
文章目录
-
- 一、关联式容器与键值对:基础概念铺垫
-
- [1.1 关联式容器 vs 序列式容器](#1.1 关联式容器 vs 序列式容器)
- [1.2 键值对`pair`的本质](#1.2 键值对
pair的本质)
- 二、set容器:有序唯一的集合
-
- [2.1 set的核心特性](#2.1 set的核心特性)
- [2.2 常用接口实战](#2.2 常用接口实战)
- [2.3 multiset:允许重复元素的set](#2.3 multiset:允许重复元素的set)
- 三、map容器:键值映射的字典
-
- [3.1 map的核心特性](#3.1 map的核心特性)
- [3.2 常用接口实战](#3.2 常用接口实战)
- [3.3 map与set的核心差异](#3.3 map与set的核心差异)
- 四、实战OJ:map与set的经典应用
- 五、注意事项
- 🚩总结
在C++ STL的容器家族中,map和set作为核心关联式容器,凭借红黑树的底层实现,兼具自动排序、高效检索的特性。
一、关联式容器与键值对:基础概念铺垫
1.1 关联式容器 vs 序列式容器
STL容器分为序列式容器 (如vector、list、deque)和关联式容器 (如map、set、multimap、multiset),核心差异在于数据存储方式和检索逻辑:
- 序列式容器:存储元素本身,底层是线性结构,检索需遍历,时间复杂度O(n);
- 关联式容器:存储
<key, value>键值对(set中value即key),底层是红黑树(平衡二叉搜索树),检索、插入、删除的时间复杂度均为O(log n),效率远超序列式容器。
1.2 键值对pair的本质
键值对是关联式容器的基础数据结构,用于表示"一一对应"的关系(如字典中的"单词-释义")。STL中pair的定义简化如下:
cpp
template <class T1, class T2>
struct pair {
T1 first; // 键key
T2 second; // 值value
// 构造函数
pair() : first(T1()), second(T2()) {}
pair(const T1& a, const T2& b) : first(a), second(b) {}
};常用操作:
- 直接构造:
pair<string, int> kv("apple", 5); - 便捷构造:
make_pair("banana", 3)(无需显式指定模板参数,更简洁); - 访问成员:通过
first和second访问键和值,如kv.first、kv.second。
二、set容器:有序唯一的集合
2.1 set的核心特性
- 存储单一类型元素,value即key,且所有元素唯一(自动去重);
- 底层是红黑树,元素默认按
less<T>规则升序排序(可自定义排序规则); - 不支持直接修改元素(会破坏红黑树的有序性),需先删除再插入。
2.2 常用接口实战
(1)初始化与遍历
cpp
#include <set>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void test_set_init() {
// 1. 列表初始化(C++11+)
set<int> s1 = {3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9}; // 自动去重+升序,结果:1,3,4,5,9
// 2. 迭代器区间初始化
int arr[] = {2, 7, 1, 8, 2};
set<int> s2(arr, arr + sizeof(arr)/sizeof(int)); // 结果:1,2,7,8
// 3. 自定义排序(降序)
set<int, greater<int>> s3 = {3, 1, 4}; // 结果:4,3,1
// 遍历方式:迭代器遍历
for (set<int>::iterator it = s1.begin(); it != s1.end(); ++it) {
cout << *it << " "; // 输出:1 3 4 5 9
}
cout << endl;
// 范围for遍历(更简洁)
for (auto e : s2) {
cout << e << " "; // 输出:1 2 7 8
}
cout << endl;
}
(2)插入与删除
cpp
void test_set_insert_erase() {
set<int> s = {1, 3, 5, 7};
// 插入:返回pair<iterator, bool>,bool表示是否插入成功(避免重复)
auto ret1 = s.insert(4); // 插入成功,ret1.second = true
auto ret2 = s.insert(3); // 重复插入,ret1.second = false
// 删除:三种方式
s.erase(5); // 按值删除(存在则删除,返回删除个数)
auto pos = s.find(7); // 按迭代器删除(先查找再删除,更安全)
if (pos != s.end()) {
s.erase(pos);
}
s.erase(s.begin(), s.find(4)); // 按区间删除(删除[begin, 4)的元素)
for (auto e : s) {
cout << e << " "; // 输出:4
}
}(3)查找与区间查询
cpp
void test_set_find() {
set<int> s = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
// find:查找值,返回迭代器(未找到返回end())
auto pos = s.find(30);
if (pos != s.end()) {
cout << "找到:" << *pos << endl; // 输出:30
}
// count:返回元素个数(set中仅0或1,用于判断存在性)
cout << "20的个数:" << s.count(20) << endl; // 1
cout << "25的个数:" << s.count(25) << endl; // 0
// 区间查询:lower_bound和upper_bound(左闭右开区间)
auto it_low = s.lower_bound(25); // 返回>=25的第一个元素(30)
auto it_up = s.upper_bound(40); // 返回>40的第一个元素(50)
cout << "区间[" << *it_low << "," << *it_up << ")" << endl; // [30,50)
// equal_range:返回pair<lower_bound, upper_bound>
auto ret = s.equal_range(30);
cout << "lower_bound: " << *ret.first << endl; // 30
cout << "upper_bound: " << *ret.second << endl; // 40
}2.3 multiset:允许重复元素的set
multiset是set的变体,核心差异是允许存储重复元素 ,其他特性与set一致:
- 插入:无返回值(无需判断重复);
- find:查找时返回中序遍历的第一个匹配元素;
- erase:按值删除时,删除所有匹配元素;按迭代器删除时,仅删除指定元素。
cpp
void test_multiset() {
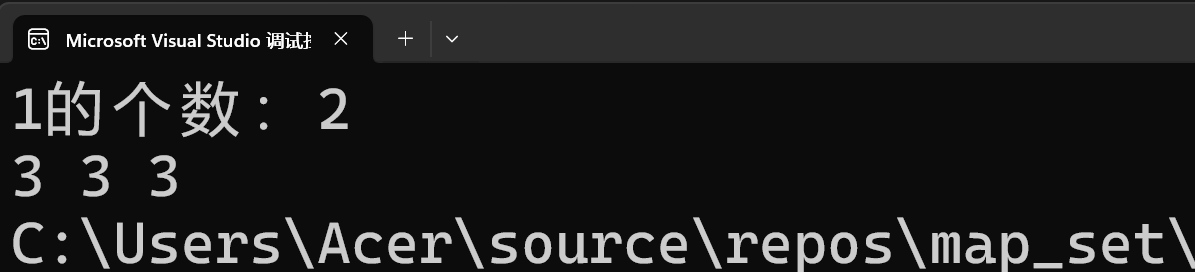
multiset<int> ms = {3, 1, 2, 1, 3, 3}; // 允许重复,排序后:1,1,2,3,3,3
cout << "1的个数:" << ms.count(1) << endl; // 2
auto pos = ms.find(3); // 返回第一个3的迭代器
while (pos != ms.end() && *pos == 3) {
cout << *pos << " "; // 输出:3 3 3
++pos;
}
ms.erase(3); // 删除所有3,结果:1,1,2
}
三、map容器:键值映射的字典
3.1 map的核心特性
- 存储
<key, value>键值对,key唯一且用于排序,value存储关联数据; - 底层是红黑树,按key的
less<T>规则默认升序排序; - 支持下标访问符
[],可直接通过key查找、插入、修改value(最常用特性)。
3.2 常用接口实战
(1)初始化与遍历
cpp
void test_map_init() {
// 1. 直接插入pair
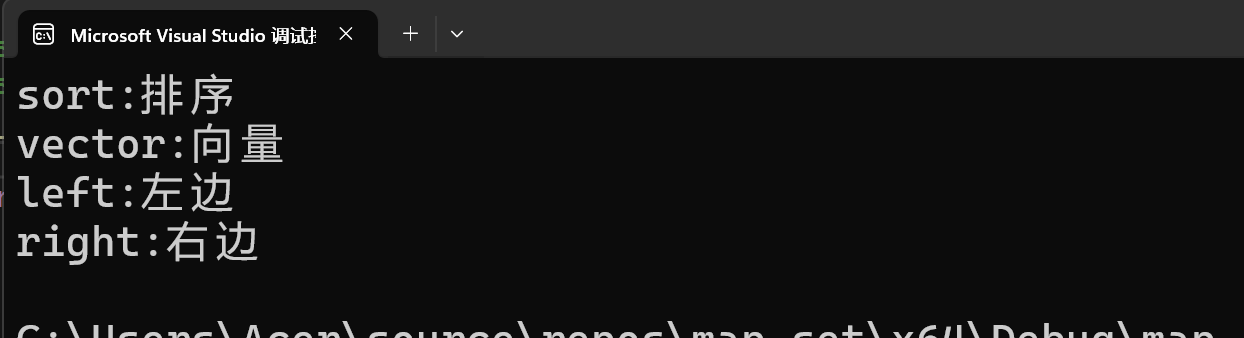
map<string, string> dict;
dict.insert(pair<string, string>("sort", "排序"));
dict.insert(make_pair("vector", "向量")); // 推荐用make_pair,更简洁
// 2. 列表初始化(C++11+)
map<string, string> dict2 = {{"left", "左边"}, {"right", "右边"}};
// 遍历:迭代器遍历
for (map<string, string>::iterator it = dict.begin(); it != dict.end(); ++it) {
// it是指向pair的指针,通过->访问first和second
cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
}
// 范围for遍历(推荐)
for (auto& kv : dict2) {
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
}
}
(2)下标[]的底层逻辑(核心重点)
map的[]是最便捷的操作,其底层实现等价于:
cpp
V& operator[](const K& key) {
// 插入键值对,若key不存在则插入pair(key, V()),返回value的引用
pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}例如:统计元素出现次数(一行代码实现)
