在高级面试中,除了对基本技术栈的掌握,面试官往往更关注你的项目经验,特别是在架构设计、性能优化及分布式系统的实际应用。本文将结合实际开发经验,深入探讨以下几个技术点:
- 项目中如何使用AOP(面向切面编程)?
- Redis在项目中的应用场景与设计?
- 如何设计Redis的Key?
- 如何实现缓存点赞数功能?
- 如何保证Redis与数据库的一致性?
1. 项目里哪块用到AOP了?
在实际开发中,AOP(面向切面编程)主要用于处理横切关注点,例如日志记录、性能监控、事务管理等,能够将这些关注点从业务逻辑中解耦出来,使代码更加清晰、易于维护。
(1) 日志记录
例如,在每次用户进行操作(如添加商品、修改用户信息等)时,可以通过AOP自动记录操作日志。
java
@Aspect
@Component
public class LoggingAspect {
@Before("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
public void logBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("Method called: " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
}
@AfterReturning("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
public void logAfterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("Method finished: " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
}
} (2) 事务管理
AOP可以用来实现事务管理,例如在方法执行前开启事务,执行后提交或回滚事务。Spring框架提供了@Transactional注解,可以方便地实现事务管理。
java
@Service
public class UserService {
@Transactional
public void updateUserInfo(User user) {
// 业务逻辑
}
} (3) 性能监控
AOP还可以用于性能监控,在方法执行前记录时间,执行后计算执行时间。
java
@Aspect
@Component
public class PerformanceAspect {
@Around("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
public Object monitorPerformance(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Method " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName() + " executed in " + (endTime - startTime) + " ms");
