目录
bean管理类常用的4个注解(作用相同,推荐使用在不同分层上)
1.快速入门
导入依赖:
XML
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.10</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>在配置文件中开启注解扫描:
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 开启注解扫描 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.qcby"/>
</beans>创建接口和实现类:
java
package com.qcby.service;
public interface UserService {
public void hello();
}
package com.qcby.service.Impl;
import com.qcby.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @Component 作用是把当前类使用IOC容器进行管理,如果没有指定名称,默认使用当前类名userServiceImpl
*/
@Component(value = "userService")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public void hello() {
System.out.println("hello IOC注解........");
}
}测试代码:
java
import com.qcby.service.UserService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Demo {
@Test
public void test1() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
userService.hello();
}
}运行结果:
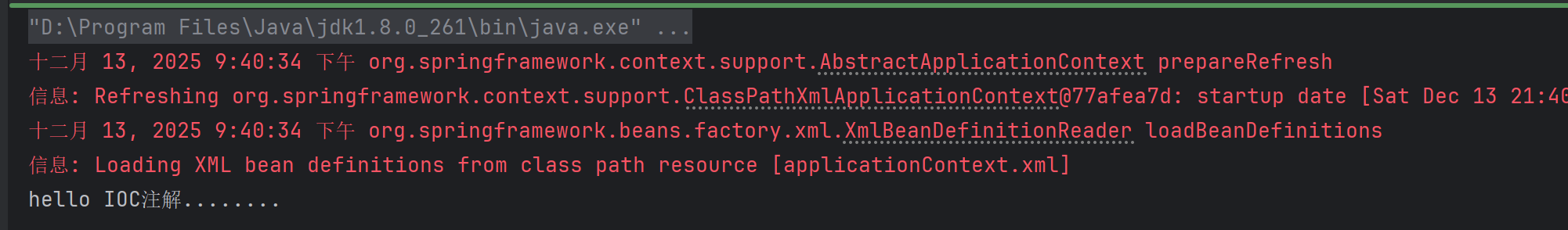
我们在实现类上面加了@Component注解,它的作用是把当前类使用IOC容器进行管理,value指定Bean的名称,如果没有指定名称,默认使用当前类名userServiceImpl
2.常用注解
bean管理类常用的4个注解(作用相同,推荐使用在不同分层上)
@Component普通的类
@Controller表现层
@Service业务层
@Repository持久层
依赖注入常用的注解
@Value用于注入普通类型(String,int,double等类型)
@Autowired默认按类型进行自动装配(引用类型)
@Qualifier和@Autowired一起使用,强制使用名称注入
@Resource JavaEE提供的注解,也被支持。使用name属性,按名称注入
对象生命周期(作用范围)注解
@Scope生命周期注解,取值singleton(默认值,单实例)和prototype(多例)
初始化方法和销毁方法注解
@PostConstruct相当于init-method
@PreDestroy相当于destroy-method
3.纯注解模式
纯注解的方式是微服务架构开发的主要方式,所以也是非常的重要。纯注解的目 的是替换掉所有的配置文件。但是需要编写配置类。
配置类:
java
package com.qcby.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* spring的配置类,替换掉applicationContext.xml
*/
//声明这个类是配置类
@Configuration
//扫描指定的包结构
@ComponentScan(value="com.qcby")
public class SpringConfig {
}实体类:
java
package com.qcby.entity;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Order {
@Value("北京")
private String address;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Order [address=" + address + "]";
}
}测试方法:
java
import com.qcby.config.SpringConfig;
import com.qcby.entity.Order;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Demo {
/**
* 需要加载配置类
*/
@Test
public void test() {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
//获取对象
Order order = (Order) context.getBean("order");
System.out.println(order);
}
}
@Configuration声明是配置类
@ComponentScan扫描具体包结构的
@Import注解Spring的配置文件可以分成多个配置的,编写多个配置类。用于导入其他配置类
@Bean注解只能写在方法上,表明使用此方法创建一个对象,对象创建完成保 存到IOC容器中
创建SpringConfig2,在SpringConfig2当中配置德鲁伊连接池:
java
package com.qcby.config;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
public class SpringConfig2 {
@Bean(name = "dataSource")
public DataSource createDataSource() {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("root");
return dataSource;
}
}在原来的配置类当中导入配置:
java
package com.qcby.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
/**
* spring的配置类,替换掉applicationContext.xml
*/
//声明这个类是配置类
@Configuration
//扫描指定的包结构
@ComponentScan(value="com.qcby")
@Import(value={SpringConfig2.class})
public class SpringConfig {
}创建实体类:
java
package com.qcby.entity;
public class Account {
private int id;
private String name;
private Double money;
public Account(String name, int id, Double money) {
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
this.money = money;
}
public Account() {
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Double getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(Double money) {
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", money=" + money + "]";
}
}持久层:
java
package com.qcby.dao;
import com.qcby.entity.Account;
import java.util.List;
public interface AccountDao {
List<Account> findAll();
}
package com.qcby.dao.Impl;
import com.qcby.dao.AccountDao;
import com.qcby.entity.Account;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Repository
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource;
@Override
public List<Account> findAll() {
List<Account> list = new ArrayList<>();
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try{
//获取连接
conn=dataSource.getConnection();
//编写sql
String sql="select * from account";
//预编译
ps=conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//查询
rs= ps.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()){
Account account=new Account();
account.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
account.setName(rs.getString("name"));
account.setMoney(rs.getDouble("money"));
list.add(account);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
try {
if (rs != null) rs.close();
if (ps != null) ps.close();
if (conn != null) conn.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return list;
}
}业务层:
java
package com.qcby.service.Impl;
import com.qcby.dao.AccountDao;
import com.qcby.entity.Account;
import com.qcby.service.AccountService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Override
public List<Account> findAll() {
return accountDao.findAll();
}
}
package com.qcby.service;
import com.qcby.entity.Account;
import java.util.List;
public interface AccountService {
List<Account> findAll();
}测试代码:
java
@Test
public void test2() {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
AccountService accountService = context.getBean(AccountService.class);
List<Account> list=accountService.findAll();
for(Account account:list){
System.out.println(account);
}
}结果:
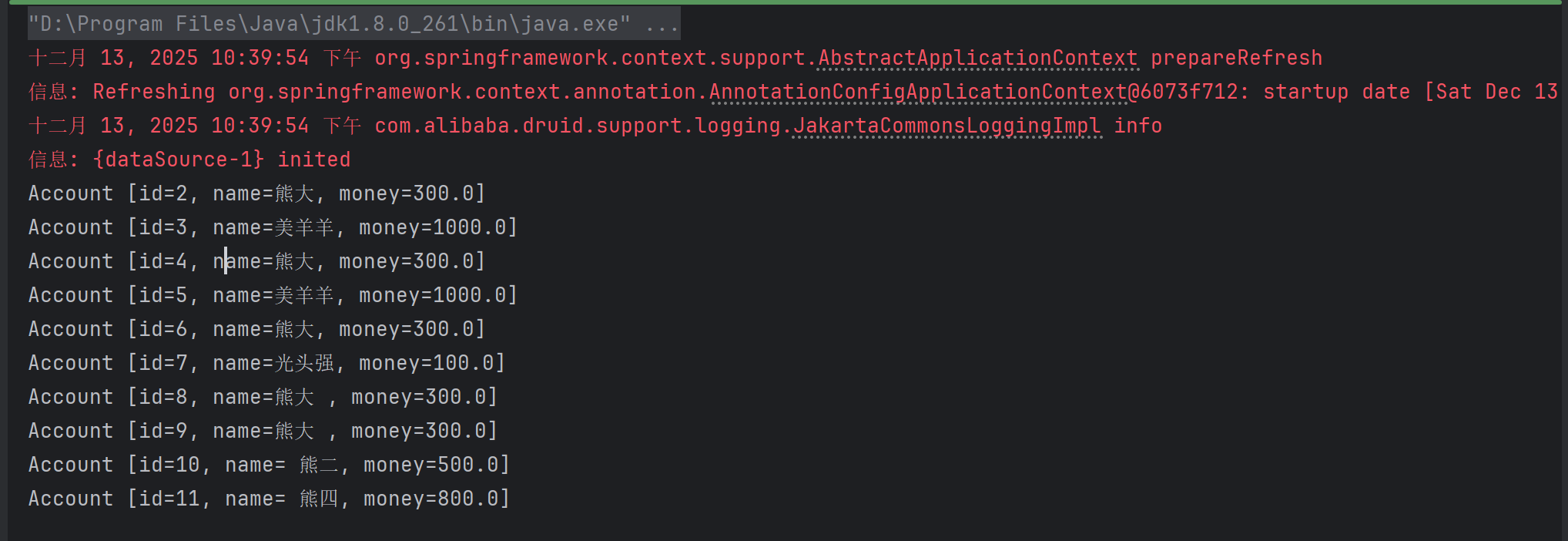
可见我们在配置类2当中的配置也生效了