ROS2 中涉及的编程语言以C++和 Python为主,ROS2 中的大多数功能两者都可以实现,在本系 列教程中,如无特殊情况,每一个案例也都会分别使用 C++和 Python 两种方案演示。本节我们将 介绍一个最基本的案例------ROS2 版本的 HelloWorld,通过学习本节内容,你可以了解 ROS2 程序 的编写、编译与执行流程。
1.3.1 案例简介
1.需求
编写 ROS2 程序,要求程序运行时,可以在终端输出文本"Helo World"。
2.准备(创建工作空间)
无论是使用 C++还是 Python 编写 ROS2 程序,都需要依赖于工作空间,在此,我们先实现工作空 间的创建与编译,打开终端,输入如下指令:
mkdir -p ws00_helloworld/src #创建工作空间以及子级目录 src,工作空间名称可以自定义
cd ws00_helloworld #进入工作空间
colcon build #编译
上述指令执行完毕,将创建 ws00_helloworld 目录,且该目录下包含 build、install、log、src 共四 个子级目录。
编译是否成功判断:
主要看编译图标的颜色:
- 绿色:编译成功
- 黄色:编译有警告,不影响代码运行
- 红色:编译有报错
3.流程简介
工作空间创建完毕后,我么可以在工作空间下的 src 目录中编写 C++或 Python 程序,且两种语言 的实现流程大致一致,主要包含如下步骤:
- 创建功能包;
- 编辑源文件;
- 编辑配置文件;
- 编译;
- 执行。
下面两节我们会介绍具体的实现细节。
1.3.2 HelloWorld(C++)
1、创建功能包
终端下,进入 ws00_helloworld/src 目录,使用如下指令创建一个 C++功能包:
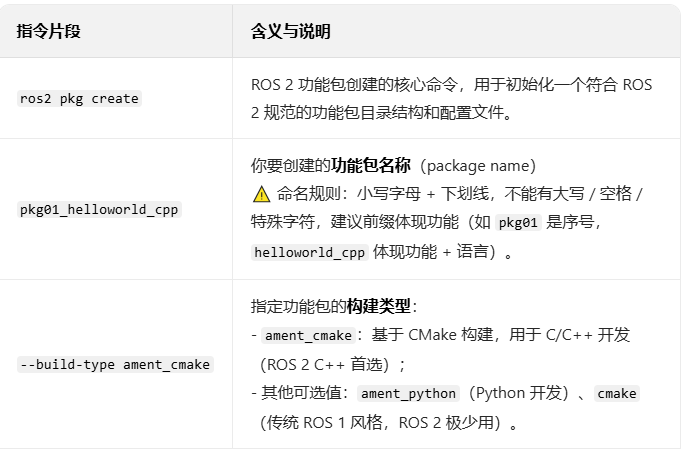
ros2 pkg create pkg01_helloworld_cpp --build-type ament_cmake --dependencies rclcpp --node-name helloworld
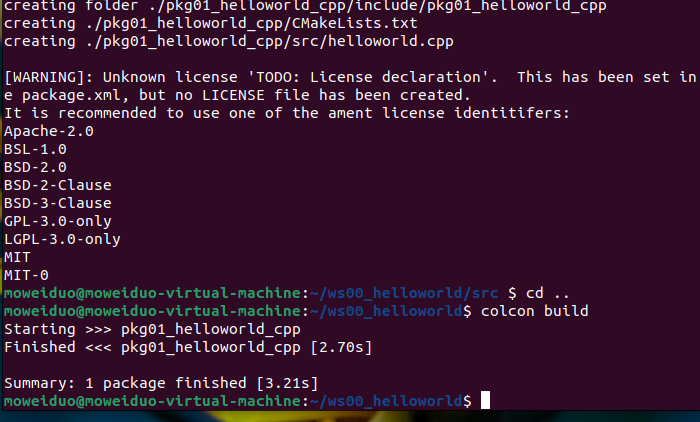
执行完毕,在 src 目录下将生成一个名为 pkg01_helloworld_cpp 的目录,且目录中已经默认生成了 一些子级文件与文件夹。
创建完功能包后,需要回到工作空间,编译代码,指令如下:
cd .. # 返回工作空间
colcon build # 重新编译
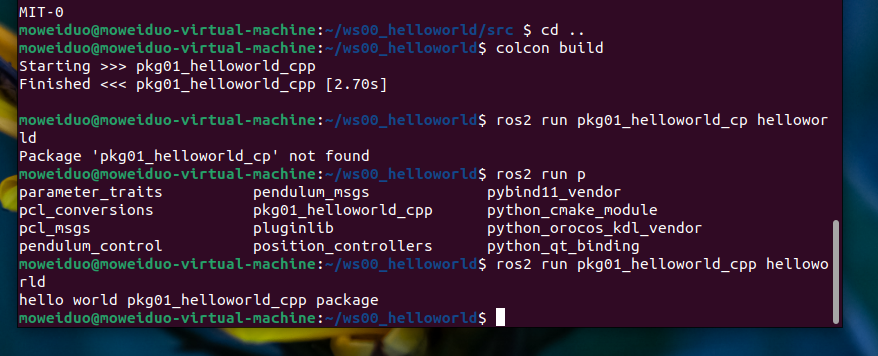
如果想运行代码:
source install/setup.bash # 刷新环境变量
. install /setup.bash # 这个也是刷新环境变量
ros2 run pkg01_helloworld_cpp helloworld
补充说明:

执行后生成的目录结构
执行该指令后,会在当前目录下生成 pkg01_helloworld_cpp 文件夹,核心结构如下:

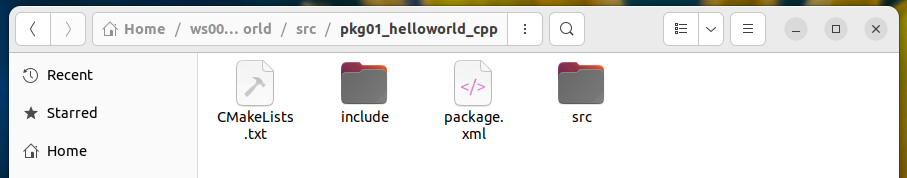
2、编辑源文件
进入 pkg01_helloworld_cpp/src 目录,该目录下有一 helloworld.cpp 文件,修改文件内容如下:
cpp
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
int main(int argc, char ** argv)
{
rclcpp::init(argc,argv);
auto node=rclcpp::Node::make_shared("helloworld_node_cpp");
RCLCPP_INFO(node->get_logger(),"hello world!");
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
}3.编辑配置文件
在步骤 1 创建功能包时所使用的指令已经默认生成且配置了配置文件,不过实际应用中经常需要自 己编辑配置文件,所以在此对相关内容做简单介绍,所使用的配置文件主要有两个,分别是功能包 下的 package.xml 与 CMakeLists.txt。
文件内容如下:
package.xml
XML
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<?xml-model href="http://download.ros.org/schema/package_format3.xsd" schematypens="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"?>
<package format="3">
<name>pkg01_helloworld_cpp</name>
<version>0.0.0</version>
<description>TODO: Package description</description>
<maintainer email="moweiduo@todo.todo">moweiduo</maintainer>
<license>TODO: License declaration</license>
<buildtool_depend>ament_cmake</buildtool_depend>
<depend>rclcpp</depend>
<test_depend>ament_lint_auto</test_depend>
<test_depend>ament_lint_common</test_depend>
<export>
<build_type>ament_cmake</build_type>
</export>
</package><depend>rclcpp</depend>:依赖库
CMakeLists.txt
cpp
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.8)
project(pkg01_helloworld_cpp)
if(CMAKE_COMPILER_IS_GNUCXX OR CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "Clang")
add_compile_options(-Wall -Wextra -Wpedantic)
endif()
# find dependencies
find_package(ament_cmake REQUIRED)
find_package(rclcpp REQUIRED)
add_executable(helloworld src/helloworld.cpp)
target_include_directories(helloworld PUBLIC
$<BUILD_INTERFACE:${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/include>
$<INSTALL_INTERFACE:include>)
target_compile_features(helloworld PUBLIC c_std_99 cxx_std_17) # Require C99 and C++17
ament_target_dependencies(
helloworld
"rclcpp"
)
install(TARGETS helloworld
DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME})
if(BUILD_TESTING)
find_package(ament_lint_auto REQUIRED)
# the following line skips the linter which checks for copyrights
# comment the line when a copyright and license is added to all source files
set(ament_cmake_copyright_FOUND TRUE)
# the following line skips cpplint (only works in a git repo)
# comment the line when this package is in a git repo and when
# a copyright and license is added to all source files
set(ament_cmake_cpplint_FOUND TRUE)
ament_lint_auto_find_test_dependencies()
endif()
ament_package()find_package(rclcpp REQUIRED) 这个是刚刚输入指令:ros2 pkg create pkg01_helloworld_cpp --build-type ament_cmake --dependencies rclcpp --node-name helloworld 的 --dependencies rclcpp生成的
add_executable(helloworld src/helloworld.cpp) :是由 --node-name helloworld 生成的
ament_target_dependencies(helloworld
"rclcpp"
) 意思是说可执行程序需要依赖于rclcpp
install(TARGETS helloworldDESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME}) 给可执行文件设置一个安装目录 在当前功能包下的lib目录
4.编译
终端下进入到工作空间,执行如下指令:
colcon build
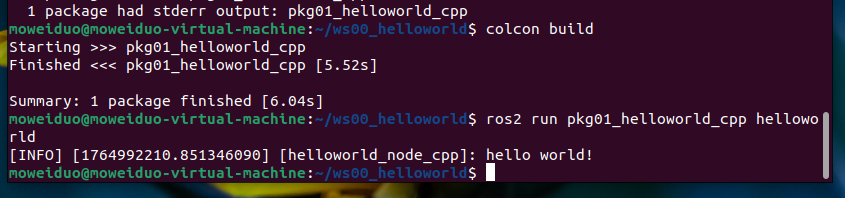
5.执行
终端下进入到工作空间,执行如下指令:
. install /setup.bash # 这个也是刷新环境变量
ros2 run pkg01_helloworld_cpp helloworld 执行程序文件
1.3.3 HelloWorld(Python)
1.创建功能包
终端下,进入 ws00_helloworld/src 目录,使用如下指令创建一个 python 功能包:
ros2 pkg create pkg02_helloworld_py --build-type ament_python --dependencies rclpy --node-name helloworld
执行完毕,在 src 目录下将生成一个名为 pkg02_helloworld_py 的目录,且目录中已经默认生成了 一些子级文件与文件夹。
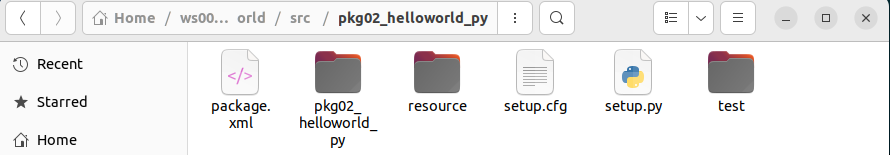
2.编辑源文件
进入 pkg02_helloworld_py/pkg02_helloworld_py 目录,该目录下有一 helloworld.py 文件,修改文 件内容如下:
python
import rclpy
def main(args=None): # 补充args参数(ROS2标准写法),与rclpy.init匹配
# 初始化 ROS2
rclpy.init(args=args)
# 创建节点
node = rclpy.create_node("helloworld_py_node")
# 输出文本
node.get_logger().info("hello world!")
# 释放资源
rclpy.shutdown()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main() # 统一4空格缩进运行指令:
. install /setup.bash
ros2 run pkg02_helloworld_py helloworld
3.编辑配置文件
与 C++类似的,在步骤 1 创建功能包时所使用的指令也已经默认生成且配置了配置文件,不过实际 应用中经常需要自己编辑配置文件,所以在此对相关内容做简单介绍,所使用的配置文件主要有两 个,分别是功能包下的 package.xml 与 setup.py。
文件内容如下:
setup.py
python
from setuptools import find_packages, setup
package_name = 'pkg02_helloworld_py'
setup(
name=package_name,
version='0.0.0',
packages=find_packages(exclude=['test']),
data_files=[
('share/ament_index/resource_index/packages',
['resource/' + package_name]),
('share/' + package_name, ['package.xml']),
],
install_requires=['setuptools'],
zip_safe=True,
maintainer='moweiduo',
maintainer_email='moweiduo@todo.todo',
description='TODO: Package description',
license='TODO: License declaration',
extras_require={
'test': [
'pytest',
],
},
# 此处是程序入口
entry_points={
'console_scripts': [
'helloworld = pkg02_helloworld_py.helloworld:main'
],
},
)注释部分以后可能需要根据实际情况修改。
package.xml
XML
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<?xml-model href="http://download.ros.org/schema/package_format3.xsd" schematypens="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"?>
<package format="3">
<name>pkg02_helloworld_py</name>
<version>0.0.0</version>
<description>TODO: Package description</description>
<maintainer email="moweiduo@todo.todo">moweiduo</maintainer>
<license>TODO: License declaration</license>
<!-- 所需要依赖 -->
<depend>rclpy</depend>
<depend> --node-name</depend>
<depend>helloworld</depend>
<test_depend>ament_copyright</test_depend>
<test_depend>ament_flake8</test_depend>
<test_depend>ament_pep257</test_depend>
<test_depend>python3-pytest</test_depend>
<export>
<build_type>ament_python</build_type>
</export>
</package>注释部分以后需要根据实际的包依赖进行添加或修改。
4.编译
终端下进入到工作空间,执行如下指令:
colcon build
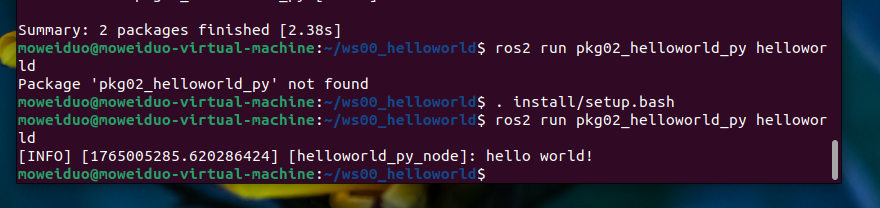
5.执行
终端下进入到工作空间,执行如下指令:
. install/setup.bash
ros2 run pkg02_helloworld_py helloworld
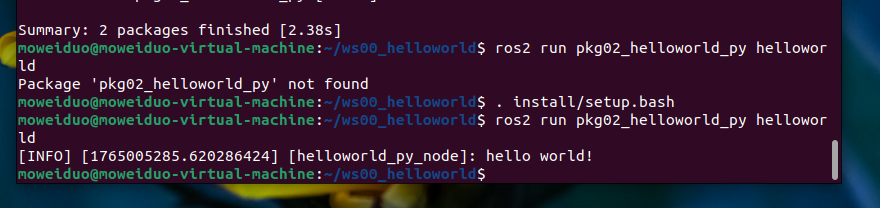
1.3.4 运行优化
每次终端中执行工作空间下的节点时,都需要调用. install/setup.bash 指令,使用不便,优化策 略是,可以将该指令的调用添加进~/setup.bash,操作格式如下:
法一:
echo "source /{工作空间路径}/install/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc
法二:
cd ~/ws00_helloworld # 先进入工作空间根目录
echo "source $(pwd)/install/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc
示例:
echo "source /home/ros2/ws00_helloworld/install/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc
以后再启动终端时,无需手动再手动刷新环境变量,使用更方便。(重启终端就好)