授权
授权是独立于认证的存在
认证是负责如何登录,认证成功 == 登录成功
认证成功之后,能访问哪些接口,哪些方法
认证方式的不同,不会影响授权
认证成功之后,能做什么能访问什么,是由授权决定的
- 查看授权的配置
-
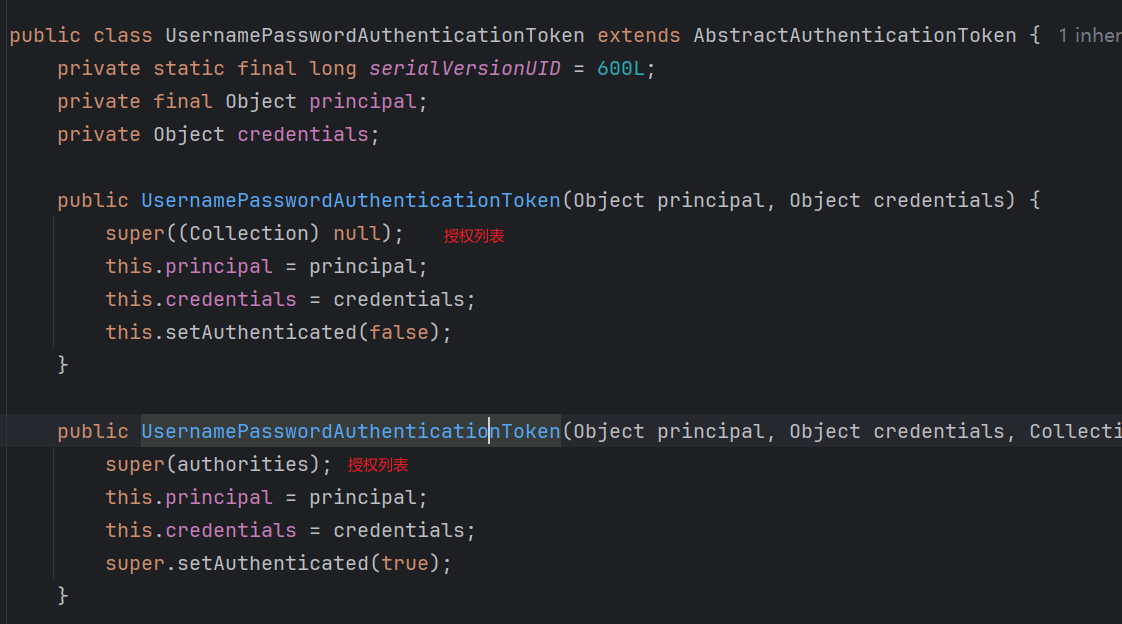
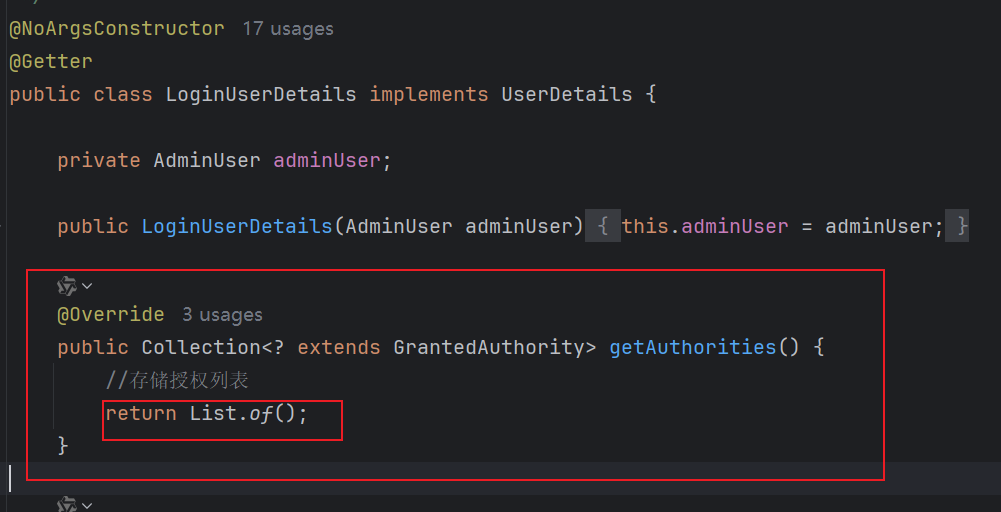
授权列表的来源,是UserDetails
-
在登录的时候,在UserDetailsService中查询出来并赋值的
-
想要给授权列表赋值,需要更改登录的逻辑
一、准备工作
在登录的时候,查询出用户的角色信息 + 菜单信息
-
角色授权
-
授权码授权
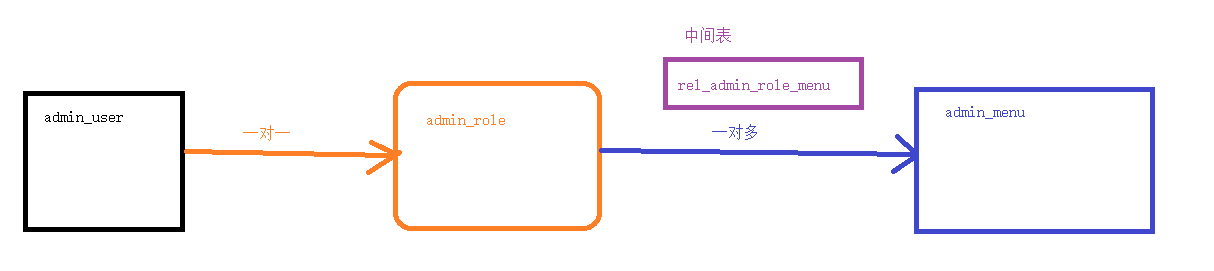
1、生成代码
根据数据库,生成三张表的代码
2、重新修改登录接口
- AdminUserService
@Override
public AdminUser getByUsername(String username) {
LambdaQueryWrapper<AdminUser> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq(AdminUser::getUsername,username);
AdminUser adminUser = getOne(queryWrapper);
if (adminUser != null){
AdminRole role = roleService.getByRid(adminUser.getRoleId().intValue());
adminUser.setAdminRole(role);
}
return adminUser;
}- AdminRoleService
@Service("adminRoleService")
public class AdminRoleServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<AdminRoleDao, AdminRole> implements AdminRoleService {
@Resource
AdminMenuService adminMenuService;
@Override
public AdminRole getByRid(Integer uid) {
AdminRole adminRole = getById(uid);
if (adminRole != null){
//查询菜单的信息
List<AdminMenu> menuList = adminMenuService.getListByRid(adminRole.getRid());
adminRole.setMenuList(menuList);
}
return adminRole;
}
}- AdminMenuDao
public interface AdminMenuDao extends BaseMapper<AdminMenu> {
@Select("select menu.* from " +
"admin_menu menu,rel_admin_role_menu rel " +
"where menu.mid = rel.mid and " +
"rel.rid = #{rid} ")
List<AdminMenu> selectListByRid(Integer rid);
}- AdminMenuService
@Service("adminMenuService")
public class AdminMenuServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<AdminMenuDao, AdminMenu> implements AdminMenuService {
@Resource
AdminMenuDao adminMenuDao;
@Override
public List<AdminMenu> getListByRid(Integer rid) {
List<AdminMenu> allList = adminMenuDao.selectListByRid(rid);
//打算区分父子级
//获取1级菜单
List<AdminMenu> oneList = allList.stream()
.filter(adminMenu -> adminMenu.getPid() == -1)
.toList();
oneList.forEach(one -> {
//获取当前循环的1级菜单的子菜单
List<AdminMenu> childList = allList.stream().map(adminMenu -> {
if (one.getMid().equals(adminMenu.getPid())) {
return adminMenu;
}
return null;
}).filter(Objects::nonNull).toList();
one.setChildList(childList);
});
return oneList;
}
}- AdminMenuServic---AI进化版
@Service("adminMenuService")
public class AdminMenuServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<AdminMenuDao, AdminMenu> implements AdminMenuService {
@Resource
AdminMenuDao adminMenuDao;
@Override
public List<AdminMenu> getListByRid(Integer rid) {
List<AdminMenu> allList = adminMenuDao.selectListByRid(rid);
// 使用stream流操作将allList按照父子级分离
// 先按pid分组
Map<Integer, List<AdminMenu>> menuMap = allList.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(AdminMenu::getPid));
// 获取一级菜单(pid为-1的菜单)
List<AdminMenu> oneList = menuMap.getOrDefault(-1, List.of());
// 为每个一级菜单设置子菜单列表
oneList.forEach(one -> {
one.setChildList(menuMap.getOrDefault(one.getMid(), List.of()));
});
return oneList;
}
}3、修改UserDetails的授权方法
@Override
public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() {
List<GrantedAuthority> list = new ArrayList<>();
//根据角色授权
AdminRole adminRole = adminUser.getAdminRole();
if (adminRole != null){
GrantedAuthority authority =
new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_" + adminRole.getCode());
list.add(authority);
}
//存储授权列表
return list;
}二、测试角色授权
编写测试接口,提前明确,哪个角色,可以访问 哪个接口。
如果一个接口写完了之后,没有配置权限,表明所有已经认证的用户,都可以访问
1、已有接口
-
/game/f1
-
/game/f2
-
/game/f3
2、已有角色
-
admin
-
test
3、设计权限
-
只有admin角色的用户,可以访问f1方法
-
只有test角色的用户,可以访问f2方法
-
只有拥有admin或者test,可以访问f3方法
4、实现设计,修改配置类
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
....
http.authorizeHttpRequests(auth -> auth
//只有admin角色的用户,可以访问f1方法
.requestMatchers("/game/f1").hasRole("admin")
//只有test角色的用户,可以访问f2方法
.requestMatchers("/game/f2").hasRole("test")
//只有拥有admin或者test,可以访问f3方法
.requestMatchers("/game/f3").hasAnyRole("admin","test")
.requestMatchers("/loginpage.html", "/login/**", "/jsonlogin", "/phoneLogin")
.permitAll()
.anyRequest()
.authenticated() //其他页面,要登录之后才能访问
);//放过登录接口,以及静态页面
return http.build();
....
}三、角色的继承
设计,让test拥有的权限,admin也拥有
admin 拥有 test的权限
// =========角色继承配置=============
@Bean
public RoleHierarchy roleHierarchy(){
RoleHierarchyImpl hierarchy = new RoleHierarchyImpl();
hierarchy.setHierarchy("ROLE_admin > ROLE_test");
return hierarchy;
}
//支持角色继承的授权管理器
public AuthorityAuthorizationManager<RequestAuthorizationContext> testRoleAuthorizationManager(){
//通过静态方法创建实例,再绑定角色来继承
AuthorityAuthorizationManager<RequestAuthorizationContext> manager =
AuthorityAuthorizationManager.hasRole("test");
manager.setRoleHierarchy(roleHierarchy());
return manager;
}http.authorizeHttpRequests(auth -> auth
.requestMatchers("/game/f2").access(testRoleAuthorizationManager())
);//放过登录接口,以及静态页面- 完整配置
// =========角色继承配置=============
@Bean
public RoleHierarchy roleHierarchy(){
RoleHierarchyImpl hierarchy = new RoleHierarchyImpl();
hierarchy.setHierarchy("ROLE_admin > ROLE_test");
return hierarchy;
}
//支持角色继承的授权管理器
public AuthorityAuthorizationManager<RequestAuthorizationContext> testRoleAuthorizationManager(){
//通过静态方法创建实例,再绑定角色来继承
AuthorityAuthorizationManager<RequestAuthorizationContext> manager =
AuthorityAuthorizationManager.hasRole("test");
manager.setRoleHierarchy(roleHierarchy());
return manager;
}
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.cors(cors -> cors.configurationSource(corsConfigurationSource()));
http.securityContext(context -> context.securityContextRepository(securityContextRepository()));
//因为当前json登录功能,和用户名密码登录功能类似,
// 所以把jsonfilter放到UsernamePasswordAuthenticaitonFilter相同的位置
http.addFilterAt(jsonFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
http.addFilterAt(phoneFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
//关闭csrf 跨域请求伪造的控制
http.csrf(csrf -> csrf.disable());
http.authorizeHttpRequests(auth -> auth
//只有admin角色的用户,可以访问f1方法
.requestMatchers("/game/f1").hasRole("admin")
//只有test角色的用户,可以访问f2方法
//.requestMatchers("/game/f2").hasRole("test")
.requestMatchers("/game/f2").access(testRoleAuthorizationManager())
//只有拥有admin或者test,可以访问f3方法
.requestMatchers("/game/f3").hasAnyRole("admin","test")
.requestMatchers("/loginpage.html", "/login/**", "/jsonlogin", "/phoneLogin")
.permitAll()
.anyRequest()
.authenticated() //其他页面,要登录之后才能访问
);//放过登录接口,以及静态页面
// ↓配置表单提交
http.formLogin(form -> {
// 确保认证信息被正确设置并保存到session中
form.loginPage("/loginpage.html") //自定义登录页面的路径
.loginProcessingUrl("/javasmlogin") //表单提交的路径
.usernameParameter("uname") //自定义用户名的参数名(默认是username)
.passwordParameter("pwd")
//Authentication 是 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken-- principal实际的值,UserDetails
.successHandler(this::createSuccessJson)
//AuthenticationException 包含了 登录失败之后的 异常信息
.failureHandler((request, response, exception) ->
createFailJson(response, exception)
)
.permitAll(); //以上提到的路径,都放行
}).authenticationManager(jsonAuthenticationManager());
//注销登录
http.logout(logout -> logout
.logoutUrl("/logout")
//退出登录的时候,返回用户信息
.logoutSuccessHandler((r, response, a) -> createSuccessJson(response, "退出登录成功!"))
.permitAll()
);
//未登录异常提示
http.exceptionHandling().authenticationEntryPoint((request, response, e) ->
createFailJson(response, "当前用户未登录,请先登录再访问"));
return http.build();
}四、权限标识授权
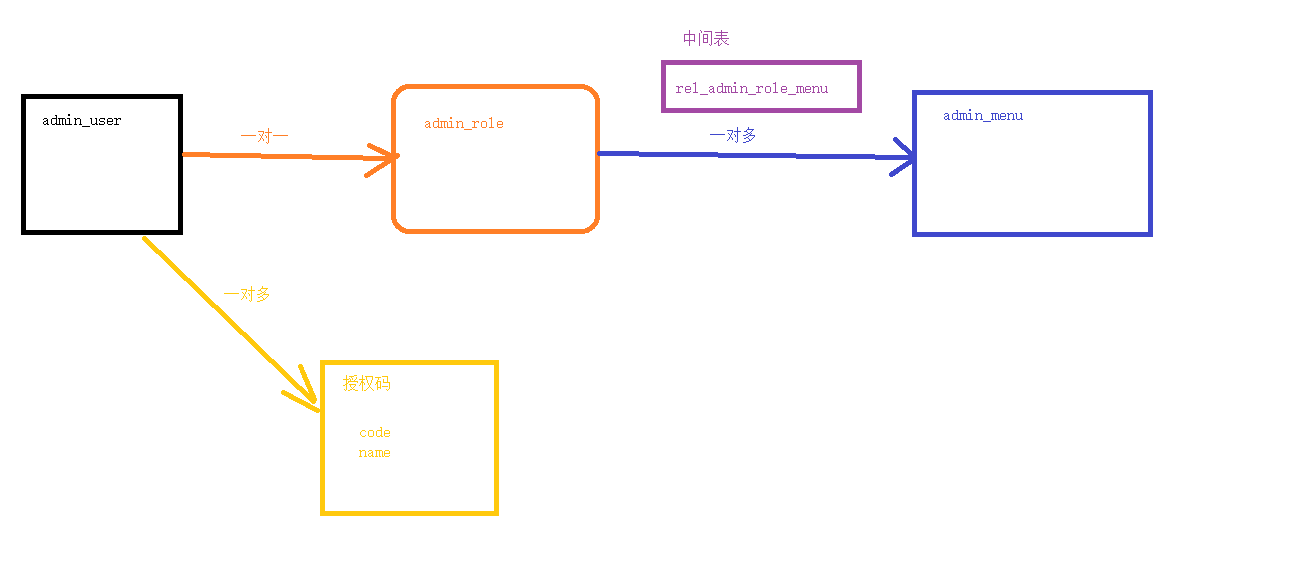
1、新建数据库
CREATE TABLE `admin_user_author` (
`aid` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`code` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`aid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;- 关系表
CREATE TABLE `rel_admin_user_author` (
`aid` int NOT NULL,
`uid` int NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`aid`,`uid`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;2、添加模拟数据
INSERT INTO `qingqing`.`admin_user_author` (`name`, `code`) VALUES ('图书', 'book');
INSERT INTO `qingqing`.`admin_user_author` (`name`, `code`) VALUES ('游戏', 'game');
INSERT INTO `qingqing`.`admin_user_author` (`name`, `code`) VALUES ('音乐', 'music');- 关系表
INSERT INTO `qingqing`.`rel_admin_user_author` (`aid`, `uid`) VALUES (1, 1004);
INSERT INTO `qingqing`.`rel_admin_user_author` (`aid`, `uid`) VALUES (2, 1004);
INSERT INTO `qingqing`.`rel_admin_user_author` (`aid`, `uid`) VALUES (3, 1004);
INSERT INTO `qingqing`.`rel_admin_user_author` (`aid`, `uid`) VALUES (1, 1008);
INSERT INTO `qingqing`.`rel_admin_user_author` (`aid`, `uid`) VALUES (2, 1010);3、生成代码
@TableField(exist = false)
private List<AdminUserAuthor> authorList;4、登录的时候,查询授权码列表
@Override
public AdminUser getByUsername(String username) {
LambdaQueryWrapper<AdminUser> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq(AdminUser::getUsername,username);
AdminUser adminUser = getOne(queryWrapper);
if (adminUser != null){
AdminRole role = roleService.getByRid(adminUser.getRoleId().intValue());
adminUser.setAdminRole(role);
//授权码
List<AdminUserAuthor> authorList = authorService.getListByUid(adminUser.getUid());
adminUser.setAuthorList(authorList);
}
return adminUser;
}@Service("adminUserAuthorService")
public class AdminUserAuthorServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<AdminUserAuthorDao, AdminUserAuthor> implements AdminUserAuthorService {
@Resource
AdminUserAuthorDao authorDao;
@Override
public List<AdminUserAuthor> getListByUid(Integer uid) {
return authorDao.selectListByUid(uid);
}
}- dao
public interface AdminUserAuthorDao extends BaseMapper<AdminUserAuthor> {
@Select("select a.* from " +
"admin_user_author a ,rel_admin_user_author rel " +
"where a.aid = rel.aid and " +
"rel.uid = #{uid} ")
List<AdminUserAuthor> selectListByUid(Integer uid);
}5、修改LoginUserDetails
@Override
public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() {
List<GrantedAuthority> list = new ArrayList<>();
//根据角色授权
AdminRole adminRole = adminUser.getAdminRole();
if (adminRole != null){
GrantedAuthority authority =
new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_" + adminRole.getCode());
list.add(authority);
}
//授权码列表
List<AdminUserAuthor> authorList = adminUser.getAuthorList();
if (authorList != null && !authorList.isEmpty()){
authorList.forEach(a ->{
list.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(a.getCode()));
});
}
//存储授权列表
return list;
}6、设计测试
-
book能访问f4
-
game能访问f5
-
book,game,music 都能访问f6
http.authorizeHttpRequests(auth -> auth
.requestMatchers("/game/f4").hasAuthority("book")
.requestMatchers("/game/f5").hasAuthority("game")
.requestMatchers("/game/f6").hasAnyAuthority("book","game","music")
.requestMatchers("/loginpage.html", "/login/**", "/jsonlogin", "/phoneLogin")
.permitAll()
.anyRequest()
.authenticated() //其他页面,要登录之后才能访问
);7、修改403返回json
http.exceptionHandling(ex -> ex
//处理 401 未登录/未认证 (用户访问未携带cookie/未通过登录)
.authenticationEntryPoint((request, response, e) -> {
createFailJson(response, "当前用户未登录,请先登录再访问");
})
//处理 403 已经登录,权限不足
.accessDeniedHandler((request, response, e) -> {
createFailJson(response, "权限不足,无法访问");
})
);有一些特殊情况下,这个请求会优先进入JavasmExceptionAdvice,从而不触发上面的 exceptionHandling
- 修改自定义异常
//import org.springframework.security.access.AccessDeniedException;
//import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
//单独的声明,处理Security产生的异常信息,直接向上抛出,不返回json,走Security的异常流程
@ExceptionHandler({AccessDeniedException.class, AuthenticationException.class})
public void handleSecurityException(Exception e) throws Exception{
throw e;
}五、授权注解
如果需要控制的url地址过多,需要大量的配置在配置类中,需要使用注解,来简化配置
- 开启注解
//securedEnabled → 开启@Secured注解
//prePostEnabled → 开启@PreAuthorize/@PostAuthorize 注解(默认已经开启)
//@Secured注解 实用性 没有@PreAuthorize好,所以很大可能用不到
@EnableMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true,prePostEnabled = true)1、@Secured
- 角色的继承会失效
@GetMapping("/f1")
@Secured("ROLE_admin")
public R f1(){
return R.ok("=====F1");
}
@Secured("ROLE_test")
@GetMapping("/f2")
public R f2(){
return R.ok("=====F2");
}
@Secured({"ROLE_admin","ROLE_test"})
@GetMapping("/f3")
public R f3(){
return R.ok("=====F3");
}2、==@PreAuthorize==
使用比较多
方法执行【之前】生效
角色继承生效
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_admin')")
@GetMapping("/f5")
public R f5(){
return R.ok("=====F5");
}
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_test')")
@GetMapping("/f6")
public R f6(){
return R.ok("=====F6");
}
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole('ROLE_admin','ROLE_test')")
@GetMapping("/f7")
public R f7(){
return R.ok("=====F7");
} @PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('game')")
@GetMapping("/f8")
public R f8(){
return R.ok("=====F8");
}
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('book')")
@GetMapping("/f9")
public R f9(){
return R.ok("=====F9");
}
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyAuthority('music','book')")
@GetMapping("/f10")
public R f10(){
return R.ok("=====F10");
}3、@PostAuthorize
方法执行【之后】,返回之前生效
用法,和@PreAuthorize一模一样,只是生效的时机不一样
方法不论是否有权限,都会被执行1次,但是能不能返回,看权限
@PostAuthorize("hasAnyAuthority('mucic','book')")
@GetMapping("/f11")
public R f11(){
System.out.println("===============这个日志会被执行,不论是否有权限================");
return R.ok("=====F11");
}4、@PreFilter
过滤参数
参数必须是集合,才能生效
@PreFilter("filterObject.ishot == 1")
@GetMapping("/f13")
public List<Game> f13(@RequestBody List<Game> list){
return list;
}5、@PostFilter
过滤返回值
返回值必须是集合,才能过滤
@GetMapping("/f12")
@PostFilter("filterObject.sort > 5")
public List<Game> f12(){
List<Game> list = gameService.list();
return list;
}六、自定义的方法去校验授权
1、测试基本原理
-
写一个自己的方法,让授权成功
-
也能像role或者Authority那样,控制方法能否访问
@Component("auth1")
public class JavasmAuthorize {
public boolean test(String code){
System.out.println(code);
//test方法,返回的数据,如果是true表示允许访问当前的方法
//如果返回false,表示没有权限访问当前方法
return false;
}
}使用
@GetMapping("/f14")
//寻找名字是auth1的bean对象,调用里面的.test方法,传入参数ttttt
@PreAuthorize("@auth1.test('ttttt')")
public R f14(){
return R.ok("-----------f14");
}2、官方验证
@Component("auth2")
public class JavasmAuthorize2 {
//code 权限标识
public boolean f1(String code) {
//获取登录用户信息
Object principal = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
if (principal instanceof LoginUserDetails) {
LoginUserDetails loginUserDetails = (LoginUserDetails) principal;
//获取授权列表
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities =
loginUserDetails.getAuthorities();
//判断 code 是否在授权列表中
return authorities
.stream()
.anyMatch(grantedAuthority ->
grantedAuthority.getAuthority().equals(code)
);
}
return false;
}
}使用
@PreAuthorize("@auth2.f1('book')")
@GetMapping("/f15")
public R f15(){
return R.ok("-----------f15");
}3、使用自己的方法
@Component("auth3")
public class JavasmAuthorize3 {
@Resource
LoginService loginService;
public boolean f1(String code){
LoginUserDetails loginUser = loginService.getLoginUser();
//授权列表
List<AdminUserAuthor> authorList = loginUser.getAdminUser().getAuthorList();
List<String> list = authorList.stream().map(AdminUserAuthor::getCode).toList();
return list.contains(code);
}
}使用
@PreAuthorize("@auth3.f1('book')")
@GetMapping("/f16")
public R f16(){
return R.ok("-----------f16");
}4、菜单授权
- 授权判定
@Component("menuAuth")
public class MenuAuthorize {
public boolean check(String url){
Object principal = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
if (principal instanceof LoginUserDetails){
LoginUserDetails loginUserDetails = (LoginUserDetails) principal;
return loginUserDetails.checkMenu(url);
}
return false;
}
}- 修改LoginUserDetails
public boolean checkMenu(String url) {
if (adminUser != null && adminUser.getAdminRole() != null) {
//获取菜单列表
List<AdminMenu> menuList = adminUser.getAdminRole().getMenuList();
//获取子菜单的Stream流
Stream<String> childUrlStream = menuList.stream()
.map(AdminMenu::getChildList)
.flatMap(Collection::stream)
.map(AdminMenu::getUrl);
//获取父菜单的Stream流
Stream<String> firstUrlStream = menuList.stream().map(AdminMenu::getUrl);
//两个流混到一起,再筛选出url地址
List<String> urlList = Stream.concat(childUrlStream, firstUrlStream).toList();
return urlList.contains(url);
}
return false;
}- 使用
@PreAuthorize("@menuAuth.check('/user/list')")
@GetMapping("/f17")
public R f17(){
return R.ok("-----------f17");
}总结
-
@PreAuthorize
-
菜单授权