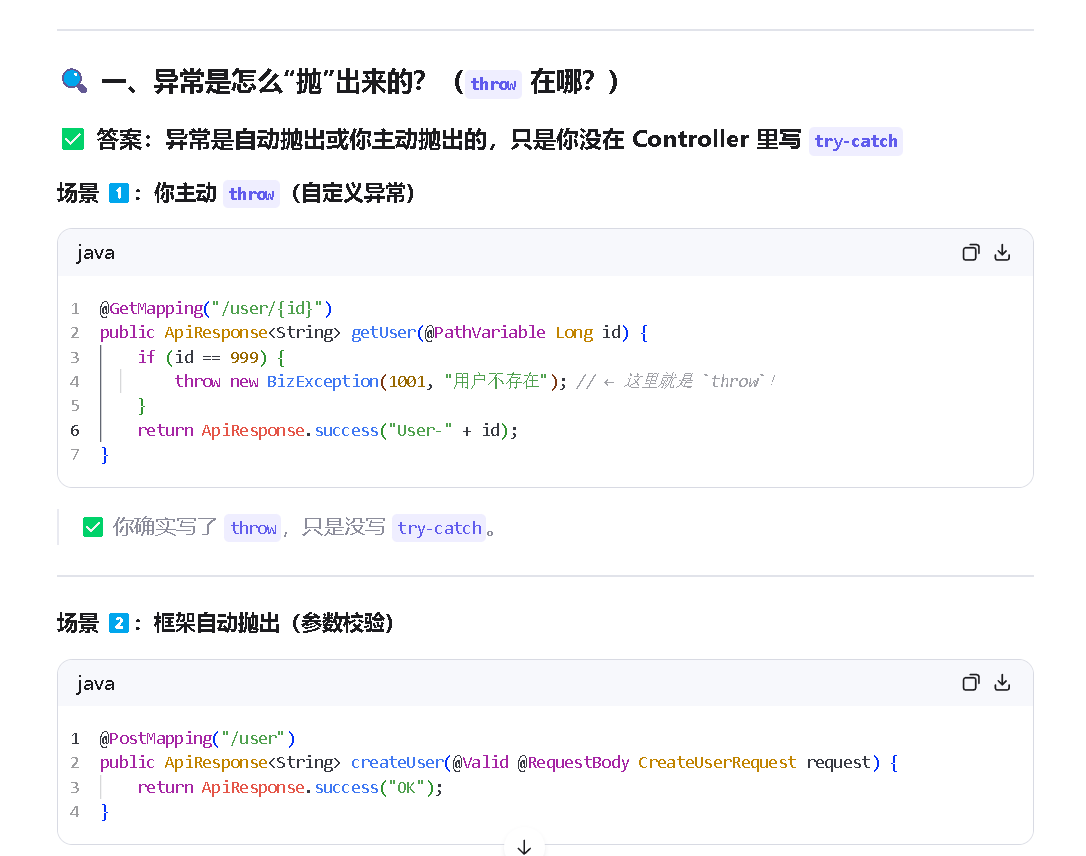
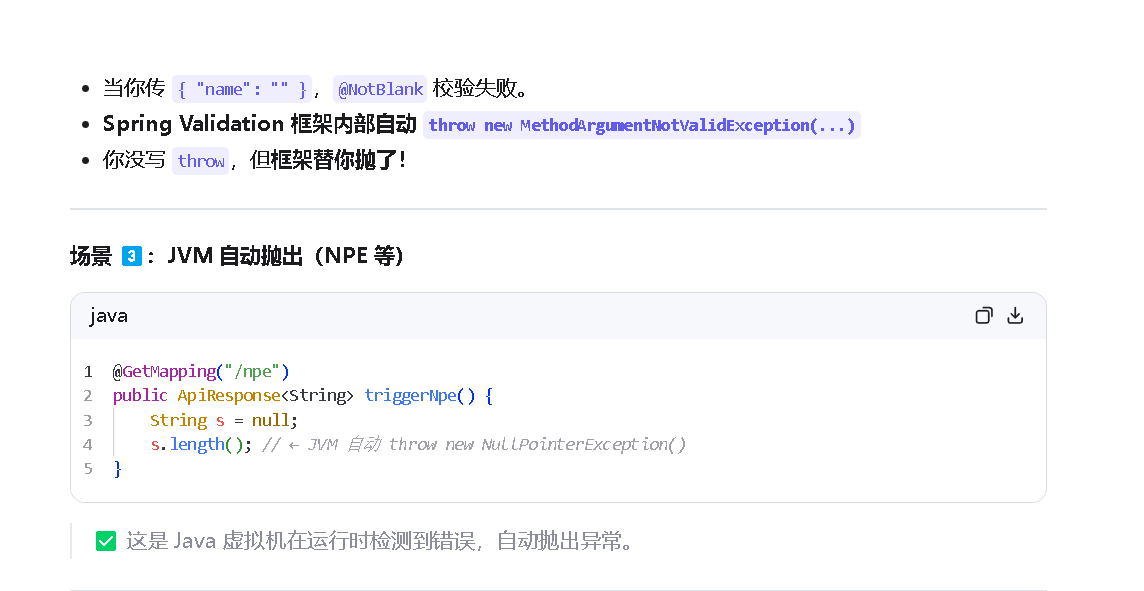
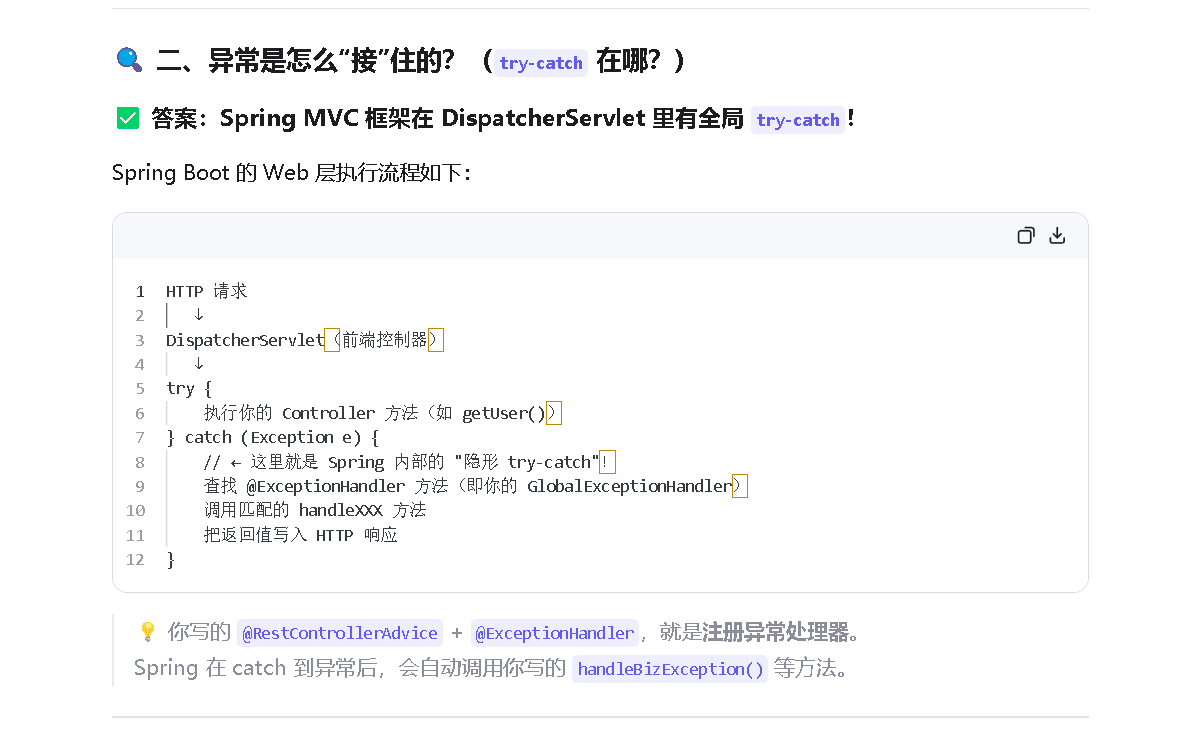
这个异常体系,在平常写代码的时候,还是会经常遇到的。
我想用一个综合全局的视角,来讲一下这个异常体系
在日常写接口的时候,我们知道这个要让程序正常的执行,
不至于崩溃
这里主要聚焦3点
1.有哪些异常
2.程序如何处理这些异常
3.接口如何处理这些异常
1.有哪些异常
- 有哪些异常?
Java 的异常体系基于 Throwable,主要分为两大类:
✅ Error(错误)
表示 JVM 无法恢复的严重问题(如 OutOfMemoryError、StackOverflowError)。
通常不需要也不应该捕获 ------ 程序无法处理,应尽快失败并报警。
✅ Exception(异常)
又分为两类:
Checked Exception(检查型异常)
编译器强制要求处理,如 IOException、SQLException。
通常表示"可预期但非程序错误"的外部问题(如文件不存在、网络中断)。
必须 try-catch 或 throws。
Unchecked Exception(非检查型异常)
继承自 RuntimeException,如 NullPointerException、IllegalArgumentException、IndexOutOfBoundsException。
通常表示程序逻辑错误,比如传参错误、状态不合法等。
编译器不强制处理,但良好的代码应主动避免或捕获。
💡 在 Web 接口开发中,我们主要关注的是 Unchecked Exception 和部分 Checked Exception(如数据库异常、网络调用异常)。
这里error,就是整个jvm崩溃了,不常见
对于Checked Exception(检查型异常),这个在idea会自己检查,这个有个小插曲,要会在idea上配置,让idea识别是哪个类型的文件
我们集中注意力看一下这个。

这个gpt总结的不全,除了这些,
项目作为一个运行的jvm实例,如果涉及到第三方的交互,都要去做异常处理。
主要,还是处理一下npe(空指针异常)
我们来介绍一下npe(空指针异常)的常见处理方法、
1.识别什么需要处理空指针异常
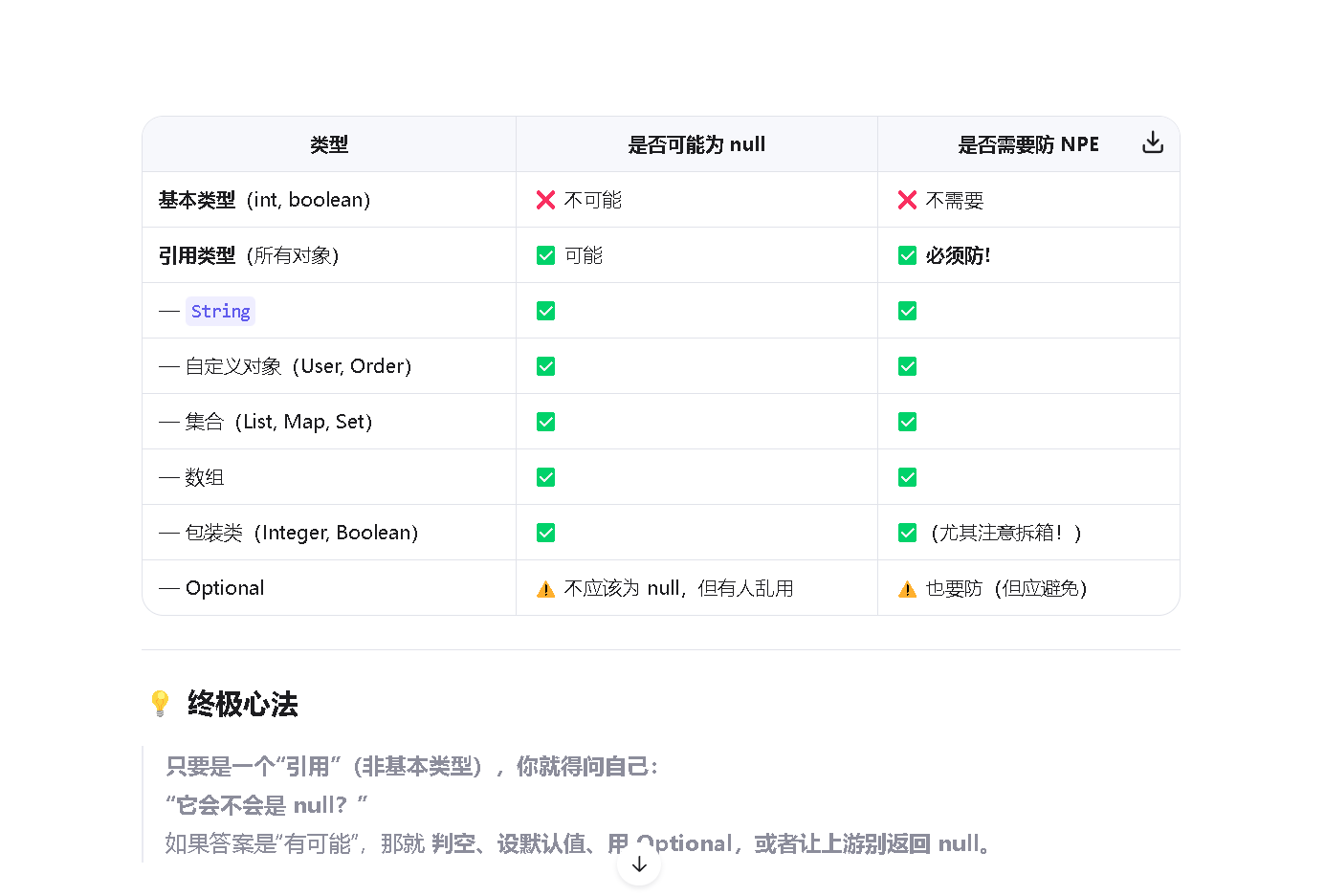
说白了,也就是我们自己设计的引用数据类型类,和系统自带的引用数据类型,比方说string和BigDecimal,都要进行空指针异常的处理。
第二个问题,如何处理这个npe
引入comon3的依赖包
Apache Commons Lang3 是 Java 开发防 NPE 的"瑞士军刀"。
只需记住三句话:
字符串判空 → StringUtils.isNotBlank(str)
集合判空 → CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(list)
对象设默认 → ObjectUtils.defaultIfNull(obj, default)
2.我们在来看看程序内部是如何处理异常的
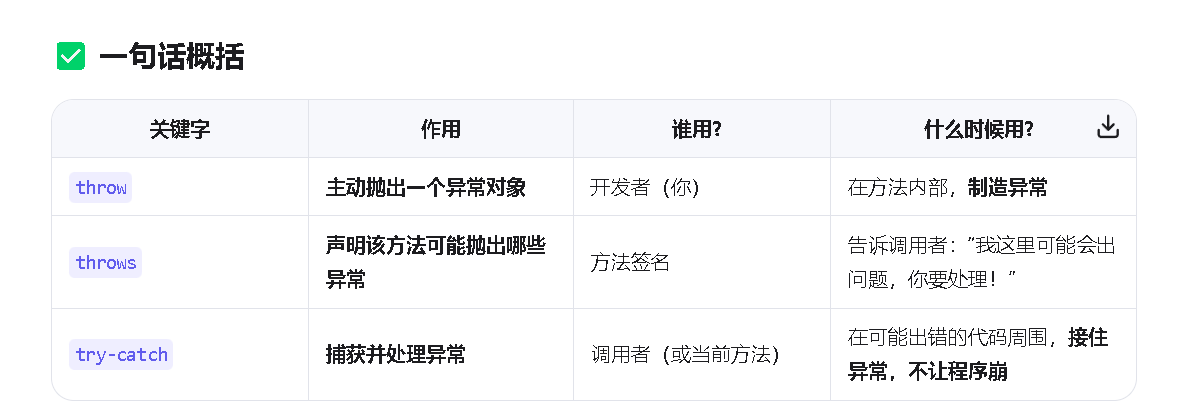
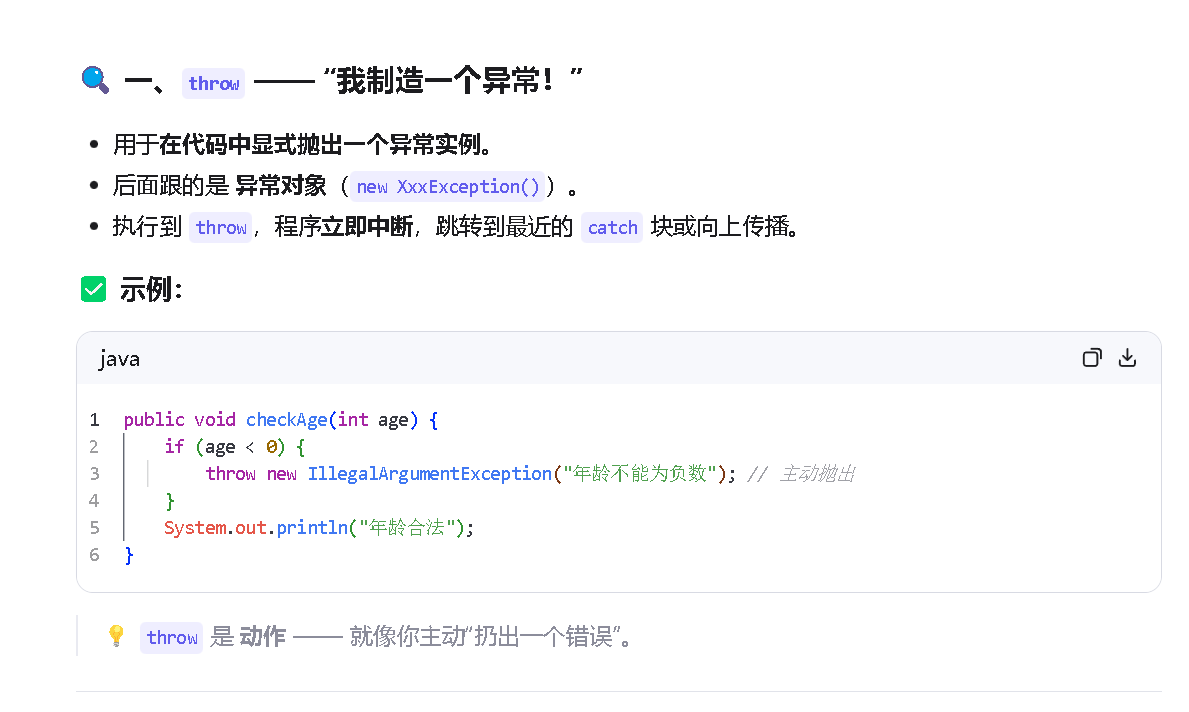
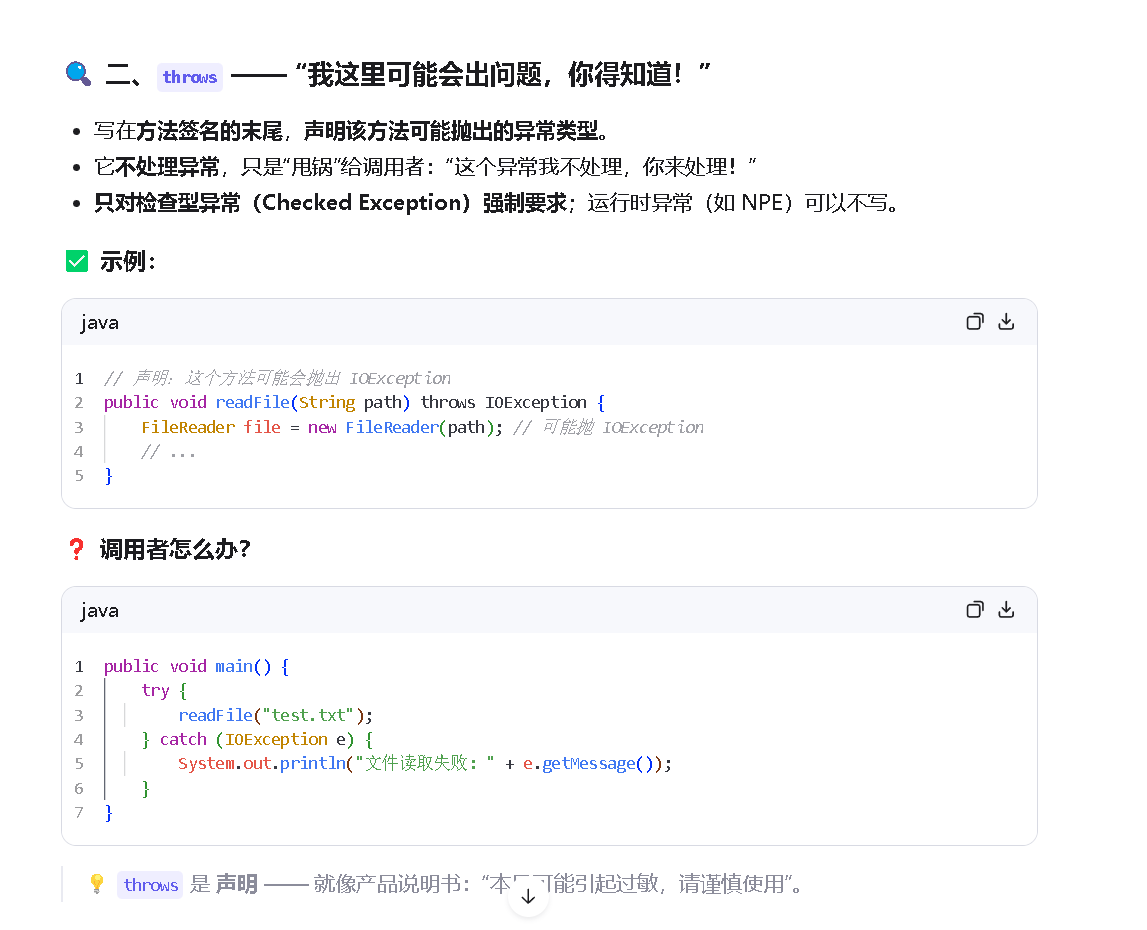
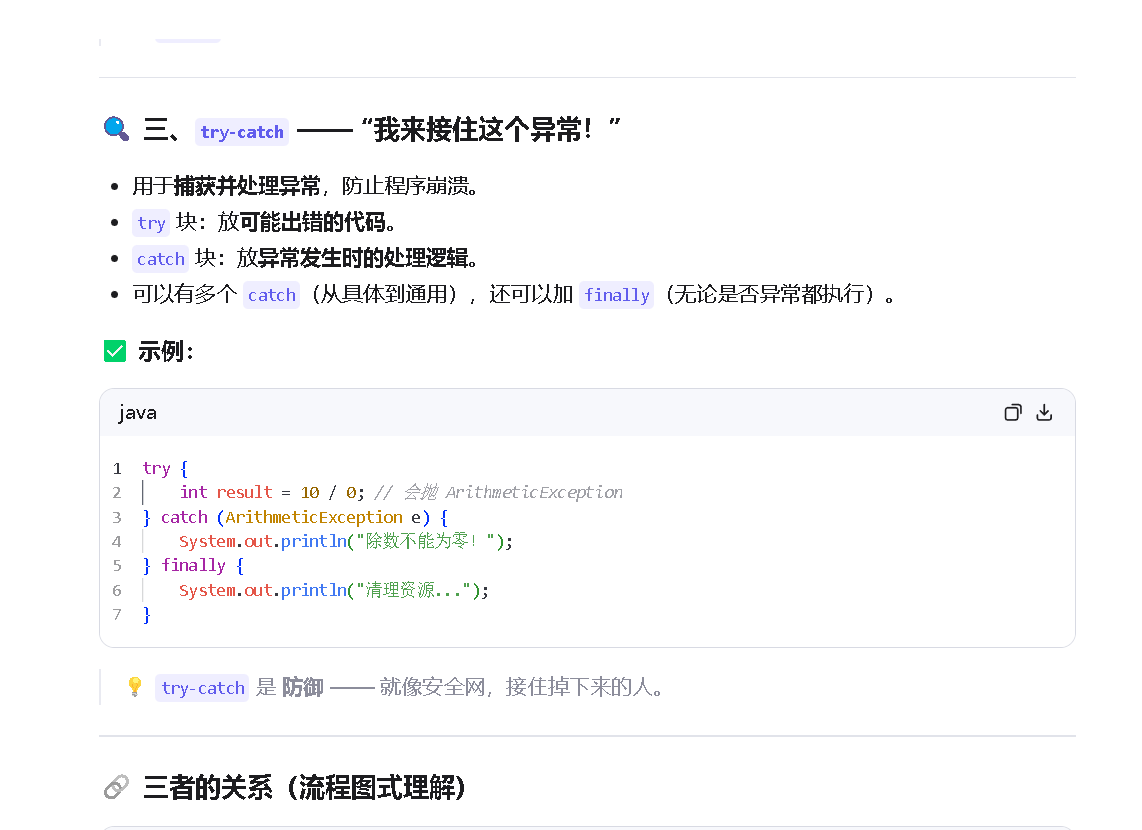
第三个:接口是如何处理接口异常的。
下面是一个 完整、可用、生产级风格的 Spring Boot 全局异常处理(Global Exception Handler)Demo,适用于 RESTful 接口开发。
我们会覆盖:
自定义业务异常
参数校验异常(@Valid)
通用运行时异常(如 NPE)
统一的 JSON 响应格式
✅ 项目依赖(Spring Boot + Validation)
确保你的 pom.xml 包含:
clike
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>第一步:定义统一响应结构 ApiResponse
clike
// src/main/java/com/example/exceptiondemo/dto/ApiResponse.java
package com.example.exceptiondemo.dto;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
public class ApiResponse<T> {
private int code;
private String message;
private T data;
public static <T> ApiResponse<T> success(T data) {
ApiResponse<T> res = new ApiResponse<>();
res.code = 200;
res.message = "success";
res.data = data;
return res;
}
public static <T> ApiResponse<T> error(int code, String message) {
ApiResponse<T> res = new ApiResponse<>();
res.code = code;
res.message = message;
return res;
}
}💡 使用 Lombok 简化 getter/setter。如果没有 Lombok,手动写即可。
第二步:自定义业务异常 BizException
clike
// src/main/java/com/example/exceptiondemo/exception/BizException.java
// src/main/java/com/example/exceptiondemo/exception/BizException.java
package com.example.exceptiondemo.exception;
public class BizException extends RuntimeException {
private final int code;
public BizException(int code, String message) {
super(message);
this.code = code;
}
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
}第三步:全局异常处理器 GlobalExceptionHandler
clike
// src/main/java/com/example/exceptiondemo/handler/GlobalExceptionHandler.java
package com.example.exceptiondemo.handler;
import com.example.exceptiondemo.dto.ApiResponse;
import com.example.exceptiondemo.exception.BizException;
import jakarta.validation.ConstraintViolationException;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.validation.BindException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;
import java.util.Objects;
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
// 1. 处理自定义业务异常
@ExceptionHandler(BizException.class)
public ResponseEntity<ApiResponse<?>> handleBizException(BizException e) {
return ResponseEntity.ok(ApiResponse.error(e.getCode(), e.getMessage()));
}
// 2. 处理 @Valid 参数校验失败(GET 请求)
@ExceptionHandler(ConstraintViolationException.class)
public ResponseEntity<ApiResponse<?>> handleConstraintViolation(ConstraintViolationException e) {
String message = e.getConstraintViolations().iterator().next().getMessage();
return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body(ApiResponse.error(400, message));
}
// 3. 处理 @Valid 参数校验失败(POST/PUT JSON)
@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
public ResponseEntity<ApiResponse<?>> handleValidationException(MethodArgumentNotValidException e) {
String message = Objects.requireNonNull(e.getBindingResult().getFieldError()).getDefaultMessage();
return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body(ApiResponse.error(400, message));
}
// 4. 处理 BindException(表单提交等)
@ExceptionHandler(BindException.class)
public ResponseEntity<ApiResponse<?>> handleBindException(BindException e) {
String message = Objects.requireNonNull(e.getBindingResult().getFieldError()).getDefaultMessage();
return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body(ApiResponse.error(400, message));
}
// 5. 处理所有未捕获的 RuntimeException(如 NPE、IllegalArgumentException)
@ExceptionHandler(RuntimeException.class)
public ResponseEntity<ApiResponse<?>> handleRuntimeException(RuntimeException e) {
// 生产环境不要暴露堆栈信息!
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
.body(ApiResponse.error(500, "系统繁忙,请稍后再试"));
}
// 6. 处理所有其他异常(兜底)
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public ResponseEntity<ApiResponse<?>> handleGenericException(Exception e) {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
.body(ApiResponse.error(500, "系统异常"));
}
}✅ @RestControllerAdvice = @ControllerAdvice + @ResponseBody,自动返回 JSON。
第四步:写一个测试 Controller
clike
// src/main/java/com/example/exceptiondemo/controller/TestController.java
package com.example.exceptiondemo.controller;
import com.example.exceptiondemo.dto.ApiResponse;
import com.example.exceptiondemo.exception.BizException;
import jakarta.validation.Valid;
import jakarta.validation.constraints.Min;
import jakarta.validation.constraints.NotBlank;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class TestController {
// 1. 正常接口
@GetMapping("/hello")
public ApiResponse<String> hello() {
return ApiResponse.success("Hello World");
}
// 2. 抛出自定义业务异常
@GetMapping("/user/{id}")
public ApiResponse<String> getUser(@PathVariable @Min(1) Long id) {
if (id == 999) {
throw new BizException(1001, "用户不存在");
}
return ApiResponse.success("User-" + id);
}
// 3. 参数校验失败(POST JSON)
@PostMapping("/user")
public ApiResponse<String> createUser(@Valid @RequestBody CreateUserRequest request) {
return ApiResponse.success("创建成功: " + request.getName());
}
// 4. 模拟 NPE
@GetMapping("/npe")
public ApiResponse<String> triggerNpe() {
String s = null;
s.length(); // 故意触发 NPE
return ApiResponse.success("不会执行到这里");
}
// DTO
public static class CreateUserRequest {
@NotBlank(message = "姓名不能为空")
private String name;
@Min(value = 18, message = "年龄不能小于18岁")
private Integer age;
// getter/setter
public String getName() { return name; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
public Integer getAge() { return age; }
public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; }
}
}第五步:启动类
xml
// src/main/java/com/example/exceptiondemo/ExceptionDemoApplication.java
package com.example.exceptiondemo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ExceptionDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ExceptionDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}✅ 测试效果(用 curl 或 Postman)
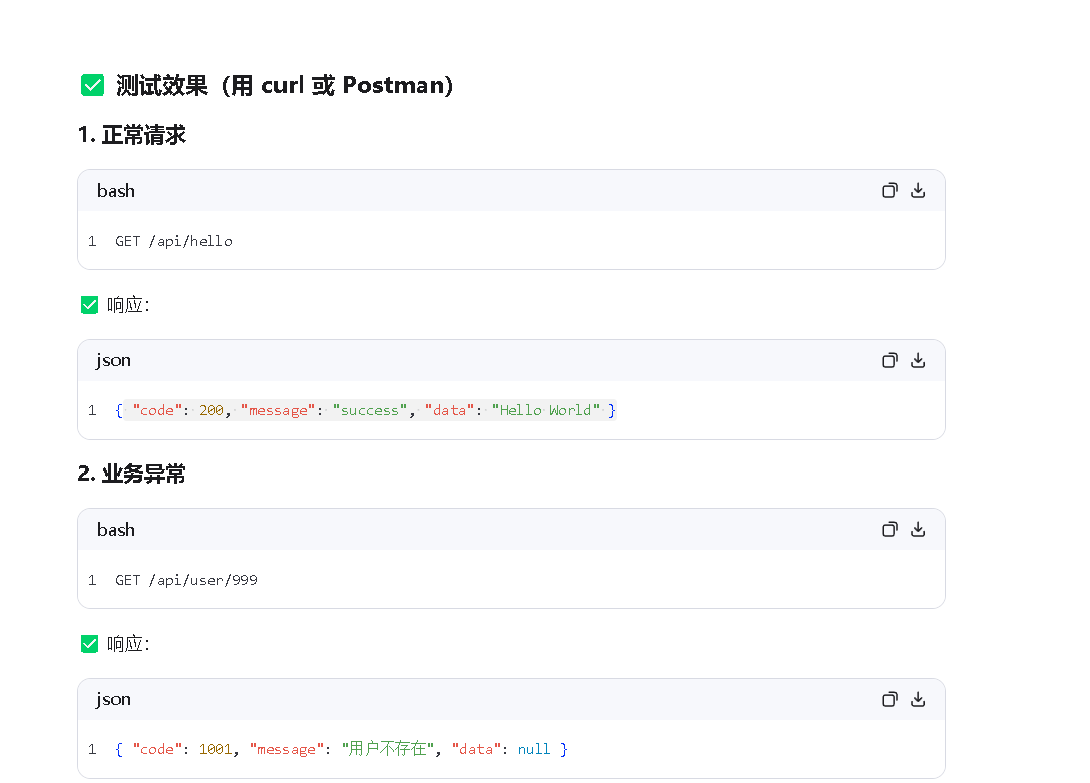
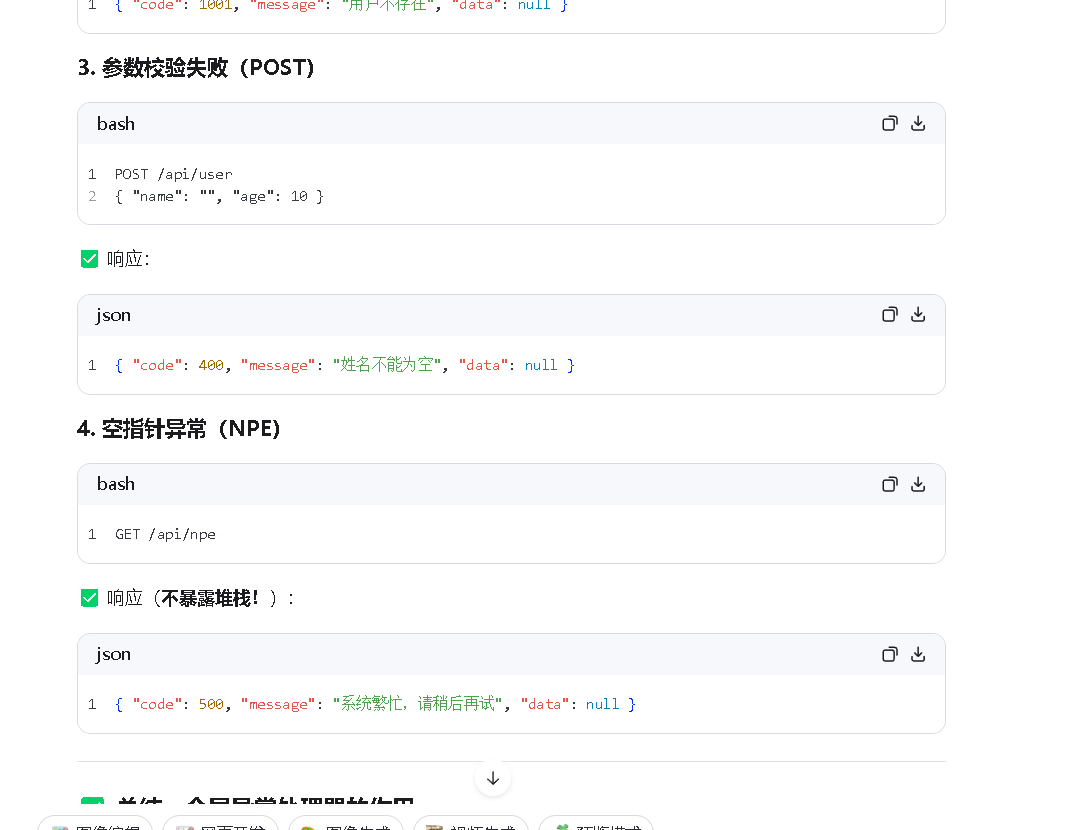
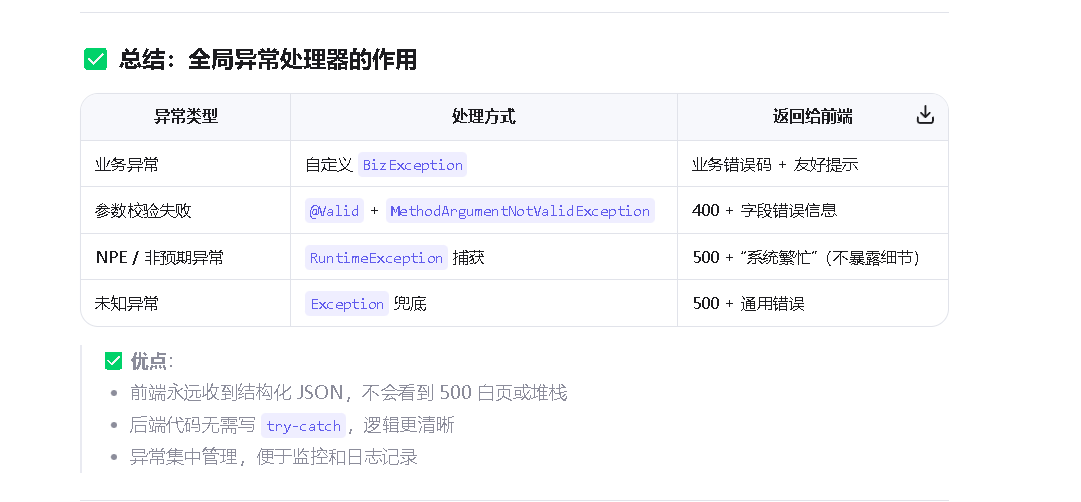
**
**
对于对前面的代码的梳理