56.Linux V4L2虚拟摄像头驱动框架(不涉及硬件)
先从应用程序出发,逐渐剖析其驱动的编写规则:
学习完本教程,你将深刻理解V4L2的工作流程,和V4L2的驱动编写,并通过实际的开发实现读取三张模拟的图片作为摄像头的输入,通过V4L2进行获取视频流。
关键字:V4L2驱动框架、video_buffer2、VIDIOC_DQBUF、video_buffer2管理流程
V4L2摄像头应用程序
总结应用程序编写如下:
- open:打开设备节点/dev/videoX
- ioctl VIDIOC_QUERYCAP:Query Capbility,查询能力,比如
- 确认它是否是"捕获设备",因为有些节点是输出设备
- 确认它是否支持mmap操作,还是仅支持read/write操作
- ioctl VIDIOC_ENUM_FMT:枚举它支持的格式
- ioctl VIDIOC_S_FMT:在上面枚举出来的格式里,选择一个来设置格式
- ioctl VIDIOC_REQBUFS:申请buffer,APP可以申请很多个buffer,但是驱动程序不一定能申请到
- ioctl VIDIOC_QUERYBUF和mmap:查询buffer信息、映射
- 如果申请到了N个buffer,这个ioctl就应该执行N次
- 执行mmap后,APP就可以直接读写这些buffer
- ioctl VIDIOC_QBUF:把buffer放入"空闲链表"
- 如果申请到了N个buffer,这个ioctl就应该执行N次
- ioctl VIDIOC_STREAMON:启动摄像头
- 这里是一个循环:使用poll/select监测buffer,然后从"完成链表"中取出buffer,处理后再放入"空闲链表"
- poll/select
- ioctl VIDIOC_DQBUF:从"完成链表"中取出buffer
- 处理:前面使用mmap映射了每个buffer的地址,处理时就可以直接使用地址来访问buffer
- ioclt VIDIOC_QBUF:把buffer放入"空闲链表"
- ioctl VIDIOC_STREAMOFF:停止摄像头
c
struct v4l2_format fmt;
//初始化参数
memset(&fmt, 0, sizeof(struct v4l2_format));
fmt.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
fmt.fmt.pix.width = 1024;
fmt.fmt.pix.height = 768;
fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat = V4L2_PIX_FMT_MJPEG;
fmt.fmt.pix.field = V4L2_FIELD_ANY;
ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_S_FMT, &fmt);使用ioctl来操作驱动中具体的函数如VIDIOC_S_FMT函数,传入对应的参数如v4l2_format 结构体
就回去执行内核中的某个函数,实现对寄存器相关的控制
驱动编写人元可以通过写文档,规定VIDIOC_S_FMT宏是什么作用,传入什么参数...(这种方式十分麻烦)
或者通过规定的函数宏定义来完成编写,体现了分层的实现,如使用v4l2框架,该框架就已经把面向应用层的接口规定了,我们只需要去实现下一层的内容函数与具体硬件那层即可,不需要关注对应用层的接口定义。
c
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <linux/types.h> /* for videodev2.h */
#include <linux/videodev2.h>
#include <poll.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <pthread.h>
/* ./video_test </dev/video0> */
static void *thread_brightness_control (void *args)
{
int fd = (int)args;
unsigned char c;
int brightness;
int delta;
struct v4l2_queryctrl qctrl;
memset(&qctrl, 0, sizeof(qctrl));
qctrl.id = V4L2_CID_BRIGHTNESS; // V4L2_CID_BASE+0;
if (0 != ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QUERYCTRL, &qctrl))
{
printf("can not query brightness\n");
return NULL;
}
printf("brightness min = %d, max = %d\n", qctrl.minimum, qctrl.maximum);
delta = (qctrl.maximum - qctrl.minimum) / 10;
struct v4l2_control ctl;
ctl.id = V4L2_CID_BRIGHTNESS; // V4L2_CID_BASE+0;
ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_G_CTRL, &ctl);
while (1)
{
c = getchar();
if (c == 'u' || c == 'U')
{
ctl.value += delta;
}
else if (c == 'd' || c == 'D')
{
ctl.value -= delta;
}
if (ctl.value > qctrl.maximum)
ctl.value = qctrl.maximum;
if (ctl.value < qctrl.minimum)
ctl.value = qctrl.minimum;
ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_S_CTRL, &ctl);
}
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
struct v4l2_fmtdesc fmtdesc;
struct v4l2_frmsizeenum fsenum;
int fmt_index = 0;
int frame_index = 0;
int i;
void *bufs[32];
int buf_cnt;
int type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
struct pollfd fds[1];
char filename[32];
int file_cnt = 0;
if (argc != 2)
{
printf("Usage: %s </dev/videoX>, print format detail for video device\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* open */
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("can not open %s\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
/* 查询能力 */
struct v4l2_capability cap;
memset(&cap, 0, sizeof(struct v4l2_capability));
if (0 == ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QUERYCAP, &cap))
{
if((cap.capabilities & V4L2_CAP_VIDEO_CAPTURE) == 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error opening device %s: video capture not supported.\n",
argv[1]);
return -1;
}
if(!(cap.capabilities & V4L2_CAP_STREAMING)) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s does not support streaming i/o\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
}
else
{
printf("can not get capability\n");
return -1;
}
while (1)
{
/* 枚举格式 */
fmtdesc.index = fmt_index; // 比如从0开始
fmtdesc.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE; // 指定type为"捕获"
if (0 != ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_ENUM_FMT, &fmtdesc))
break;
frame_index = 0;
while (1)
{
/* 枚举这种格式所支持的帧大小 */
memset(&fsenum, 0, sizeof(struct v4l2_frmsizeenum));
fsenum.pixel_format = fmtdesc.pixelformat;
fsenum.index = frame_index;
if (ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_ENUM_FRAMESIZES, &fsenum) == 0)
{
printf("format %s,%d, framesize %d: %d x %d\n", fmtdesc.description, fmtdesc.pixelformat, frame_index, fsenum.discrete.width, fsenum.discrete.height);
}
else
{
break;
}
frame_index++;
}
fmt_index++;
}
/* 设置格式 */
struct v4l2_format fmt;
memset(&fmt, 0, sizeof(struct v4l2_format));
fmt.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
fmt.fmt.pix.width = 1024;
fmt.fmt.pix.height = 768;
fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat = V4L2_PIX_FMT_MJPEG;
fmt.fmt.pix.field = V4L2_FIELD_ANY;
if (0 == ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_S_FMT, &fmt))
{
printf("set format ok: %d x %d\n", fmt.fmt.pix.width, fmt.fmt.pix.height);
}
else
{
printf("can not set format\n");
return -1;
}
/*
* 申请buffer
*/
struct v4l2_requestbuffers rb;
memset(&rb, 0, sizeof(struct v4l2_requestbuffers));
rb.count = 32;
rb.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
rb.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
if (0 == ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_REQBUFS, &rb))
{
/* 申请成功后, mmap这些buffer */
buf_cnt = rb.count;
for(i = 0; i < rb.count; i++) {
struct v4l2_buffer buf;
memset(&buf, 0, sizeof(struct v4l2_buffer));
buf.index = i;
buf.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
buf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
if (0 == ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QUERYBUF, &buf))
{
/* mmap */
bufs[i] = mmap(0 /* start anywhere */ ,
buf.length, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd,
buf.m.offset);
if(bufs[i] == MAP_FAILED) {
perror("Unable to map buffer");
return -1;
}
}
else
{
printf("can not query buffer\n");
return -1;
}
}
printf("map %d buffers ok\n", buf_cnt);
}
else
{
printf("can not request buffers\n");
return -1;
}
/* 把所有buffer放入"空闲链表" */
for(i = 0; i < buf_cnt; ++i) {
struct v4l2_buffer buf;
memset(&buf, 0, sizeof(struct v4l2_buffer));
buf.index = i;
buf.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
buf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
if (0 != ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QBUF, &buf))
{
perror("Unable to queue buffer");
return -1;
}
}
printf("queue buffers ok\n");
/* 启动摄像头 */
if (0 != ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_STREAMON, &type))
{
perror("Unable to start capture");
return -1;
}
printf("start capture ok\n");
/* 创建线程用来控制亮度 */
pthread_t thread;
pthread_create(&thread, NULL, thread_brightness_control, (void *)fd);
while (1)
{
/* poll */
memset(fds, 0, sizeof(fds));
fds[0].fd = fd;
fds[0].events = POLLIN;
if (1 == poll(fds, 1, -1))
{
/* 把buffer取出队列 */
struct v4l2_buffer buf;
memset(&buf, 0, sizeof(struct v4l2_buffer));
buf.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
buf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
if (0 != ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_DQBUF, &buf))
{
perror("Unable to dequeue buffer");
return -1;
}
/* 把buffer的数据存为文件 */
sprintf(filename, "video_raw_data_%04d.jpg", file_cnt++);
int fd_file = open(filename, O_RDWR | O_CREAT, 0666);
if (fd_file < 0)
{
printf("can not create file : %s\n", filename);
}
printf("capture to %s\n", filename);
write(fd_file, bufs[buf.index], buf.bytesused);
close(fd_file);
/* 把buffer放入队列 */
if (0 != ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QBUF, &buf))
{
perror("Unable to queue buffer");
return -1;
}
}
}
if (0 != ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_STREAMOFF, &type))
{
perror("Unable to stop capture");
return -1;
}
printf("stop capture ok\n");
close(fd);
return 0;
}驱动框架V4L2
参考资料:
- 深入理解linux内核v4l2框架之videobuf2:https://blog.csdn.net/yyjsword/article/details/9243717
- V4L2框架-videobuf2:https://blog.csdn.net/u013904227/article/details/81054611
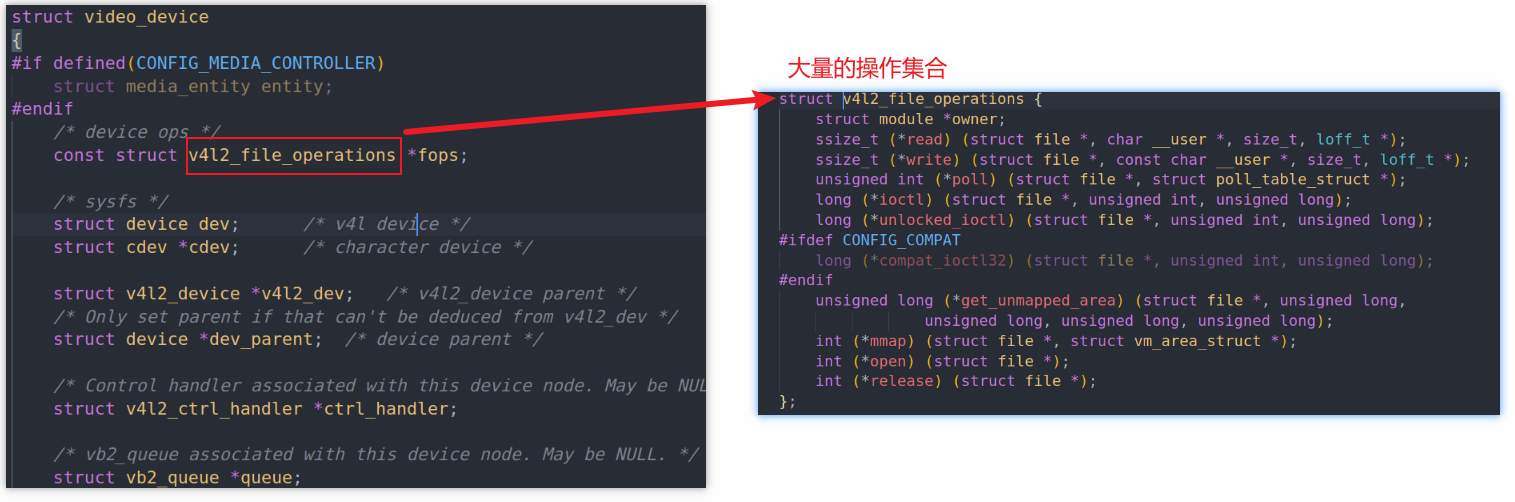
V4L2设备驱动程序的核心是:video_device结构体,它里面有2大成员
- v4l2_file_operations结构体:实现具体的open/read/write/ioctl/mmap操作
- v4l2_ioctl_ops结构体:v4l2_file_operations结构体一般使用video_ioctl2函数,它要调用v4l2_ioctl_ops结构体
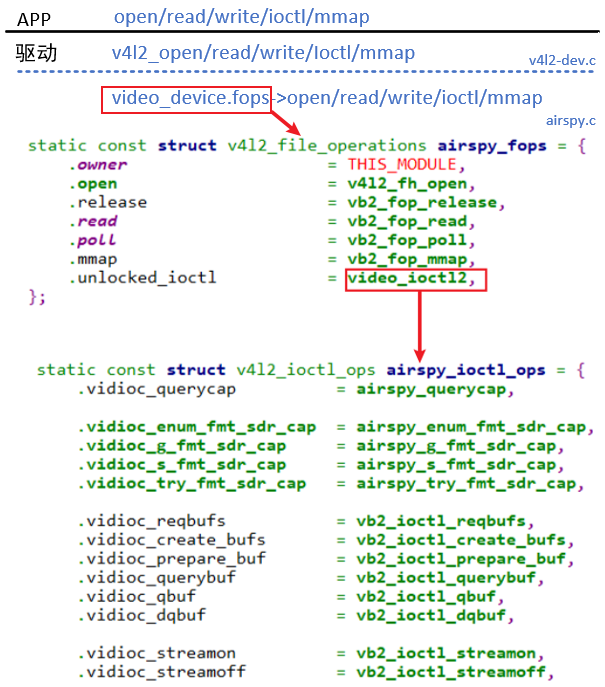
首先看看open函数
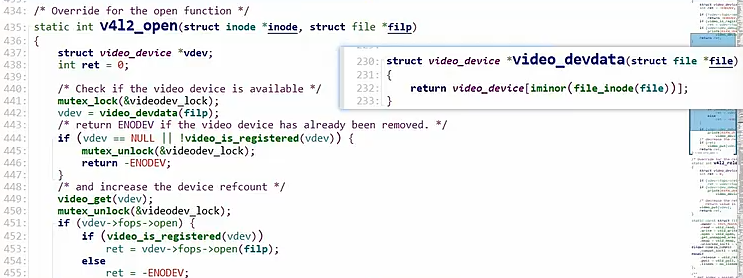
通过次设备号找到设备结构体,接着去执行下面的fop->open函数
read函数:
也是根据次设备号得到video_device,接着调用下面的read函数
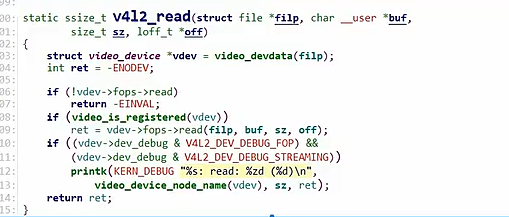
对于ioctl函数
可以看到已经写好的驱动框架最终都会调用我们需要实现的fops函数
video_device结构体

摄像头驱动就是围绕着video_device做工作,
总结:

应用程序使用规定的固定的ioctl来实现对摄像头的驱动
驱动程序就需要对某个ioctl实现具体的操作步骤,使这些ioctl来实现对应的功能。
V4L2实现了APP - 》 驱动 的中间层,接口层
APP open/write/read/relase
V4L2 | 提供标准接口
Driver 实现接口中的函数即可
接口层 (v4l2-dev.c)
从上往下看
v4l2-dev.c文件中(以open函数举例)
c
/* Override for the open function */
static int v4l2_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
struct video_device *vdev;
int ret = 0;
/* Check if the video device is available */
mutex_lock(&videodev_lock);
vdev = video_devdata(filp);
/* return ENODEV if the video device has already been removed. */
if (vdev == NULL || !video_is_registered(vdev)) {
mutex_unlock(&videodev_lock);
return -ENODEV;
}
/* and increase the device refcount */
video_get(vdev);
mutex_unlock(&videodev_lock);
if (vdev->fops->open) {
if (video_is_registered(vdev))
ret = vdev->fops->open(filp);
else
ret = -ENODEV;
}
if (vdev->dev_debug & V4L2_DEV_DEBUG_FOP)
printk(KERN_DEBUG "%s: open (%d)\n",
video_device_node_name(vdev), ret);
/* decrease the refcount in case of an error */
if (ret)
video_put(vdev);
return ret;
}
static const struct file_operations v4l2_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = v4l2_read,
.write = v4l2_write,
.open = v4l2_open,
.get_unmapped_area = v4l2_get_unmapped_area,
.mmap = v4l2_mmap,
.unlocked_ioctl = v4l2_ioctl,
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
.compat_ioctl = v4l2_compat_ioctl32,
#endif
.release = v4l2_release,
.poll = v4l2_poll,
.llseek = no_llseek,
};APP 使用open函数 -> .open = v4l2_open, - > 找到v4l2_open函数 -> 实现 vdev->fops->open(filp); 自定义的open函数,我们只需要去声明这个vdev->fops->open函数能显示相应的功能即可
c
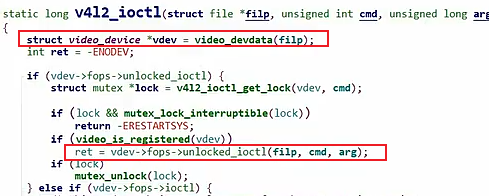
static long v4l2_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
struct video_device *vdev = video_devdata(filp); //根据次设备号得到一个video_device
int ret = -ENODEV;
if (vdev->fops->unlocked_ioctl) {
struct mutex *lock = v4l2_ioctl_get_lock(vdev, cmd);
if (lock && mutex_lock_interruptible(lock))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
if (video_is_registered(vdev))
ret = vdev->fops->unlocked_ioctl(filp, cmd, arg);
if (lock)
mutex_unlock(lock);
} else if (vdev->fops->ioctl) {
struct mutex *m = &vdev->v4l2_dev->ioctl_lock;
if (cmd != VIDIOC_DQBUF && mutex_lock_interruptible(m))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
if (video_is_registered(vdev))
ret = vdev->fops->ioctl(filp, cmd, arg);
if (cmd != VIDIOC_DQBUF)
mutex_unlock(m);
} else
ret = -ENOTTY;
return ret;
}同理,对于传入一个ioctl命令会 -> .unlocked_ioctl = v4l2_ioctl, - > vdev->fops->unlocked_ioctl(filp, cmd, arg)最后调用vedio_dev中的fops中的unlocked_ioctl函数,并把cmd传给他
可以看到我们最终需要实现video_device结构体的完善工作
v4l2框架只提供中转作用,会通过次设备号得到video_device结构体,然后调用video_device下面定义的硬件相关的函数
我们只需要学习v4l2框架后,实现对应函数中底层对硬件相关的操作即可,这就是分层的思想
后面肯定涉及video_device的1.申请、2.设置(初始化)、3.注册结构体
驱动层
从下往上看
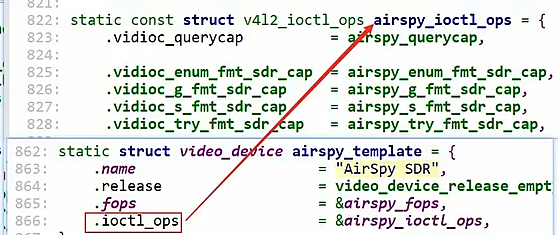
从这个结构体出发(以airspy.c为例)
参考drivers\media\usb\airspy\airspy.c:
c
static struct video_device airspy_template = {
.name = "AirSpy SDR",
.release = video_device_release_empty,
.fops = &airspy_fops,
.ioctl_ops = &airspy_ioctl_ops,
};
// a.分配/设置video_device结构体
s->vdev = airspy_template; //airspy_template函数
// 初始化一个v4l2_device结构体(起辅助作用)
/* Register the v4l2_device structure */
s->v4l2_dev.release = airspy_video_release;
ret = v4l2_device_register(&intf->dev, &s->v4l2_dev);
// video_device和4l2_device建立联系
s->vdev.v4l2_dev = &s->v4l2_dev;
// 注册video_device结构体
ret = video_register_device(&s->vdev, VFL_TYPE_SDR, -1);
__video_register_device
// 根据次设备号把video_device结构体放入数组
video_device[vdev->minor] = vdev;
// 注册字符设备驱动程序
vdev->cdev->ops = &v4l2_fops;
vdev->cdev->owner = owner;
ret = cdev_add(vdev->cdev, MKDEV(VIDEO_MAJOR, vdev->minor), 1);v4l2_device结构体是对操作vedio_device其辅助作用,里面不仅指向了vedio_device结构体,而且还加了各种锁
video_register_device调用了__video_register_device,内部根据次设备号把video_device结构体放入数组,然后通过vdev->cdev->ops = &v4l2_fops;指向了v4l2的接口层
简单查看一下probe函数解析
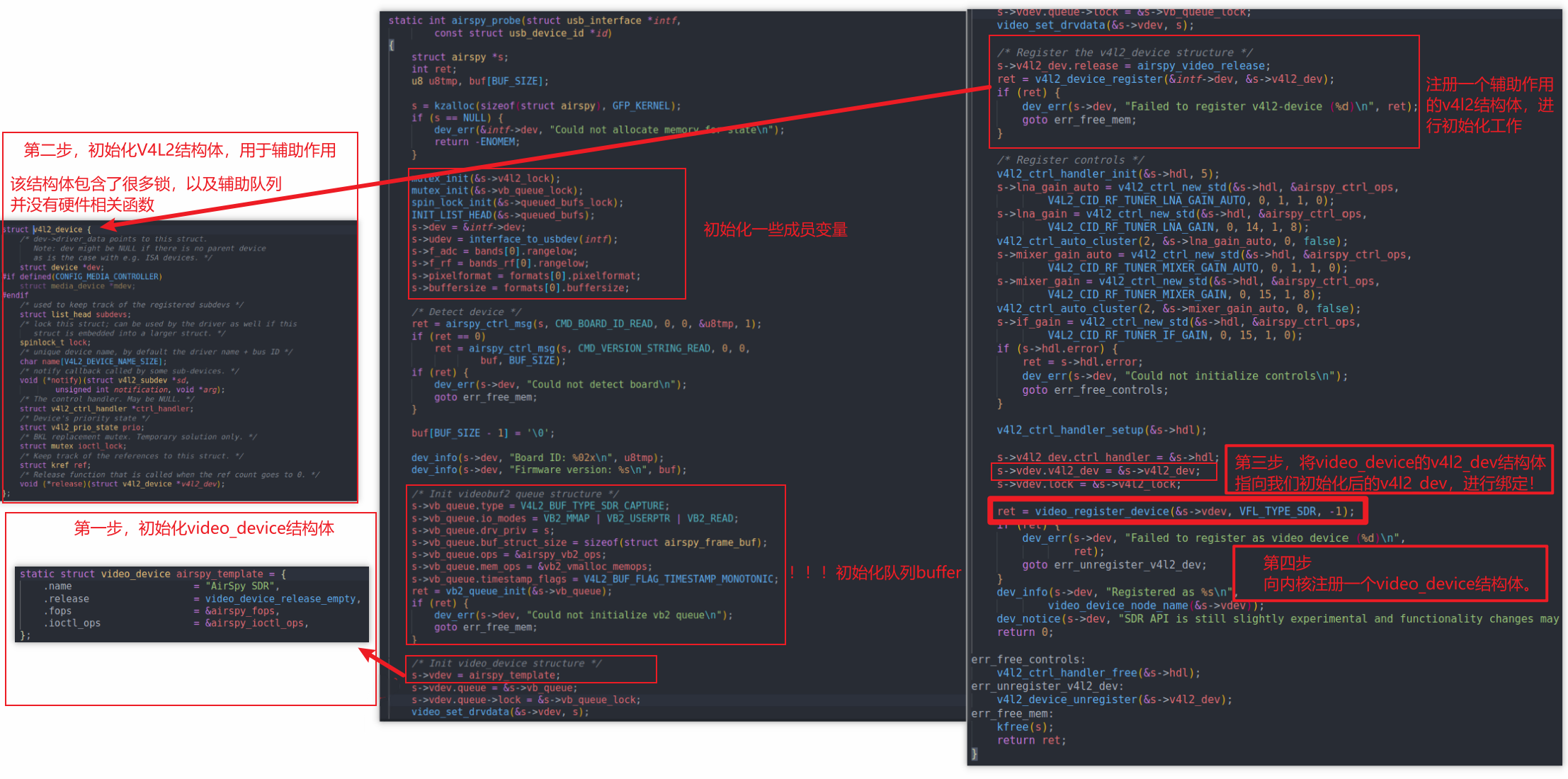
总体来说就是
video_device的1.申请、2.设置(初始化)、3.注册结构体
当然还有一些buffer的初始化工作
c
// 定义视频设备类型枚举值,用于标识不同类型的视频相关设备
#define VFL_TYPE_GRABBER 0 // 视频采集设备类型(如摄像头等图像采集设备)
#define VFL_TYPE_VBI 1 // 垂直消隐期数据设备类型(用于处理电视信号中的垂直消隐期数据)
#define VFL_TYPE_RADIO 2 // 无线电设备类型(如调频收音机等音频接收设备)
#define VFL_TYPE_SUBDEV 3 // 子设备类型(通常指视频设备的辅助组件或子模块)
#define VFL_TYPE_SDR 4 // 软件定义无线电设备类型(通过软件实现信号处理的无线电设备)
#define VFL_TYPE_MAX 5 // 设备类型数量上限,用于边界检查等场景
// 注册一个视频设备
//video_register_device会根据类型来向内核注册,有以上可选项
ret = video_register_device(vdev, VFL_TYPE_SDR, -1);
// 参数说明:
// vdev:指向要注册的视频设备结构体的指针
// VFL_TYPE_SDR:指定设备类型为软件定义无线电设备,我们注册一个视频采集设备类型即可
// -1:表示让系统自动分配设备号
// 返回值:ret为注册操作的结果,0通常表示成功,非0表示失败video_register_device
-》 vdev->cdev->ops = &v4l2_fops;
c
static const struct file_operations v4l2_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = v4l2_read,
.write = v4l2_write,
.open = v4l2_open,
.get_unmapped_area = v4l2_get_unmapped_area,
.mmap = v4l2_mmap,
.unlocked_ioctl = v4l2_ioctl,
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
.compat_ioctl = v4l2_compat_ioctl32,
#endif
.release = v4l2_release,
.poll = v4l2_poll,
.llseek = no_llseek,
};最后还是调用 file_operations v4l2_fops中的定义函数
video_device是内核中用来表示摄像头驱动的结构体,我们其实不是很关心她,而是要清楚整个调用流程,最后落脚点还是编写V4L2的相关硬件操作函数。
video_device中ioctl调用流程
video_device中两个重要的变量,fops和ioctl_ops,其中ioctl_ops指向了v4l2_ioctl_ops结构体,该结构提提供了很多ioctl的处理函数
这些ioctl被分为2类:
- INFO_FL_STD:标准的,无需特殊的代码来处理,APP的调用可以直达这些处理函数
- INFO_FL_FUNC:这类ioctl需要特殊处理,比如对于
VIDIOC_ENUM_FMT,它需要根据设备的类型分别枚举:
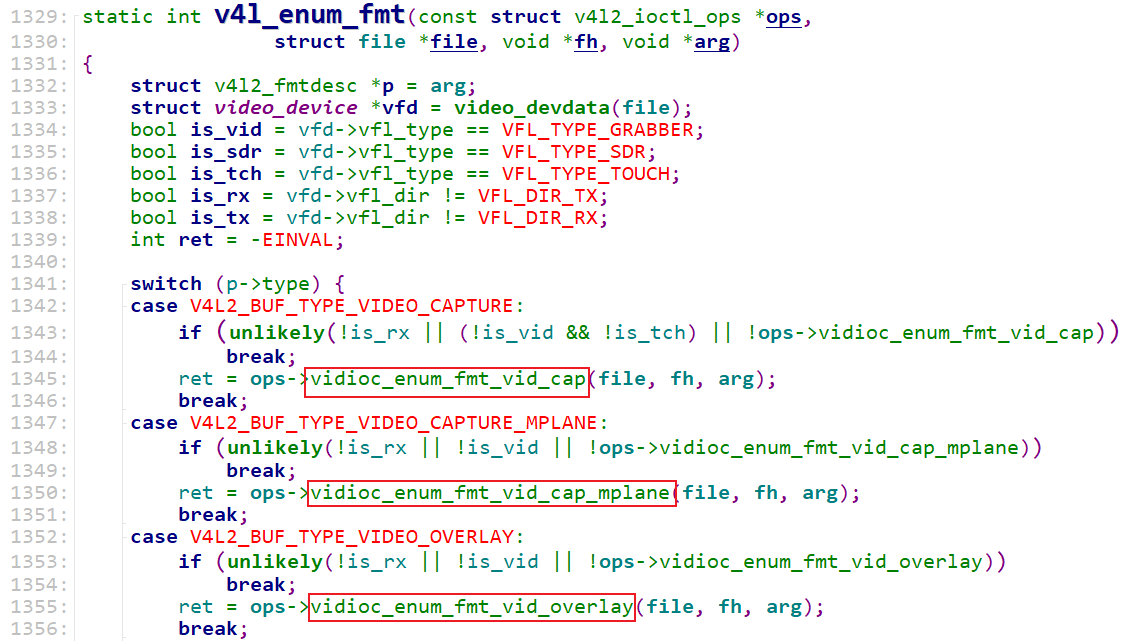
简单地说,这2类ioctl的差别在于:
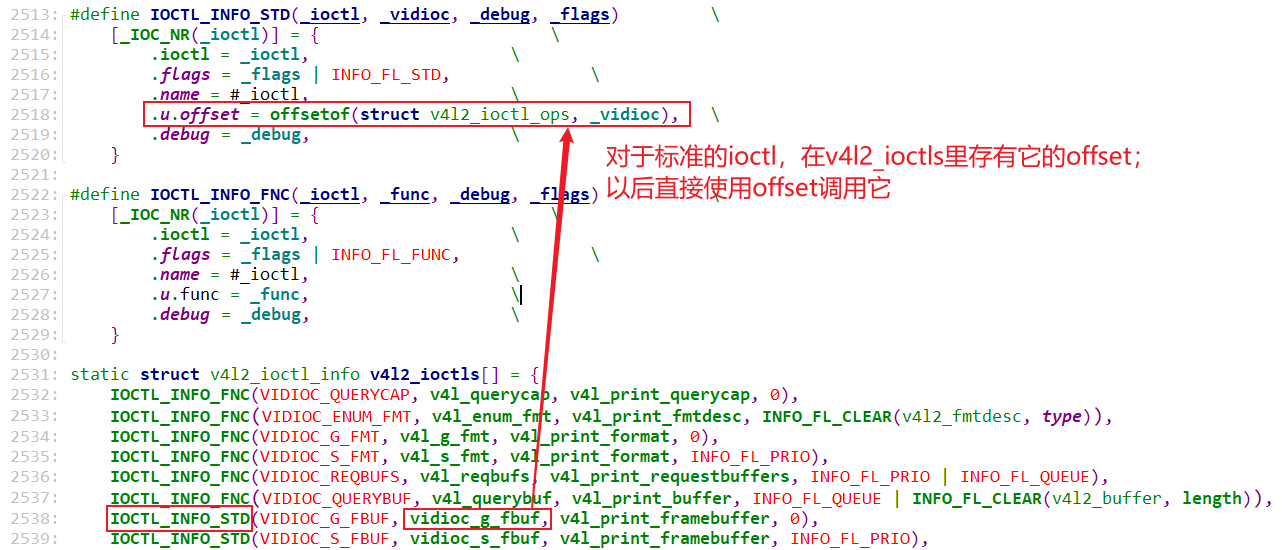
- INFO_FL_STD:APP发出的ioctl直接调用底层的video_device->ioctl_ops->xxxx(...)
- INFO_FL_FUNC:APP发出的ioctl,交给
drivers\media\v4l2-core\v4l2-ioctl.c,它先进行一些特殊处理后,再调用底层的video_device->ioctl_ops->xxxx(...) - 特殊函数处理:

标准的函数处理
怎么区分这些ioctl呢?drivers\media\v4l2-core\v4l2-ioctl.c中有个数组:
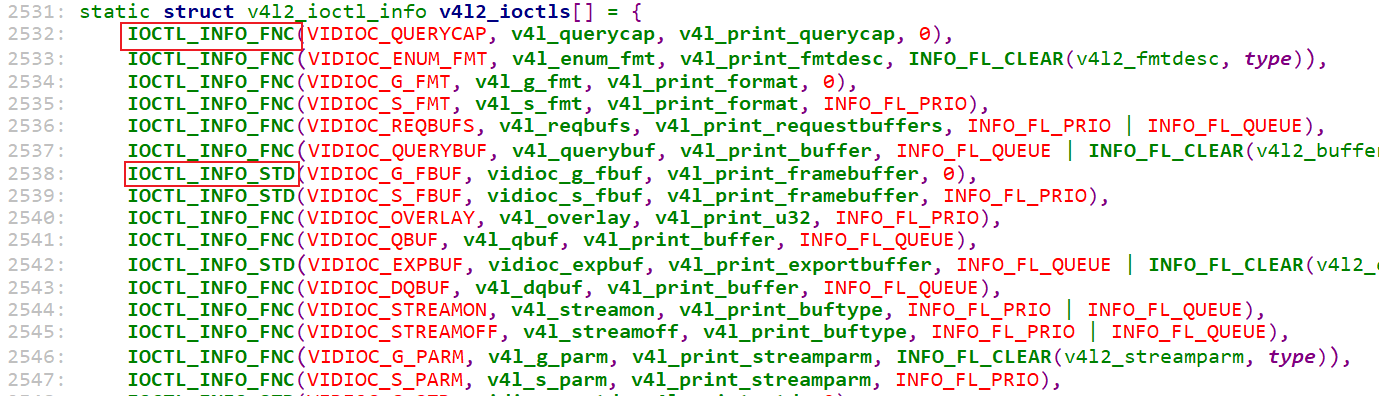
这个数组里,每一项都表示一个ioctl:
-
使用
IOCTL_INFO_FNC定义的数组项,表示它是INFO_FL_FUNC类型的
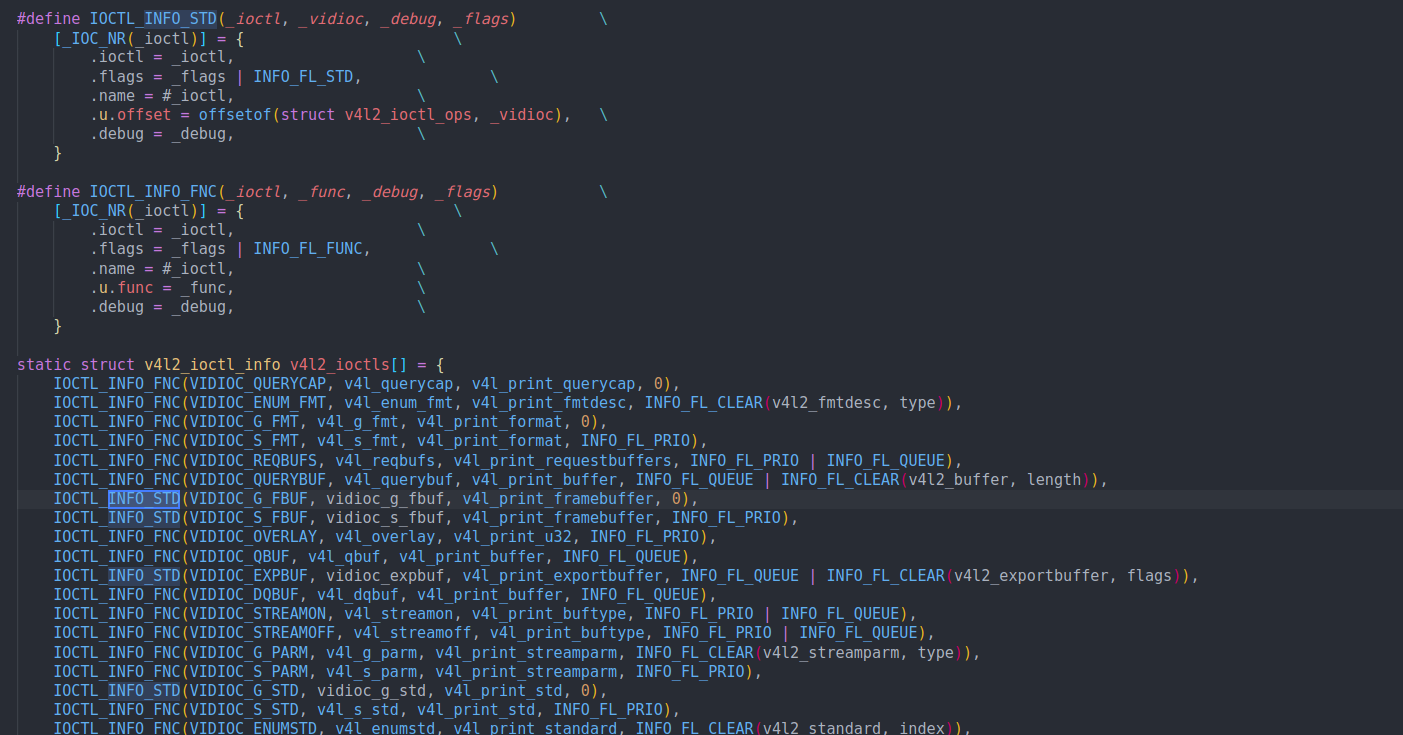
-
使用
IOCTL_INFO_STD定义的数组项,表示它是INFO_FL_STD类型的
1.2.2 调用流程
APP调用摄像头的ioctl,流程为:
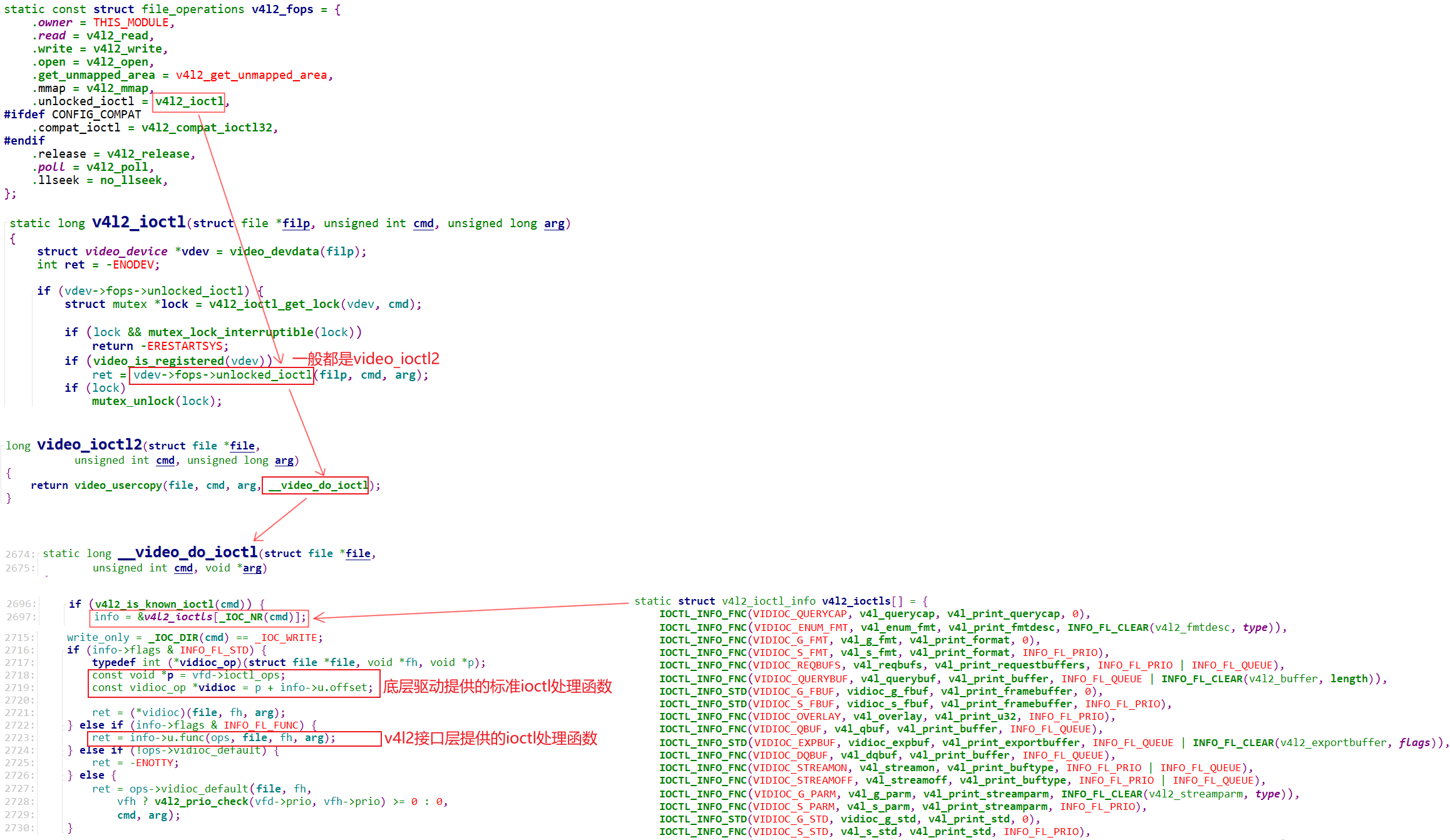
将ioctl做成一个数组,这数组里面有非常多 的ioctl
标准的内核已经实现了,特殊的需要我们自己在v4l2接口层提供的ioctl 处理函数中去实现。
最后根据用户传入的ioctl来实现数组中 的相关函数
Video_buffer2的内核实现
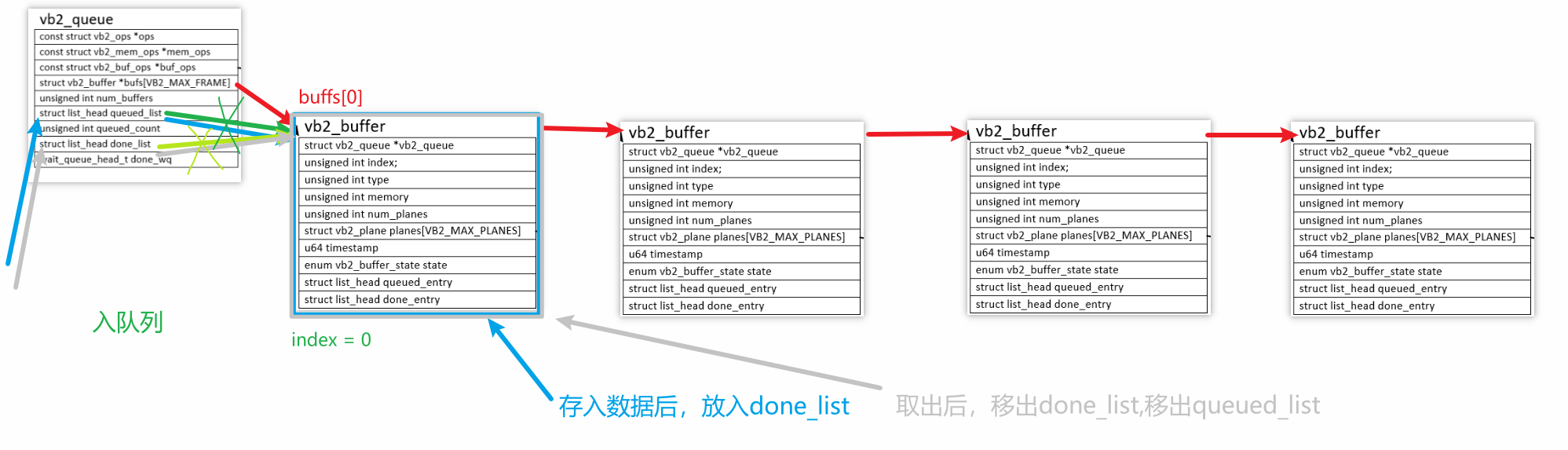
APP操作buffer的示意图如下:
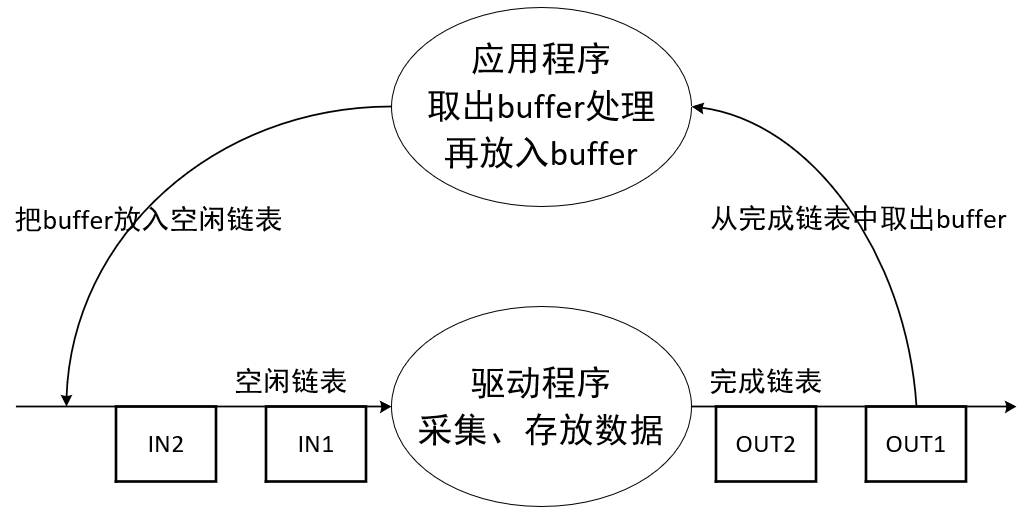
驱动程序中如何管理这些buffer呢?
1.3.1 videobuffer2缓冲区结构体
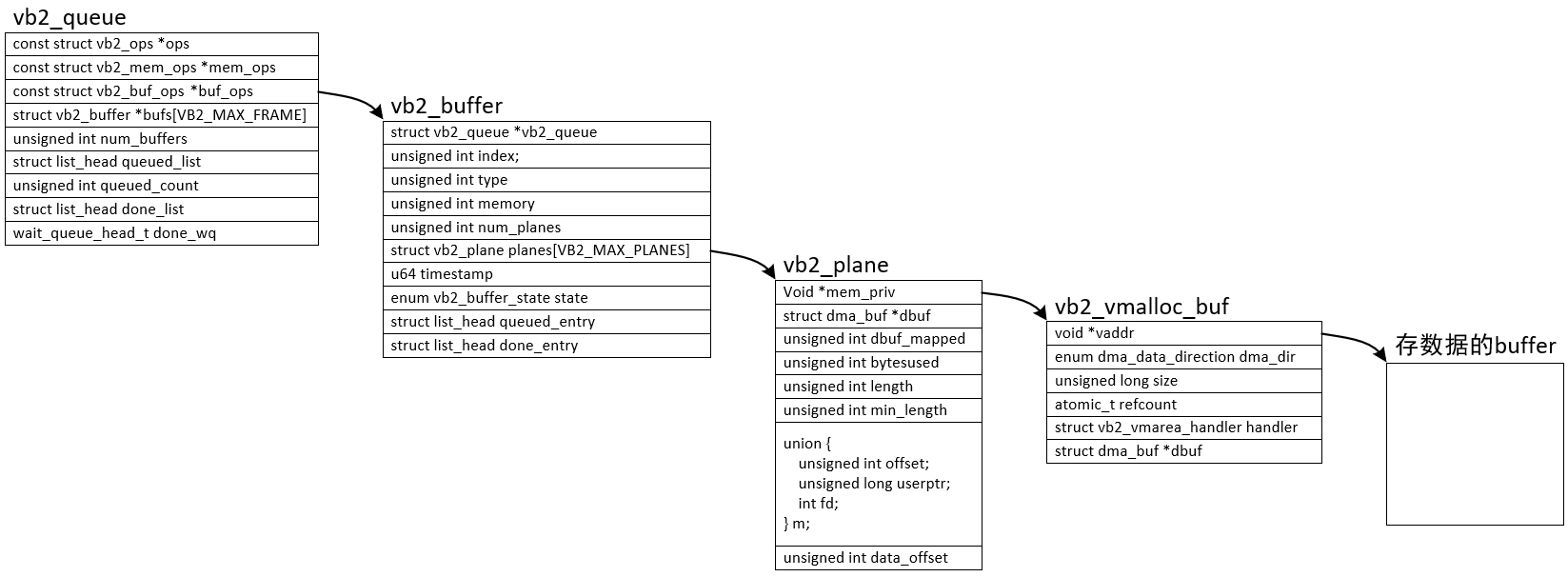
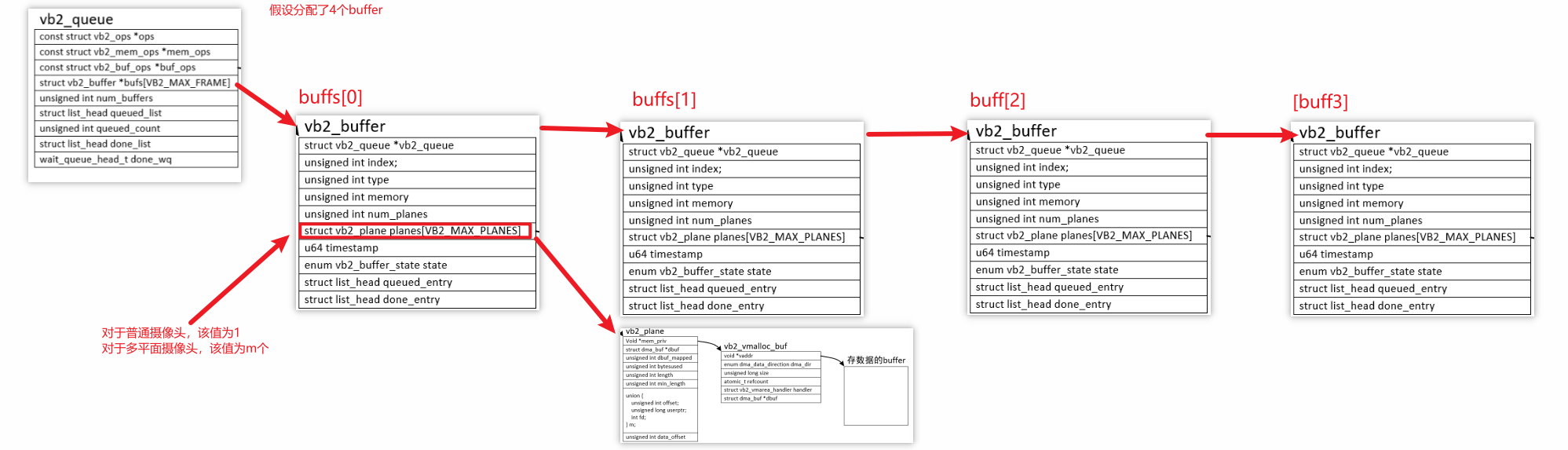
分配流程:
- 驱动程序初始化时,就构造了vb2_queue,这是"buffer的队列",一开始里面没有"buffer"
- APP调用ioctl VIDIOC_REQBUFS向驱动申请N个buffer
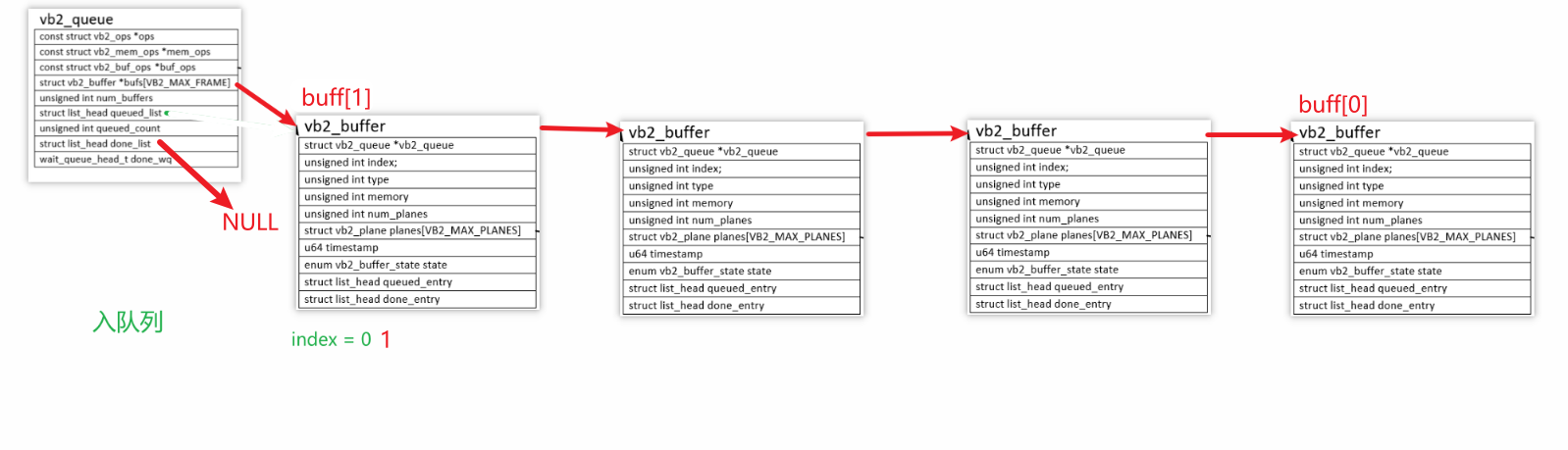
- 驱动程序分配n(n<=N)个vb2_buffer结构体,然后
- 对于普通摄像头,还分配一个vb2_plane结构体、vb2_vmalloc_buf结构体,最后分配存数据的buffer
- 对于多平面摄像头,给每个vb2_buffer分配多个"vb2_plane结构体、vb2_vmalloc_buf结构体、存数据的buffer"

入队列流程:
- APP调用ioctl VIDIOC_QBUF
- 驱动程序根据其index找到vb2_buffer
- 把这个vb2_buffer放入链表vb2_queue.queued_list

硬件驱动接收到数据后,比如URB传输完成后:
- 从链表vb2_queue.queued_list找到(但是不移除)vb2_buffer
- 把硬件数据存入vb2_buffer
- 把vb2_buffer放入链表vb2_queue.done_list

出队列流程:
- APP调用ioctl VIDIOC_DQBUF
- 驱动程序从链表vb2_queue.done_list取出并移除第1个vb2_buffer
- 驱动程序也把这个vb2_buffer从链表vb2_queue.queued_list移除
后面的准备操作(由APP调用VIDIOC_QBUF):
- 重新入队,使用QBUFFER再入队,该buffer就等待下一次填充!
- 它与之前的 "缓冲区入队(
VIDIOC_QBUF)" 形成闭环,共同实现 "空闲缓冲→驱动填充→应用读取→重新入队" 的循环。
值得注意的是:我们需要定一个结构体来包含vb2_buffer,并且能指向下一个vb2_buffer的结构体
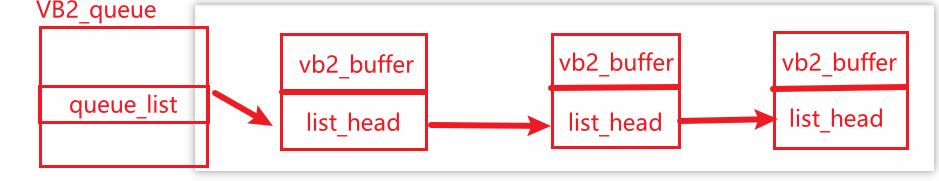
单独的vb2_buffer是无法指向下一个结点的,定义这个结构体的要求是vb2_buffer应该在结构体最前面,结构体的第一个成员的内存地址,和结构体本身的首地址完全相同 (没有偏移量)。这个特性是 "vb2_buffer 放最前面" 的技术基石 。框架能识别的 "通用缓冲区单元",只有 struct vb2_buffer 这个标准结构体 ,很多函数传入的参数只有vb2_buffer的首地址,通过这个首地址,让框架的 vb2_buffer* 能 "反向找到"自定义结构体,
如果list_head放到最前面,那么通过宏container_of传入的参数根本就找不到自定义结构体的首地址而是一个错误的地址(野指针)。
参考如下:
c
struct Camera_frame_buf{ //自定义结构体
vb2_buffer vb;
list_head list;
};list只提供链表的作用,同时需要提供查找下一个空闲buffer的函数,并将本次空的buffer出队列填充数据后上报数据量,并设置当前buffer为完成状态 然后供APP使用
c
static struct Camera_frame_buf *camera_get_next_buf(void)
{
unsigned long flags;
struct Camera_frame_buf *buf = NULL;
if (list_empty(&camera_dev.queued_list))
goto leave;
buf = list_entry(camera_dev.queued_list.next,
struct Camera_frame_buf, list);
list_del(&buf->list);
leave:
return buf;
};app使用完毕后将该buffer重新入队
V4L2中使用vb2_queue来管理缓冲区,里面有3个操作结构体:
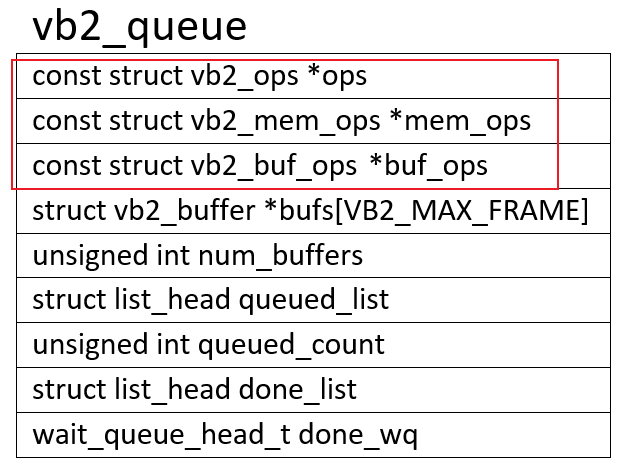
const struct vb2_buf_ops *buf_ops:在用户空间、内核空间之间传递buffer信息
const struct vb2_mem_ops *mem_ops:分配内存用的回调函数
const struct vb2_ops *ops:硬件相关的回调函数
这3个ops的层次图如下:
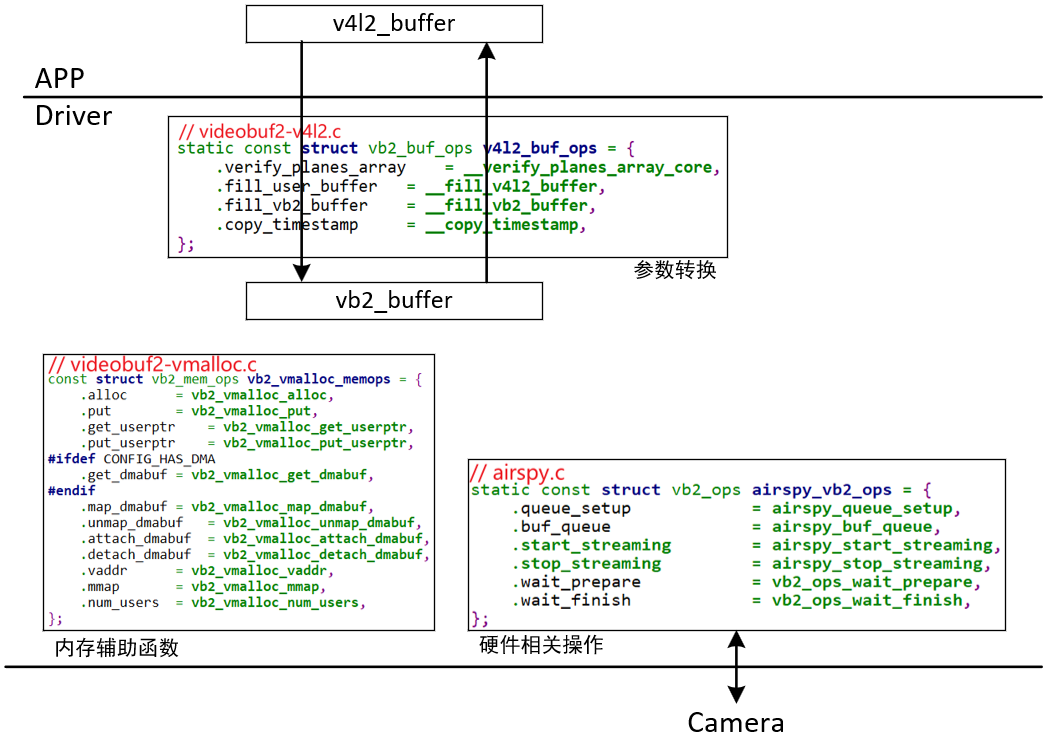
v4l2_buffer是提供给APP使用的,设置起来非常简单,当驱动实现起来需要更加完善的更加复杂的vb2_buffer结构体,两者之间的转换依靠vb2_buf_ops结构体中的两个函数fill_user_buffer和fill_vb2_buffer来完成的,自动填充某些信息
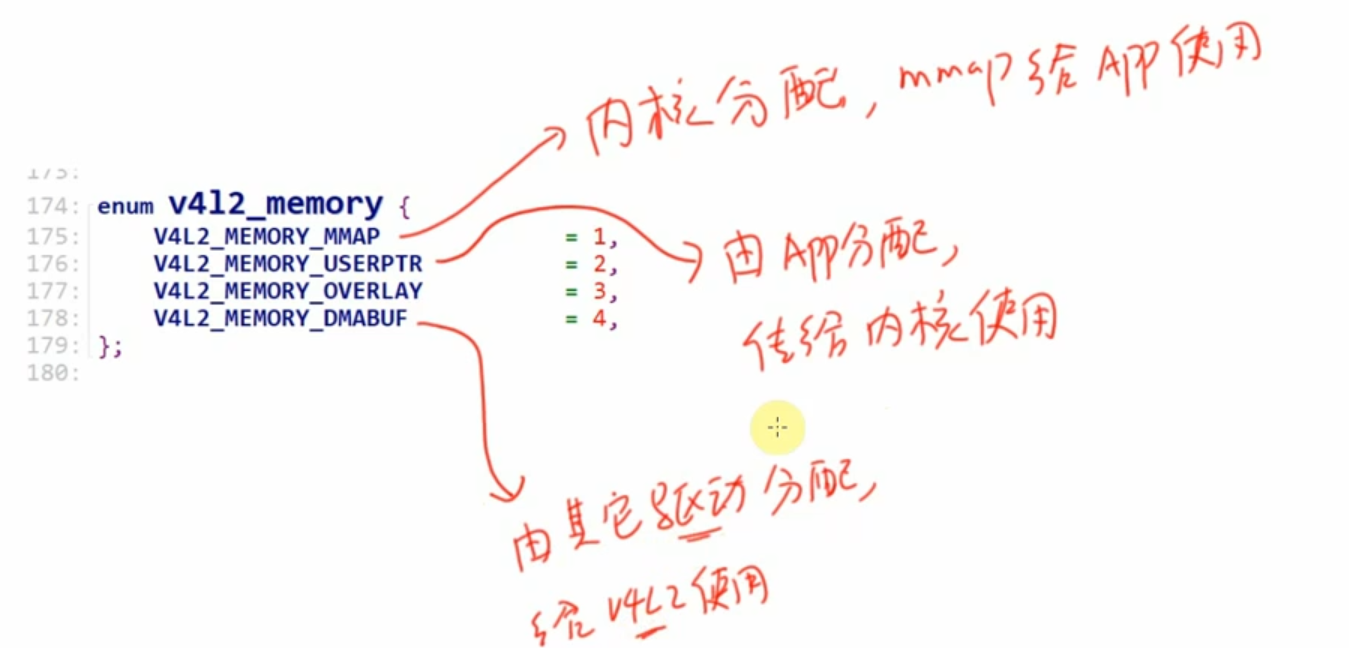
buf的类型可以是
c
static struct video_device airspy_template = {
.name = "AirSpy SDR",
.release = video_device_release_empty,
.fops = &airspy_fops,
.ioctl_ops = &airspy_ioctl_ops,
};
/* 构造一个vb2_queue */
/* Init videobuf2 queue structure */
s->vb_queue.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_SDR_CAPTURE;
s->vb_queue.io_modes = VB2_MMAP | VB2_USERPTR | VB2_READ;
s->vb_queue.drv_priv = s;
s->vb_queue.buf_struct_size = sizeof(struct airspy_frame_buf);
s->vb_queue.ops = &airspy_vb2_ops; // vb2_ops, 硬件相关的操作函数
s->vb_queue.mem_ops = &vb2_vmalloc_memops; // vb2_mem_ops, 辅助结构体,用于mem ops(alloc、mmap)
s->vb_queue.timestamp_flags = V4L2_BUF_FLAG_TIMESTAMP_MONOTONIC;
ret = vb2_queue_init(&s->vb_queue);
q->buf_ops = &v4l2_buf_ops; // vb2_buf_ops, 用于APP和驱动传递参数
// 分配/设置video_device结构体
s->vdev = airspy_template;
s->vdev.queue = &s->vb_queue; // 指向前面构造的vb2_queue
// 初始化一个v4l2_device结构体(起辅助作用)
/* Register the v4l2_device structure */
s->v4l2_dev.release = airspy_video_release;
ret = v4l2_device_register(&intf->dev, &s->v4l2_dev);
// video_device和4l2_device建立联系
s->vdev.v4l2_dev = &s->v4l2_dev;
// 注册video_device结构体
ret = video_register_device(&s->vdev, VFL_TYPE_SDR, -1);
__video_register_device
// 根据次设备号把video_device结构体放入数组
video_device[vdev->minor] = vdev;
// 注册字符设备驱动程序
vdev->cdev->ops = &v4l2_fops;
vdev->cdev->owner = owner;
ret = cdev_add(vdev->cdev, MKDEV(VIDEO_MAJOR, vdev->minor), 1);编写驱动
使用v4l2框架进行开发
- 搭建驱动框架
c
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/usb.h>
#include <media/v4l2-device.h>
#include <media/v4l2-ioctl.h>
#include <media/v4l2-ctrls.h>
#include <media/v4l2-event.h>
#include <media/videobuf2-vmalloc.h>
/* intermediate buffers with raw data from the USB device */
struct Camera_frame_buf {
struct vb2_buffer vb; /* common v4l buffer stuff -- must be first */
struct list_head list;
};
static struct Camera_dev
{
struct v4l2_device v4l2_dev;
struct vb2_queue vb_queue;
struct mutex vb_queue_lock;
struct mutex v4l2_lock;
struct Camera_frame_buf buffer;
struct list_head queued_bufs;
struct video_device v_dev;
};
struct Camera_dev camera_dev;
static struct Camera_frame_buf *camera_get_next_buf(struct Camera_dev *s)
{
unsigned long flags;
struct Camera_frame_buf *buf = NULL;
if (list_empty(&s->queued_bufs))
goto leave;
buf = list_entry(s->queued_bufs.next,
struct Camera_frame_buf, list);
list_del(&buf->list);
leave:
return buf;
};
//下面大部分函数都是内核提供的
static const struct v4l2_file_operations camera_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = ,
};
static const struct v4l2_ioctl_ops camera_ioctl_ops = {
//各种ioctl操作函数
};
static struct vb2_ops camera_vb2_ops = {
};
const struct vb2_mem_ops camera_vb2_mem_ops ={
}
static struct video_device g_vdev = {
.name = "Camera_Dev",
.release = video_device_release_empty, //内核函数
.fops = &camera_fops,
.ioctl_ops = &camera_ioctl_ops,
};
static void camera_video_release(struct v4l2_device *v)
{
//空函数
}
//分配/设置/注册video_device
static int __init virtual_driver_init(void){
int ret = 0;
/*
* 1.初始化video_device
* 2.初始化buffer队列,和video_device进行绑定 -
* 3.注册v4l2_device结构体,和video_device进行绑定
* 4.向内核注册video_device结构体
*
*/
camera_dev.vb_queue.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE ;
camera_dev.vb_queue.io_modes = VB2_MMAP | VB2_USERPTR | VB2_READ;
camera_dev.vb_queue.drv_priv = NULL;
camera_dev.vb_queue.buf_struct_size = sizeof(struct Camera_frame_buf);
camera_dev.vb_queue.ops = &camera_vb2_ops;
camera_dev.vb_queue.vb2_mem_ops =&vb2_vmalloc_memops; //内核提供的内存分配函数
camera_dev.vb_queue.timestamp_flags = V4L2_BUF_FLAG_MAPPED;
ret = vb2_queue_init(&camera_dev.vb_queue);
if (ret) {
printk("Could not initialize vb2 queue\n");
return -1;
}
camera_dev.v_dev = g_vdev;
camera_dev.v_dev.queue = &camera_dev.vb_queue;
camera_dev.v_dev.queue->lock = &Camera_dev->vb_queue_lock;
camera_dev.v_dev.release = camera_video_release;
ret = v4l2_device_register(NULL,camera_dev.v4l2_dev );
if (ret) {
printk("Failed to register v4l2-device (%d)\n", ret);
return -1;
}
camera_dev.v_dev.v4l2_dev = &camera_dev.v4l2_dev;
camera_dev.v_dev.lock = &camera_dev.v4l2_lock;
ret = video_register_device(&camera_dev.v_dev, VFL_TYPE_GRABBER, -1);
if (ret) {
printk("Failed to register as video device(%d)\n", ret);
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
static void __exit virtual_driver_exit(void){
mutex_lock(&camera_dev.v4l2_lock);
mutex_lock(&camera_dev.vb_queue_lock);
v4l2_device_disconnect(&camera_dev.v4l2_dev);
video_unregister_device(&camera_dev.v_dev);
mutex_unlock(&camera_dev.v4l2_lock);
mutex_unlock(&camera_dev.vb_queue_lock);
v4l2_device_put(&camera_dev.v4l2_dev);
}
module_init(virtual_driver_init);
module_exit(virtual_driver_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");- 继续完成框架
c
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/usb.h>
#include <media/v4l2-device.h>
#include <media/v4l2-ioctl.h>
#include <media/v4l2-ctrls.h>
#include <media/v4l2-event.h>
#include <media/videobuf2-vmalloc.h>
/* intermediate buffers with raw data from the USB device */
struct Camera_frame_buf {
struct vb2_buffer vb; /* common v4l buffer stuff -- must be first */
struct list_head list;
};
static struct Camera_dev
{
struct v4l2_device v4l2_dev;
struct vb2_queue vb_queue;
struct mutex vb_queue_lock;
struct mutex v4l2_lock;
struct Camera_frame_buf buffer;
struct list_head queued_bufs;
struct video_device v_dev;
};
struct Camera_dev camera_dev;
static struct Camera_frame_buf *camera_get_next_buf(struct Camera_dev *s)
{
unsigned long flags;
struct Camera_frame_buf *buf = NULL;
if (list_empty(&s->queued_bufs))
goto leave;
buf = list_entry(s->queued_bufs.next,
struct Camera_frame_buf, list);
list_del(&buf->list);
leave:
return buf;
};
static int camera_querycap(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_capability *cap)
{
}
static int camera_enum_fmt_vid_cap(struct file *file, void *priv,
struct v4l2_fmtdesc *f)
{
}
static int camera_g_fmt_cap(struct file *file, void *priv,
struct v4l2_format *f)
{
}
static const int camera_enum_framesizes(struct file *file, void *fh,struct v4l2_frmsizeenum *fsize){
}
static int camera_s_fmt_cap(struct file *file, void *priv,
struct v4l2_format *f)
{
}
static int camare_queue_setup(struct vb2_queue *vq,
const struct v4l2_format *fmt, unsigned int *nbuffers,
unsigned int *nplanes, unsigned int sizes[], void *alloc_ctxs[])
{
}
static void camare_buf_queue(struct vb2_buffer *vb)
{
}
static int camare_start_streaming(struct vb2_queue *vq, unsigned int count)
{
}
static void camare_stop_streaming(struct vb2_queue *vq)
{
}
//下面函数都是内核提供的用于APP-》open/read/mmap ->
static const struct v4l2_file_operations camera_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = v4l2_fh_open,
.release = vb2_fop_release,
.read = vb2_fop_read,
.poll = vb2_fop_poll,
.mmap = vb2_fop_mmap,
.unlocked_ioctl = video_ioctl2,
};
static const struct v4l2_ioctl_ops camera_ioctl_ops = {
//各种ioctl操作函数,需要什么添加什么,需要自己编写
//查询能力
.vidioc_querycap = camera_querycap,
//枚举它支持的格式
.vidioc_enum_fmt_vid_cap = camera_enum_fmt_vid_cap,
.vidioc_g_fmt_vid_cap = camera_g_fmt_cap,
.vidioc_enum_framesizes = camera_enum_framesizes,
//设置格式
.vidioc_s_fmt_vid_cap = camera_s_fmt_cap,
//下面都是内核提供的操作buffer的内容
.vidioc_reqbufs = vb2_ioctl_reqbufs,
.vidioc_create_bufs = vb2_ioctl_create_bufs,
.vidioc_prepare_buf = vb2_ioctl_prepare_buf,
.vidioc_querybuf = vb2_ioctl_querybuf,
.vidioc_qbuf = vb2_ioctl_qbuf,
.vidioc_dqbuf = vb2_ioctl_dqbuf,
.vidioc_streamon = vb2_ioctl_streamon,
.vidioc_streamoff = vb2_ioctl_streamoff,
};
static struct vb2_ops camera_vb2_ops = {
//buffer的几个关键函数
.queue_setup = camare_queue_setup,
.buf_queue = camare_buf_queue,
.start_streaming = camare_start_streaming,
.stop_streaming = camare_stop_streaming,
//下面两个函数由内核提供
.wait_prepare = vb2_ops_wait_prepare,
.wait_finish = vb2_ops_wait_finish,
};
static struct video_device g_vdev = {
.name = "Camera_Dev",
.release = video_device_release_empty, //内核函数
.fops = &camera_fops,
.ioctl_ops = &camera_ioctl_ops,
};
static void camera_video_release(struct v4l2_device *v)
{
//空函数
}
//分配/设置/注册video_device
static int __init virtual_driver_init(void){
int ret = 0;
/*
* 1.初始化video_device
* 2.初始化buffer队列,和video_device进行绑定 -
* 3.注册v4l2_device结构体,和video_device进行绑定
* 4.向内核注册video_device结构体
*
*/
camera_dev.vb_queue.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE ;
camera_dev.vb_queue.io_modes = VB2_MMAP | VB2_USERPTR | VB2_READ;
camera_dev.vb_queue.drv_priv = NULL;
camera_dev.vb_queue.buf_struct_size = sizeof(struct Camera_frame_buf);
camera_dev.vb_queue.ops = &camera_vb2_ops;
camera_dev.vb_queue.mem_ops =&vb2_vmalloc_memops; //内核提供的内存分配函数
camera_dev.vb_queue.timestamp_flags = V4L2_BUF_FLAG_TIMESTAMP_MONOTONIC;
ret = vb2_queue_init(&camera_dev.vb_queue);
if (ret) {
printk("Could not initialize vb2 queue\n");
return -1;
}
camera_dev.v_dev = g_vdev;
camera_dev.v_dev.queue = &camera_dev.vb_queue;
mutex_init(&camera_dev.vb_queue_lock);
camera_dev.v_dev.queue->lock = &camera_dev->vb_queue_lock;
camera_dev.v_dev.release = camera_video_release;
ret = v4l2_device_register(NULL,&camera_dev.v4l2_dev);
if (ret) {
printk("Failed to register v4l2-device (%d)\n", ret);
return -1;
}
camera_dev.v_dev.v4l2_dev = &camera_dev.v4l2_dev;
mutex_init(&camera_dev.v4l2_lock);
camera_dev.v_dev.lock = &camera_dev.v4l2_lock;
ret = video_register_device(&camera_dev.v_dev, VFL_TYPE_GRABBER, -1);
if (ret) {
printk("Failed to register as video device(%d)\n", ret);
return -1;
}
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&camera_dev.queued_bufs); //初始化队列
return 0;
}
static void __exit virtual_driver_exit(void){
mutex_lock(&camera_dev.v4l2_lock);
mutex_lock(&camera_dev.vb_queue_lock);
v4l2_device_disconnect(&camera_dev.v4l2_dev);
video_unregister_device(&camera_dev.v_dev);
mutex_unlock(&camera_dev.v4l2_lock);
mutex_unlock(&camera_dev.vb_queue_lock);
v4l2_device_put(&camera_dev.v4l2_dev);
}
module_init(virtual_driver_init);
module_exit(virtual_driver_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");流程梳理:
一、调用普通的操作集合
APP - > open/read/write/mmap/unlocked_ioctl/release
-> .open = v4l2_open,
-> 调用v4l2-dev.c文件中的操作集合中的v4l2_open函数
-> 调用vdev->fops->open ,即调用与v4l2_device绑定的video_device下面的.fops
-> v4l2_file_operations结构体下对应的函数
-> v4l2_fh_open
c
static const struct file_operations v4l2_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = v4l2_read,
.write = v4l2_write,
.open = v4l2_open,
.get_unmapped_area = v4l2_get_unmapped_area,
.mmap = v4l2_mmap,
.unlocked_ioctl = v4l2_ioctl,
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
.compat_ioctl = v4l2_compat_ioctl32,
#endif
.release = v4l2_release,
.poll = v4l2_poll,
.llseek = no_llseek,
};
c
static struct video_device g_vdev = {
.name = "Camera_Dev",
.release = video_device_release_empty, //内核函数
.fops = &camera_fops,
.ioctl_ops = &camera_ioctl_ops,
};
c
static const struct v4l2_file_operations camera_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = v4l2_fh_open,
.release = vb2_fop_release,
.read = vb2_fop_read,
.poll = vb2_fop_poll,
.mmap = vb2_fop_mmap,
.unlocked_ioctl = video_ioctl2,
};二、调用各种ioctl
流程是先调用file_operations下面的unlocked_ioctl绑定的结构体
.unlocked_ioctl = v4l2_ioctl,
-> vdev->fops->unlocked_ioctl(filp, cmd, arg); 调用video_device下面的v4l2_file_operations结构体(fops)->unlocked_ioctl
-> .unlocked_ioctl = video_ioctl2,
c
long video_ioctl2(struct file *file,
unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
return video_usercopy(file, cmd, arg, __video_do_ioctl);
}主要负责内核空间与用户空间之间的数据拷贝,识别ioctl指令后调用实际的 IO 控制处理函数------__video_do_ioctl 函数:根据传入的 cmd 参数,分发到对应的具体处理函数
整个流程:
用户空间通过 ioctl () 系统调用发起请求 -> 内核空间的 video_ioctl2 () 接收请求 -> 调用 video_usercopy () 进行安全的数据处理 -> 最终由__video_do_ioctl () 执行具体的设备操作。
__video_do_ioctl ()里面检测是否是标准的ioctl或者是特殊的ioctl,如果是标准的怎么去执行,如果是特殊的怎么去执行,上面有讲
c
static long __video_do_ioctl(struct file *file,
unsigned int cmd, void *arg)
{
struct video_device *vfd = video_devdata(file);
const struct v4l2_ioctl_ops *ops = vfd->ioctl_ops;
bool write_only = false;
struct v4l2_ioctl_info default_info;
const struct v4l2_ioctl_info *info;
void *fh = file->private_data;
struct v4l2_fh *vfh = NULL;
int dev_debug = vfd->dev_debug;
long ret = -ENOTTY;
if (ops == NULL) {
pr_warn("%s: has no ioctl_ops.\n",
video_device_node_name(vfd));
return ret;
}
if (test_bit(V4L2_FL_USES_V4L2_FH, &vfd->flags))
vfh = file->private_data;
if (v4l2_is_known_ioctl(cmd)) {
info = &v4l2_ioctls[_IOC_NR(cmd)];
if (!test_bit(_IOC_NR(cmd), vfd->valid_ioctls) &&
!((info->flags & INFO_FL_CTRL) && vfh && vfh->ctrl_handler))
goto done;
if (vfh && (info->flags & INFO_FL_PRIO)) {
ret = v4l2_prio_check(vfd->prio, vfh->prio);
if (ret)
goto done;
}
} else {
default_info.ioctl = cmd;
default_info.flags = 0;
default_info.debug = v4l_print_default;
info = &default_info;
}
write_only = _IOC_DIR(cmd) == _IOC_WRITE;
if (info->flags & INFO_FL_STD) {
typedef int (*vidioc_op)(struct file *file, void *fh, void *p);
const void *p = vfd->ioctl_ops;
const vidioc_op *vidioc = p + info->u.offset;
ret = (*vidioc)(file, fh, arg);
} else if (info->flags & INFO_FL_FUNC) {
ret = info->u.func(ops, file, fh, arg);
} else if (!ops->vidioc_default) {
ret = -ENOTTY;
} else {
ret = ops->vidioc_default(file, fh,
vfh ? v4l2_prio_check(vfd->prio, vfh->prio) >= 0 : 0,
cmd, arg);
}
done:
if (dev_debug & (V4L2_DEV_DEBUG_IOCTL | V4L2_DEV_DEBUG_IOCTL_ARG)) {
if (!(dev_debug & V4L2_DEV_DEBUG_STREAMING) &&
(cmd == VIDIOC_QBUF || cmd == VIDIOC_DQBUF))
return ret;
v4l_printk_ioctl(video_device_node_name(vfd), cmd);
if (ret < 0)
pr_cont(": error %ld", ret);
if (!(dev_debug & V4L2_DEV_DEBUG_IOCTL_ARG))
pr_cont("\n");
else if (_IOC_DIR(cmd) == _IOC_NONE)
info->debug(arg, write_only);
else {
pr_cont(": ");
info->debug(arg, write_only);
}
}
return ret;
}其中 如果是INFO_FL_STD标准的ioctl直接找到 函数执行的指针 = v4l2_file_operations结构体指针 + offset(偏移地址),并通过 (*vidioc)(file, fh, arg)进行执行这个标准的ioctl
如果是INFO_FL_FUNC特殊的ioctl
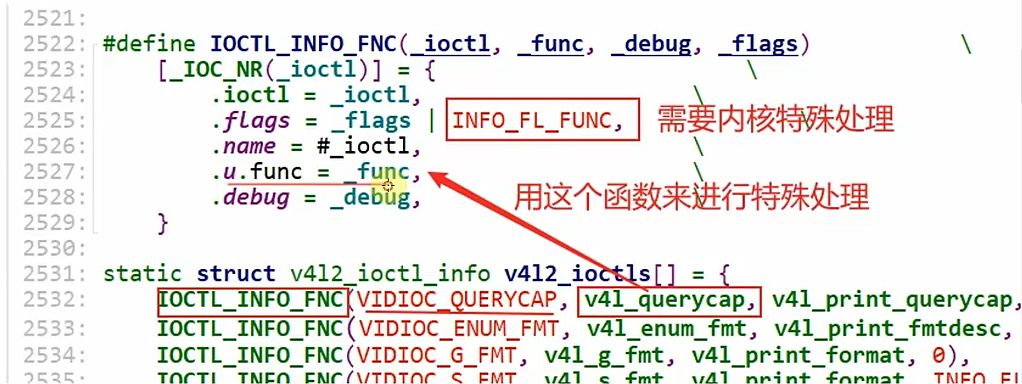
-》IOCTL_INFO_FNC(VIDIOC_QUERYCAP, v4l_querycap, v4l_print_querycap, 0),声明u.func就是v4l_querycap函数,
-》info->u.func(ops, file, fh, arg); 来调用v4l_querycap函数
-》v4l_querycap函数 1. 数据结构转换 2. 设置内核版本 3. **调用驱动具体实现 ** 4。增强设备能力 5. 驱动正确性检查
-》3.调用驱动具体实现就是ops->vidioc_querycap(file, fh, cap)
-》即调用v4l2_ioctl_ops下面的vidioc_querycap绑定的函数进行运行
c
if (info->flags & INFO_FL_STD) {
typedef int (*vidioc_op)(struct file *file, void *fh, void *p);
const void *p = vfd->ioctl_ops;
const vidioc_op *vidioc = p + info->u.offset;
ret = (*vidioc)(file, fh, arg);
} else if (info->flags & INFO_FL_FUNC) {
ret = info->u.func(ops, file, fh, arg);
} else if (!ops->vidioc_default) {
ret = -ENOTTY;
} else {
ret = ops->vidioc_default(file, fh,
vfh ? v4l2_prio_check(vfd->prio, vfh->prio) >= 0 : 0,
cmd, arg);
}
c
#define IOCTL_INFO_FNC(_ioctl, _func, _debug, _flags) \
[_IOC_NR(_ioctl)] = { \
.ioctl = _ioctl, \
.flags = _flags | INFO_FL_FUNC, \
.name = #_ioctl, \
.u.func = _func, \
.debug = _debug, \
}
//以下面ioctl内容举例:
IOCTL_INFO_FNC(VIDIOC_QUERYCAP, v4l_querycap, v4l_print_querycap, 0)
c
static int v4l_querycap(const struct v4l2_ioctl_ops *ops,
struct file *file, void *fh, void *arg)
{
struct v4l2_capability *cap = (struct v4l2_capability *)arg;
int ret;
cap->version = LINUX_VERSION_CODE;
ret = ops->vidioc_querycap(file, fh, cap);
cap->capabilities |= V4L2_CAP_EXT_PIX_FORMAT;
/*
* Drivers MUST fill in device_caps, so check for this and
* warn if it was forgotten.
*/
WARN_ON(!(cap->capabilities & V4L2_CAP_DEVICE_CAPS) ||
!cap->device_caps);
cap->device_caps |= V4L2_CAP_EXT_PIX_FORMAT;
return ret;
}
c
static const struct v4l2_ioctl_ops camera_ioctl_ops = {
//各种ioctl操作函数,需要什么添加什么,需要自己编写
//查询能力
.vidioc_querycap = camera_querycap,
....
}vb2_buffer的管理代码梳理
完整代码
最后实现所有相关函数
c
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/usb.h>
#include <media/v4l2-device.h>
#include <media/v4l2-ioctl.h>
#include <media/v4l2-ctrls.h>
#include <media/v4l2-event.h>
#include <media/videobuf2-vmalloc.h>
extern unsigned char red[8230];
extern unsigned char green[8265];
extern unsigned char bule[8267] ;
/* intermediate buffers with raw data from the USB device */
struct Camera_frame_buf {
struct vb2_buffer vb; /* common v4l buffer stuff -- must be first */
struct list_head list;
};
static struct Camera_dev
{
struct v4l2_device v4l2_dev;
struct vb2_queue vb_queue;
struct mutex vb_queue_lock;
struct mutex v4l2_lock;
struct Camera_frame_buf buffer;
struct list_head queued_bufs;
struct video_device v_dev;
struct timer_list timer;
};
struct Camera_dev camera_dev;
static int copy_cnt;
static struct Camera_frame_buf *camera_get_next_buf(void)
{
unsigned long flags;
struct Camera_frame_buf *buf = NULL;
if (list_empty(&camera_dev.queued_bufs))
goto leave;
buf = list_entry(camera_dev.queued_bufs.next,
struct Camera_frame_buf, list);
list_del(&buf->list);
leave:
return buf;
};
static int camera_querycap(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_capability *cap)
{
//初始化参数
strlcpy(cap->driver,"camera_querycap", sizeof(cap->driver));
strlcpy(cap->card, camera_dev.v_dev.name, sizeof(cap->card));
//设置能力
cap->device_caps = V4L2_CAP_VIDEO_CAPTURE | V4L2_CAP_STREAMING |
V4L2_CAP_READWRITE ;
cap->capabilities = cap->device_caps | V4L2_CAP_DEVICE_CAPS;
return 0;
}
static int camera_enum_fmt_vid_cap(struct file *file, void *priv,
struct v4l2_fmtdesc *f)
{
if (f->index > 0 )
return -EINVAL;
strlcpy(f->description, "motion jpeg", sizeof(f->description));
f->pixelformat = V4L2_PIX_FMT_MJPEG;
return 0;
}
static int camera_g_fmt_cap(struct file *file, void *priv,
struct v4l2_format *f)
{
struct v4l2_pix_format * pix= &f->fmt.pix;
pix->width = 800;
pix->height = 600;
pix->field = V4L2_FIELD_NONE;
pix->pixelformat = V4L2_PIX_FMT_MJPEG;
pix->bytesperline = 0;
return 0;
}
static const int camera_enum_framesizes(struct file *file, void *fh,struct v4l2_frmsizeenum *fsize){
if (fsize->index > 0)
{
return -EINVAL;
}
fsize->type = V4L2_FRMIVAL_TYPE_DISCRETE;
fsize->discrete.width = 800 ;
fsize->discrete.height = 600 ;
return 0;
}
static int camera_s_fmt_cap(struct file *file, void *priv,
struct v4l2_format *f)
{
if (f->type != V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE)
{
return -EINVAL;
}
if (f->fmt.pix.pixelformat !=V4L2_PIX_FMT_MJPEG)
{
return -EINVAL;
}
f->fmt.pix.width = 800;
f->fmt.pix.height = 600;
return 0;
}
/* Videobuf2 operations */
static int camare_queue_setup(struct vb2_queue *vq,
const struct v4l2_format *fmt, unsigned int *nbuffers,
unsigned int *nplanes, unsigned int sizes[], void *alloc_ctxs[])
{
/* Need at least 8 buffers */
if (vq->num_buffers + *nbuffers < 8)
*nbuffers = 8 - vq->num_buffers;
*nplanes = 1;
sizes[0] = PAGE_ALIGN(800 * 600 * 2);
return 0;
}
static void camare_buf_queue(struct vb2_buffer *vb)
{
struct Camera_frame_buf *buf =
container_of(vb, struct Camera_frame_buf, vb);
list_add_tail(&buf->list, &camera_dev.queued_bufs);
}
static void timer_fun(unsigned long arg){
//构造数据
// 获得第1个空闲buffer
struct Camera_frame_buf *fbuf = camera_get_next_buf();
void *ptr;
if (fbuf)
{
//写入buffer
ptr = vb2_plane_vaddr(&fbuf->vb, 0);
if (copy_cnt<=60)
{
memcpy(ptr,red,sizeof(red));
vb2_set_plane_payload(&fbuf->vb,0,sizeof(red));
}else if (copy_cnt<=120)
{
memcpy(ptr,green,sizeof(green));
vb2_set_plane_payload(&fbuf->vb,0,sizeof(green));
}else{
memcpy(ptr,bule,sizeof(bule));
vb2_set_plane_payload(&fbuf->vb,0,sizeof(bule));
}
//调用vb2_buffer_done
vb2_buffer_done(&fbuf->vb,VB2_BUF_STATE_DONE);
}
copy_cnt ++;
if (copy_cnt>180)
{
copy_cnt = 0;
}
//再次设置超时时间
mod_timer(&camera_dev.timer,jiffies+HZ/30);
}
static int camare_start_streaming(struct vb2_queue *vq, unsigned int count)
{
setup_timer(&camera_dev.timer,timer_fun,0);
camera_dev.timer.expires = jiffies + HZ/30;
add_timer(&camera_dev.timer);
return 0;
}
static void camare_stop_streaming(struct vb2_queue *vq)
{
del_timer(&camera_dev.timer);
while (!list_empty(&camera_dev.queued_bufs)) {
struct Camera_frame_buf *buf;
buf = list_entry(camera_dev.queued_bufs.next,
struct Camera_frame_buf, list);
list_del(&buf->list);
vb2_buffer_done(&buf->vb, VB2_BUF_STATE_ERROR);
}
}
//下面函数都是内核提供的用于APP-》open/read/mmap ->
static const struct v4l2_file_operations camera_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = v4l2_fh_open,
.release = vb2_fop_release,
.read = vb2_fop_read,
.poll = vb2_fop_poll,
.mmap = vb2_fop_mmap,
.unlocked_ioctl = video_ioctl2,
};
static const struct v4l2_ioctl_ops camera_ioctl_ops = {
//各种ioctl操作函数,需要什么添加什么,需要自己编写
//查询能力
.vidioc_querycap = camera_querycap,
//枚举它支持的格式
.vidioc_enum_fmt_vid_cap = camera_enum_fmt_vid_cap,
.vidioc_enum_framesizes = camera_enum_framesizes,
//设置格式
.vidioc_s_fmt_vid_cap = camera_s_fmt_cap,
.vidioc_g_fmt_vid_cap = camera_g_fmt_cap,
//下面都是内核提供的操作buffer的内容
.vidioc_reqbufs = vb2_ioctl_reqbufs,
.vidioc_create_bufs = vb2_ioctl_create_bufs,
.vidioc_prepare_buf = vb2_ioctl_prepare_buf,
.vidioc_querybuf = vb2_ioctl_querybuf,
.vidioc_qbuf = vb2_ioctl_qbuf,
.vidioc_dqbuf = vb2_ioctl_dqbuf,
.vidioc_streamon = vb2_ioctl_streamon,
.vidioc_streamoff = vb2_ioctl_streamoff,
};
static struct vb2_ops camera_vb2_ops = {
//buffer的几个关键函数
.queue_setup = camare_queue_setup,
.buf_queue = camare_buf_queue,
.start_streaming = camare_start_streaming,
.stop_streaming = camare_stop_streaming,
//下面两个函数由内核提供
.wait_prepare = vb2_ops_wait_prepare,
.wait_finish = vb2_ops_wait_finish,
};
static struct video_device g_vdev = {
.name = "Camera_Dev",
.release = video_device_release_empty, //内核函数
.fops = &camera_fops,
.ioctl_ops = &camera_ioctl_ops,
};
static void camera_video_release(struct v4l2_device *v)
{
//空函数
}
//分配/设置/注册video_device
static int __init virtual_driver_init(void){
int ret = 0;
/*
* 1.初始化video_device
* 2.初始化buffer队列,和video_device进行绑定 -
* 3.注册v4l2_device结构体,和video_device进行绑定
* 4.向内核注册video_device结构体
*
*/
camera_dev.vb_queue.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE ;
camera_dev.vb_queue.io_modes = VB2_MMAP | VB2_USERPTR | VB2_READ;
camera_dev.vb_queue.drv_priv = NULL;
camera_dev.vb_queue.buf_struct_size = sizeof(struct Camera_frame_buf);
camera_dev.vb_queue.ops = &camera_vb2_ops;
camera_dev.vb_queue.mem_ops =&vb2_vmalloc_memops; //内核提供的内存分配函数
camera_dev.vb_queue.timestamp_flags = V4L2_BUF_FLAG_TIMESTAMP_MONOTONIC;
ret = vb2_queue_init(&camera_dev.vb_queue);
if (ret) {
printk("Could not initialize vb2 queue\n");
return -1;
}
camera_dev.v_dev = g_vdev;
camera_dev.v_dev.queue = &camera_dev.vb_queue;
mutex_init(&camera_dev.vb_queue_lock);
camera_dev.v_dev.queue->lock = &camera_dev.vb_queue_lock;
camera_dev.v_dev.release = camera_video_release;
strcpy(camera_dev.v4l2_dev.name,"g_v4l2_dev");
ret = v4l2_device_register(NULL,&camera_dev.v4l2_dev);
if (ret) {
printk("Failed to register v4l2-device (%d)\n", ret);
return -1;
}
camera_dev.v_dev.v4l2_dev = &camera_dev.v4l2_dev;
mutex_init(&camera_dev.v4l2_lock);
camera_dev.v_dev.lock = &camera_dev.v4l2_lock;
ret = video_register_device(&camera_dev.v_dev, VFL_TYPE_GRABBER, -1);
if (ret) {
printk("Failed to register as video device(%d)\n", ret);
return -1;
}
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&camera_dev.queued_bufs); //初始化队列
return 0;
}
static void __exit virtual_driver_exit(void){
mutex_lock(&camera_dev.v4l2_lock);
mutex_lock(&camera_dev.vb_queue_lock);
v4l2_device_disconnect(&camera_dev.v4l2_dev);
video_unregister_device(&camera_dev.v_dev);
mutex_unlock(&camera_dev.v4l2_lock);
mutex_unlock(&camera_dev.vb_queue_lock);
v4l2_device_put(&camera_dev.v4l2_dev);
}
module_init(virtual_driver_init);
module_exit(virtual_driver_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");简单报错处理
1,modprobe 模块后
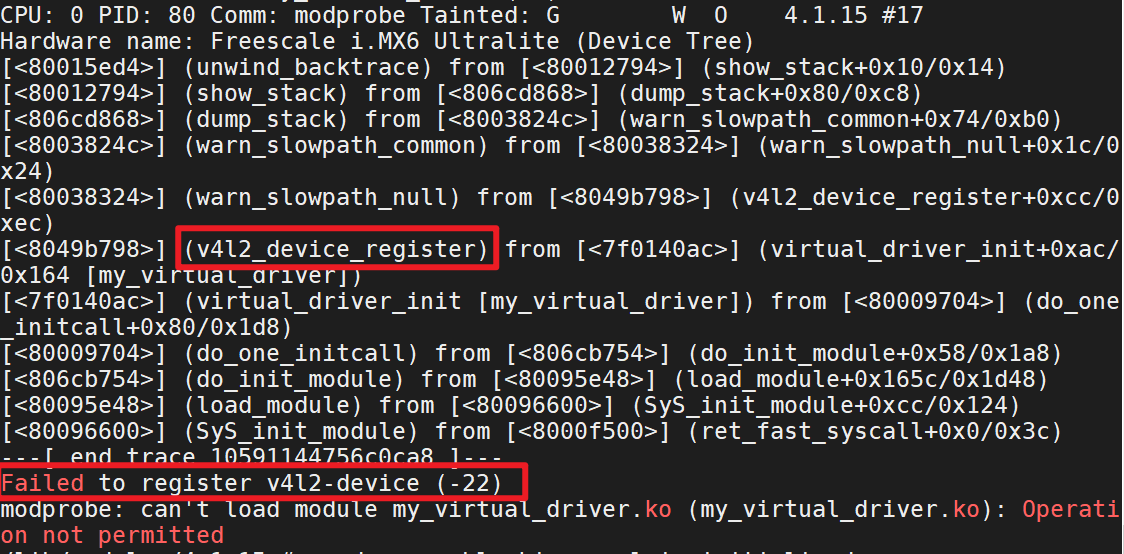
c
ret = v4l2_device_register(NULL,&camera_dev.v4l2_dev);注册失败
查看v4l2_device_register函数具体过程
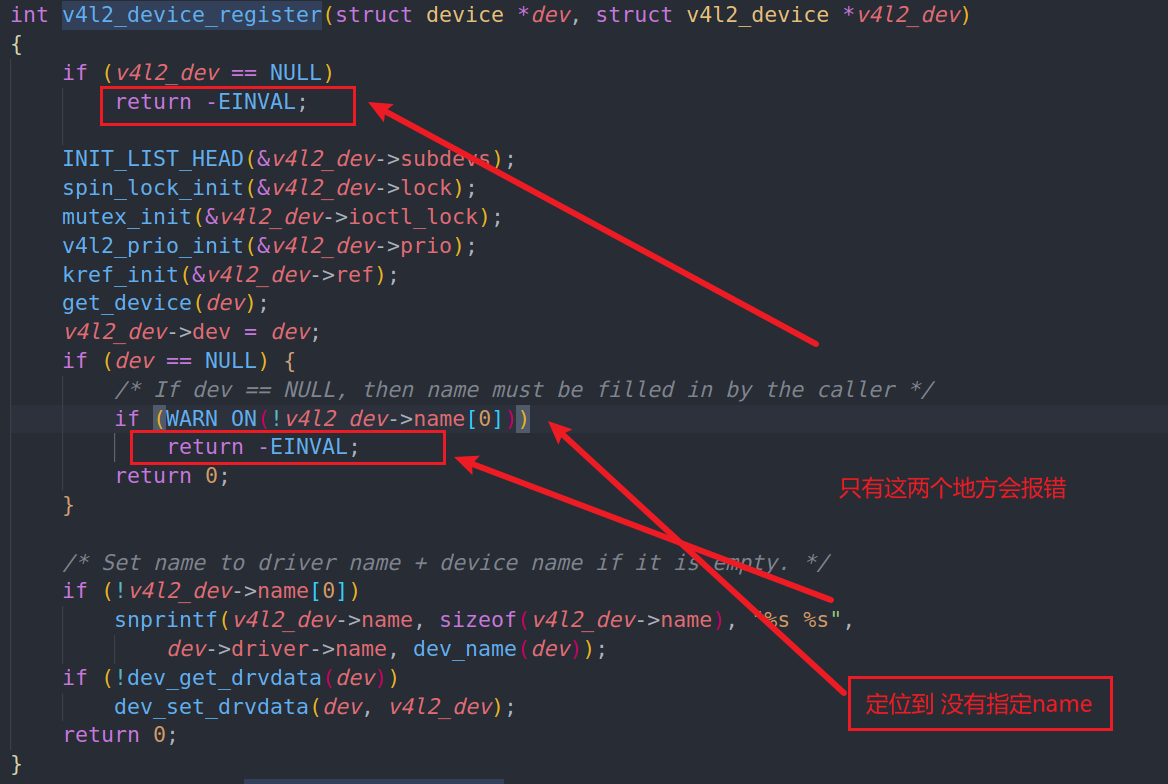
c
strcpy(camera_dev.v4l2_dev.name,"v4l2_dev");
ret = v4l2_device_register(NULL,&camera_dev.v4l2_dev); 2. can not request buffers
c
static const struct v4l2_ioctl_ops camera_ioctl_ops = {
//各种ioctl操作函数,需要什么添加什么,需要自己编写
//查询能力
.vidioc_querycap = camera_querycap,
//枚举它支持的格式
.vidioc_enum_fmt_vid_cap = camera_enum_fmt_vid_cap,
.vidioc_enum_framesizes = camera_enum_framesizes,
//设置格式
.vidioc_s_fmt_vid_cap = camera_s_fmt_cap,
//.vidioc_g_fmt_vid_cap = camera_g_fmt_cap,
//下面都是内核提供的操作buffer的内容
.vidioc_reqbufs = vb2_ioctl_reqbufs,
.vidioc_create_bufs = vb2_ioctl_create_bufs,
.vidioc_prepare_buf = vb2_ioctl_prepare_buf,
.vidioc_querybuf = vb2_ioctl_querybuf,
.vidioc_qbuf = vb2_ioctl_qbuf,
.vidioc_dqbuf = vb2_ioctl_dqbuf,
.vidioc_streamon = vb2_ioctl_streamon,
.vidioc_streamoff = vb2_ioctl_streamoff,
};注释掉vidioc_g_fmt_vid_cap函数后
c
./video_test /dev/video1
format motion jpeg,1196444237, framesize 0: 800 x 600
set format ok: 800 x 600
can not request bufferscan not request buffers为应用程序请求buffer后无法请求,切没有错误提醒,我们在应用程序使用
c
perror("request buffers")显示无效的参数
c
int vb2_ioctl_reqbufs(struct file *file, void *priv,
struct v4l2_requestbuffers *p)
{
struct video_device *vdev = video_devdata(file);
int res = __verify_memory_type(vdev->queue, p->memory, p->type);
if (res)
return res;
if (vb2_queue_is_busy(vdev, file))
return -EBUSY;
res = __reqbufs(vdev->queue, p);
/* If count == 0, then the owner has released all buffers and he
is no longer owner of the queue. Otherwise we have a new owner. */
if (res == 0)
vdev->queue->owner = p->count ? file->private_data : NULL;
return res;
}__verify_memory_type会去校验三个参数queue、memory、type
查看queue的初始化工作
c
camera_dev.vb_queue.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE ;
camera_dev.vb_queue.io_modes = VB2_MMAP | VB2_USERPTR | VB2_READ;
camera_dev.vb_queue.drv_priv = NULL;
camera_dev.vb_queue.buf_struct_size = sizeof(struct Camera_frame_buf);
camera_dev.vb_queue.ops = &camera_vb2_ops;
camera_dev.vb_queue.mem_ops =&vb2_vmalloc_memops; //内核提供的内存分配函数
camera_dev.vb_queue.timestamp_flags = V4L2_BUF_FLAG_TIMESTAMP_MONOTONIC;
ret = vb2_queue_init(&camera_dev.vb_queue);
if (ret) {
printk("Could not initialize vb2 queue\n");
return -1;
}
camera_dev.v_dev = g_vdev;
camera_dev.v_dev.queue = &camera_dev.vb_queue;查看queue.type的类型是否正确
确定无误后按照流程走一遍
app传入一个ioctl去请求reqbufs,最后来到drivers/media/v4l2-core/v4l2-ioctl.c
c
static struct v4l2_ioctl_info v4l2_ioctls[] = {
IOCTL_INFO_FNC(VIDIOC_REQBUFS, v4l_reqbufs, v4l_print_requestbuffers, INFO_FL_PRIO | INFO_FL_QUEUE),
}去执行了v4l_reqbufs
c
static int v4l_reqbufs(const struct v4l2_ioctl_ops *ops,
struct file *file, void *fh, void *arg)
{
struct v4l2_requestbuffers *p = arg;
int ret = check_fmt(file, p->type);
if (ret)
return ret;
CLEAR_AFTER_FIELD(p, memory);
return ops->vidioc_reqbufs(file, fh, p);
}首先会check_fmt,然后调用ops->vidioc_reqbufs绑定的函数
c
.vidioc_reqbufs = vb2_ioctl_reqbufs
c
int vb2_ioctl_reqbufs(struct file *file, void *priv,
struct v4l2_requestbuffers *p)
{
struct video_device *vdev = video_devdata(file);
int res = __verify_memory_type(vdev->queue, p->memory, p->type);
if (res)
return res;
if (vb2_queue_is_busy(vdev, file))
return -EBUSY;
res = __reqbufs(vdev->queue, p);
/* If count == 0, then the owner has released all buffers and he
is no longer owner of the queue. Otherwise we have a new owner. */
if (res == 0)
vdev->queue->owner = p->count ? file->private_data : NULL;
return res;
}那么一定是这两个函数中的某个if返回了负数导致出错的
先看来check_fmt函数
c
static int check_fmt(struct file *file, enum v4l2_buf_type type)
{
struct video_device *vfd = video_devdata(file);
const struct v4l2_ioctl_ops *ops = vfd->ioctl_ops;
bool is_vid = vfd->vfl_type == VFL_TYPE_GRABBER;
bool is_vbi = vfd->vfl_type == VFL_TYPE_VBI;
bool is_sdr = vfd->vfl_type == VFL_TYPE_SDR;
bool is_rx = vfd->vfl_dir != VFL_DIR_TX;
bool is_tx = vfd->vfl_dir != VFL_DIR_RX;
if (ops == NULL)
return -EINVAL;
switch (type) {
case V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE:
if (is_vid && is_rx &&
(ops->vidioc_g_fmt_vid_cap || ops->vidioc_g_fmt_vid_cap_mplane))
return 0;
break;
case V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE_MPLANE:
if (is_vid && is_rx && ops->vidioc_g_fmt_vid_cap_mplane)
return 0;
break;
case V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_OVERLAY:
if (is_vid && is_rx && ops->vidioc_g_fmt_vid_overlay)
return 0;
break;
case V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_OUTPUT:
if (is_vid && is_tx &&
(ops->vidioc_g_fmt_vid_out || ops->vidioc_g_fmt_vid_out_mplane))
return 0;
break;
case V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_OUTPUT_MPLANE:
if (is_vid && is_tx && ops->vidioc_g_fmt_vid_out_mplane)
return 0;
break;
case V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_OUTPUT_OVERLAY:
if (is_vid && is_tx && ops->vidioc_g_fmt_vid_out_overlay)
return 0;
break;
case V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VBI_CAPTURE:
if (is_vbi && is_rx && ops->vidioc_g_fmt_vbi_cap)
return 0;
break;
case V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VBI_OUTPUT:
if (is_vbi && is_tx && ops->vidioc_g_fmt_vbi_out)
return 0;
break;
case V4L2_BUF_TYPE_SLICED_VBI_CAPTURE:
if (is_vbi && is_rx && ops->vidioc_g_fmt_sliced_vbi_cap)
return 0;
break;
case V4L2_BUF_TYPE_SLICED_VBI_OUTPUT:
if (is_vbi && is_tx && ops->vidioc_g_fmt_sliced_vbi_out)
return 0;
break;
case V4L2_BUF_TYPE_SDR_CAPTURE:
if (is_sdr && is_rx && ops->vidioc_g_fmt_sdr_cap)
return 0;
break;
default:
break;
}
return -EINVAL;
}匹配到V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE
c
if (is_vid && is_rx &&
(ops->vidioc_g_fmt_vid_cap || ops->vidioc_g_fmt_vid_cap_mplane))
return 0;
break;看到是否定义了struct v4l2_ioctl_ops *ops下的vidioc_g_fmt_vid_cap
检查自己写的结构体v4l2_ioctl_ops看到没有定义vidioc_g_fmt_vid_cap函数
当应用程序通过 ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_G_FMT, &fmt) 命令查询视频捕获格式时,驱动会调用 vidioc_g_fmt_vid_cap 函数。且必须要提前声明,于是就找到了这个错误!
drivers/media/v4l2-core/v4l2-ioctl.c
check_fmt函数规定了不同类型的video_device结构体必须设置的参数或需要声明的函数
在数据传输的重点就是
c
static void timer_fun(unsigned long arg){
//构造数据
// 获得第1个空闲buffer
struct Camera_frame_buf *fbuf = camera_get_next_buf();
void *ptr;
if (fbuf)
{
//写入buffer
ptr = vb2_plane_vaddr(&fbuf->vb, 0);
if (copy_cnt<=60)
{
memcpy(ptr,red,sizeof(red));
vb2_set_plane_payload(&fbuf->vb,0,sizeof(red));
}else if (copy_cnt<=120)
{
memcpy(ptr,green,sizeof(green));
vb2_set_plane_payload(&fbuf->vb,0,sizeof(green));
}else{
memcpy(ptr,bule,sizeof(bule));
vb2_set_plane_payload(&fbuf->vb,0,sizeof(bule));
}
//调用vb2_buffer_done
vb2_buffer_done(&fbuf->vb,VB2_BUF_STATE_DONE);
}
copy_cnt ++;
if (copy_cnt>180)
{
copy_cnt = 0;
}
//再次设置超时时间
mod_timer(&camera_dev.timer,jiffies+HZ/30);
}使用定时器每30ms传输到buffer中使用的函数为memcpy,数据传输完毕后使用vb2_set_plane_payload函数进行上报传输数据的个数,在调用vb2_buffer_done函数来结束本次数据传输,然后交给buf_queue来管理。他会按照我们前面讲的那样使用buffer缓冲区来完成数据传输本次完成后应用程序可通过 VIDIOC_DQBUF 取出该缓冲区并读取数据
3.应用程序和驱动程序分配了不同的buffer个数
应用程序想要申请4个buffer,但是我们 的驱动程序分配了8个,会导致数组越界的问题
我们允许定义一个较大的buffer数组,这样就不会越界,比如分配32个buffer数组
4.对于特定的开发板上运行驱动问题
imx6ull是直接将vb2的驱动编译进入内核 的,无需手动加载,而STM32MP157则只能作为模块编译,且内核版本不一样,驱动不能共用,下面来解决这个问题。
有些驱动中关于vb2的相关依赖驱动(videobuf2下面的Makefile文件里面需要编译的模块),无法编译进内核,需要先编译模块,在加载这些依赖驱动
加载依赖驱动后,显示无法注册video_register_device(),切提出一个警告WARN
c
int __video_register_device(struct video_device *vdev, int type, int nr,
int warn_if_nr_in_use, struct module *owner)
{
int i = 0;
int ret;
int minor_offset = 0;
int minor_cnt = VIDEO_NUM_DEVICES;
const char *name_base;
/* A minor value of -1 marks this video device as never
having been registered */
vdev->minor = -1;
/* the release callback MUST be present */
if (WARN_ON(!vdev->release))
return -EINVAL;
/* the v4l2_dev pointer MUST be present */
if (WARN_ON(!vdev->v4l2_dev))
return -EINVAL;
....
return ret;
}定位警告的位置
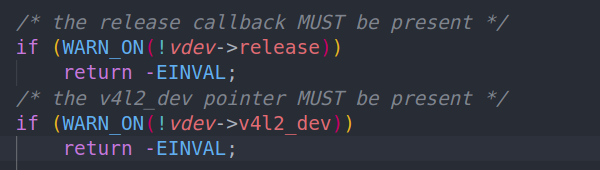
是否有提供video_device结构体的release函数,是否初始化 了v4l2_dev结构体进行了绑定
c
static struct video_device g_vdev = {
.name = "Camera_Dev",
.release = video_device_release_empty, //内核函数
.fops = &camera_fops,
.ioctl_ops = &camera_ioctl_ops,
};
...
camera_dev.v_dev.v4l2_dev = &camera_dev.v4l2_dev;
....这两个我们都有
而不同内核要求不一样
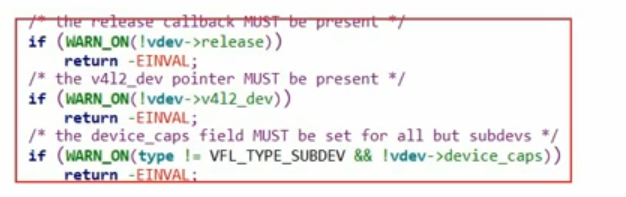
上面这个内核版本需要提供
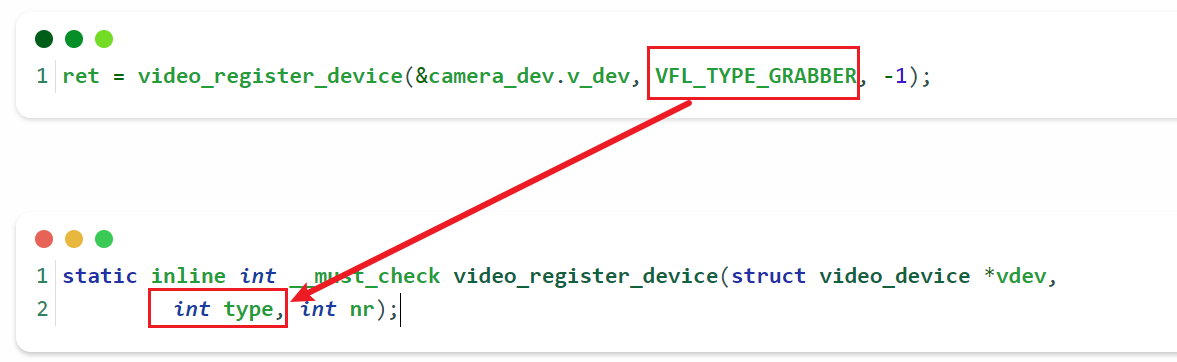
传递了类型为GRABBER,但是没有定义video_device的device_caps,显然我们没有定义这个,那么这个版本的内核需要定义一下这个变量即可解决
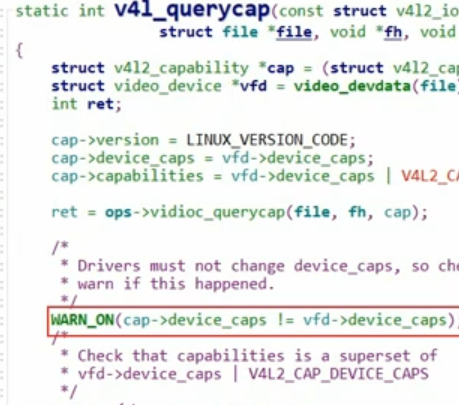
再次编译后,发现出现警告,函数在V4l_querycap 查询设备能力的时候
前面定义的设备能力device_caps不等于绑定的查询能力函数中定义的能力,一致即可