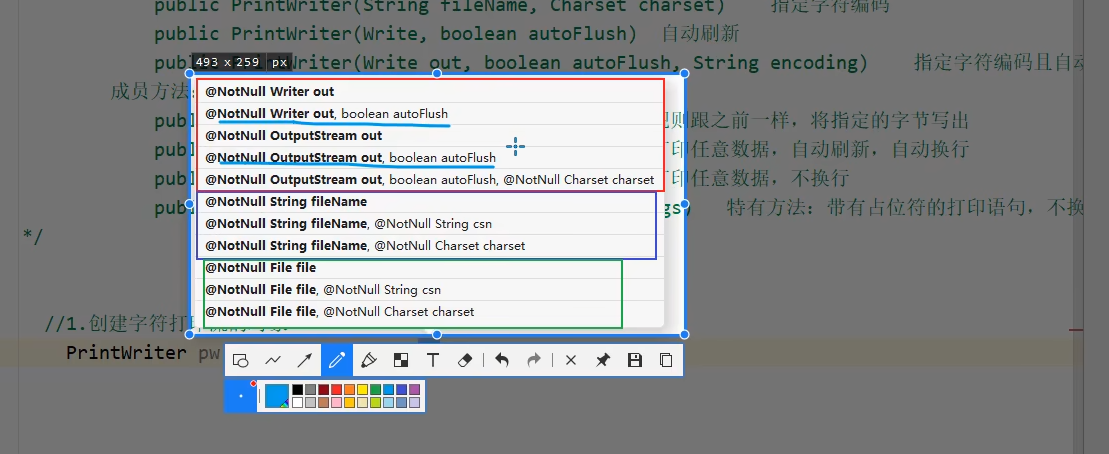
一定要指明是否自动刷新,因为字符流有缓冲区,所以经常用蓝色线指出的那两个代码
例如,如果autoFlush不指明true,那就无法自动刷新,即无法把缓冲区中的内容写入文件中,会一直存放到缓冲区,如图:
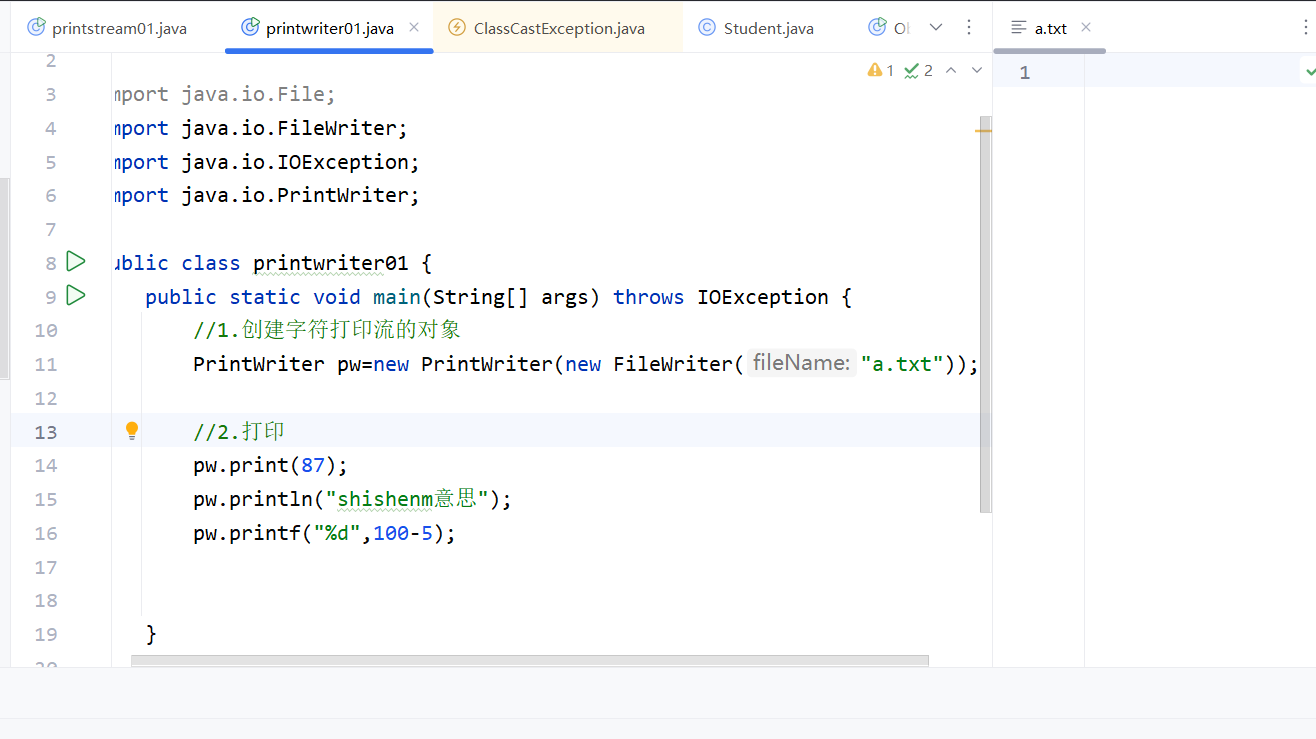
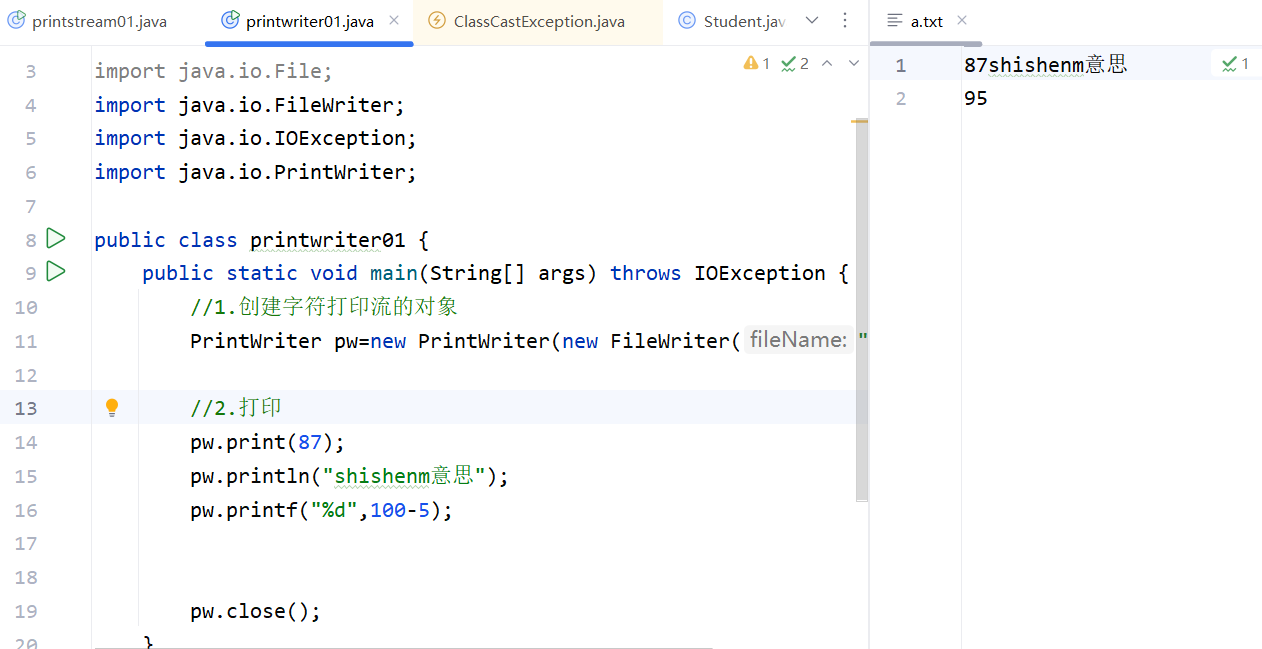
flush和close才会把缓冲区中的内容放到文件中,这里没有写close,也没有flush,所以文件是空的。如果有close,结果会不一样:
5.5 打印流printstream和输出流sout的关系
1.system.out是调用的system类的out变量,经过查验,out是一个printstream类的变量。
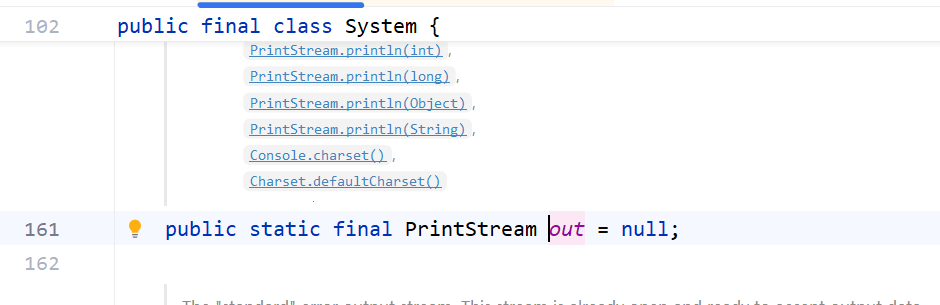
2.所以可以调用字节打印流的成员方法,如println 、print、printf等,所以就有system.out.println输出流了。
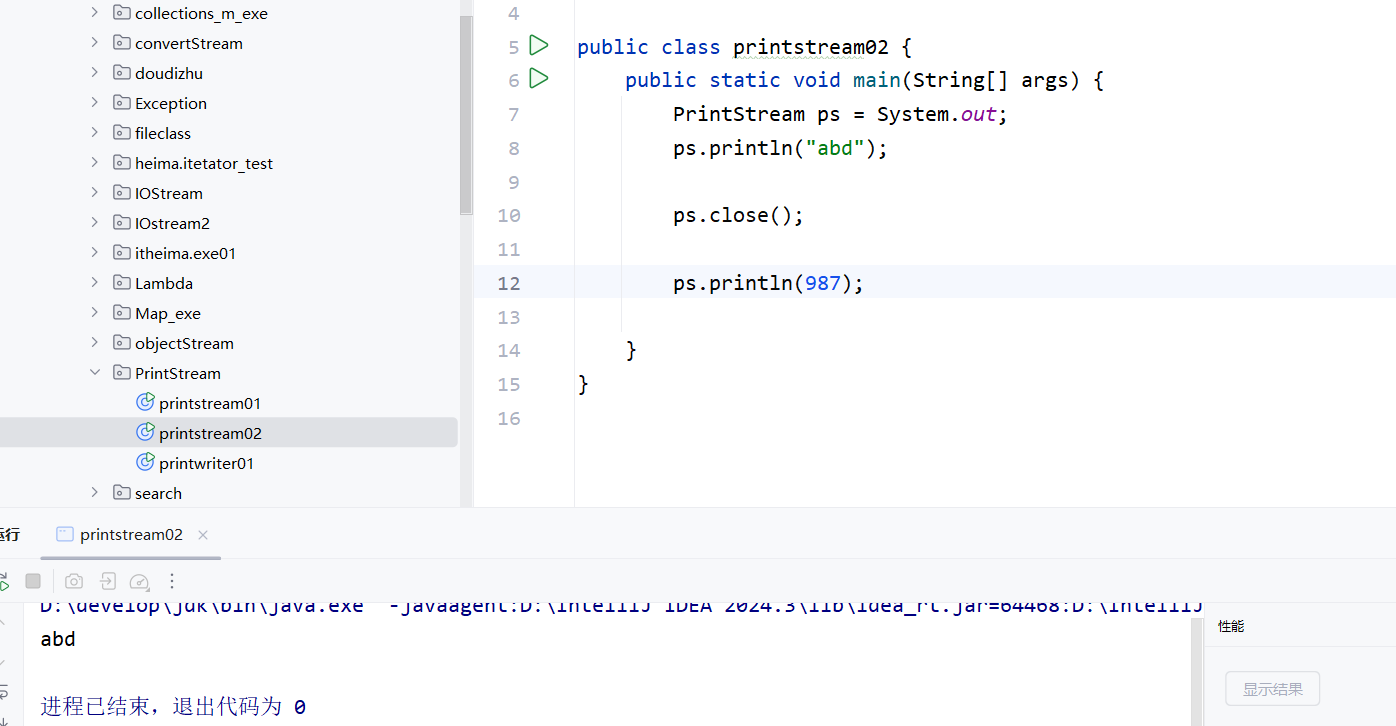
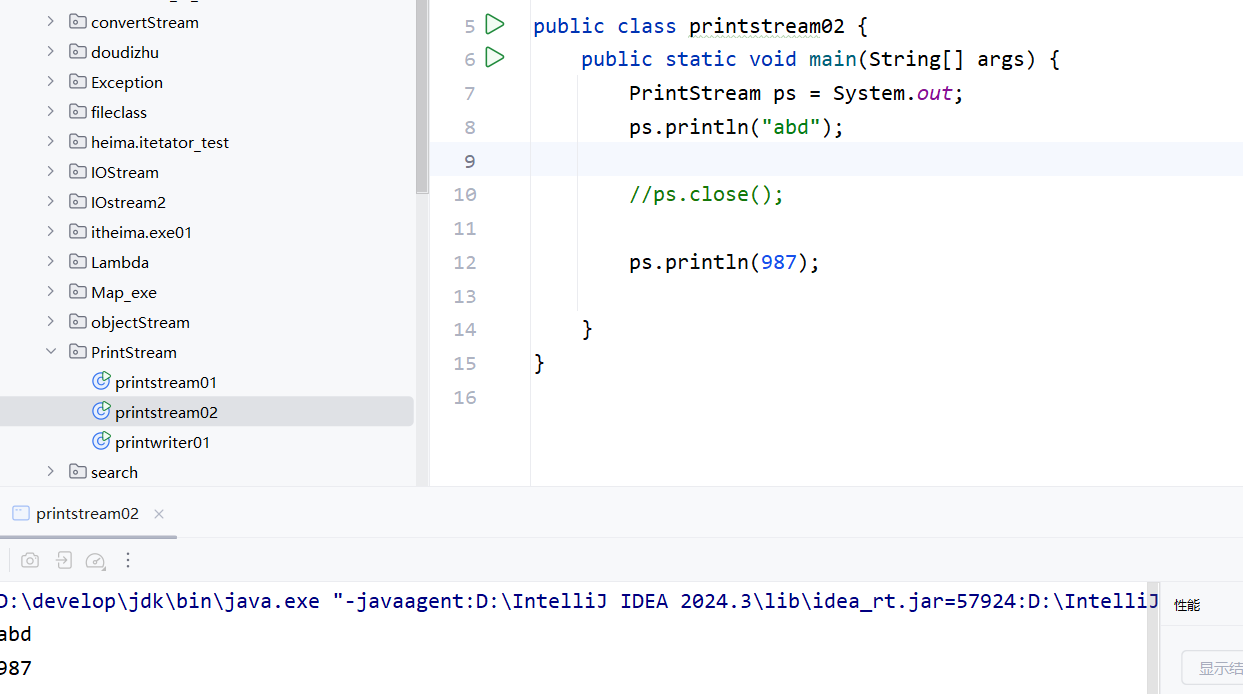
- 这个out变量指向的不是文件,而是控制台,所以打印的内容都会呈现在控制台上。
4.这个out变量得到的printstream流是不能关闭的,如果关闭,后续再用sout打印,则失败。
5.6 总结

六、压缩流(文件数据<<--------->>ZipEntry对象)
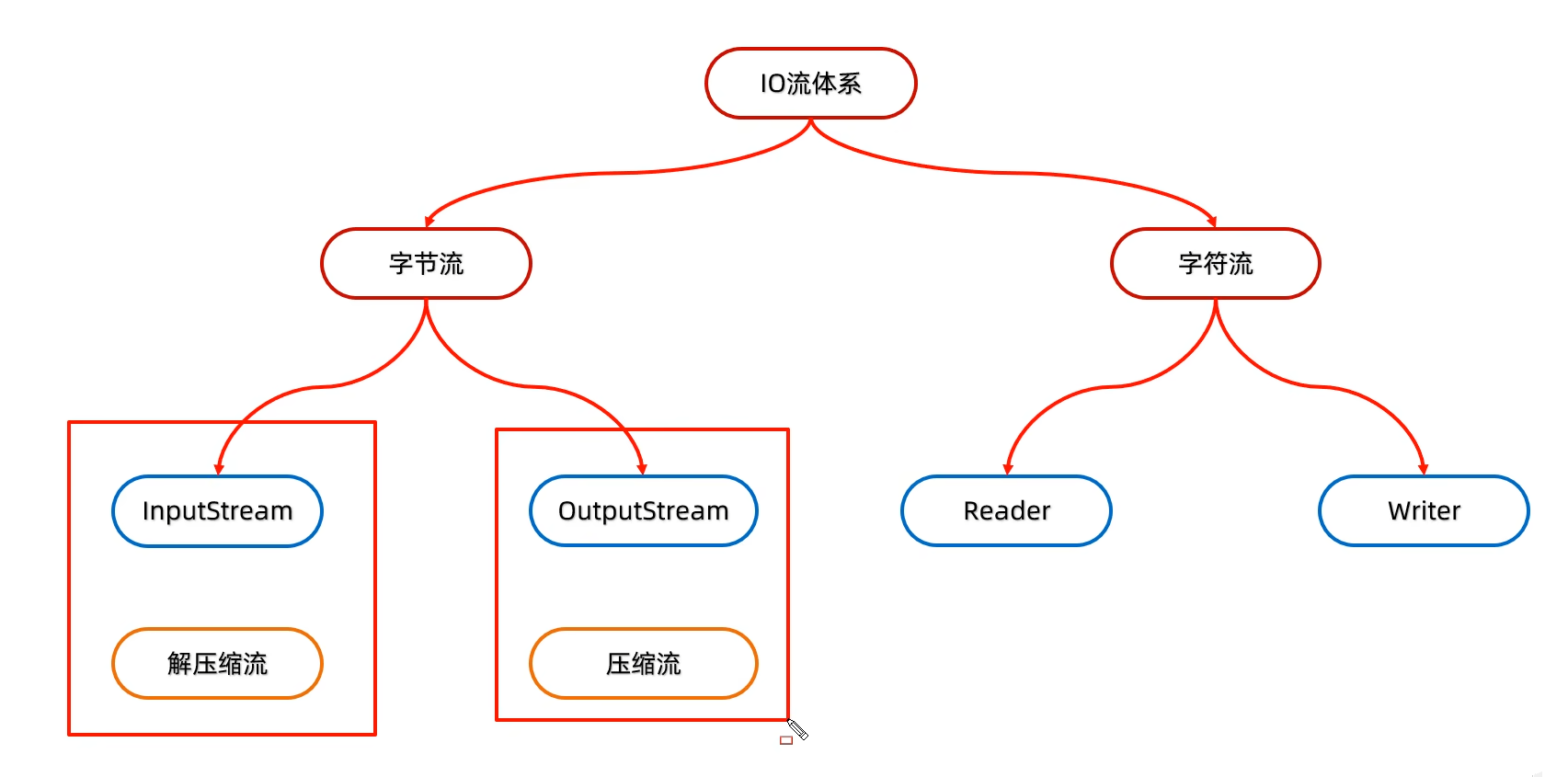
解压缩流是读取/输入流,读取压缩包;压缩流是写入/输出流,写入压缩包。
6.1 解压缩流

代码
java
package com.zipStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.zip.ZipEntry;
import java.util.zip.ZipInputStream;
public class zipstream01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//解压的本质:把压缩包里面的每一个文件和文件夹读取出来,按照层级拷贝到目的地当中
File src=new File("D:\\AAA.zip");
File des=new File("D:\\");
getzip(src,des);
}
public static void getzip(File src,File des) throws IOException {
//创建一个解压缩流用来读取压缩包中的数据
ZipInputStream zip=new ZipInputStream(new FileInputStream(src));
//要先获取到压缩包里的每一个zipentry对象
ZipEntry entry; //表示当前在压缩包中获取到的文件或文件夹 ,跟file差不多
while((entry=zip.getNextEntry())!=null){
System.out.println(entry);
if(entry.isDirectory()){
//文件夹:需要在目的地des处创建一个同样的文件夹。
File f=new File(des,entry.toString());
f.mkdirs();
}else{
//文件:需要读取压缩包中的文件,并把他存放到目的地des文件夹中(按照层级目录进行存放)
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(new File(des,entry.toString()));
int b;//此时zip已经getnextentry()变得光标指向了一个文件,所以zip.read()就能读取该文件的数据
while((b=zip.read())!=-1){
fos.write(b);
}
fos.close();
zip.closeEntry();//因为你打开了getnextentry()该文件的entry字节流,所以要关闭。
}
}
zip.close();//要关闭整个压缩包的字节流。
}
}输出结果:
zipEntry其实就是压缩包里面每个文件或文件夹的路径。遍历zip流getNextEntry()得到每一个文件或文件夹路径。
java
AAA/
AAA/aaa/
AAA/aaa/hhh.txt
AAA/aaa.txt
AAA/bbb/
AAA/bbb/kkkkkk.txt
AAA/bbb/zzzzzz.txt
AAA/bbb.txt
AAA/ccc.txt6.2 压缩流------压缩单个文件
代码
java
package com.zipStream;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.zip.ZipEntry;
import java.util.zip.ZipOutputStream;
public class zipstream02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建file对象白表示要压缩的文件