return result;
}
} 2. 项目中Redis怎么用的?
Redis作为一个高效的内存数据库,通常在大规模项目中用于加速数据访问,常见的使用场景包括缓存、队列、分布式锁等。
(1) 缓存(最常见的用途)
在项目中,Redis可以用作数据库查询的缓存层,减少对数据库的访问压力。例如,当查询某个商品的详细信息时,可以先查询Redis缓存,如果缓存存在直接返回结果,不存在则查询数据库并将结果放入缓存中。
java
public Product getProductById(Long productId) {
String cacheKey = "product:" + productId;
Product product = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(cacheKey);
if (product == null) {
product = productRepository.findById(productId);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(cacheKey, product, 10, TimeUnit.MINUTES); // 设置缓存过期时间
}
return product;
} (2) 队列
Redis还可以用于处理消息队列,尤其适合处理高并发场景。通过Redis的LPUSH、BRPOP等命令,可以轻松实现生产者-消费者模式。
java
// 生产者
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush("orderQueue", orderId);
// 消费者
String orderId = redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPop("orderQueue"); (3) 分布式锁
在分布式系统中,Redis可以作为分布式锁的实现工具,防止同一时间内多个节点执行相同的操作。
java
public boolean acquireLock(String lockKey) {
return redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(lockKey, "locked", 30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} 3. Redis的Key怎么设计?
合理的Redis Key设计对于系统的性能和可维护性至关重要。设计Key时要考虑避免Key冲突、减少存储空间占用、提高数据访问效率等因素。
(1) 避免使用过长的Key
建议Key长度控制在较短的范围内,避免存储过长的字符串影响性能。例如:
plaintext
"user:123:profile" // 用户ID为123的资料
"product:456:details" // 商品ID为456的详细信息 (2) 使用命名空间前缀
为了避免Key冲突,可以使用"命名空间 + 唯一标识符"的形式。例如,使用user:123:cart来存储用户购物车信息,order:987:status来存储订单状态。
(3) 根据数据结构选择合适的Key类型
根据存储的数据类型选择合适的Redis数据结构。Redis提供了多种数据结构,如字符串(String)、哈希(Hash)、列表(List)、集合(Set)、有序集合(Sorted Set)等。
plaintext
"user:123:cart" --> List
"user:123:tags" --> Set
"order:987:status" --> Hash 4. 缓存点赞数如何实现? 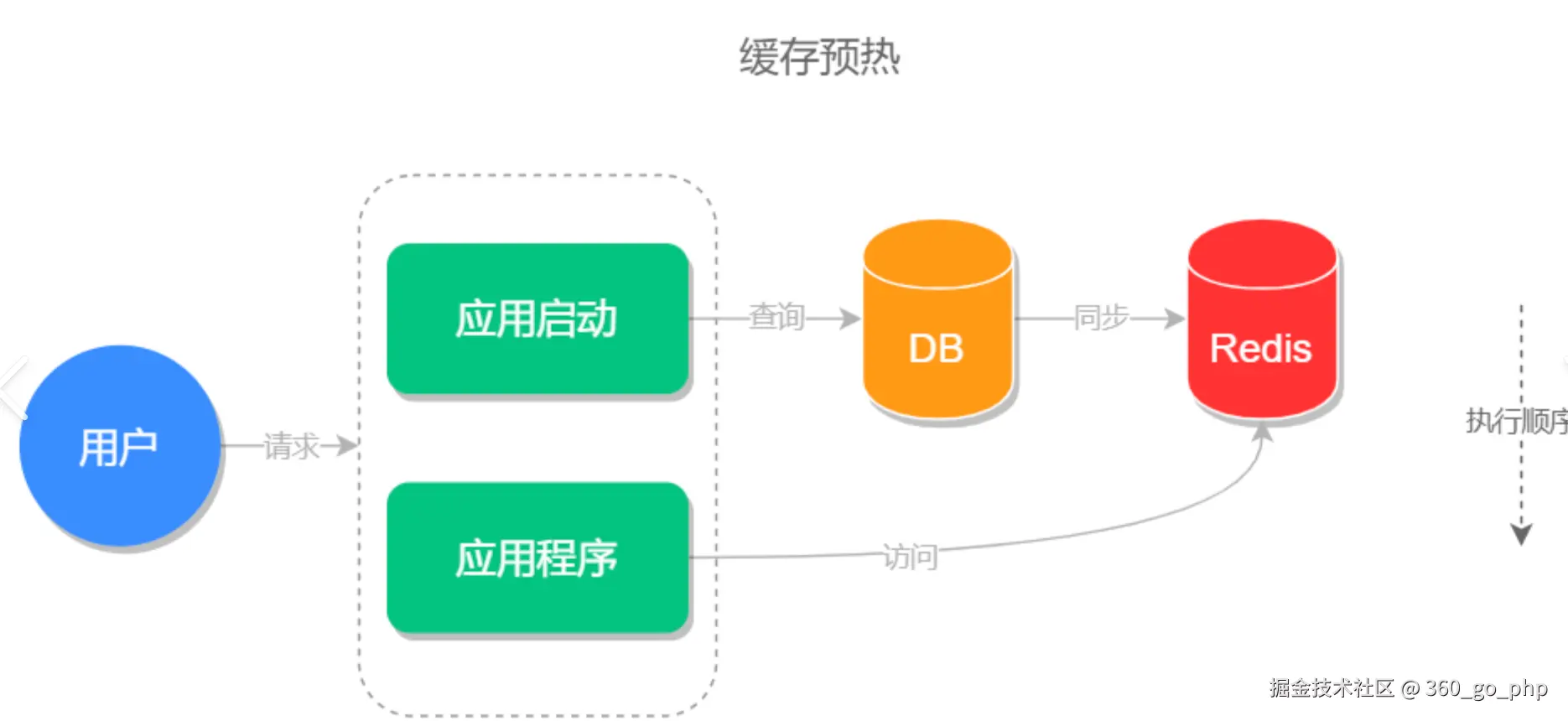 编辑
编辑
实现缓存点赞数时,使用Redis的INCRBY命令可以高效地更新点赞数,并且避免频繁访问数据库。
(1) 简单实现 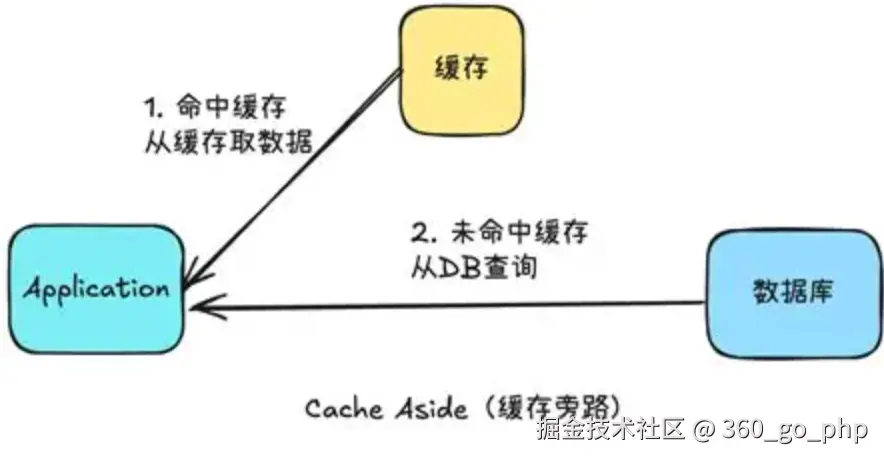 编辑
编辑
每当用户点赞时,我们直接在Redis中增加点赞数,而不需要每次都查询数据库。
java
public void likePost(Long postId) {
String key = "post:" + postId + ":likes";
redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment(key, 1); // 点赞数加1
} (2) 展示点赞数 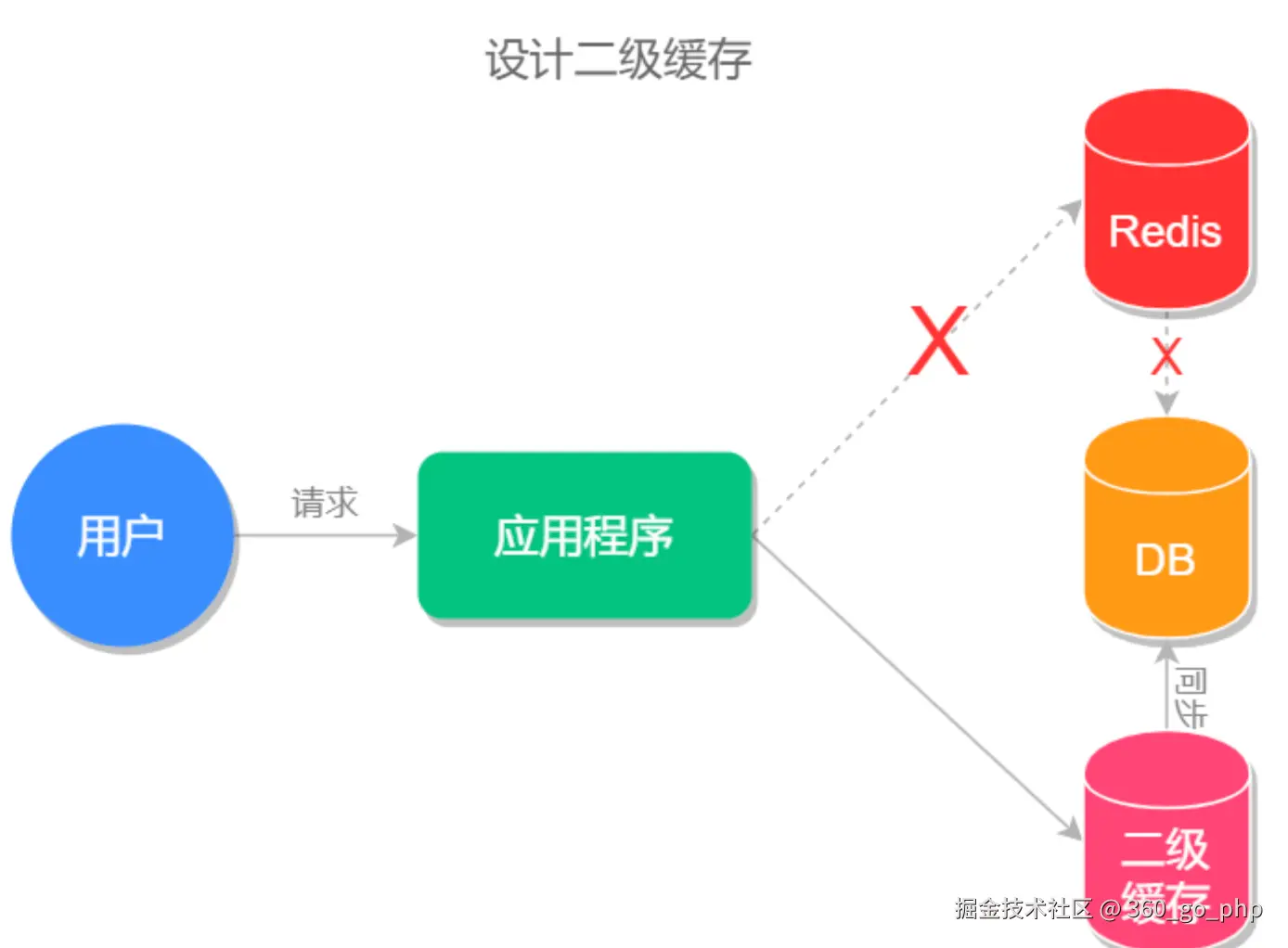 编辑
编辑
当需要展示点赞数时,我们首先从Redis获取数据,如果Redis中不存在则从数据库获取并缓存。
java
public Long getLikesCount(Long postId) {
String key = "post:" + postId + ":likes";
Long likesCount = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (likesCount == null) {
likesCount = postRepository.getLikesCount(postId); // 从数据库获取
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, likesCount); // 缓存点赞数
}
return likesCount;
} 5. 如何保证Redis和数据库一致性? 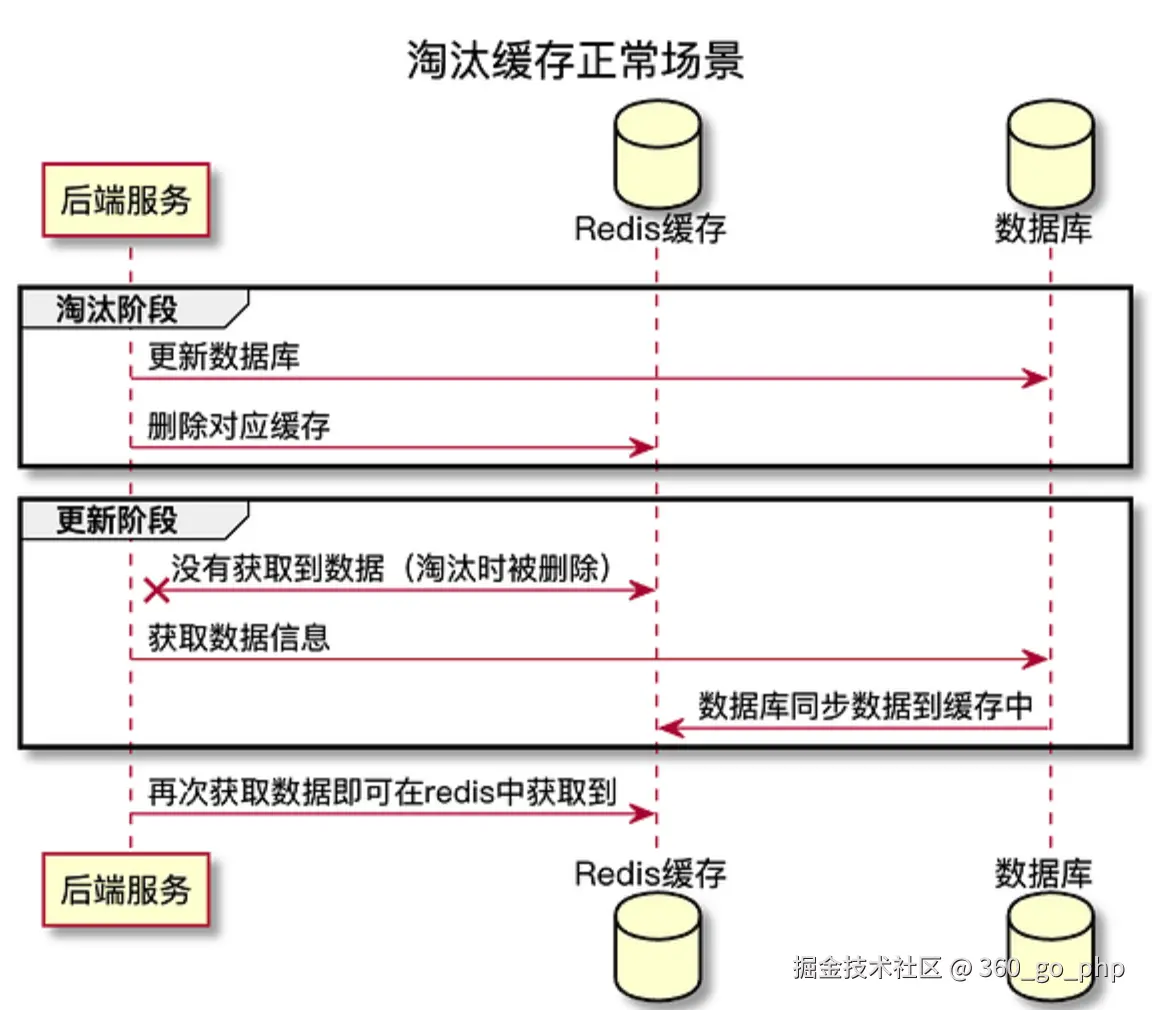 编辑
编辑
保证Redis与数据库的一致性是分布式系统中的一大挑战,常见的方案有以下几种:
(1) 缓存更新策略 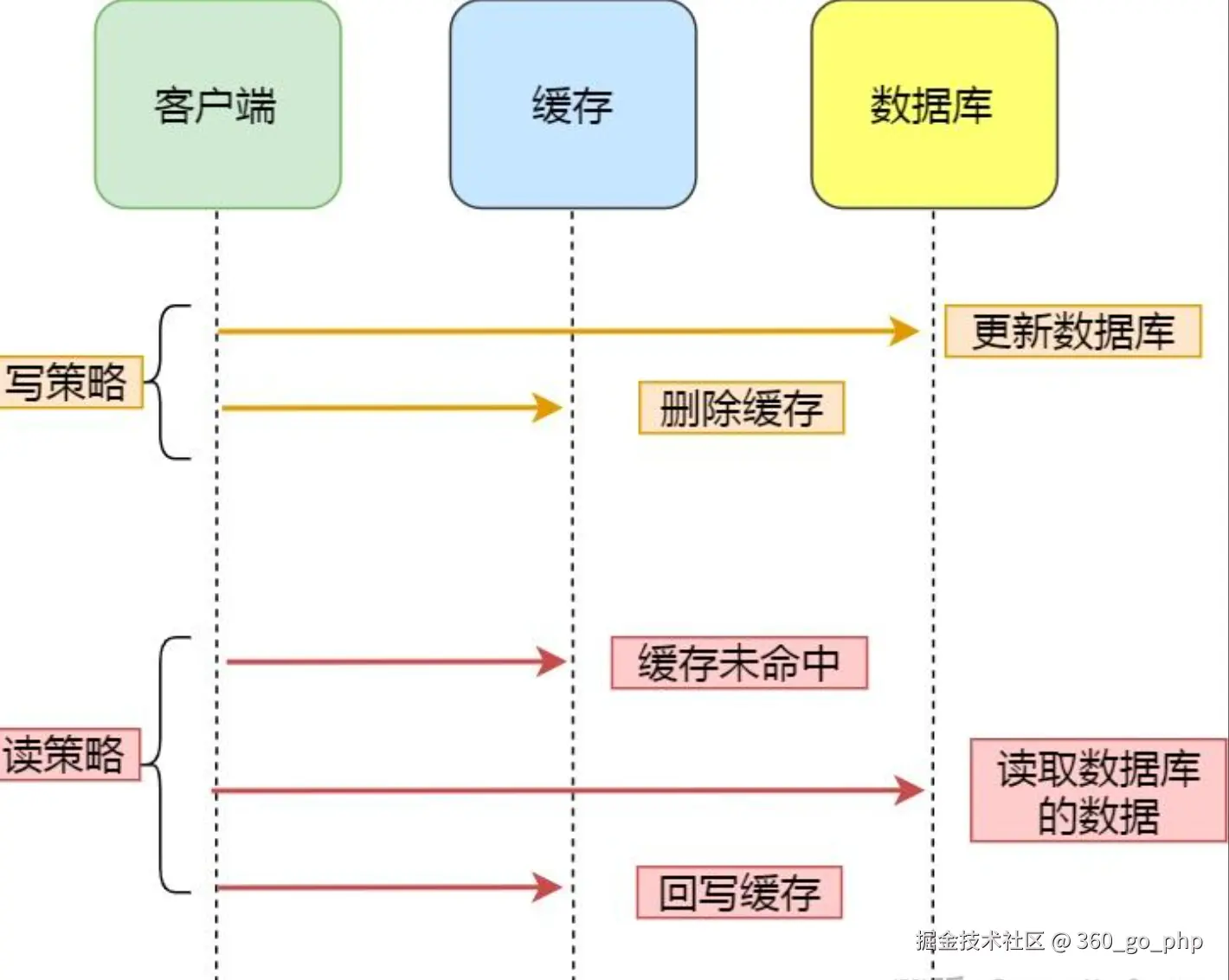 编辑
编辑
- 写入时更新(Write-Through):每次更新数据库时,同时更新Redis缓存。
- 异步更新:使用消息队列(如Kafka)将更新操作异步化,避免直接在业务流程中同步更新数据库和Redis。
java
public void updateProduct(Product product) {
productRepository.save(product);
// 异步更新缓存
updateCache(product);
} (2) 缓存失效策略 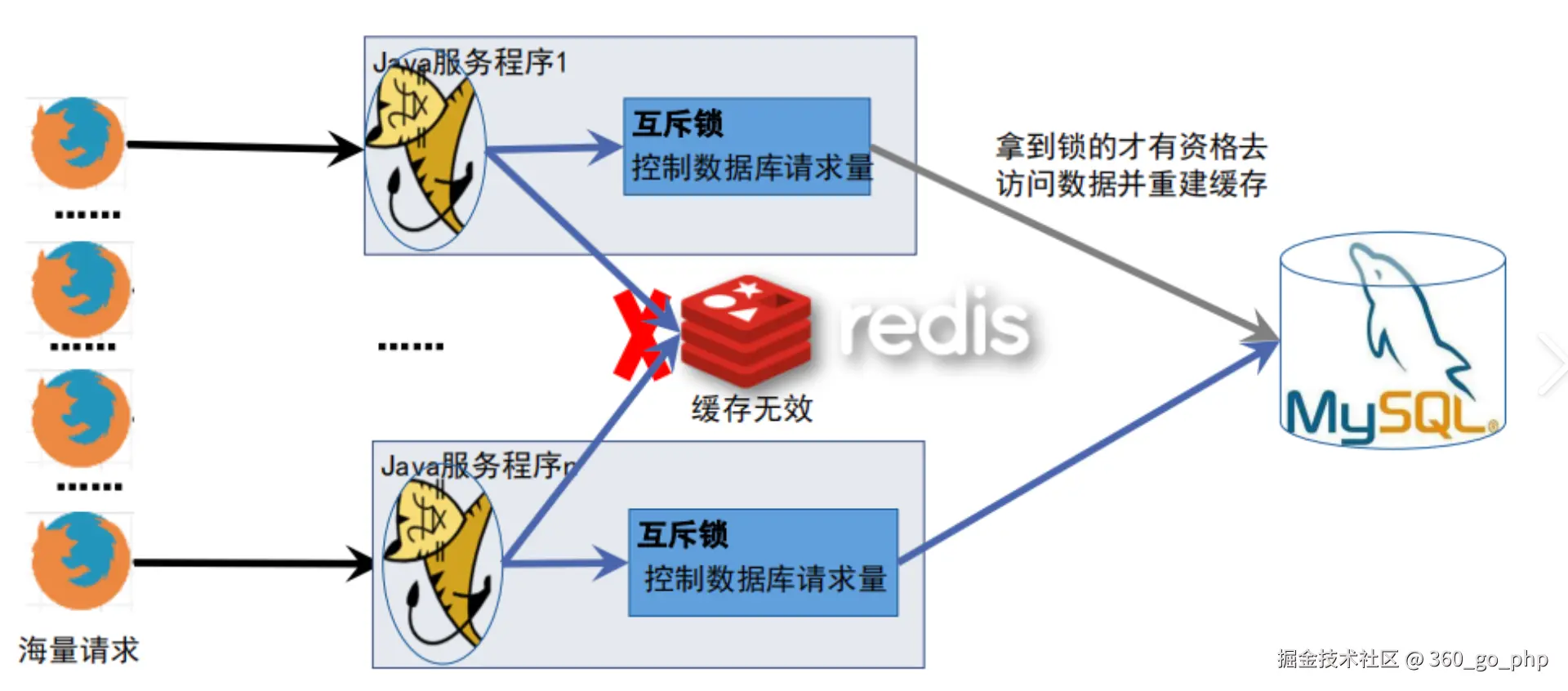 编辑
编辑
设置合理的缓存过期时间,避免缓存数据长期不更新。常见策略是采用短期缓存,并定期刷新缓存数据。
(3) 双写一致性  编辑
编辑
使用事务确保缓存与数据库的双写一致性。例如,使用Redis事务或Lua脚本保证操作的原子性。
lua
-- Lua脚本,保证在Redis中的操作原子性
local result = redis.call('SET', KEYS[1], ARGV[1])
if result then
redis.call('PUBLISH', 'cacheUpdate', KEYS[1])
end
return result 总结 编辑
编辑
本文讨论了AOP、Redis的使用场景、缓存设计等高级开发话题。在现代Web应用中,合理的架构设计和性能优化能够显著提升系统的响应速度和可扩展性。面试过程中,掌握这些高级技术点,能够帮助你展示出对复杂系统设计和性能优化的深刻理解,从而提升面试的成功率。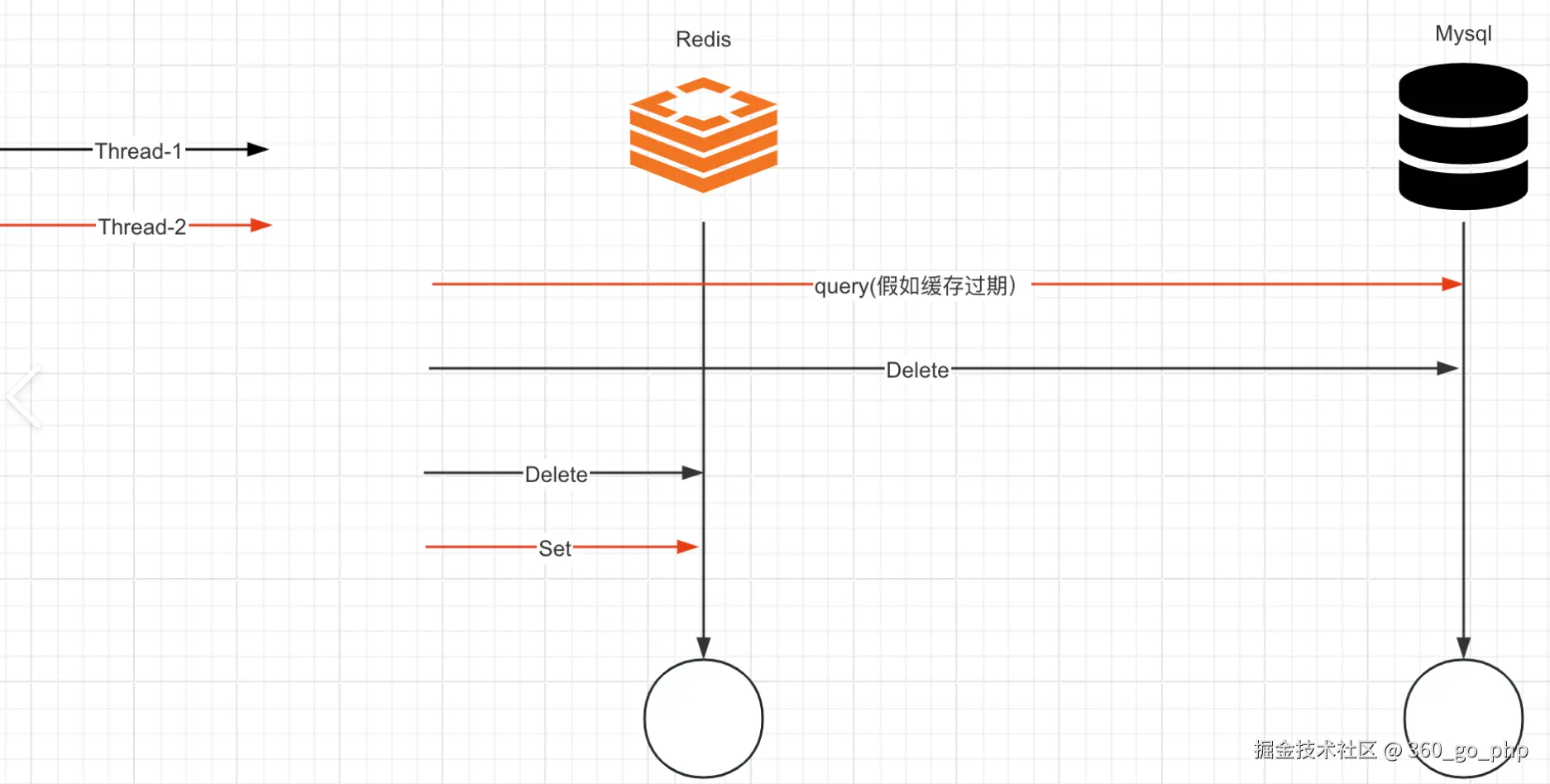 编辑
编辑