前言
上篇文章Paimon源码解读 -- Compaction-1.MergeTreeCompactTask解析了Paimon-Compaction阶段的大概流程,而最后发现,真正去将文件采用特点算法合并的类是KeyValueFileWriterFactory中createRollingMergeTreeFileWriter()和createRollingChangelogFileWriter()创建的---RollingFileWriter
一.KeyValueFileWriterFactory中的两个核心调用方法
1.createRollingMergeTreeFileWriter()和createRollingChangelogFileWriter()
(1) 俩方法代码
java
public RollingFileWriter<KeyValue, DataFileMeta> createRollingMergeTreeFileWriter(
int level, FileSource fileSource) {
// 创建RollingFileWriter,后续由其进行写入合并操作
return new RollingFileWriter<>(
() ->
createDataFileWriter(
formatContext.pathFactory(level).newPath(),
level,
fileSource), // 创建SingleFileWriter写入器,这里的参数是懒加载Supplier包装的
suggestedFileSize // 这里suggestedFileSize其实就是配置的target-file-size大小
);
}
public RollingFileWriter<KeyValue, DataFileMeta> createRollingChangelogFileWriter(int level) {
return new RollingFileWriter<>(
() ->
createDataFileWriter(
formatContext.pathFactory(level).newChangelogPath(), // 和上面的createRollingMergeTreeFileWriter()的参数不同
level,
FileSource.APPEND),
suggestedFileSize);
}(2) 调用的createDataFileWriter()
作用:开启瘦模式(配置'data-file.thin-mode'绑定,默认是false),采用KeyValueThinDataFileWriterImpl;否则,都是普通模式,采用KeyValueDataFileWriterImpl
java
private KeyValueDataFileWriter createDataFileWriter(
Path path, int level, FileSource fileSource) {
return formatContext.thinModeEnabled() // 是否开启瘦模式,通过配置'data-file.thin-mode'绑定,默认是false
? new KeyValueThinDataFileWriterImpl( // 瘦模式:仅存储增量变更更数据
fileIO,
formatContext.writerFactory(level),
path,
new KeyValueThinSerializer(keyType, valueType)::toRow,
keyType,
valueType,
formatContext.extractor(level),
schemaId,
level,
formatContext.compression(level),
options,
fileSource,
fileIndexOptions)
: new KeyValueDataFileWriterImpl( // 普通模式:存储完整数据,全量写入/覆盖
fileIO,
formatContext.writerFactory(level),
path,
new KeyValueSerializer(keyType, valueType)::toRow,
keyType,
valueType,
formatContext.extractor(level),
schemaId,
level,
formatContext.compression(level),
options,
fileSource,
fileIndexOptions);
}2.涉及的SingleFileWriter类
整体的情况如下 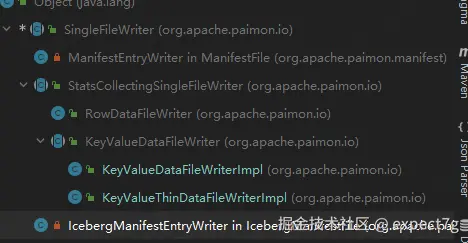
(1) SingleFileWriter类 -- 核心1
<1> 属性和构造函数
java
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SingleFileWriter.class);
protected final FileIO fileIO; // 抽象文件IO接口
protected final Path path; // 路径
private final Function<T, InternalRow> converter; // 类型转换器,将原始kv记录转为Paimon内部行的InternalRow类型
private FormatWriter writer; // 写入器
private PositionOutputStream out; // 文件输出流
private long recordCount; // 写入的记录数
protected boolean closed; // 是否关闭写入器
public SingleFileWriter(
FileIO fileIO,
FormatWriterFactory factory,
Path path,
Function<T, InternalRow> converter,
String compression,
boolean asyncWrite) {
this.fileIO = fileIO;
this.path = path;
this.converter = converter;
try {
// 1.创建文件输出流,异步或者同步
out = fileIO.newOutputStream(path, false); // false说明不是overwrite覆盖操作,而是into操作
if (asyncWrite) {
out = new AsyncPositionOutputStream(out);
}
// 步骤2:创建具体格式的写入器(如ParquetWriter)
writer = factory.create(out, compression);
} catch (IOException e) {
LOG.warn(
"Failed to open the bulk writer, closing the output stream and throw the error.",
e);
if (out != null) {