File src=new File("D:\\桌面\\a.txt");
//创建file 对象表示压缩包的位置
File des=new File("D:\\桌面");
ToZip(src,des);
}
public static void ToZip(File src,File des) throws IOException {
//1.创建压缩流关联压缩包,只要是压缩包就要用压缩流来关联
ZipOutputStream zos=new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File(des,"a.zip")));
//2.创建ZipEntry对象,表示压缩包里的每一个文件和文件夹
ZipEntry entry=new ZipEntry("a.txt"); //参数是文件在该压缩包的相对路径
//3.把zipEntry对象放入压缩包当中
zos.putNextEntry(entry);
//4.此时entry里面还是空的,要把src的文件数据拷贝到entry中
//读取压缩包和写入压缩包数据都用zip/zos的read()或write()方法
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(src);
int b;
while ((b=fis.read())!=-1){
zos.write(b);
}
fis.close();
zos.closeEntry();
zos.close();
}
}输出结果

6.3 压缩流------压缩文件夹
zip压缩流的new fileoutstream(new file(路径一定是 xxx.zip))
java
package com.zipStream;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.zip.ZipEntry;
import java.util.zip.ZipOutputStream;
public class zipstream03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建file对象表示要压缩的文件夹
File src=new File("D:\\AAA");
//2.创建 file对象表示压缩包放在哪里(压缩包的父级路径)
File desparent=new File(src.getParent());//D:\\
//3.创建file对象表示压缩包的路径
File des=new File(desparent,src.getName()+".zip");//D:\\AAA.zip
//4.创建压缩流关联压缩包
ZipOutputStream zos=new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(des));
//5.获取src里面的每一个文件,变成zipEntry对象,放入压缩包当中。
toZip(src,zos,src.getName());//第三个参数传递的是aaa
//6.释放资源
zos.close();
}
//数据源,压缩流,压缩包内部路径
public static void toZip(File src,ZipOutputStream zos,String pathname) throws IOException {
//1.进入src文件夹
File[] files = src.listFiles();
//2.遍历数组
for (File file : files) {
if(file.isFile()){
//3.如果是文件---变成ZipEntry对象,放入压缩包当中
ZipEntry entry=new ZipEntry(pathname+"\\"+file.getName());//这个参数要填文件在压缩包的内部路径
zos.putNextEntry(entry);
//读取文件中的数据,写到压缩包
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(file);
int b;
while ((b=fis.read())!=-1){
zos.write(b);
}
fis.close();
zos.closeEntry();
}else {
//4.如果是文件夹----递归
toZip(file,zos,pathname+"\\"+file.getName());
}
}
}
}AAA----BBB----c.txt
AAA文件夹的getname+BBB文件夹的getname+file.getname()就是c.txt
七、Commons-io 工具包



Commons是第三方工具包,一般都是jar压缩包,需要下载并复制到lib文件夹中。lib文件夹是专门负责存放第三方库的文件夹。
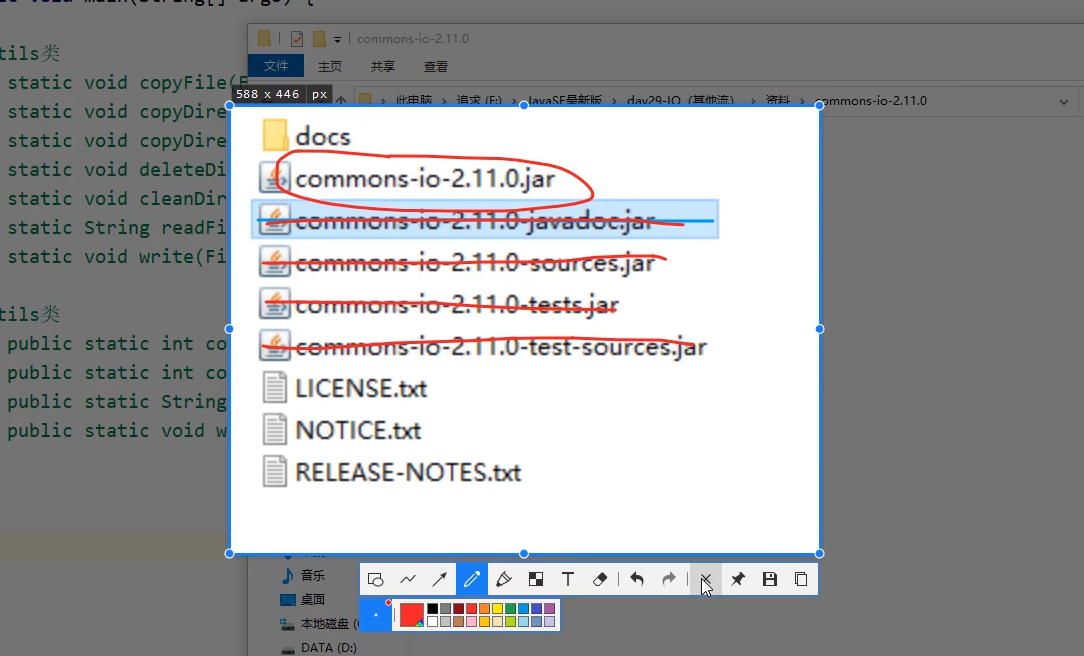
解压Commons工具包后看到:很多jar包,但只有第一个是我们想要的,于是复制它并粘贴到lib文件夹。之后右击该jar包,选择 Add as library ,点击OK
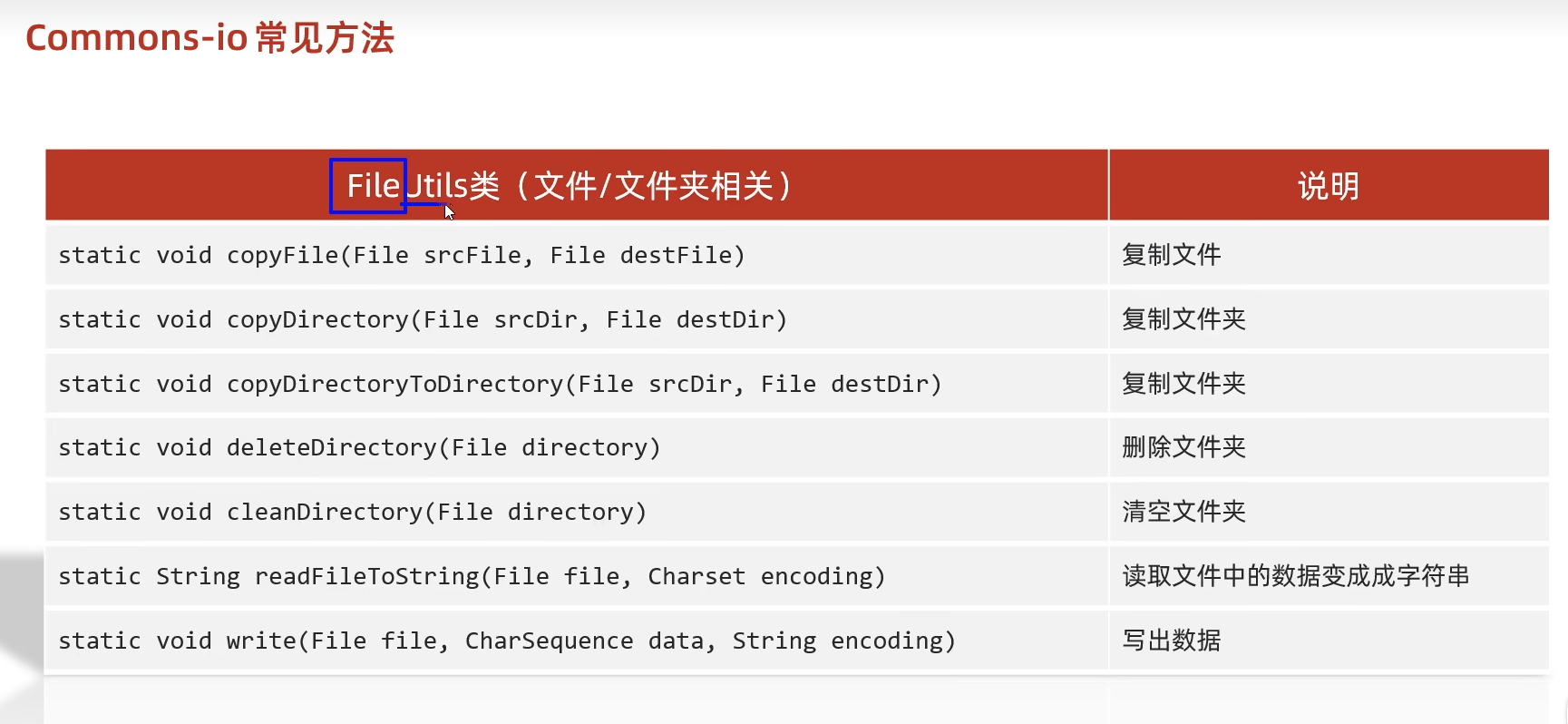

代码示例: