JSR107
在我们了解SpringBoot缓存深入的时候,我们首先需要了解JSR107。
JSR:
- 是Java Specification Requset 的缩写,Java规范请求;
- 其是Java提供的一个接口规范,类似于jdbc规范,但是没有具体的实现,具体的实现就是redis等这些缓存。
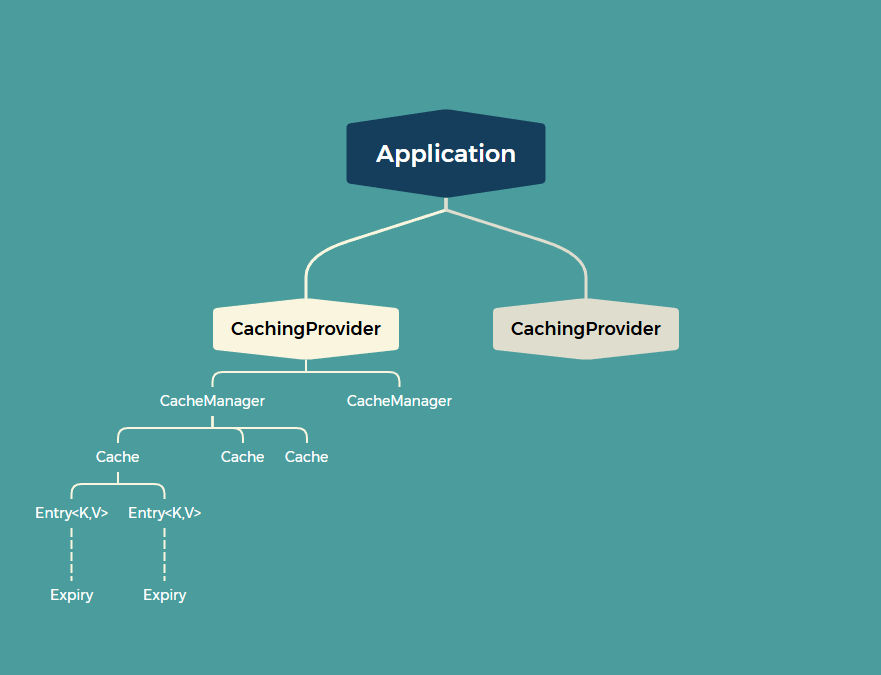
JSR107核心接口:
- CachingProvider(缓存提供者):创建,配置,获取,管理和控制多个CacheManager;
- CacheManager(缓存管理器):创建,配置,获取,管理和控制多个唯一命名的Cache,Cache存在于CacheManager的上下文中,一个CacheManager仅对应一个CachingProvider;
- Cache(缓存):是由CacheManager管理的,CacheManager仅对应一个Cache的生命周期,Cache存在于CacheManager的上下文中。类似于map的数据结构,并临时存储以key为索引的值。一个Cache仅被一个CacheManager所拥有;
- Entry(缓存键值对):是一个存储在Cache中的key-value对;
- Expiry(缓存时效):每一个存储在Cache中的条目都有一个定义的有效期。一旦超过这个时间,条目就会自动过期,过期后,条目将不可用访问,更新和删除操作。缓存有效期可以通过ExpiryPolicy设置。
要使用JSR107需要导入相关的maven依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.cache</groupId>
<artifactId>cache-api</artifactId>
</dependency>Spring的缓存抽象
Spring Cache:
- 只负责维护抽象层,具体的实战由自己的技术选型来决定;
- 将缓存处理和缓存技术解除耦合;
- 每次调用缓存功能方法时,Spring会检查指定参数的目标方法是否已经被调用;
- 如果有就直接从缓存中获取方法调用后的结果,如果没有就调用方法并缓存结果返回给用户,下次直接从缓存中获取即可。
当我们使用Spring Cache缓存抽象的时候,我们需要关注两点:
- 确定那些方法需要被缓存;
- 缓存策略。
Spring 缓存使用
重要概念和缓存注解
在正式开始进入SpringCache实战之间,我们需要先了解一下Spring Cache 的缓存注解和几个重要概念。
|----------------|------------------------------|
| 概率/注解 | 作用 |
| Cache | 缓存接口,定义缓存操作。实现有RedisCache等 |
| CacheManaer | 缓存管理器,管理各种缓存(Cache)组件 |
| @Cacheable | 主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存 |
| @CacheEvict | 清空缓存 |
| @CachePut | 保证方法被调用,又希望结果被缓存 |
| @EnableCaching | 开启缓存注解 |
| keyGenerator | 缓存数据时key生成 |
| serialize | 缓存数据时value序列化策略 |
说明:
@Cacheable标注在方法上,表示该方法的结果需要被缓存起来;- 缓存的键由
keyGenerator的策略决定,缓存的值的形式是由serialize决定(序列化还是json格式); - 标注上该注解之后,在缓存时效内再次调用该方法将不会调用方法本身而是直接从缓存中获取结果;
@CachePut也是标注在方法上,和@Cacheable相似也会将方法的返回值存储起来,不同的是标注@CachePut的方法每次都会被调用,而且每次都会将结果缓存起来,适用对象的更新。
环境搭建
首先我们要创建数据库表结构
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `department`;
CREATE TABLE `department` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`department_name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `employee`;
CREATE TABLE `employee` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`email` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`gender` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`d_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;然后添加maven依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.9.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
<!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.guslegend</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringCacheDemo</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>接下来生成实体类,controller层,service层,mapper层。
还有我们需要开启mybatis的驼峰映射,和配置日志级别,方便我们查看sql语句,看缓存是否生效。

缓存初体验
首先我们需要再启动类上添加@EnableCaching,允许使用缓存。
Cacheable
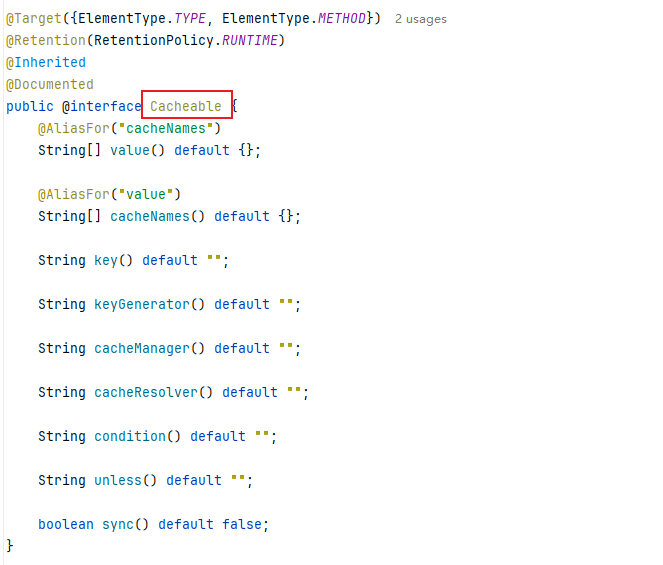
|------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------|
| 属性名 | 描述 |
| cacheNames/value | 指定缓存的名字,用于区分不同缓存组件;可通过该属性指定缓存键值,将一个缓存键值分到多个缓存中。 |
| key | 缓存数据时的 key 值,默认使用方法参数值,支持 SpEL 表达式生成 key。 |
| keyGenerator | 缓存的生成策略,与 key 功能一致,支持自定义生成规则。 |
| cacheManager | 定义缓存管理器(如 ConcurrentHashMap、Redis 等)。 |
| cacheResolver | 与 cacheManager 功能一致,二者选其一。 |
| condition | 指定缓存的条件,满足条件时才缓存(如#id>0 表示入参大于 0 时缓存),支持 SpEL 表达式。 |
| unless | 缓存后判断条件,满足时不缓存(如#result==null 表示结果为 null 时不缓存),支持 SpEL 表达式。 |
| sync | 是否使用异步模式进行缓存。 |
注意:
- 即满足condition又满足unless条件的也不进行缓存;
- 使用异步模式进行缓存时(sync=true):unless条件将不被支持。
|---------------|--------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|------------------------|
| 名字 | 位置 | 描述 | 示例 |
| methodName | root object | 当前被调用的方法名 | #root.methodName |
| method | root object | 当前被调用的方法 | #root.method.name |
| target | root object | 当前被调用的目标对象 | #root.target |
| targetClass | root object | 当前被调用的目标对象类 | root.targetClass |
| args | root object | 当前被调用的方法的参数列表 | #root.args[0] |
| caches | root object | 当前方法调用使用的缓存列表(如 cacheNames={"cache1","cache2"} 则有两个 cache) | #root.caches[0].name |
| argument name | evaluation context | 方法参数的名字,可直接用 #参数名或 #p0/#a0(0 代表参数索引) | #iban, #a0, #p0 |
| result | evaluation context | 方法执行后的返回值(仅当方法执行之后判断有效,如 cacheable 的 unless、cachePut 的表达式、cacheEvict 的beforeInvocation=false) | #result |
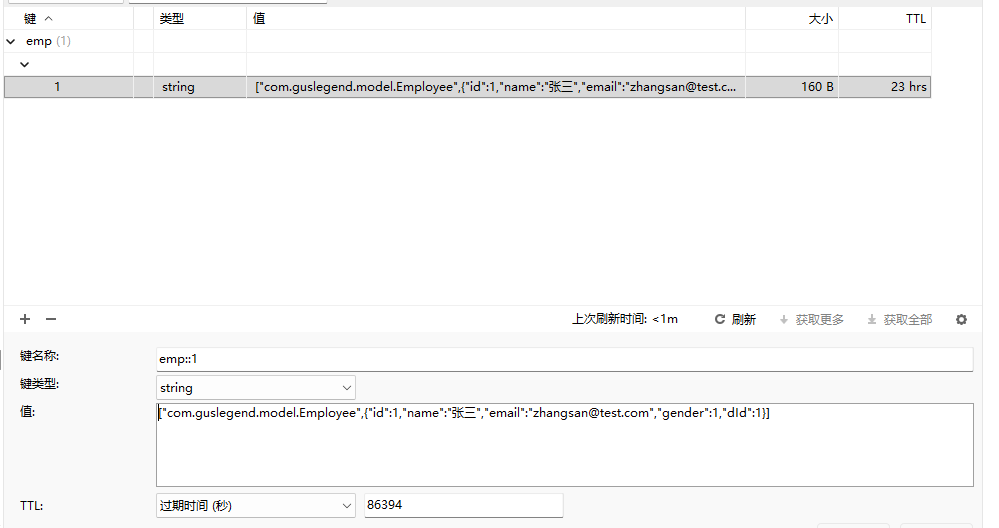
实战,进行两次查询方法,只出现一次sql语句
@GetMapping("/{id}")
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "emp",key = "#id",condition = "#id>0",unless = "#result == null ")
public Employee getEmpById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
return employeeService.getEmpById(id);
}@Cacheable源码分析
- 在运行方法之间会先去查询Cache(缓存组件),按照cacheNames指定的名字获取(CacheManager)先获取相应的缓存,第一次获取缓存如果没有Cache组件会自动创建;
- 去Cache里面查找缓存的内容,使用的key默认就是方法的参数;key默认是使用keyGenerator生成的,默认使用SimpleKeyGenerator;
- 没有查询到缓存就调用目标方法;
- 将目标方法返回的结果放到缓存里面。
@CachePut @CacheEnvict @CacheConfig
@CachePut
调用方法,有更新缓存数据,一般用于更新操作,在更新缓存时一定要和想要更新的缓存有相同的缓存名称和相同的key(可类比同一张表的同一条数据)。
@PutMapping("/update")
@CachePut(cacheNames = "emp",key = "#employee.id")
public void updateEmp(@RequestBody Employee employee) {
employeeService.updateEmployee(employee);
}@CacheEnvict
缓存清除,清除缓存时要指定缓存的名字和key,相当于告诉数据库要删除哪个表中的哪个数据,key默认为参数值。
属性:
-
value/cacheNames:缓存的名字;
-
key:缓存的键;
-
allEnries:是否清除指定缓存中的所有键值对,默认为false,设置为true时会清除缓存中的所有键值对,与key属性二选一使用;
-
beforeInvocation:在@CacheEnvict注解的方法调用之间清除指定缓存,默认为false,即在方法调用之后清除缓存,设置为true时则会在方法调用之间清除缓存(子啊方法调用之前还是之后清除缓存的区别在于方法调用时是否会出现异常,若不出现异常,这两种设置没有区别,若出现异常,设置为在方法调用之后清除缓存则不起作用,因为方法调用失败了)。
@Delete("/{id}") @CacheEvict(cacheNames = "emp",key = "#id",beforeInvocation = true) public void deleteEmp(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) { employeeService.deleteEmployee(id); }
@CacheConfig
作用:标注在类上,抽取缓存相关的公共配置,可抽取的公共配置有缓存的名字,主键生成器等
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface CacheConfig {
String[] cacheNames() default {};
String keyGenerator() default "";
String cacheManager() default "";
String cacheResolver() default "";
}实列:通过@CacheConfig的cacheNames属性指定缓存的名字之后,该类中的其他缓存注解就不必再写value或者cacheName了,会使用该名字作为value或cacheName的值,也会遵循就近原则。
@Service
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "emp")
public class EmployeeServiceImpl implements EmployeeService {
@Autowired
private EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;
@Override
@Cacheable(key = "#empId")
public Employee getEmpById(int empId) {
return employeeMapper.getEmpById(empId);
}
}自定义RedisCacheManager
通过前面运用缓存,我们发现缓存乱码了
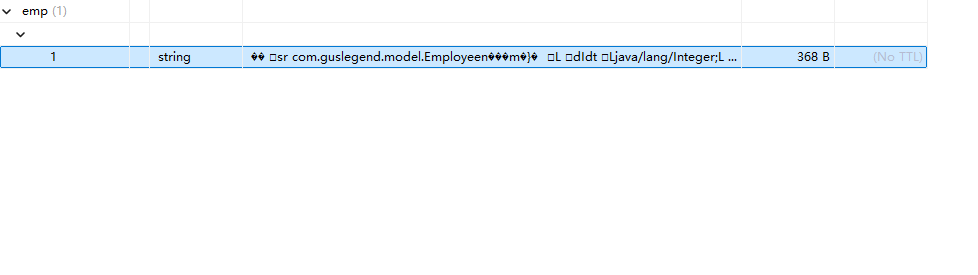
这时我们就需要自定义RedisCacheManager将其加入到SpringIOC容器中解决这个问题
@Configuration
public class CacheConfig {
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory
redisConnectionFactory) {
// 分别创建String和JSON格式序列化对象,对缓存数据key和value进行转换
RedisSerializer<String> strSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jacksonSeial =
new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
// 解决查询缓存转换异常的问题
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jacksonSeial.setObjectMapper(om);
// 定制缓存数据序列化方式及时效
RedisCacheConfiguration config =
RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofDays(1))
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair
.fromSerializer(strSerializer))
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair
.fromSerializer(jacksonSeial))
.disableCachingNullValues();
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = RedisCacheManager
.builder(redisConnectionFactory).cacheDefaults(config).build();
return cacheManager;
}
}