鸿蒙学习实战之路 - 应用间链接最佳实践
应用间链接是实现应用间无缝交互的关键技术,合理使用可以显著提升用户体验
关于本文
本文基于华为官方文档整理,结合实际开发经验,提供 HarmonyOS 应用间链接的实用指南
- 本文并不能代替官方文档,所有内容基于官方文档+实践记录
- 所有代码示例都有详细注释,建议自己动手尝试
- 基本所有关键功能都会附上对应的文档链接,强烈建议你点看看看
- 本文将通过实际案例介绍应用间链接的实现方式和最佳实践
代码测试环境
确保你的开发环境符合以下要求:
| 软件/工具 | 版本要求 |
|---|---|
| HarmonyOS SDK | API Level 11+ |
| TypeScript | 5.0+ |
| DevEco Studio | 4.1+ |
| 设备要求 | 支持 HarmonyOS NEXT 的真机或模拟器 |
概述
应用间链接是指在不同应用之间建立通信和交互的技术。在 HarmonyOS 中,应用间链接主要通过以下几种方式实现:
- App Linking:系统级深度链接,支持直接跳转到应用内指定页面
- startAbility:通过能力启动实现应用间跳转
- Web 拦截跳转:在 Web 场景下实现应用间跳转
应用场景示例
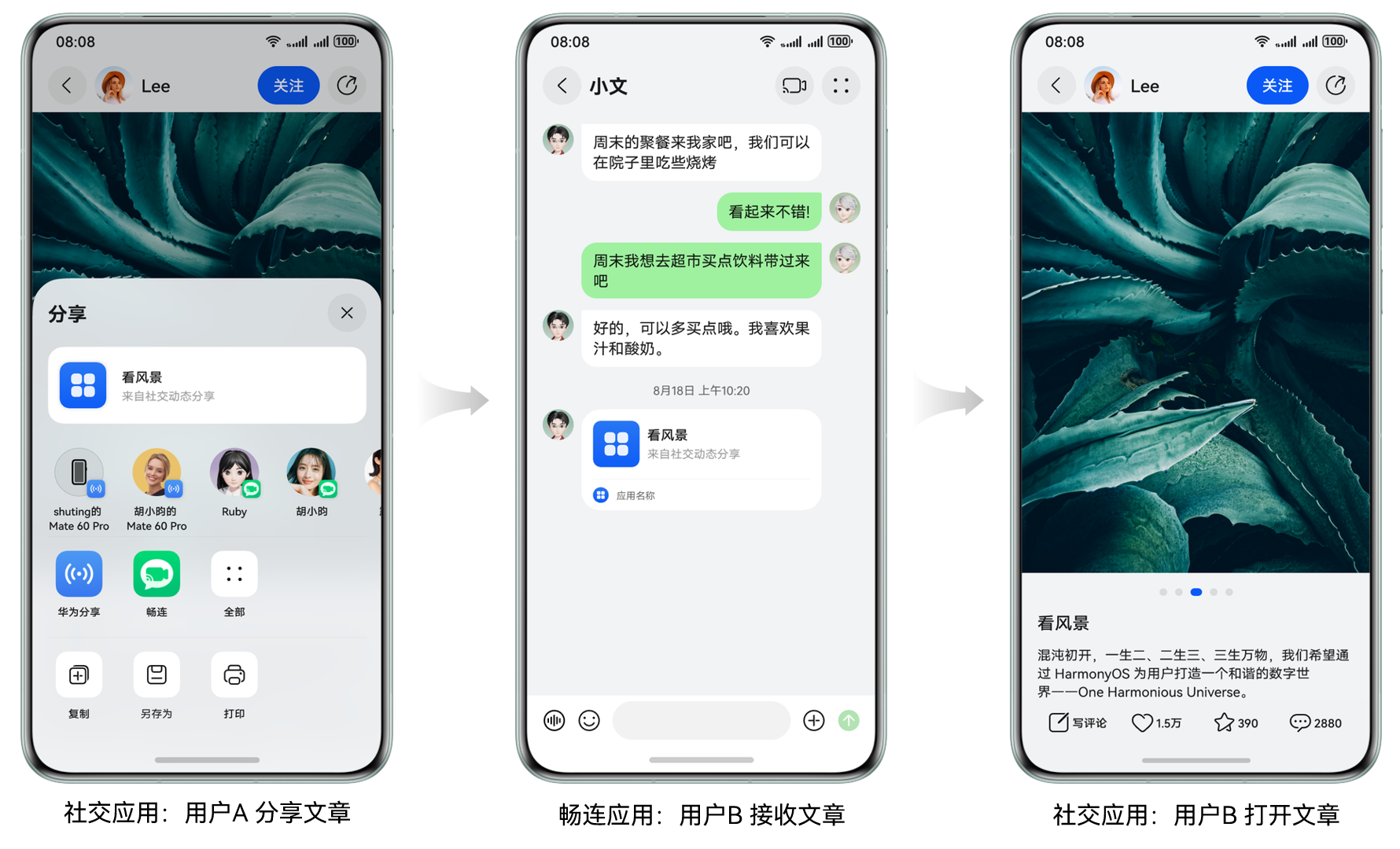
社交分享跳转
- 用户 A 在社交应用中看到一篇文章,通过分享功能发送给好友 B
- 好友 B 点击链接后,直接打开社交应用并定位到该篇文章,而非应用首页
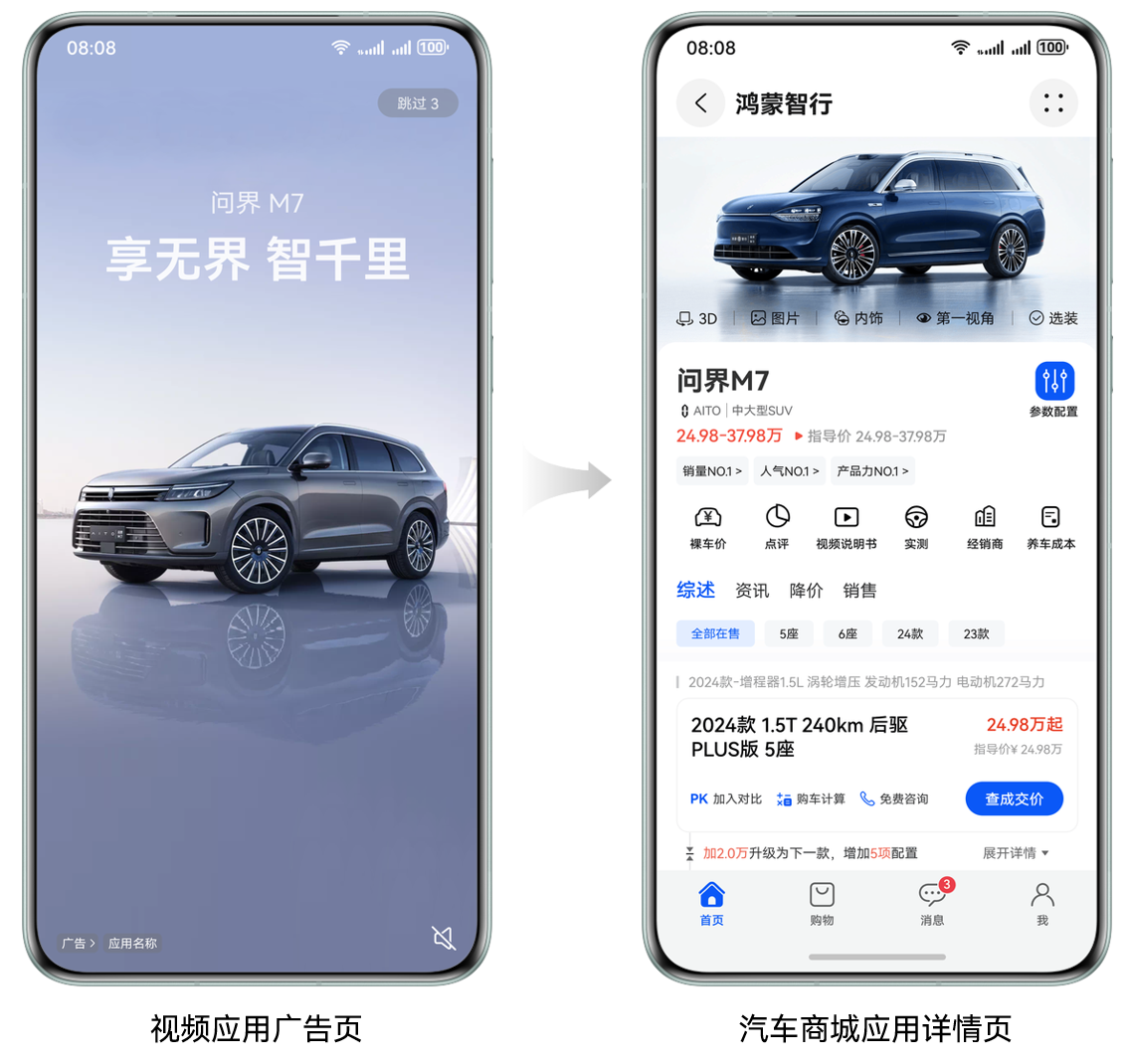
广告跳转
- 视频应用中播放汽车商城应用的促销广告
- 点击广告后直接打开电商应用并跳转至促销活动页面,用户无需在应用内搜索或导航
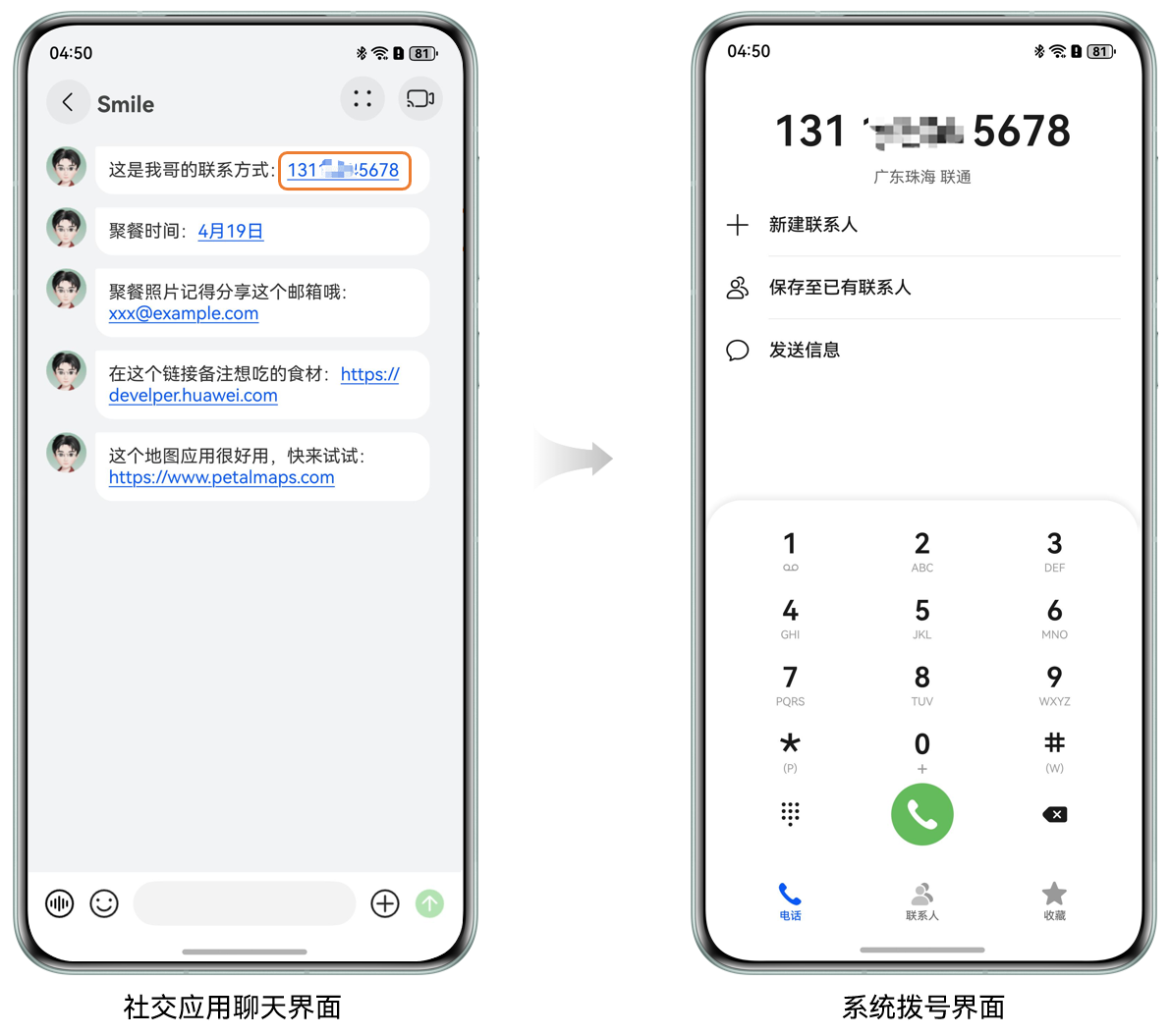
特殊文本识别跳转
- 聊天界面识别到电话号码
- 用户点击电话号码后直接打开系统拨号界面,方便用户拨打电话
本文将从以下几个方面介绍 HarmonyOS 应用间链接的最佳实践:
- App Linking 的基本概念和使用方法
- startAbility 实现应用间跳转
- Web 拦截跳转的实现方式
- 应用间链接的安全考虑
- 实际案例分析
1. App Linking 基本概念和使用
1.1 什么是 App Linking
App Linking(应用链路)是 HarmonyOS 操作系统提供的一项系统级深度链接功能,它允许用户通过 HTTPS 链接直接跳转到应用中的指定页面,无论应用是否已安装。
1.2 App Linking 的优势
- 统一链接:同一个链接可以在不同平台和场景下使用
- 跨应用跳转:支持在不同 HarmonyOS 应用之间无缝跳转
- 灵活配置:可以自定义链接的行为和参数
- 用户体验好:无需用户手动查找应用,直接跳转至目标页面
- 延迟链接:支持应用安装后恢复之前的跳转意图
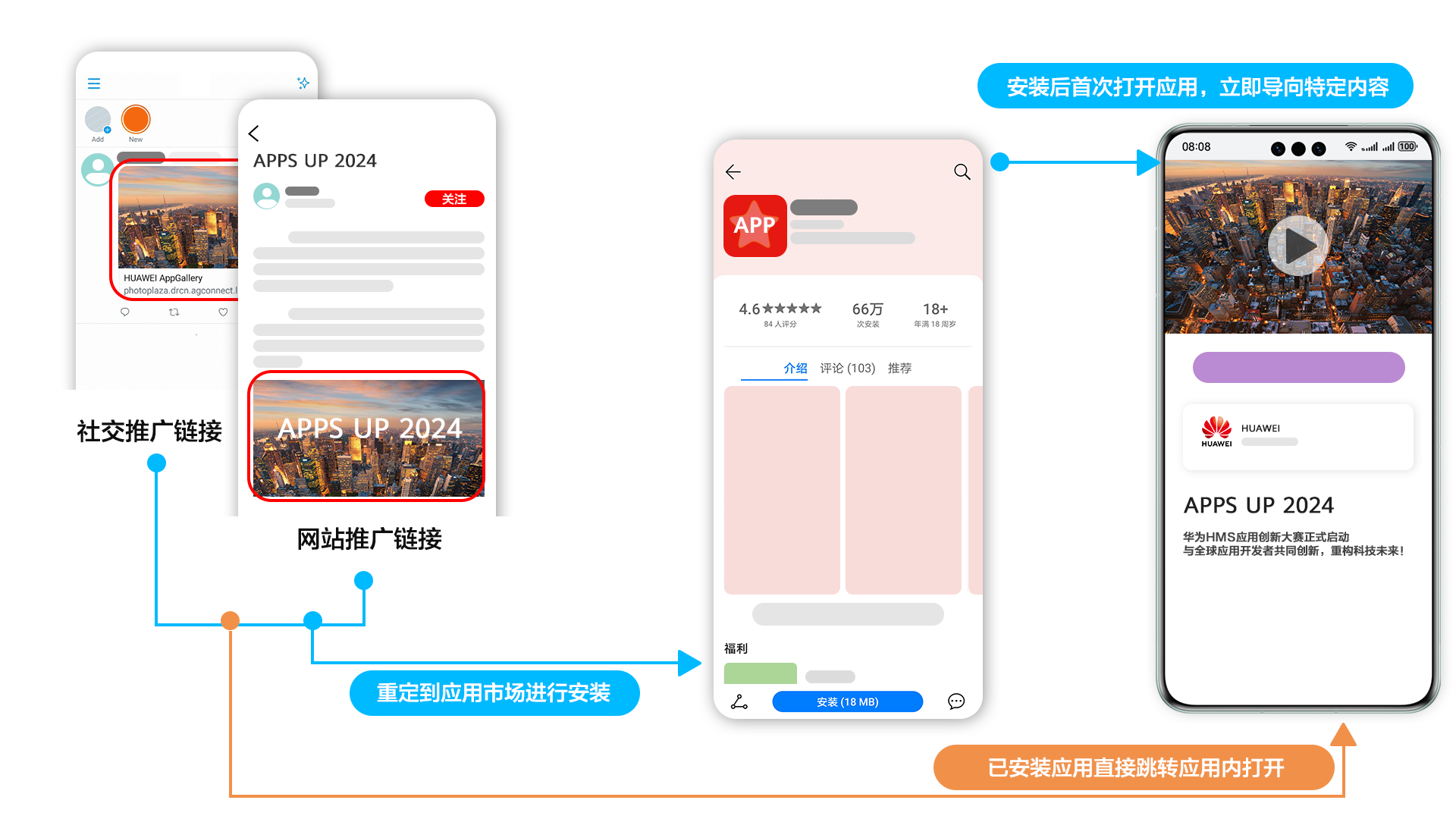
基于安全性和用户体验的全面考量,建议优先采用 App Linking 技术。与 Deep Linking 相比,App Linking 提供了更高的安全性,避免了仿冒风险,并提升了用户在应用间跳转时的整体使用体验。
1.3 实现 App Linking
1.3.1 配置应用链接信息
在 module.json5 中配置应用链接信息:
json5
{
module: {
name: "entry",
type: "entry",
description: "应用入口模块",
mainElement: "EntryAbility",
deviceTypes: ["phone", "tablet"],
distro: {
deliveryWithInstall: true,
moduleName: "entry",
moduleType: "entry",
},
abilities: [
{
name: "EntryAbility",
srcEntry: "./ets/entryability/EntryAbility.ts",
description: "应用入口能力",
icon: "$media:icon",
label: "应用间链接示例",
startWindowIcon: "$media:icon",
startWindowBackground: "$color:start_window_background",