cpp
void test_map_count() {
string arr[] = {"苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "西瓜"};
map<string, int> countMap;
// 统计次数:key不存在时插入并初始化value为0,再++;存在时直接++
for (auto& str : arr) {
countMap[str]++;
}
for (auto& kv : countMap) {
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl; // 苹果:3 西瓜:2 香蕉:1
}
}(3)插入与修改
cpp
void test_map_insert_modify() {
map<int, string> student;
// 插入:三种方式
student.insert(make_pair(101, "张三"));
student.insert(pair<int, string>(102, "李四"));
student[103] = "王五"; // 下标插入(最简洁)
// 修改value:通过迭代器或下标
student[102] = "李小四"; // 下标直接修改
auto pos = student.find(101);
if (pos != student.end()) {
pos->second = "张大三"; // 迭代器修改
}
for (auto& kv : student) {
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
// 输出:101:张大三 102:李小四 103:王五
}
}3.3 map与set的核心差异
| 特性 | set | map |
|---|---|---|
| 数据结构 | 单一元素(value=key) | 键值对<key, value> |
| 核心用途 | 去重、排序、集合操作 | 键值映射、字典、统计计数 |
| 元素修改 | 不支持直接修改(需删后插) | 支持修改value,不支持修改key |
| 下标访问 | 不支持 | 支持[]通过key访问value |
| 内存占用 | 较低(仅存key) | 较高(存key+value) |
| 插入返回值 | pair<iterator, bool> |
pair<iterator, bool> |
四、实战OJ:map与set的经典应用
cpp
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* next;
Node* random;
Node(int _val) : val(_val), next(nullptr), random(nullptr) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if (!head) return nullptr;
map<Node*, Node*> nodeMap; // 原节点 -> 复制节点
// 第一次遍历:复制节点,建立映射
Node* cur = head;
while (cur) {
nodeMap[cur] = new Node(cur->val);
cur = cur->next;
}
// 第二次遍历:设置next和random指针
cur = head;
while (cur) {
nodeMap[cur]->next = nodeMap[cur->next]; // 复制next
nodeMap[cur]->random = nodeMap[cur->random]; // 复制random
cur = cur->next;
}
return nodeMap[head];
}
};
cpp
class Solution {
public:
// 自定义比较规则:频率降序,频率相同则字典序升序
struct Compare {
bool operator()(const pair<string, int>& a, const pair<string, int>& b) {
return a.second > b.second || (a.second == b.second && a.first < b.first);
}
};
vector<string> topKFrequent(vector<string>& words, int k) {
// 1. 统计频率
map<string, int> countMap;
for (auto& word : words) {
countMap[word]++;
}
// 2. 转换为vector排序(map是双向迭代器,不支持sort)
vector<pair<string, int>> freqVec(countMap.begin(), countMap.end());
sort(freqVec.begin(), freqVec.end(), Compare());
// 3. 提取前K个单词
vector<string> res;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
res.push_back(freqVec[i].first);
}
return res;
}
};解法2:multimap排序(利用红黑树自动排序)
cpp
vector<string> topKFrequent(vector<string>& words, int k) {
map<string, int> countMap;
for (auto& word : words) {
countMap[word]++;
}
// multimap按频率降序排序(key为频率,value为单词)
multimap<int, string, greater<int>> freqMap;
for (auto& kv : countMap) {
freqMap.insert(make_pair(kv.second, kv.first));
}
// 提取结果(频率相同时,multimap按插入顺序排列,恰好符合字典序)
vector<string> res;
auto it = freqMap.begin();
while (k-- && it != freqMap.end()) {
res.push_back(it->second);
++it;
}
return res;
}解法3:set特性 + 仿函数(空间最优)
cpp
vector<string> topKFrequent(vector<string>& words, int k) {
map<string, int> countMap;
for (auto& word : words) {
countMap[word]++;
}
// set按自定义规则排序,自动去重(此处无重复,仅利用排序特性)
struct Compare {
bool operator()(const pair<string, int>& a, const pair<string, int>& b) {
return a.second > b.second || (a.second == b.second && a.first < b.first);
}
};
set<pair<string, int>, Compare> freqSet(countMap.begin(), countMap.end());
// 提取前K个
vector<string> res;
auto it = freqSet.begin();
while (k-- && it != freqSet.end()) {
res.push_back(it->first);
++it;
}
return res;
}
cpp
vector<int> intersection(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
// 去重排序
set<int> s1(nums1.begin(), nums1.end());
set<int> s2(nums2.begin(), nums2.end());
vector<int> res;
auto it1 = s1.begin(), it2 = s2.begin();
// 双指针遍历,查找交集
while (it1 != s1.end() && it2 != s2.end()) {
if (*it1 < *it2) {
++it1;
} else if (*it2 < *it1) {
++it2;
} else {
res.push_back(*it1);
++it1;
++it2;
}
}
return res;
}五、注意事项
5.1 自定义排序规则
无论是map还是set,都可通过传入仿函数或lambda表达式自定义排序规则:
cpp
// 按字符串长度降序排序
struct StrLenCompare {
bool operator()(const string& a, const string& b) {
return a.size() > b.size() || (a.size() == b.size() && a < b);
}
};
set<string, StrLenCompare> s = {"apple", "banana", "pear"};
// 结果:banana(6)、apple(5)、pear(4)5.2 常见易错点
- 修改set的元素:set的元素是const的,直接修改会破坏红黑树结构,需先删除再插入;
- map的key重复插入 :insert方法插入重复key会失败,若需修改value,应使用
[]或先删除再插入; - 迭代器失效:map/set的插入、删除操作不会导致其他迭代器失效(红黑树的特性),仅被删除的迭代器失效;
- 效率误区 :若无需排序,优先使用
unordered_map/unordered_set(哈希表实现,平均时间复杂度O(1)),效率更高。
5.3 适用场景总结
- 用
set:需要去重、排序、集合操作(交集、并集、差集); - 用
map:需要键值映射、统计计数、字典功能; - 用
multiset/multimap:需要允许重复key的场景; - 用
unordered_*:无需排序,追求极致检索效率。
🚩总结
