🚀简介:每天都在变得更智能的AI
想象一下,有一个由AI科学家组成的团队在你的研究实验室里工作。其中一位专长于遗传学,另一位专长于药理学,还有一位资深研究员负责协调一切。而最吸引人的部分是:这个团队会从每一次实验中学习,并且每天都在进步。
传统的AI系统使用静态提示------它们遵循指令但从不改进。自我改进的智能体则不同:它们从经验中学习,相互协作,并通过强化学习不断优化自身性能。
阅读完本指南后,您将了解到:
-
为什么静态提示还不够
-
如何构建多智能体训练系统
-
三个关键算法(SFT、PPO、上下文多臂老虎机)
-
如何实现并评估你自己的自我改进智能体
🤔问题:为何静态提示会失败
局限性
❌ 无适应性 --- 提示无法适应新情况 ❌ 无学习能力 --- 同样的错误永远重复 ❌ 无协作性 --- 每个AI独立工作 ❌ 手动更新 --- 你需要不断重写提示
解决方案:分层训练
我们不是用一种算法来处理所有事情,而是使用:
-
监督学习用于创意头脑风暴
-
强化学习用于复杂决策
-
上下文多臂老虎机用于战略选择
不妨把它想象成一个真正的研究实验室:初级研究人员、资深科学家和一位导师------每个人的学习方式都不同。
🏗️完整架构
这就是我们正在构建的系统:
按回车键或点击以查看全尺寸图像
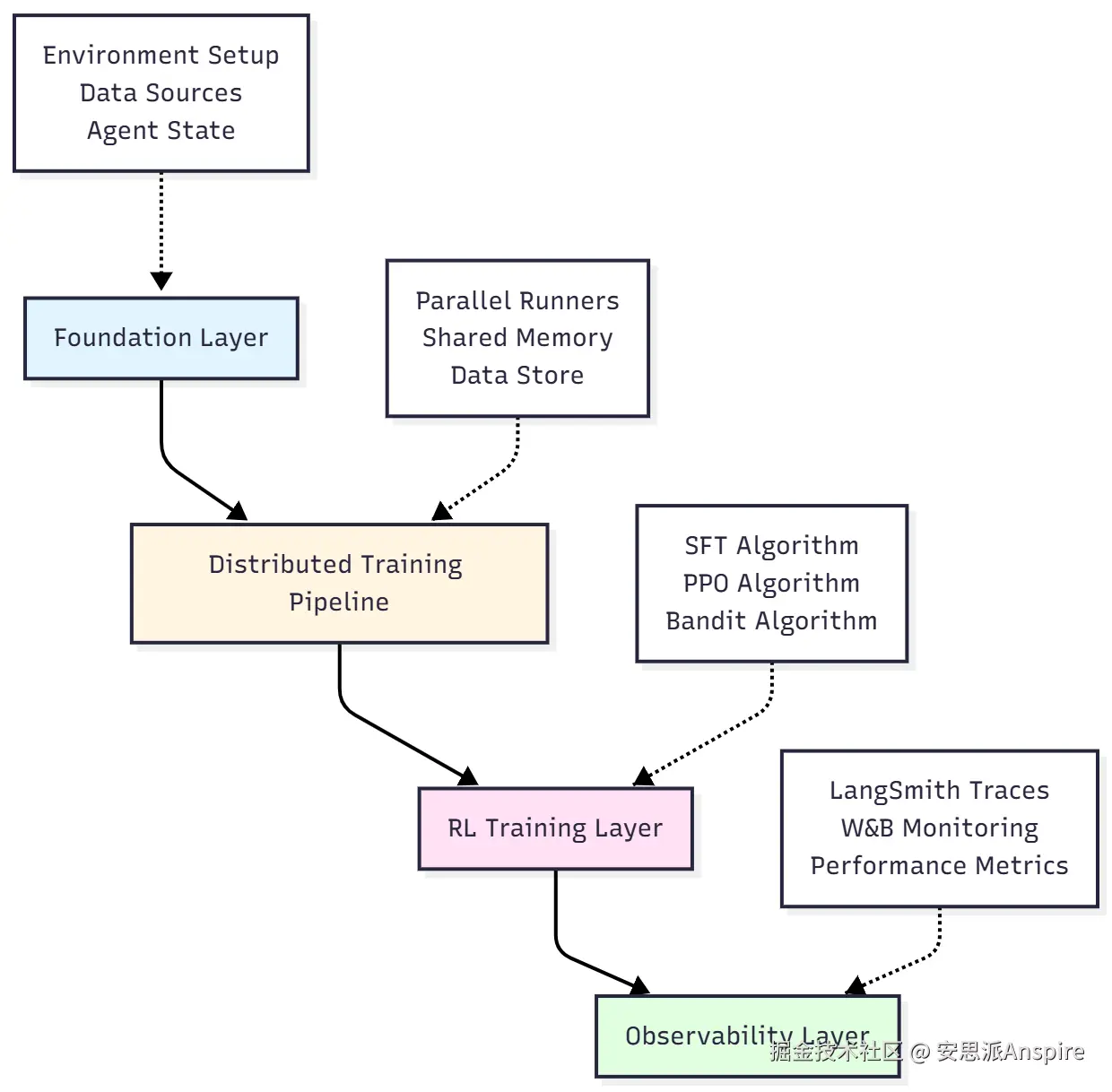
层分解
1. 基础层
-
API配置和依赖项
-
知识库(PubMedQA数据集 --- 1000个医学问题)
-
共享内存结构(AgentState)
-
科学工具(PubMed搜索、蛋白质数据库)
2. 分布式训练管道
-
多个智能体并行运行(4个并发滚动)
-
体验收集的中央数据存储库
-
用于管理多个模型的大语言模型代理
3. 强化学习训练层
-
SFT:从成功案例中学习
-
PPO:通过试错学习
-
上下文多臂老虎机:学习选择策略
4. 可观测性层
-
实时奖励追踪
-
深度追踪分析
-
绩效仪表盘
按回车键或点击以查看全尺寸图像

👥 认识您的AI研究团队
我们正在组建一个由9名专业代理组成的分层团队:
按回车键或点击以查看全尺寸图像
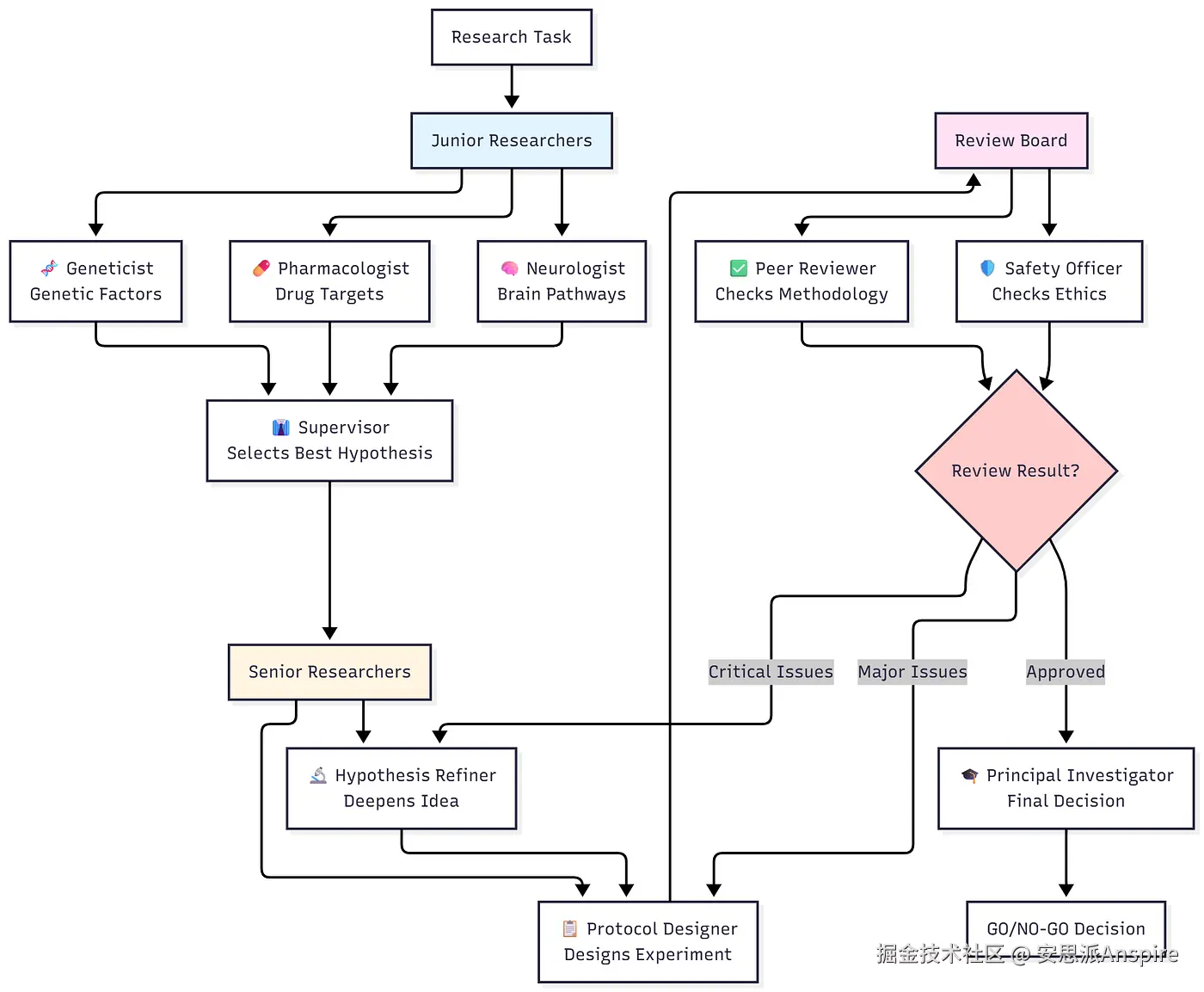
工作流程
-
三名初级研究人员(并行)集思广益提出假设
-
主管选出最有前途的
-
高级研究人员完善并设计详细方案
-
审核委员会对质量和安全进行评估
-
如果需要重大修订则循环返回
-
PI做出最终决定(继续/停止)
按回车键或点击以查看全尺寸图像
🎯三种训练算法详解
层级结构的每一层学习方式都不同:
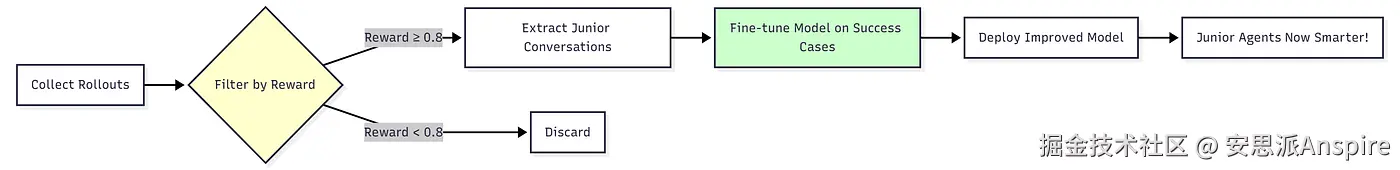
1️⃣ 有监督微调(SFT)------初级研究员
**它的作用:**通过研究成功案例来学习
流程:
按回车键或点击以查看全尺寸图像
示例:
bash
# Before Training
Hypothesis: "Study genes in Alzheimer's" # Too vague
# After SFT Training
Hypothesis: "Investigate the role of APOE4 variants in amyloid-beta
clearance dysfunction in early-onset Alzheimer's disease, supported
by recent findings in Nature Genetics (2024)" # Specific, evidence-based关键指标:
-
训练数据:约200个高质量对话
-
训练时间:在单GPU上2 - 4小时
-
改进:假设质量提高35%
2️⃣近端策略优化(PPO)------高级研究员
**它的作用:**通过探索和反馈进行学习
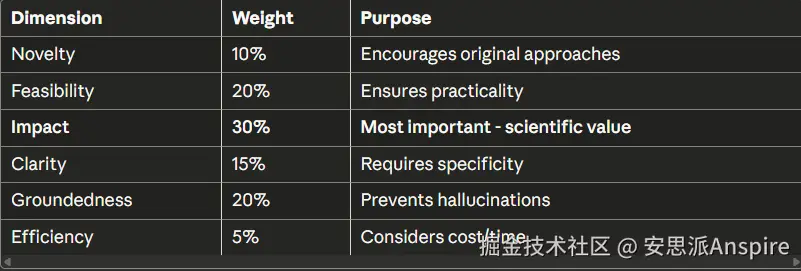
奖励函数:
我们使用6个维度,而不是简单的"好/坏":
按回车键或点击以查看全尺寸图像
学习循环:
按回车键或点击以查看全尺寸图像
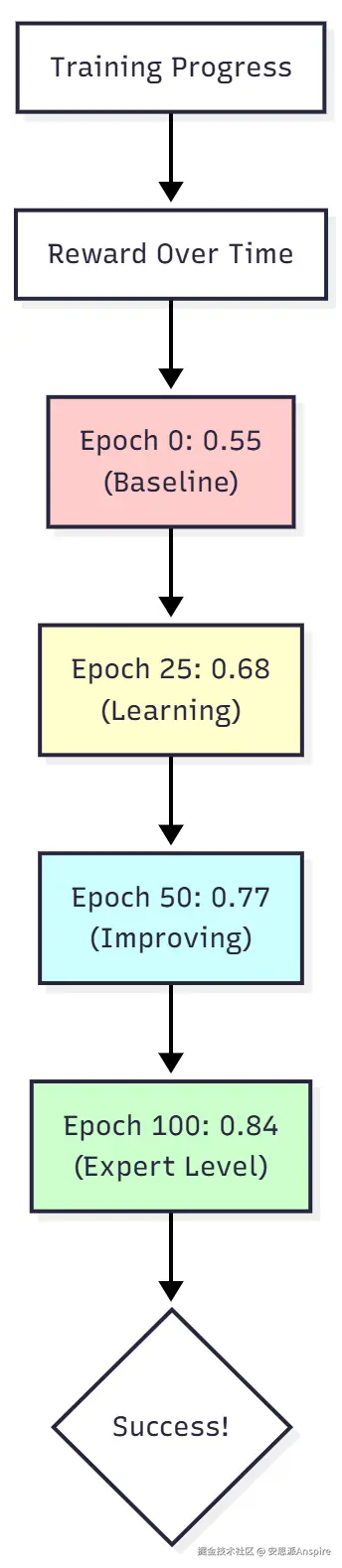
示例结果:
ini
# Training Progress
Epoch 0: Avg Reward = 0.55 # Baseline (mediocre protocols)
Epoch 25: Avg Reward = 0.68 # Learning...
Epoch 50: Avg Reward = 0.77 # Strong improvement
Epoch 100: Avg Reward = 0.84 # Expert-level performance!
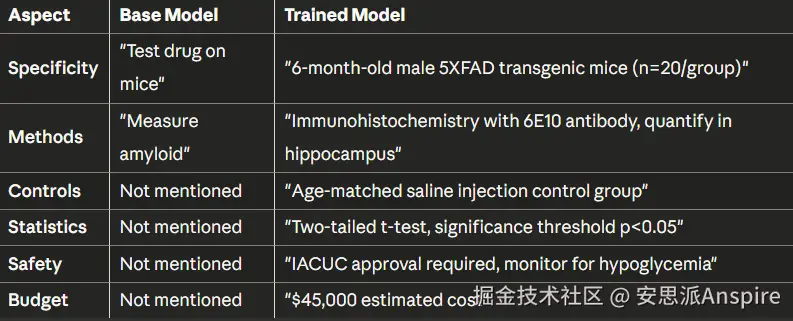
# Improvement: +53%实际输出比较:
PPO之前:
标题:测试药物在小鼠身上步骤: 1. 获取小鼠2. 给药3. 测量结果
PPO之后:
yaml
Title: Pre-Clinical Evaluation of Liraglutide on Amyloid-β
Pathology in 5XFAD Mouse Model
Steps:
1. Animal Model: 6-month-old male 5XFAD transgenic mice (n=20/group)
2. Treatment: Liraglutide 25 nmol/kg/day, subcutaneous, 8 weeks
3. Control Group: Age-matched saline injections
4. Primary Endpoint: Immunohistochemistry with 6E10 antibody
5. Quantification: Amyloid plaque burden in hippocampus/cortex
6. Statistics: Two-tailed t-test, significance p<0.05
Safety: IACUC approval required. Monitor for hypoglycemia.
Budget: $45,000差异十分显著------从模糊不清到达到发表标准。
3️⃣ 上下文多臂老虎机 --- 监督者
**它的作用:**学习哪些假设能带来成功
挑战:
每个研究周期都会提出3个假设。主管必须选择一个。但是哪个会导致最好的结果呢?
学习方式:
按回车键或点击以查看全尺寸图像

学习模式示例:
yaml
# After 200 decisions, the supervisor learns:
Pattern 1: "Hypotheses mentioning specific proteins (APOE4, TREM2)
tend to succeed" → Success rate: 82%
Pattern 2: "Vague hypotheses about 'inflammation' or 'oxidative stress'
tend to fail" → Success rate: 31%
Pattern 3: "Drug repurposing ideas (GLP-1, metformin) show high impact"
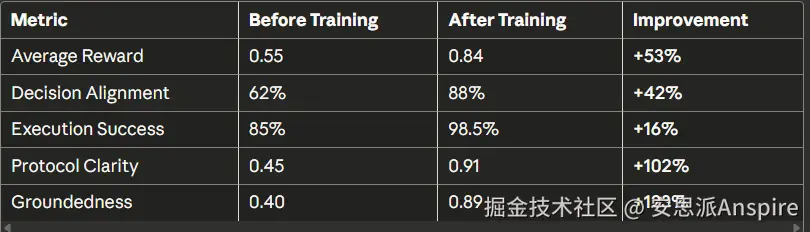
→ Success rate: 88%性能:
-
训练前:与专家的决策一致性为62%
-
训练后:88%的决策一致性
-
改进幅度:+42%
🛠️实施:分步指南
第一阶段:设置
安装依赖项:
ini
# Fast installation with uv
uv pip install langchain langgraph langchain_openai \
tavily-python agentlightning[verl,apo] \
unsloth[pt231] datasets wandb pandas rich配置 API 密钥:
lua
import os
os.environ['OPENAI_API_KEY'] = 'your-key'
os.environ['TAVILY_API_KEY'] = 'your-key'
os.environ['WANDB_API_KEY'] = 'your-key'
os.environ['LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2'] = 'true'阶段2:加载数据
python
from datasets import load_dataset
def load_research_data():
# Load PubMedQA dataset
dataset = load_dataset("pubmed_qa", "pqa_l")
df = dataset['train'].to_pandas()
tasks = []
for _, row in df.iterrows():
task = {
'id': str(row['PUBMED_ID']),
'goal': row['QUESTION'], # Research question
'context': " ".join(row['CONTEXTS']), # Scientific papers
'expected_decision': row['final_decision'] # Ground truth
}
tasks.append(task)
# 80/20 split
split = int(0.8 * len(tasks))
return tasks[:split], tasks[split:]
train_data, val_data = load_research_data()
print(f"✅ Loaded {len(train_data)} training samples")阶段3:定义代理状态
共享内存结构:
python
from typing import TypedDict, List, Literal
from langchain_core.messages import BaseMessage
class AgentState(TypedDict):
# Control flow
messages: List[BaseMessage]
sender: str # For ReAct loops
turn_count: int
# Junior phase
initial_hypotheses: List[dict]
# Supervisor phase
selected_hypothesis: dict
# Senior phase
experimental_protocol: dict
# Review phase
peer_review: dict
safety_review: dict
# Final output
final_decision: str # "GO" or "NO-GO"
final_evaluation: dict阶段4:构建多智能体图
scss
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
def build_research_graph():
workflow = StateGraph(AgentState)
# Add all 9 agent nodes
for agent_name in ["Geneticist", "Pharmacologist", "Neurologist",
"Supervisor", "HypothesisRefiner", "ProtocolDesigner",
"PeerReviewer", "SafetyOfficer", "PrincipalInvestigator"]:
workflow.add_node(agent_name, create_agent_node(agent_name))
# Add tool execution node
workflow.add_node("execute_tools", ToolNode(all_tools))
# Define workflow edges
workflow.add_edge(START, "Geneticist")
workflow.add_edge(START, "Pharmacologist")
workflow.add_edge(START, "Neurologist")
# All juniors → Supervisor
workflow.add_edge("Geneticist", "Supervisor")
workflow.add_edge("Pharmacologist", "Supervisor")
workflow.add_edge("Neurologist", "Supervisor")
# Supervisor → Senior team
workflow.add_edge("Supervisor", "HypothesisRefiner")
workflow.add_edge("HypothesisRefiner", "ProtocolDesigner")
# Protocol → Review board
workflow.add_edge("ProtocolDesigner", "PeerReviewer")
workflow.add_edge("PeerReviewer", "SafetyOfficer")
# Conditional routing after review
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"SafetyOfficer",
route_based_on_severity, # Smart routing function
{
"CRITICAL": "HypothesisRefiner", # Start over
"MAJOR": "ProtocolDesigner", # Revise protocol
"APPROVED": "PrincipalInvestigator" # Move forward
}
)
workflow.add_edge("PrincipalInvestigator", END)
return workflow.compile()
graph = build_research_graph()
print("✅ Multi-agent workflow built!")第五阶段:创建奖励系统
大语言模型作为裁判的评估器:
python
def protocol_evaluator(protocol, scientific_context):
"""Score protocol on 6 dimensions"""
evaluator_llm = ChatOpenAI(model="mixtral-8x7b")
prompt = f"""
You are expert scientists evaluating this protocol:
CONTEXT: {scientific_context}
PROTOCOL: {protocol}
Rate 0.0-1.0 on:
- Novelty
- Feasibility
- Impact
- Clarity
- Groundedness (evidence-based)
- Efficiency
"""
scores = evaluator_llm.evaluate(prompt)
return scores
def get_weighted_reward(scores):
"""Combine scores with priorities"""
return (
0.10 * scores['novelty'] +
0.20 * scores['feasibility'] +
0.30 * scores['impact'] + # Most important!
0.15 * scores['clarity'] +
0.20 * scores['groundedness'] +
0.05 * scores['efficiency']
)阶段6:建立培训基础设施
分布式执行:
makefile
import agentlightning as agl
# Run 4 agents in parallel
strategy = {
"type": "cs", # Client-Server
"n_runners": 4,
"server_port": 48000
}
# LLM Proxy for model routing
proxy_config = {
"port": 48001,
"model_list": [
{"model_name": "Qwen/Qwen2-1.5B-Instruct",
"litellm_params": {"model": "ollama/qwen2:1.5b"}},
{"model_name": "senior_researcher_llm", # Training target
"litellm_params": {"model": "ollama/llama3"}},
{"model_name": "mistralai/Mixtral-8x7B-Instruct-v0.1",
"litellm_params": {"model": "ollama/mixtral"}}
]
}
# Real-time monitoring
monitoring_hook = WandbLoggingHook(project_name="AI-Research-Lab")阶段7:主训练循环
ini
def full_training_pipeline():
# === Phase 1: Initial Data Collection ===
print("📊 Phase 1: Gathering baseline data...")
trainer = agl.Trainer(
n_runners=4,
strategy=strategy,
hooks=[monitoring_hook]
)
agent = MedicalResearchAgent(graph, protocol_evaluator)
trainer.dev(agent, train_data[:10]) # Quick 10-sample run
# === Phase 2: Train Junior Researchers (SFT) ===
print("🎓 Phase 2: Training juniors with SFT...")
sft_trainer = agl.Trainer(algorithm=SFTOnSuccess())
sft_trainer.fit(agent) # Learns from successful traces
# === Phase 3: Train Senior Researchers (PPO) ===
print("🎮 Phase 3: Training seniors with PPO...")
ppo_config = {
"algorithm": {"adv_estimator": "grpo"},
"data": {"train_batch_size": 4},
"actor_rollout_ref": {
"model": {"path": "meta-llama/Llama-3-8B-Instruct"}
},
"trainer": {
"total_training_steps": 100,
"test_freq": 10
}
}
ppo_trainer = agl.Trainer(
algorithm=agl.VERL(ppo_config),
n_runners=4,
strategy=strategy,
adapter=custom_adapter,
hooks=[monitoring_hook]
)
ppo_trainer.fit(agent, train_data, val_data)
# === Phase 4: Train Supervisor (Contextual Bandit) ===
print("🎰 Phase 4: Training supervisor with bandit...")
bandit_trainer = agl.Trainer(algorithm=ContextualBandit())
bandit_trainer.fit(agent)
print("✅ Training complete!")
# Execute
full_training_pipeline()📊评估与结果
定量指标
学习曲线可视化:
最终结果表:
按回车键或点击以查看全尺寸图像
定性分析
并排比较:
按回车键或点击以查看全尺寸图像
🎯关键要点与最佳实践
✅ 应该做的事
-
针对不同角色采用不同算法 ------ SFT用于创意,PPO用于复杂推理,Bandits用于选择
-
设计多维度奖励------捕捉细微的质量差异,而不仅仅是"好/坏"
-
实现可观测性 ------ LangSmith追踪 + W&B监控
-
从小处着手,逐步扩展 --- 在全面训练前用10个样本验证概念
-
过滤训练数据 --- 从成功(奖励 ≥ 0.8)中学习,而非失败
❌ 禁忌事项
-
不要用一种算法解决所有问题------不同的任务需要不同的学习方法
-
不要跳过验证 --- 始终预留20%用于测试
-
不要忽视定性评估------数字并不能说明全部情况
-
不要在所有数据上进行训练 --- 质量 > 数量
-
不要忘记安全限制 --- MAX_TURNS可防止无限循环
🔴常见陷阱
**问题:**PPO奖励在初始改善后下降
**解决方案:**降低学习率(1e-6 → 1e-7),增加批量大小
**问题:**智能体虚构出上下文中不存在的事实
**解决方案:**增加接地性权重(0.20 → 0.35),惩罚无根据的主张
**问题:**训练因GPU内存不足而崩溃
**解决方案:**使用梯度检查点、减小批量大小或使用4位量化
💡 最终思考
自我改进的AI智能体代表了我们构建AI系统方式的根本性转变。我们不再手动编写提示并寄希望于它们能起作用,而是创建这样的系统:
✨从经验中学习 🤝智能协作 📈持续改进 🎯为复杂目标优化
你在这里学到的框架------使用专门算法的分层训练------其应用范围远远超出医学研究:
-
软件工程:初级开发者编写代码,资深开发者审核,负责人做决策
-
内容创作:作者起草,编辑润色,出版者审批
-
商业战略:分析师负责研究,顾问负责综合,高管负责决策
未来并不在于更大的模型或更长的提示。它在于学会学习的智能系统。
现在就去打造令人惊叹的东西吧!🚀