skills: [
{
entities: ["entity.system.home"],
actions: ["action.system.home"],
},
{
actions: ["ohos.want.action.viewData"],
uris: [
{
scheme: "https",
host: "example.com",
path: "/app/*",
},
],
},
],
},
],
},
}1.3.2 处理链接跳转
在 EntryAbility.ts 中处理链接跳转:
typescript
import { UIAbility, Want, AbilityConstant } from "@kit.AbilityKit";
import { hilog } from "@kit.PerformanceAnalysisKit";
import { Configuration } from "@kit.ConfigurationKit";
export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility {
onCreate(want: Want, launchParam: AbilityConstant.LaunchParam) {
hilog.info(0x0000, "EntryAbility", "%{public}s", "Ability onCreate");
// 处理应用链接跳转
this.handleAppLinking(want);
}
onNewWant(want: Want, launchParam: AbilityConstant.LaunchParam) {
hilog.info(0x0000, "EntryAbility", "%{public}s", "Ability onNewWant");
// 处理新的应用链接跳转
this.handleAppLinking(want);
}
// 处理应用链接跳转的方法
private handleAppLinking(want: Want) {
if (want.uri) {
hilog.info(
0x0000,
"EntryAbility",
"Received app linking: %{public}s",
want.uri
);
// 解析 URI 参数
const url = new URL(want.uri);
const path = url.pathname;
const params = new URLSearchParams(url.search);
// 根据路径和参数执行相应操作
if (path.startsWith("/app/detail")) {
const id = params.get("id");
if (id) {
// 跳转到详情页
this.context.startAbility({
bundleName: this.context.applicationInfo.bundleName,
abilityName: "DetailAbility",
parameters: {
itemId: id,
},
});
}
}
}
}
onDestroy() {
hilog.info(0x0000, "EntryAbility", "%{public}s", "Ability onDestroy");
}
onWindowStageCreate(windowStage: any) {
// 设置主页面
windowStage.loadContent("pages/Index", (err, data) => {
if (err.code) {
hilog.error(
0x0000,
"EntryAbility",
"Failed to load content: %{public}s",
JSON.stringify(err)
);
return;
}
});
}
// 其他生命周期方法...
}1.3.3 发起 App Linking 跳转
在其他应用中发起 App Linking 跳转:
typescript
import { businessError } from "@kit.BasicServicesKit";
import { openLink } from "@kit.LinkKit";
// 发起应用链接跳转
async function launchAppLinking() {
try {
await openLink({
url: "https://example.com/app/detail?id=12345",
});
console.log("App linking launched successfully");
} catch (error) {
console.error("Failed to launch app linking:", error as businessError);
}
}2. 使用 startAbility 实现应用间跳转
2.1 startAbility 概述
startAbility 是 HarmonyOS 提供的一种能力启动机制,可以用于在不同应用之间跳转,支持传递复杂参数。
2.2 实现应用间跳转
2.2.1 配置能力信息
在目标应用的 module.json5 中配置能力信息:
json5
{
module: {
abilities: [
{
name: "DetailAbility",
srcEntry: "./ets/abilities/DetailAbility.ts",
description: "详情页能力",
icon: "$media:icon",
label: "详情页",
skills: [
{
actions: ["ohos.want.action.detailView"],
entities: ["entity.system.default"],
},
],
},
],
},
}2.2.2 发起能力跳转
在源应用中发起能力跳转:
typescript
import { context } from "@kit.ArkUI";
import { businessError } from "@kit.BasicServicesKit";
// 发起应用间能力跳转
async function startOtherAbility() {
try {
await context.startAbility({
bundleName: "com.example.targetapp",
abilityName: "DetailAbility",
action: "ohos.want.action.detailView",
parameters: {
itemId: "12345",
itemName: "示例商品",
itemPrice: 99.9,
},
});
console.log("Ability launched successfully");
} catch (error) {
console.error("Failed to launch ability:", error as businessError);
}
}2.2.3 接收能力参数
在目标应用的 DetailAbility.ts 中接收参数:
typescript
import { UIAbility, Want, AbilityConstant } from "@kit.AbilityKit";
import { hilog } from "@kit.PerformanceAnalysisKit";
export default class DetailAbility extends UIAbility {
onCreate(want: Want, launchParam: AbilityConstant.LaunchParam) {
hilog.info(0x0000, "DetailAbility", "%{public}s", "Ability onCreate");
// 接收参数
if (want.parameters) {
const itemId = want.parameters.itemId;
const itemName = want.parameters.itemName;
const itemPrice = want.parameters.itemPrice;
hilog.info(
0x0000,
"DetailAbility",
"Received params: id=%{public}s, name=%{public}s, price=%{public}f",
itemId,
itemName,
itemPrice
);
// 保存参数,供页面使用
this.context.abilityInfo.parameters = want.parameters;
}
}
// 其他生命周期方法...
}3. Web 拦截跳转
3.1 Web 拦截跳转概述
Web 拦截跳转是指在应用中加载 Web 页面时,拦截特定的 URL 请求并跳转到应用内的相应页面。
3.2 实现 Web 拦截跳转
typescript
import { Web } from '@kit.ArkUI';
import { WebviewController } from '@kit.ArkUI';
import { context } from '@kit.ArkUI';
@Entry
@Component
struct WebPage {
private webviewController: WebviewController = new WebviewController();
build() {
Column() {
Web({
src: 'https://example.com',
controller: this.webviewController
})
.javaScriptAccess(true)
.onUrlLoadIntercept((event) => {
const url = event.url;
// 拦截特定 URL
if (url.startsWith('https://example.com/app/')) {
// 解析 URL 参数
const urlObj = new URL(url);
const path = urlObj.pathname;
const params = new URLSearchParams(urlObj.search);
// 根据路径跳转到应用内页面
if (path.startsWith('/app/detail')) {
const id = params.get('id');
if (id) {
// 跳转到详情页
router.pushUrl({
url: `pages/DetailPage?id=${id}`
});
}
}
// 阻止默认的 URL 加载
return true;
}
// 允许其他 URL 正常加载
return false;
})
}
}
}4. 应用间链接的安全考虑
4.1 验证链接来源
在处理应用间链接时,应该验证链接的来源和完整性,防止恶意链接攻击。
typescript
// 验证链接来源
private validateLink(url: string): boolean {
try {
const urlObj = new URL(url);
// 验证域名
const allowedDomains = ['example.com', 'trusted-domain.com'];
if (!allowedDomains.includes(urlObj.host)) {
console.error('Invalid domain:', urlObj.host);
return false;
}
// 验证路径
if (!urlObj.pathname.startsWith('/app/')) {
console.error('Invalid path:', urlObj.pathname);
return false;
}
return true;
} catch (error) {
console.error('Invalid URL:', error);
return false;
}
}4.2 限制敏感操作
对于涉及敏感操作的链接,应该要求用户确认或进行身份验证。
typescript
// 处理敏感操作链接
private handleSensitiveLink(url: string) {
if (url.includes('/app/payment')) {
// 要求用户确认
promptAction.showDialog({
title: '支付确认',
message: '您确定要进行支付操作吗?',
buttons: [
{ text: '取消', color: '#FF0000' },
{ text: '确认', color: '#007DFF' }
]
}).then(result => {
if (result.index === 1) {
// 用户确认后执行支付操作
this.processPayment(url);
}
});
}
}5. 应用间链接最佳实践总结
5.1 选择合适的链接方式
| 链接方式 | 适用场景 | 优势 |
|---|---|---|
| App Linking | 需要跨平台、跨应用的统一链接 | 统一链接,用户体验好 |
| startAbility | 需要传递复杂参数的应用间跳转 | 参数传递灵活,功能强大 |
| Web 拦截跳转 | Web 页面中的应用内跳转 | 无缝集成 Web 和原生页面 |
5.2 设计原则
- 简洁明了:链接地址应该简洁易记,避免复杂的参数
- 一致性:同一功能的链接在不同场景下应该保持一致
- 可测试性:链接应该易于测试和调试
- 可扩展性:链接设计应该考虑未来功能扩展的需要
5.3 性能优化
- 减少参数大小:避免在链接中传递过大的参数
- 异步处理:链接处理逻辑应该异步执行,避免阻塞主线程
- 缓存机制:对于频繁访问的链接,可以考虑使用缓存
结语
应用间链接是 HarmonyOS 应用开发中的重要技术,可以显著提升应用间的交互体验。本文介绍了三种主要的应用间链接方式:App Linking、startAbility 和 Web 拦截跳转,并提供了详细的实现代码和最佳实践。
希望本文的内容能够对你有所帮助,祝你在鸿蒙开发之路上越走越远!
参考文档: