【算法介绍】
基于YOLOv11的阿尔兹海默症严重程度检测系统是一种创新的医疗辅助工具,旨在通过先进的计算机视觉技术提高阿尔兹海默症的早期诊断和病情监测效率。阿尔兹海默症是一种渐进性的神经退行性疾病,通常表现为认知障碍、记忆丧失和语言障碍等症状,早期诊断对于控制疾病发展至关重要。
该系统利用YOLOv11模型,这是一种在目标检测领域具有卓越性能的深度学习模型。通过对医学影像(如MRI或CT扫描)的分析,YOLOv11能够准确提取出与阿尔兹海默症相关的有价值特征。这些特征不仅可以帮助医生快速识别阿尔兹海默症的早期病变,还能够追踪病变区域的变化,从而监测病情的进展。
此外,基于YOLOv11的系统还能够提供个性化的病情分析。由于阿尔兹海默症患者的病变特征和进展速度可能因人而异,该系统能够为每位患者提供独特的影像特征分析,进而辅助医生制定更加精准和有效的治疗方案。
总之,基于YOLOv11的阿尔兹海默症严重程度检测系统为医生提供了一种高效、准确的辅助诊断工具,有望改善阿尔兹海默症患者的诊断体验和治疗效果。
【效果展示】
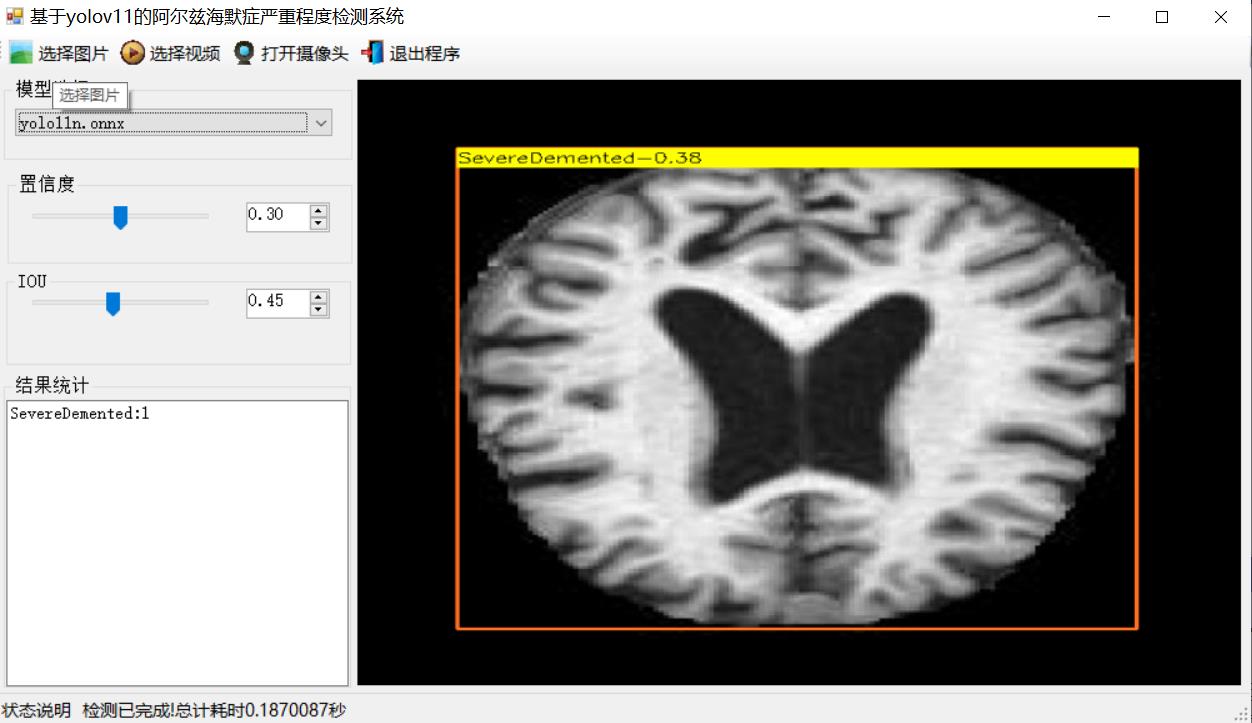
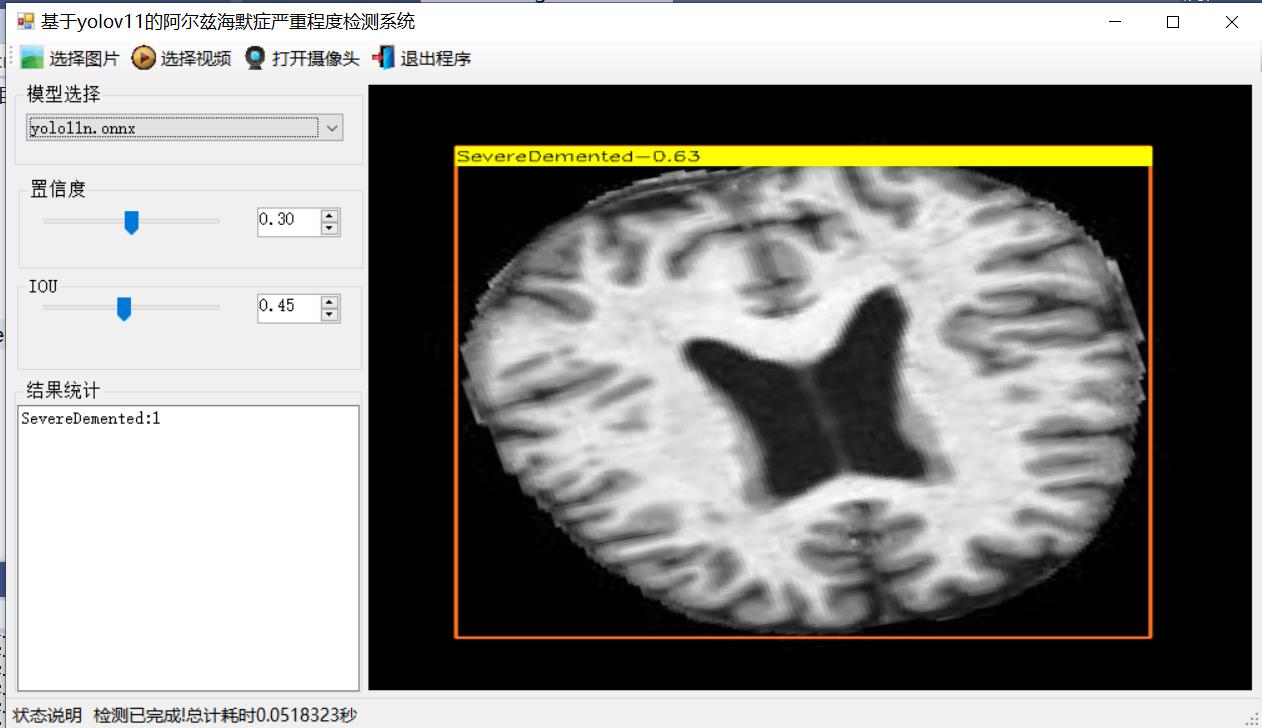
【测试环境】
windows10 x64系统
VS2019
netframework4.7.2
opencvsharp4.9.0
onnxruntime1.22.0
【模型可以检测出类别】
ModerateDemented
MildDemented
SevereDemented
NonDemented
VeryMildDemented
【训练数据集介绍】
超声波图像阿尔兹海默症严重程度检测数据集VOC+YOLO格式3288张5类别-CSDN博客
【训练信息】
|-----------------|-------|
| 参数 | 值 |
| 训练集图片数 | 2959 |
| 验证集图片数 | 329 |
| 训练map | 99.4% |
| 训练精度(Precision) | 97.6% |
| 训练召回率(Recall) | 98.1% |
验证集测试精度信息
|------------------|--------|-----------|-------|-------|-------|----------|
| Class | Images | Instances | P | R | mAP50 | mAP50-95 |
| all | 329 | 329 | 0.976 | 0.981 | 0.994 | 0.994 |
| ModerateDemented | 86 | 86 | 1 | 0.987 | 0.995 | 0.995 |
| MildDemented | 77 | 77 | 0.93 | 1 | 0.992 | 0.992 |
| SevereDemented | 52 | 52 | 0.989 | 0.962 | 0.994 | 0.994 |
| NonDemented | 56 | 56 | 1 | 0.959 | 0.993 | 0.993 |
| VeryMildDemented | 58 | 58 | 0.96 | 1 | 0.995 | 0.995 |
【界面设计】
using DeploySharp.Data;
using OpenCvSharp;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Drawing;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace FIRC
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public bool videoStart = false;//视频停止标志
string weightsPath = Application.StartupPath + "\\weights";//模型目录
YoloDetector detetor = new YoloDetector();//推理引擎
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
CheckForIllegalCrossThreadCalls = false;//线程更新控件不报错
}
private void LoadWeightsFromDir()
{
var di = new DirectoryInfo(weightsPath);
foreach(var fi in di.GetFiles("*.onnx"))
{
comboBox1.Items.Add(fi.Name);
}
if(comboBox1.Items.Count>0)
{
comboBox1.SelectedIndex = 0;
}
else
{
tssl_show.Text = "未找到模型,请关闭程序,放入模型到weights文件夹!";
tsb_pic.Enabled = false;
tsb_video.Enabled = false;
tsb_camera.Enabled = false;
}
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
LoadWeightsFromDir();//从目录加载模型
}
public string GetResultString(DetResult[] result)
{
Dictionary<string, int> resultDict = new Dictionary<string, int>();
for (int i = 0; i < result.Length; i++)
{
if(resultDict.ContainsKey( result[i].Category) )
{
resultDict[result[i].Category]++;
}
else
{
resultDict[result[i].Category] =1;
}
}
var resultStr = "";
foreach(var item in resultDict)
{
resultStr += string.Format("{0}:{1}\r\n",item.Key,item.Value);
}
return resultStr;
}
private void tsb_pic_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
OpenFileDialog ofd = new OpenFileDialog();
ofd.Filter = "*.*|*.bmp;*.jpg;*.jpeg;*.tiff;*.tiff;*.png";
if (ofd.ShowDialog() != DialogResult.OK) return;
tssl_show.Text = "正在检测中...";
Task.Run(() => {
var sw = new Stopwatch();
sw.Start();
Mat image = Cv2.ImRead(ofd.FileName);
detetor.SetParams(Convert.ToSingle(numericUpDown1.Value), Convert.ToSingle(numericUpDown2.Value));
var results=detetor.Inference(image);
var resultImage = detetor.DrawImage(image, results);
sw.Stop();
pb_show.Image = OpenCvSharp.Extensions.BitmapConverter.ToBitmap(resultImage);
tb_res.Text = GetResultString(results);
tssl_show.Text = "检测已完成!总计耗时"+sw.Elapsed.TotalSeconds+"秒";
});
}
public void VideoProcess(string videoPath)
{
Task.Run(() => {
detetor.SetParams(Convert.ToSingle(numericUpDown1.Value), Convert.ToSingle(numericUpDown2.Value));
VideoCapture capture = new VideoCapture(videoPath);
if (!capture.IsOpened())
{
tssl_show.Text="视频打开失败!";
return;
}
Mat frame = new Mat();
var sw = new Stopwatch();
int fps = 0;
while (videoStart)
{
capture.Read(frame);
if (frame.Empty())
{
Console.WriteLine("data is empty!");
break;
}
sw.Start();
var results = detetor.Inference(frame);
var resultImg = detetor.DrawImage(frame,results);
sw.Stop();
fps = Convert.ToInt32(1 / sw.Elapsed.TotalSeconds);
sw.Reset();
Cv2.PutText(resultImg, "FPS=" + fps, new OpenCvSharp.Point(30, 30), HersheyFonts.HersheyComplex, 1.0, new Scalar(255, 0, 0), 3);
//显示结果
pb_show.Image = OpenCvSharp.Extensions.BitmapConverter.ToBitmap(resultImg);
tb_res.Text = GetResultString(results);
Thread.Sleep(5);
}
capture.Release();
pb_show.Image = null;
tssl_show.Text = "视频已停止!";
tsb_video.Text = "选择视频";
});
}
public void CameraProcess(int cameraIndex=0)
{
Task.Run(() => {
detetor.SetParams(Convert.ToSingle(numericUpDown1.Value), Convert.ToSingle(numericUpDown2.Value));
VideoCapture capture = new VideoCapture(cameraIndex);
if (!capture.IsOpened())
{
tssl_show.Text = "摄像头打开失败!";
return;
}
Mat frame = new Mat();
var sw = new Stopwatch();
int fps = 0;
while (videoStart)
{
capture.Read(frame);
if (frame.Empty())
{
Console.WriteLine("data is empty!");
break;
}
sw.Start();
var results = detetor.Inference(frame);
var resultImg = detetor.DrawImage(frame, results);
sw.Stop();
fps = Convert.ToInt32(1 / sw.Elapsed.TotalSeconds);
sw.Reset();
Cv2.PutText(resultImg, "FPS=" + fps, new OpenCvSharp.Point(30, 30), HersheyFonts.HersheyComplex, 1.0, new Scalar(255, 0, 0), 3);
//显示结果
pb_show.Image = OpenCvSharp.Extensions.BitmapConverter.ToBitmap(resultImg);
tb_res.Text = GetResultString(results);
Thread.Sleep(5);
}
capture.Release();
pb_show.Image = null;
tssl_show.Text = "摄像头已停止!";
tsb_camera.Text = "打开摄像头";
});
}
private void tsb_video_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if(tsb_video.Text=="选择视频")
{
OpenFileDialog ofd = new OpenFileDialog();
ofd.Filter = "视频文件(*.*)|*.mp4;*.avi";
if (ofd.ShowDialog() != DialogResult.OK) return;
videoStart = true;
VideoProcess(ofd.FileName);
tsb_video.Text = "停止";
tssl_show.Text = "视频正在检测中...";
}
else
{
videoStart = false;
}
}
private void tsb_camera_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (tsb_camera.Text == "打开摄像头")
{
videoStart = true;
CameraProcess(0);
tsb_camera.Text = "停止";
tssl_show.Text = "摄像头正在检测中...";
}
else
{
videoStart = false;
}
}
private void tsb_exit_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
videoStart = false;
this.Close();
}
private void trackBar1_Scroll(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
numericUpDown1.Value = Convert.ToDecimal(trackBar1.Value / 100.0f);
}
private void trackBar2_Scroll(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
numericUpDown2.Value = Convert.ToDecimal(trackBar2.Value / 100.0f);
}
private void numericUpDown1_ValueChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
trackBar1.Value = (int)(Convert.ToSingle(numericUpDown1.Value) * 100);
}
private void numericUpDown2_ValueChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
trackBar2.Value = (int)(Convert.ToSingle(numericUpDown2.Value) * 100);
}
private void comboBox1_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
tssl_show.Text="加载模型:"+comboBox1.Text;
detetor.LoadWeights(weightsPath+"\\"+comboBox1.Text);
tssl_show.Text = "模型加载已完成!";
}
}
}【训练步骤】
使用YOLO11训练自己的数据集需要遵循一些基本的步骤。YOLO11是YOLO系列模型的一个版本,它在前代基础上做了许多改进,包括但不限于更高效的训练流程和更高的精度。以下是训练自己YOLO格式数据集的详细步骤:
一、 准备环境
-
安装必要的软件:确保你的计算机上安装了Python(推荐3.6或更高版本),以及CUDA和cuDNN(如果你打算使用GPU进行加速)。
-
安装YOLO11库:你可以通过GitHub克隆YOLOv8的仓库或者直接通过pip安装YOLO11。例如:
pip install ultralytics
二、数据准备
- 组织数据结构:按照YOLO的要求组织你的数据文件夹。通常,你需要一个包含图像和标签文件的目录结构,如:
dataset/
├── images/
│ ├── train/
│ └── val/
├── labels/
│ ├── train/
│ └── val/
其中,train和val分别代表训练集和验证集。且images文件夹和labels文件夹名字不能随便改写或者写错,否则会在训练时候找不到数据集。
- 标注数据:使用合适的工具对图像进行标注,生成YOLO格式的标签文件。每个标签文件应该是一个.txt文件,每行表示一个边界框,格式为:
<类别ID> <中心点x> <中心点y> <宽度> <高度>
这些值都是相对于图像尺寸的归一化值。
- 创建数据配置文件:创建一个.yaml文件来定义你的数据集,包括路径、类别列表等信息。例如:
yaml
dataset.yaml
path: ./dataset # 数据集根目录
train: images/train # 训练图片相对路径
val: images/val # 验证图片相对路径
nc: 2 # 类别数
names: ['class1', 'class2'] # 类别名称
三、模型训练
-
加载预训练模型:可以使用官方提供的预训练模型作为起点,以加快训练速度并提高性能。
-
配置训练参数:根据需要调整训练参数,如批量大小、学习率、训练轮次等。这通常可以通过命令行参数或配置文件完成。
-
开始训练:使用YOLO11提供的命令行接口开始训练过程。例如:
yolo train data=dataset.yaml model=yolo11n.yaml epochs=100 imgsz=640
更多参数如下:
| 参数 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
model |
None |
Specifies the model file for training. Accepts a path to either a .pt pretrained model or a .yaml configuration file. Essential for defining the model structure or initializing weights. |
data |
None |
Path to the dataset configuration file (e.g., coco8.yaml). This file contains dataset-specific parameters, including paths to training and validation data , class names, and number of classes. |
epochs |
100 |
Total number of training epochs. Each epoch represents a full pass over the entire dataset. Adjusting this value can affect training duration and model performance. |
time |
None |
Maximum training time in hours. If set, this overrides the epochs argument, allowing training to automatically stop after the specified duration. Useful for time-constrained training scenarios. |
patience |
100 |
Number of epochs to wait without improvement in validation metrics before early stopping the training. Helps prevent overfitting by stopping training when performance plateaus. |
batch |
16 |
Batch size, with three modes: set as an integer (e.g., batch=16), auto mode for 60% GPU memory utilization (batch=-1), or auto mode with specified utilization fraction (batch=0.70). |
imgsz |
640 |
Target image size for training. All images are resized to this dimension before being fed into the model. Affects model accuracy and computational complexity. |
save |
True |
Enables saving of training checkpoints and final model weights. Useful for resuming training ormodel deployment. |
save_period |
-1 |
Frequency of saving model checkpoints, specified in epochs. A value of -1 disables this feature. Useful for saving interim models during long training sessions. |
cache |
False |
Enables caching of dataset images in memory (True/ram), on disk (disk), or disables it (False). Improves training speed by reducing disk I/O at the cost of increased memory usage. |
device |
None |
Specifies the computational device(s) for training: a single GPU (device=0), multiple GPUs (device=0,1), CPU (device=cpu), or MPS for Apple silicon (device=mps). |
workers |
8 |
Number of worker threads for data loading (per RANK if Multi-GPU training). Influences the speed of data preprocessing and feeding into the model, especially useful in multi-GPU setups. |
project |
None |
Name of the project directory where training outputs are saved. Allows for organized storage of different experiments. |
name |
None |
Name of the training run. Used for creating a subdirectory within the project folder, where training logs and outputs are stored. |
exist_ok |
False |
If True, allows overwriting of an existing project/name directory. Useful for iterative experimentation without needing to manually clear previous outputs. |
pretrained |
True |
Determines whether to start training from a pretrained model. Can be a boolean value or a string path to a specific model from which to load weights. Enhances training efficiency and model performance. |
optimizer |
'auto' |
Choice of optimizer for training. Options include SGD, Adam, AdamW, NAdam, RAdam, RMSProp etc., or auto for automatic selection based on model configuration. Affects convergence speed and stability. |
verbose |
False |
Enables verbose output during training, providing detailed logs and progress updates. Useful for debugging and closely monitoring the training process. |
seed |
0 |
Sets the random seed for training, ensuring reproducibility of results across runs with the same configurations. |
deterministic |
True |
Forces deterministic algorithm use, ensuring reproducibility but may affect performance and speed due to the restriction on non-deterministic algorithms. |
single_cls |
False |
Treats all classes in multi-class datasets as a single class during training. Useful for binary classification tasks or when focusing on object presence rather than classification. |
rect |
False |
Enables rectangular training, optimizing batch composition for minimal padding. Can improve efficiency and speed but may affect model accuracy. |
cos_lr |
False |
Utilizes a cosine learning rate scheduler, adjusting the learning rate following a cosine curve over epochs. Helps in managing learning rate for better convergence. |
close_mosaic |
10 |
Disables mosaic data augmentation in the last N epochs to stabilize training before completion. Setting to 0 disables this feature. |
resume |
False |
Resumes training from the last saved checkpoint. Automatically loads model weights, optimizer state, and epoch count, continuing training seamlessly. |
amp |
True |
Enables AutomaticMixed Precision (AMP) training, reducing memory usage and possibly speeding up training with minimal impact on accuracy. |
fraction |
1.0 |
Specifies the fraction of the dataset to use for training. Allows for training on a subset of the full dataset, useful for experiments or when resources are limited. |
profile |
False |
Enables profiling of ONNX and TensorRT speeds during training, useful for optimizing model deployment. |
freeze |
None |
Freezes the first N layers of the model or specified layers by index, reducing the number of trainable parameters. Useful for fine-tuning or transfer learning . |
lr0 |
0.01 |
Initial learning rate (i.e. SGD=1E-2, Adam=1E-3) . Adjusting this value is crucial for the optimization process, influencing how rapidly model weights are updated. |
lrf |
0.01 |
Final learning rate as a fraction of the initial rate = (lr0 * lrf), used in conjunction with schedulers to adjust the learning rate over time. |
momentum |
0.937 |
Momentum factor for SGD or beta1 for Adam optimizers, influencing the incorporation of past gradients in the current update. |
weight_decay |
0.0005 |
L2 regularization term, penalizing large weights to prevent overfitting. |
warmup_epochs |
3.0 |
Number of epochs for learning rate warmup, gradually increasing the learning rate from a low value to the initial learning rate to stabilize training early on. |
warmup_momentum |
0.8 |
Initial momentum for warmup phase, gradually adjusting to the set momentum over the warmup period. |
warmup_bias_lr |
0.1 |
Learning rate for bias parameters during the warmup phase, helping stabilize model training in the initial epochs. |
box |
7.5 |
Weight of the box loss component in the loss_function, influencing how much emphasis is placed on accurately predicting bouding box coordinates. |
cls |
0.5 |
Weight of the classification loss in the total loss function, affecting the importance of correct class prediction relative to other components. |
dfl |
1.5 |
Weight of the distribution focal loss, used in certain YOLO versions for fine-grained classification. |
pose |
12.0 |
Weight of the pose loss in models trained for pose estimation, influencing the emphasis on accurately predicting pose keypoints. |
kobj |
2.0 |
Weight of the keypoint objectness loss in pose estimation models, balancing detection confidence with pose accuracy. |
label_smoothing |
0.0 |
Applies label smoothing, softening hard labels to a mix of the target label and a uniform distribution over labels, can improve generalization. |
nbs |
64 |
Nominal batch size for normalization of loss. |
overlap_mask |
True |
Determines whether object masks should be merged into a single mask for training, or kept separate for each object. In case of overlap, the smaller mask is overlayed on top of the larger mask during merge. |
mask_ratio |
4 |
Downsample ratio for segmentation masks, affecting the resolution of masks used during training. |
dropout |
0.0 |
Dropout rate for regularization in classification tasks, preventing overfitting by randomly omitting units during training. |
val |
True |
Enables validation during training, allowing for periodic evaluation of model performance on a separate dataset. |
plots |
False |
Generates and saves plots of training and validation metrics, as well as prediction examples, providing visual insights into model performance and learning progression. |
这里,data参数指向你的数据配置文件,model参数指定使用的模型架构,epochs设置训练轮次,imgsz设置输入图像的大小。
四、监控与评估
-
监控训练过程:观察损失函数的变化,确保模型能够正常学习。
-
评估模型:训练完成后,在验证集上评估模型的性能,查看mAP(平均精确度均值)等指标。
-
调整超参数:如果模型的表现不佳,可能需要调整超参数,比如增加训练轮次、改变学习率等,并重新训练模型。
五、使用模型
- 导出模型:训练完成后,可以将模型导出为ONNX或其他格式,以便于部署到不同的平台。比如将pytorch转成onnx模型可以输入指令
yolo export model=best.pt format=onnx
这样就会在pt模块同目录下面多一个同名的onnx模型best.onnx
下表详细说明了可用于将YOLO模型导出为不同格式的配置和选项。这些设置对于优化导出模型的性能、大小和跨各种平台和环境的兼容性至关重要。正确的配置可确保模型已准备好以最佳效率部署在预期的应用程序中。
| 参数 | 类型 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
format |
str |
'torchscript' |
Target format for the exported model, such as 'onnx', 'torchscript', 'tensorflow', or others, defining compatibility with various deployment environments. |
imgsz |
int or tuple |
640 |
Desired image size for the model input. Can be an integer for square images or a tuple (height, width) for specific dimensions. |
keras |
bool |
False |
Enables export to Keras format for Tensorflow SavedModel, providing compatibility with TensorFlow serving and APIs. |
optimize |
bool |
False |
Applies optimization for mobile devices when exporting to TorchScript, potentially reducing model size and improving performance. |
half |
bool |
False |
Enables FP16 (half-precision) quantization, reducing model size and potentially speeding up inference on supported hardware. |
int8 |
bool |
False |
Activates INT8 quantization, further compressing the model and speeding up inference with minimal accuracy loss, primarily for edge devices. |
dynamic |
bool |
False |
Allows dynamic input sizes for ONNX, TensorRT and OpenVINO exports, enhancing flexibility in handling varying image dimensions. |
simplify |
bool |
True |
Simplifies the model graph for ONNX exports with onnxslim, potentially improving performance and compatibility. |
opset |
int |
None |
Specifies the ONNX opset version for compatibility with different ONNX parsers and runtimes. If not set, uses the latest supported version. |
workspace |
float |
4.0 |
Sets the maximum workspace size in GiB for TensorRT optimizations, balancing memory usage and performance. |
nms |
bool |
False |
Adds Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) to the CoreML export, essential for accurate and efficient detection post-processing. |
batch |
int |
1 |
Specifies export model batch inference size or the max number of images the exported model will process concurrently in predict mode. |
device |
str |
None |
Specifies the device for exporting: GPU (device=0), CPU (device=cpu), MPS for Apple silicon (device=mps) or DLA for NVIDIA Jetson (device=dla:0 or device=dla:1). |
调整这些参数可以定制导出过程,以满足特定要求,如部署环境、硬件约束和性能目标。选择适当的格式和设置对于实现模型大小、速度和精度之间的最佳平衡至关重要。
导出格式:
可用的YOLO11导出格式如下表所示。您可以使用format参数导出为任何格式,即format='onnx'或format='engine'。您可以直接在导出的模型上进行预测或验证,即yolo predict model=yolo11n.onnx。导出完成后,将显示您的模型的使用示例。
| 导出格式 | 格式参数 | 模型 | 属性 | 参数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pytorch | - | yolo11n.pt |
✅ | - |
| torchscript | torchscript |
yolo11n.torchscript |
✅ | imgsz, optimize, batch |
| onnx | onnx |
yolo11n.onnx |
✅ | imgsz, half, dynamic, simplify, opset, batch |
openvino |
openvino |
yolo11n_openvino_model/ |
✅ | imgsz, half, int8, batch |
| tensorrt | engine |
yolo11n.engine |
✅ | imgsz, half, dynamic, simplify, workspace, int8, batch |
| CoreML | coreml |
yolo11n.mlpackage |
✅ | imgsz, half, int8, nms, batch |
| TF SaveModel | saved_model |
yolo11n_saved_model/ |
✅ | imgsz, keras, int8, batch |
| TF GraphDef | pb |
yolo11n.pb |
❌ | imgsz, batch |
| TF Lite | tflite |
yolo11n.tflite |
✅ | imgsz, half, int8, batch |
| TF Edge TPU | edgetpu |
yolo11n_edgetpu.tflite |
✅ | imgsz |
| TF.js | tfjs |
yolo11n_web_model/ |
✅ | imgsz, half, int8, batch |
| PaddlePaddle | paddle |
yolo11n_paddle_model/ |
✅ | imgsz, batch |
| MNN | mnn |
yolo11n.mnn |
✅ | imgsz, batch, int8, half |
| NCNN | ncnn |
yolo11n_ncnn_model/ |
✅ | imgsz, half, batch |
- 测试模型:在新的数据上测试模型,确保其泛化能力良好。
以上就是使用YOLO11训练自己数据集的基本步骤。请根据实际情况调整这些步骤中的具体细节。希望这些信息对你有所帮助!
【常用评估参数介绍】
在目标检测任务中,评估模型的性能是至关重要的。你提到的几个术语是评估模型性能的常用指标。下面是对这些术语的详细解释:
- Class :
- 这通常指的是模型被设计用来检测的目标类别。例如,一个模型可能被训练来检测车辆、行人或动物等不同类别的对象。
- Images :
- 表示验证集中的图片数量。验证集是用来评估模型性能的数据集,与训练集分开,以确保评估结果的公正性。
- Instances :
- 在所有图片中目标对象的总数。这包括了所有类别对象的总和,例如,如果验证集包含100张图片,每张图片平均有5个目标对象,则Instances为500。
- P(精确度Precision) :
- 精确度是模型预测为正样本的实例中,真正为正样本的比例。计算公式为:Precision = TP / (TP + FP),其中TP表示真正例(True Positives),FP表示假正例(False Positives)。
- R(召回率Recall) :
- 召回率是所有真正的正样本中被模型正确预测为正样本的比例。计算公式为:Recall = TP / (TP + FN),其中FN表示假负例(False Negatives)。
- mAP50 :
- 表示在IoU(交并比)阈值为0.5时的平均精度(mean Average Precision)。IoU是衡量预测框和真实框重叠程度的指标。mAP是一个综合指标,考虑了精确度和召回率,用于评估模型在不同召回率水平上的性能。在IoU=0.5时,如果预测框与真实框的重叠程度达到或超过50%,则认为该预测是正确的。
- mAP50-95 :
- 表示在IoU从0.5到0.95(间隔0.05)的范围内,模型的平均精度。这是一个更严格的评估标准,要求预测框与真实框的重叠程度更高。在目标检测任务中,更高的IoU阈值意味着模型需要更准确地定位目标对象。mAP50-95的计算考虑了从宽松到严格的多个IoU阈值,因此能够更全面地评估模型的性能。
这些指标共同构成了评估目标检测模型性能的重要框架。通过比较不同模型在这些指标上的表现,可以判断哪个模型在实际应用中可能更有效。
【使用步骤】
使用步骤:
(1)首先根据官方框架ultralytics安装教程安装好yolov11环境,并根据官方export命令将自己pt模型转成onnx模型,然后去github仓库futureflsl/firc-csharp-projects找到源码
(2)使用vs2019打开sln项目,选择x64 release并且修改一些必要的参数,比如输入shape等,点击运行即可查看最后效果
特别注意如果运行报错了,请参考我的博文进行重新引用我源码的DLL:[C#]opencvsharp报错System.Memory,Version=4.0.1.2,Culture=neutral,PublicKeyToken=cc7b13fcd2ddd51"版本高于所引_未能加载文件或程序集"system.memory, version=4.0.1.2, culture-CSDN博客
【提供文件】
C#源码
yolo11n.onnx模型(不提供pytorch模型)
训练的map,P,R曲线图(在weights\results.png)
测试图片(在test_img文件夹下面)
特别注意这里不提供训练数据集