1 源码实现
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.cuda.amp import autocast
class CategoryContrastiveDistillation(nn.Module):
"""
简化的类别对比蒸馏(CCD)损失模块。
参考自:Chen et al., Category contrastive distillation with self-supervised classification[citation:1]
和 StAlK 中利用均值教师进行特征对齐的思想[citation:6]。
"""
def init(self, num_classes, feat_dim, temperature=0.1, momentum=0.999):
super().init()
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.temperature = temperature
self.momentum = momentum
注册缓冲区,用于存储教师和学生的类别原型(记忆库)
self.register_buffer("teacher_prototype", torch.zeros(num_classes, feat_dim))
self.register_buffer("student_prototype", torch.zeros(num_classes, feat_dim))
初始化原型为随机值(实践中可用第一批数据初始化)
nn.init.normal_(self.teacher_prototype, mean=0, std=0.01)
nn.init.normal_(self.student_prototype, mean=0, std=0.01)
@torch.no_grad()
def _update_prototype(self, features, labels, prototype_bank):
"""动量更新类别记忆库"""
for idx in range(self.num_classes):
mask = (labels == idx)
if mask.any():
计算当前批次中该类所有样本特征的均值
class_feat_mean = features[mask].mean(dim=0)
动量更新:新原型 = momentum * 旧原型 + (1 - momentum) * 当前均值
prototype_bank[idx] = self.momentum * prototype_bank[idx] + (1 - self.momentum) * class_feat_mean
可选:对原型进行L2归一化,方便计算余弦相似度
prototype_bank[idx] = F.normalize(prototype_bank[idx].unsqueeze(0), dim=1).squeeze(0)
def forward(self, student_feat, teacher_feat, labels):
"""
计算类别对比蒸馏损失。
Args:
student_feat: 学生模型特征,形状 [batch_size, feat_dim]
teacher_feat: 教师模型特征,形状 [batch_size, feat_dim]
labels: 样本真实标签,形状 [batch_size]
Returns:
ccd_loss: 类别对比蒸馏损失
"""
batch_size = student_feat.shape[0]
1. 动量更新教师和学生的类别原型记忆库
self._update_prototype(teacher_feat.detach(), labels, self.teacher_prototype)
self._update_prototype(student_feat.detach(), labels, self.student_prototype)
2. 计算学生特征与所有教师原型的相似度(作为"软目标")
相似度矩阵: [batch_size, num_classes]
这里使用点积相似度,假设特征和原型都已L2归一化
sim_student_to_teacher_proto = torch.mm(F.normalize(student_feat, dim=1),
F.normalize(self.teacher_prototype, dim=1).t())
3. 计算教师特征与所有教师原型的相似度(作为"软标签")
sim_teacher_to_own_proto = torch.mm(F.normalize(teacher_feat.detach(), dim=1),
F.normalize(self.teacher_prototype, dim=1).t())
4. 应用温度缩放,将相似度转换为概率分布
student_dist = F.log_softmax(sim_student_to_teacher_proto / self.temperature, dim=1)
teacher_dist = F.softmax(sim_teacher_to_own_proto / self.temperature, dim=1)
5. 计算KL散度损失,让学生特征与原型的相似度分布接近教师特征与原型的分布
ccd_loss = F.kl_div(student_dist, teacher_dist, reduction='batchmean') * (self.temperature ** 2)
6. (可选) 引入一个辅助的"学生原型-教师原型"对齐损失
直接最小化学生原型和教师原型之间的距离,进一步稳定训练
proto_alignment_loss = F.mse_loss(self.student_prototype, self.teacher_prototype.detach())
总CCD损失是两项的加权和
total_ccd_loss = ccd_loss + 0.5 * proto_alignment_loss
return total_ccd_loss
============ 如何在主训练循环中使用 ============
假设已有:student_model, teacher_model, optimizer, dataloader
num_classes = 100, feature_dim = 256
ccd_criterion = CategoryContrastiveDistillation(num_classes=100, feat_dim=256, temperature=0.1)
for images, labels in dataloader:
images, labels = images.cuda(), labels.cuda()
# 1. 前向传播,获取特征和logits
# 假设模型返回一个元组 (logits, feature)
student_logits, student_feat = student_model(images)
with torch.no_grad(): # 教师模型不计算梯度
# 教师模型通常使用学生模型的EMA参数[citation:6]
teacher_logits, teacher_feat = teacher_model(images)
# 2. 计算各项损失
# a. 标准交叉熵损失
ce_loss = F.cross_entropy(student_logits, labels)
# b. 传统知识蒸馏损失 (软化标签)
temp = 4.0
kd_loss = F.kl_div(F.log_softmax(student_logits / temp, dim=1),
F.softmax(teacher_logits / temp, dim=1),
reduction='batchmean') * (temp * temp)
# c. 类别对比蒸馏损失
ccd_loss = ccd_criterion(student_feat, teacher_feat, labels)
# 3. 组合总损失 (权重需要调参)
lambda_kd = 0.5
lambda_ccd = 1.0
total_loss = ce_loss + lambda_kd * kd_loss + lambda_ccd * ccd_loss
# 4. 反向传播与优化
optimizer.zero_grad()
total_loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 5. (关键) 更新教师模型为学生的EMA
# tau为EMA动量,例如0.999
tau = 0.999
for param_s, param_t in zip(student_model.parameters(), teacher_model.parameters()):
param_t.data = tau * param_t.data + (1 - tau) * param_s.data
2 流程图与解析
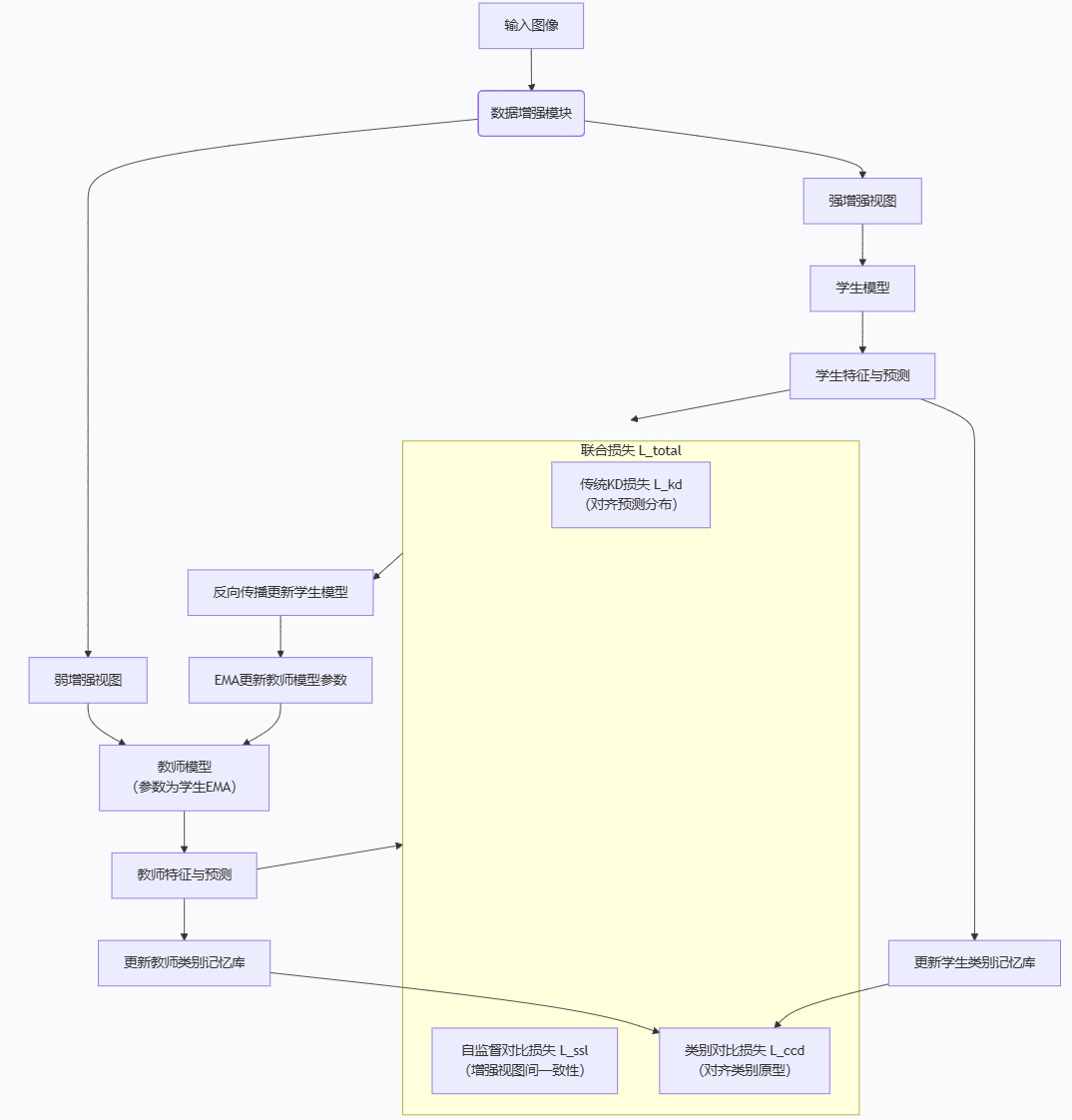
流程关键点解读:
-
双分支输入:同一张图像经过不同的数据增强(如强增强和弱增强),分别输入学生和教师模型。
-
教师模型更新 :教师模型的参数通常采用学生模型参数的指数移动平均(EMA) 获得,这是一个稳定知识源的关键技巧-6。
-
记忆库 :教师和学生模型分别维护一个动态的类别记忆库 ,用于存储和更新每个类别的特征原型(通常使用当前批次的特征滑动平均更新)-1。
-
损失函数:总损失是多项损失的加权和,核心包括:
-
传统知识蒸馏损失(L_kd):让学生模型的 softened logits 去匹配教师模型的。
-
自监督对比损失(L_ssl):例如,让学生模型对同一图像不同增强视图的特征表示尽可能接近(正样本),而与其他图像的特征表示远离(负样本)。
-
类别对比蒸馏损失(L_ccd) :这是核心创新点。它计算学生特征与其所有教师类别原型的相似度分布,并与one-hot标签或教师预测分布进行对比损失计算,从而让学生特征向正确的教师类别原型靠近,并远离其他类别原型
-