abort();
}
throw new UncheckedIOException(e);
}
// 3.初始化记录数和closed
this.recordCount = 0;
this.closed = false;
}<2> write()和writeBundle()
写入的核心逻辑如下
- 将record转为Paimon内部行类型
InternalRow - 调用写入器去将转后的数据写入
- 记录写入数据量
- 流式返回转换后的数据供子类统计收集;批式什么也不返回
java
// 流式写入
@Override
public void write(T record) throws IOException {
// 调writeImpl去写入数据
writeImpl(record);
}
// 批量写入
public void writeBundle(BundleRecords bundle) throws IOException {
if (closed) {
throw new RuntimeException("Writer has already closed!");
}
try {
// CASE-1: 写入器 instanceof BundleFormatWriter
if (writer instanceof BundleFormatWriter) {
((BundleFormatWriter) writer).writeBundle(bundle); // 调批量写入器的writeBundle()方法去写入
}
// CASE-2: 写入器不是BundleFormatWriter实现类
else {
// 遍历批,进行一条一条write
for (InternalRow row : bundle) {
writer.addElement(row);
}
}
// 记录批量写入数据
recordCount += bundle.rowCount();
} catch (Throwable e) {
LOG.warn("Exception occurs when writing file " + path + ". Cleaning up.", e);
abort();
throw e;
}
}
// 核心写入逻辑
protected InternalRow writeImpl(T record) throws IOException {
if (closed) {
throw new RuntimeException("Writer has already closed!");
}
try {
// 1.将record转为Paimon内部行类型InternalRow
InternalRow rowData = converter.apply(record);
// 2.调用写入器(如ParquetWriter)去将rowData写入
writer.addElement(rowData);
// 3.写入记录数++
recordCount++;
// 4.返回转换后的行数据(供子类统计收集使用)
return rowData;
} catch (Throwable e) {
LOG.warn("Exception occurs when writing file " + path + ". Cleaning up.", e);
abort();
throw e;
}
}<3> recordCount()和reachTargetSize()
java
// 返回已记录的写入总数
@Override
public long recordCount() {
return recordCount;
}
// 文件滚动的标记,后续由RollingFileWriter去调用
public boolean reachTargetSize(boolean suggestedCheck, long targetSize) throws IOException {
// 检查已写入的文件是否达到了目标文件大小target-file-size
return writer.reachTargetSize(suggestedCheck, targetSize);
}<4> abort()
java
// 中止写入,并清理资源和文件
@Override
public void abort() {
// 关闭写入器
if (writer != null) {
IOUtils.closeQuietly(writer);
writer = null;
}
// 关闭输出流
if (out != null) {
IOUtils.closeQuietly(out);
out = null;
}
// 删除该path路径下写入的文件
fileIO.deleteQuietly(path);
}(2) StatsCollectingSingleFileWriter类
<1> 属性和构造函数
java
@Nullable private final SimpleStatsExtractor simpleStatsExtractor; // 批量写入场景下,从文件中提取的字段统计信息
@Nullable private SimpleStatsCollector simpleStatsCollector = null; // 流式写入场景下,实时收集的字段统计信息
@Nullable private SimpleColStats[] noneStats = null; // 禁用统计时的默认值,数组中每个元素都是SimpleColStats.NONE
private final boolean isStatsDisabled; // 是否禁用统计收集,若所有字段的统计收集器都是NoneSimpleColStatsCollector,则为 true
public StatsCollectingSingleFileWriter(
FileIO fileIO,
FormatWriterFactory factory,
Path path,
Function<T, InternalRow> converter,
RowType writeSchema,
@Nullable SimpleStatsExtractor simpleStatsExtractor,
String compression,
SimpleColStatsCollector.Factory[] statsCollectors,
boolean asyncWrite) {
// 1.调用父类SingleFileWriter的构造函数
super(fileIO, factory, path, converter, compression, asyncWrite);
// 2.初始化
this.simpleStatsExtractor = simpleStatsExtractor;
if (this.simpleStatsExtractor == null) {
this.simpleStatsCollector = new SimpleStatsCollector(writeSchema, statsCollectors);
}
Preconditions.checkArgument(
statsCollectors.length == writeSchema.getFieldCount(),
"The stats collector is not aligned to write schema.");
this.isStatsDisabled =
Arrays.stream(SimpleColStatsCollector.create(statsCollectors))
.allMatch(p -> p instanceof NoneSimpleColStatsCollector);
if (isStatsDisabled) {
this.noneStats =
IntStream.range(0, statsCollectors.length)
.mapToObj(i -> SimpleColStats.NONE)
.toArray(SimpleColStats[]::new);
}
}<2> write()和writeBundle()
java
@Override
public void write(T record) throws IOException {
// 步1.调用父类SingleFileWriter.writeImpl(),将记录序列化并写入文件中,返回序列化后的InternalRow
InternalRow rowData = writeImpl(record);
// 步2.若开启实时统计,则调用SimpleStatsCollector.collect()收集当前记录的字段统计
if (simpleStatsCollector != null && !simpleStatsCollector.isDisabled()) {
simpleStatsCollector.collect(rowData);
}
}
@Override
public void writeBundle(BundleRecords bundle) throws IOException {
Preconditions.checkState(
simpleStatsExtractor != null,
"Can't write bundle without simpleStatsExtractor, we may lose all the statistical information");
// 调用父类SingleFileWriter批量写入逻辑(不实时收集统计,后续从文件提取)
super.writeBundle(bundle);
}<3> fieldStats()
java
// 提取最终的字段统计信息
public SimpleColStats[] fieldStats() throws IOException {
Preconditions.checkState(closed, "Cannot access metric unless the writer is closed.");
// CASE-1: 批量写入场景,从文件中提取
if (simpleStatsExtractor != null) {
if (isStatsDisabled) {
return noneStats;
} else {
return simpleStatsExtractor.extract(fileIO, path);
}
}
// CASE-2: 单条写入场景,从SimpleStatsCollector实时收集器中提取
else {
return simpleStatsCollector.extract();
}
}(3) KeyValueDataFileWriter类 -- 核心2
<1> 相关属性
java
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(KeyValueDataFileWriter.class);
// 公共状态属性
protected final RowType keyType;
protected final RowType valueType;
private final long schemaId; // Schema版本ID
private final int level; // 文件所属level层级
// 统计信息相关
private final SimpleStatsConverter keyStatsConverter; // Key统计信息转换器(将 SimpleColStats 转为二进制存储的 SimpleStats)
private final SimpleStatsConverter valueStatsConverter; // Value统计信息转换器(将 SimpleColStats 转为二进制存储的 SimpleStats)
private final InternalRowSerializer keySerializer;
private final FileSource fileSource;
@Nullable private final DataFileIndexWriter dataFileIndexWriter; // 文件索引写入器(生成布隆过滤器 / 区间索引,优化查询性能)
// 用于查询时,快速过滤
private BinaryRow minKey = null; // 写入文件的最小主键
private InternalRow maxKey = null; // 写入文件的最大主
private long minSeqNumber = Long.MAX_VALUE; // 写入文件最小sequenceNumber
private long maxSeqNumber = Long.MIN_VALUE; // 写入文件最大sequenceNumber
private long deleteRecordCount = 0; // 写入文件删除记录数<2> 构造函数
java
public KeyValueDataFileWriter(
FileIO fileIO,
FormatWriterFactory factory,
Path path,
Function<KeyValue, InternalRow> converter,
RowType keyType,
RowType valueType,
RowType writeRowType,
@Nullable SimpleStatsExtractor simpleStatsExtractor,
long schemaId,
int level,
String compression,
CoreOptions options,
FileSource fileSource,
FileIndexOptions fileIndexOptions) {
// 1.调用父类StatsCollectingSingleFileWriter的构造函数
super(
fileIO,
factory,
path,
converter,
writeRowType,
simpleStatsExtractor,
compression,
StatsCollectorFactories.createStatsFactories(
options, writeRowType.getFieldNames(), keyType.getFieldNames()),
options.asyncFileWrite());
// 2.初始化公共状态属性
this.keyType = keyType;
this.valueType = valueType;
this.schemaId = schemaId;
this.level = level;
// 3.初始化统计信息相关属性
this.keyStatsConverter = new SimpleStatsConverter(keyType);
this.valueStatsConverter = new SimpleStatsConverter(valueType, options.statsDenseStore());
this.keySerializer = new InternalRowSerializer(keyType);
this.fileSource = fileSource;
this.dataFileIndexWriter =
DataFileIndexWriter.create(
fileIO, dataFileToFileIndexPath(path), valueType, fileIndexOptions);
}<3> write()
java
@Override
public void write(KeyValue kv) throws IOException {
// 步骤1.调父类StatsCollectingSingleFileWriter.write(),将kv数据序列化写入Data File中
super.write(kv);
// 步骤2:写入文件索引(如布隆过滤器,优化点查性能)
if (dataFileIndexWriter != null) {
dataFileIndexWriter.write(kv.value());
}
// 步骤3:更新min/max key(要求写入记录已排序,否则minKey仅取第一条,maxKey取最后一条)
updateMinKey(kv);
updateMaxKey(kv);
// 步骤4:更新最小/最大序列号(处理乱序更新)
updateMinSeqNumber(kv);
updateMaxSeqNumber(kv);
// 步骤5:统计删除记录数(Retract类型为删除)
if (kv.valueKind().isRetract()) {
deleteRecordCount++;
}
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("Write to Path " + path + " key value " + kv.toString(keyType, valueType));
}
}
private void updateMinKey(KeyValue kv) {
if (minKey == null) {
minKey = keySerializer.toBinaryRow(kv.key()).copy();
}
}
private void updateMaxKey(KeyValue kv) {
maxKey = kv.key();
}
private void updateMinSeqNumber(KeyValue kv) {
minSeqNumber = Math.min(minSeqNumber, kv.sequenceNumber());
}
private void updateMaxSeqNumber(KeyValue kv) {
maxSeqNumber = Math.max(maxSeqNumber, kv.sequenceNumber());
}<4> result()
java
// 生成文件元数据
@Override
@Nullable
public DataFileMeta result() throws IOException {
if (recordCount() == 0) {
return null;
}
// 1.调用子类实现的fetchKeyValueStats,获取key和value的全部统计信息
Pair<SimpleColStats[], SimpleColStats[]> keyValueStats = fetchKeyValueStats(fieldStats());
// 2.将key和value的统计信息转换成二进制存储的SimpleStats
SimpleStats keyStats = keyStatsConverter.toBinaryAllMode(keyValueStats.getKey());
Pair<List<String>, SimpleStats> valueStatsPair =
valueStatsConverter.toBinary(keyValueStats.getValue());
// 3.生成文件索引结构
DataFileIndexWriter.FileIndexResult indexResult =
dataFileIndexWriter == null
? DataFileIndexWriter.EMPTY_RESULT
: dataFileIndexWriter.result();
// 4.构造DataFileMeta元数据信息
return new DataFileMeta(
path.getName(),
fileIO.getFileSize(path),
recordCount(),
minKey,
keySerializer.toBinaryRow(maxKey).copy(),
keyStats,
valueStatsPair.getValue(),
minSeqNumber,
maxSeqNumber,
schemaId,
level,
indexResult.independentIndexFile() == null
? Collections.emptyList()
: Collections.singletonList(indexResult.independentIndexFile()),
deleteRecordCount,
indexResult.embeddedIndexBytes(),
fileSource,
valueStatsPair.getKey(),
null);
}(4) KeyValueThinDataFileWriterImpl类 -- 瘦模式DF写入器
采用瘦模式(配置'data-file.thin-mode'绑定,默认是false),Data File只包含_SEQUENCE_NUMBER_和_ROW_KIND_和value字段,不存储key字段
<1> 构造函数
步骤如下:
- 父类构造调用
- 构建所有字段ID->字段索引的映射,放入idToIndexs的Map中,结构为:
[字段1->索引3, 字段2->索引7, ...] - 获取key字段索引在idToIndex中对应的字段索引,放入keyStatMapping数组中,结构为:
[key字段1:索引1, key字段2:索引3, ...]
注意:主键字段ID = 主键key的映射ID - SpecialFields.KEY_FIELD_ID_START,其实就是主键key的映射ID - Integer.MAX_VALUE / 2,why?因为底层Key的映射id为ID = 1073741823 + (field-id),因此,需要减去1073741823(也就是Integer.MAX_VALUE / 2)
java
public KeyValueThinDataFileWriterImpl(
FileIO fileIO,
FormatWriterFactory factory,
Path path,
Function<KeyValue, InternalRow> converter,
RowType keyType,
RowType valueType,
@Nullable SimpleStatsExtractor simpleStatsExtractor,
long schemaId,
int level,
String compression,
CoreOptions options,
FileSource fileSource,
FileIndexOptions fileIndexOptions) {
super(
fileIO,
factory,
path,
converter,
keyType,
valueType,
KeyValue.schema(RowType.of(), valueType), // 不传入key的schema,只传入value的schema
simpleStatsExtractor,
schemaId,
level,
compression,
options,
fileSource,
fileIndexOptions); // 父类构造调用
// 步1.构建所有字段ID->字段索引的映射,放入idToIndex
Map<Integer, Integer> idToIndex = new HashMap<>(valueType.getFieldCount());
for (int i = 0; i < valueType.getFieldCount(); i++) {
idToIndex.put(valueType.getFields().get(i).id(), i);
}
// 步2.获取key字段索引在idToIndex中对应的字段索引,放入keyStatMapping数组中
this.keyStatMapping = new int[keyType.getFieldCount()];
for (int i = 0; i < keyType.getFieldCount(); i++) {
keyStatMapping[i] =
idToIndex.get(
// 注意:主键字段ID = 主键key的映射ID - SpecialFields.KEY_FIELD_ID_START,其实就是主键key的映射ID - Integer.MAX_VALUE / 2,why?
// 因为底层Key的映射id为ID = 1073741823 + (field-id),因此需要减去1073741823(也就是Integer.MAX_VALUE / 2)
keyType.getFields().get(i).id() - SpecialFields.KEY_FIELD_ID_START);
}
}<2> fetchKeyValueStats() -- 提取key和value的统计信息
瘦模式下rowStats结构:[0:_SEQUENCE_NUMBER_, 1:_ROW_KIND_, 2:value字段1, 3:value字段2, ...]
因此,数组需要从第3个位置开始截断,最后的结构:[0:value字段1, 1:value字段2, ...] 然后根据构造函数获取的keyStatMapping中存储的key字段对应的索引位置,去获取key的值,形成keyStats,最后包装成Pair.of(keyStats, valFieldStats)返回
java
/**
* 获取key和value的统计信息
* @param rowStats
* @return
*/
@Override
Pair<SimpleColStats[], SimpleColStats[]> fetchKeyValueStats(SimpleColStats[] rowStats) {
int numKeyFields = keyType.getFieldCount();
// 步骤1:截取value字段的统计信息(跳过前2个:_SEQUENCE_NUMBER_、_ROW_KIND_)
// 瘦模式下rowStats结构:[0:_SEQUENCE_NUMBER_, 1:_ROW_KIND_, 2:value字段1, 3:value字段2, ...]
SimpleColStats[] valFieldStats = Arrays.copyOfRange(rowStats, 2, rowStats.length);
// 最后valFieldStats的结构:[0:value字段1, 1:value字段2, ...]
// 步骤2:从value统计中映射出key统计(核心:使用keyStatMapping)
SimpleColStats[] keyStats = new SimpleColStats[numKeyFields];
for (int i = 0; i < keyStatMapping.length; i++) {
// keyStatMapping[i]是构造函数阶段构造好的key字段对应的索引位置,从valFieldStats中取对应统计
// 比如keyStatMapping中存的索引是[1,3,4,2],那么就去valFieldStats数据中,取[1,3,4,2]这几个位置的值,然后合成keyStats
keyStats[i] = valFieldStats[keyStatMapping[i]];
}
return Pair.of(keyStats, valFieldStats); // 返回key统计和value统计,对于瘦模式来说,全部都是value,因此valFieldStats原封不动,不需要把key的移除
}(5) KeyValueDataFileWriterImpl类 -- 普通模式DF写入器
java
public class KeyValueDataFileWriterImpl extends KeyValueDataFileWriter {
public KeyValueDataFileWriterImpl(
FileIO fileIO,
FormatWriterFactory factory,
Path path,
Function<KeyValue, InternalRow> converter,
RowType keyType,
RowType valueType,
@Nullable SimpleStatsExtractor simpleStatsExtractor,
long schemaId,
int level,
String compression,
CoreOptions options,
FileSource fileSource,
FileIndexOptions fileIndexOptions) {
super(
fileIO,
factory,
path,
converter,
keyType,
valueType,
KeyValue.schema(keyType, valueType), // 传入完整的schema(key+value)
simpleStatsExtractor,
schemaId,
level,
compression,
options,
fileSource,
fileIndexOptions);
}
@Override
Pair<SimpleColStats[], SimpleColStats[]> fetchKeyValueStats(SimpleColStats[] rowStats) {
// 步骤1:获取主键字段数量
int numKeyFields = keyType.getFieldCount();
// 步骤2:拆分统计信息并返回
return Pair.of(
// 主键统计:截取rowStats前numKeyFields个(0 ~ numKeyFields-1)
Arrays.copyOfRange(rowStats, 0, numKeyFields),
// 值统计:跳过主键+2个系统字段(_SEQUENCE_NUMBER_、_ROW_KIND_),截取剩余部分
Arrays.copyOfRange(rowStats, numKeyFields + 2, rowStats.length ));
}二.总结
-
数据写入流程: 类
SingleFileWriter的write()实现的- 将record数据转为Paimon内部识别的行类型
InternalRow - 调用写入器(如
ParquetWriter)将转化后的数据写入 - 记录写入数
- 流式写入,返回
InternalRow的数据;批式写入,不返回这些
批量写入注意:
- 若写入器不是批量写入器,则遍历批,去一个一个写入
- 若写入器是批量写入器,则直接调其
writeBundle()去批量写入
- 子类
KeyValueDataFileWriter会继续记录写入的文件索引、更新min和max的主键、更新min和max的sequnceNumber、统计回撤数
- 将record数据转为Paimon内部识别的行类型
-
生成
DataFileMeta:类KeyValueDataFileWriter及其子类实现的- 调用子类实现的
fetchKeyValueStats():获取Key和Value的统计信息 - 将Key和Value的统计信息转为二进制存储
SimpleStats - 生成文件索引结构
- 构造
DataFileMeta元数据信息
- 调用子类实现的
-
瘦模式补充:
配置'data-file.thin-mode'绑定,默认是false,该模式下Data File只包含_SEQUENCE_NUMBER_和_ROW_KIND_和value字段,不存储key字段- 构造函数阶段:
- 调父类构造函数
- 构建所有字段的ID和索引映射map,放入idToIndexs 中,结构为:
[字段1->索引2, 字段2->索引1, 字段3->索引3, ...] - 获取Key字段索引,放入数组keyStatMapping 中,结构为:
[key字段1:索引1, key字段2:索引3, ...]
fetchKeyValueStats():瘦模式下rowStats结构为:[0:_SEQUENCE_NUMBER_, 1:_ROW_KIND_, 2:value字段1, 3:value字段2, ...]- 将rowStats从第三个位置开始阶段,最终结构为:
[0:value字段1, 1:value字段2, ...] - 根据keyStatMapping中存储的key字段对应的索引位置,去获取key的值给keyStats
- 最后包装成
Pair.of(keyStats, valFieldStats)返回
- 将rowStats从第三个位置开始阶段,最终结构为:
- 构造函数阶段: