前置头文件
cpp
.PHONY:all
all:UdpServer UdpClient
UdpServer:UdpServer.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++17
UdpClient:UdpClient.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++17
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -f UdpClient UdpServer
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <mutex>
#include <pthread.h>
class Mutex
{
public:
Mutex()
{
pthread_mutex_init(&_lock, nullptr);
}
void Lock()
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&_lock);
}
void Unlock()
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_lock);
}
pthread_mutex_t *Get()
{
return &_lock;
}
~Mutex()
{
pthread_mutex_destroy(&_lock);
}
private:
pthread_mutex_t _lock;
};
class LockGuard
{
public:
LockGuard(Mutex *_mutex):_mutexp(_mutex)
{
_mutexp->Lock();
}
~LockGuard()
{
_mutexp->Unlock();
}
private:
Mutex *_mutexp;
};
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "Mutex.hpp"
class Cond
{
public:
Cond()
{
pthread_cond_init(&_cond, nullptr);
}
void Wait(Mutex &lock)
{
int n = pthread_cond_wait(&_cond, lock.Get());
}
void NotifyOne()
{
int n = pthread_cond_signal(&_cond);
(void)n;
}
void NotifyAll()
{
int n = pthread_cond_broadcast(&_cond);
(void)n;
}
~Cond()
{
pthread_cond_destroy(&_cond);
}
private:
pthread_cond_t _cond;
};
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <filesystem> // C++17 文件操作
#include <fstream>
#include <ctime>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <memory>
#include <sstream>
#include "Mutex.hpp"
// 规定出场景的日志等级
enum class LogLevel
{
DEBUG,
INFO,
WARNING,
ERROR,
FATAL
};
// 日志转换成为字符串
std::string Level2String(LogLevel level)
{
switch (level)
{
case LogLevel::DEBUG:
return "Debug";
case LogLevel::INFO:
return "Info";
case LogLevel::WARNING:
return "Warning";
case LogLevel::ERROR:
return "Error";
case LogLevel::FATAL:
return "Fatal";
default:
return "Unknown";
}
}
// 根据时间戳,获取可读性较强的时间信息
// 20XX-08-04 12:27:03
std::string GetCurrentTime()
{
// 1. 获取时间戳
time_t currtime = time(nullptr);
// 2. 如何把时间戳转换成为20XX-08-04 12:27:03
struct tm currtm;
localtime_r(&currtime, &currtm);
// 3. 转换成为字符串
char timebuffer[64];
snprintf(timebuffer, sizeof(timebuffer), "%4d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d",
currtm.tm_year + 1900,
currtm.tm_mon + 1,
currtm.tm_mday,
currtm.tm_hour,
currtm.tm_min,
currtm.tm_sec);
return timebuffer;
}
// 策略模式,策略接口
// 1. 刷新的问题 -- 假设我们已经有了一条完整的日志,string->设备(显示器,文件)
// 基类方法
class LogStrategy
{
public:
// 不同模式核心是刷新方式的不同
virtual ~LogStrategy() = default;
virtual void SyncLog(const std::string &logmessage) = 0;
};
// 控制台日志策略,就是日志只向显示器打印,方便我们debug
// 显示器刷新
class ConsoleLogStrategy : public LogStrategy
{
public:
~ConsoleLogStrategy()
{
}
void SyncLog(const std::string &logmessage) override
{
{
LockGuard lockguard(&_lock);
std::cout << logmessage << std::endl;
}
}
private:
// 显示器也是临界资源,保证输出线程安全
Mutex _lock;
};
// 默认路径和日志名称
const std::string logdefaultdir = "log";
const static std::string logfilename = "test.log";
// 文件日志策略
// 文件刷新
class FileLogStrategy : public LogStrategy
{
public:
// 构造函数,建立出来指定的目录结构和文件结构
FileLogStrategy(const std::string &dir = logdefaultdir,
const std::string filename = logfilename)
: _dir_path_name(dir), _filename(filename)
{
LockGuard lockguard(&_lock);
if (std::filesystem::exists(_dir_path_name))
{
return;
}
try
{
std::filesystem::create_directories(_dir_path_name);
}
catch (const std::filesystem::filesystem_error &e)
{
std::cerr << e.what() << "\r\n";
}
}
// 将一条日志信息写入到文件中
void SyncLog(const std::string &logmessage) override
{
{
LockGuard lockguard(&_lock);
std::string target = _dir_path_name;
target += "/";
target += _filename;
// 追加方式
std::ofstream out(target.c_str(), std::ios::app); // append
if (!out.is_open())
{
return;
}
out << logmessage << "\n"; // out.write
out.close();
}
}
~FileLogStrategy()
{
}
private:
std::string _dir_path_name; // log
std::string _filename; // hello.log => log/hello.log
Mutex _lock;
};
// 具体的日志类
// 1. 定制刷新策略
// 2. 构建完整的日志
class Logger
{
public:
Logger()
{
}
void EnableConsoleLogStrategy()
{
_strategy = std::make_unique<ConsoleLogStrategy>();
}
void EnableFileLogStrategy()
{
_strategy = std::make_unique<FileLogStrategy>();
}
// 内部类,实现RAII风格的日志格式化和刷新
// 这个LogMessage,表示一条完整的日志对象
class LogMessage
{
public:
// RAII风格,构造的时候构建好日志头部信息
LogMessage(LogLevel level, std::string &filename, int line, Logger &logger)
: _curr_time(GetCurrentTime()),
_level(level),
_pid(getpid()),
_filename(filename),
_line(line),
_logger(logger)
{
// stringstream不允许拷贝,所以这里就当做格式化功能使用
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "[" << _curr_time << "] "
<< "[" << Level2String(_level) << "] "
<< "[" << _pid << "] "
<< "[" << _filename << "] "
<< "[" << _line << "]"
<< " - ";
_loginfo = ss.str();
}
// 重载 << 支持C++风格的日志输入,使用模版,表示支持任意类型
template <typename T>
LogMessage &operator<<(const T &info)
{
std::stringstream ss;
ss << info;
_loginfo += ss.str();
return *this;
}
// RAII风格,析构的时候进行日志持久化,采用指定的策略
~LogMessage()
{
if (_logger._strategy)
{
_logger._strategy->SyncLog(_loginfo);
}
}
private:
std::string _curr_time; // 日志时间
LogLevel _level; // 日志等级
pid_t _pid; // 进程pid
std::string _filename;
int _line;
std::string _loginfo; // 一条合并完成的,完整的日志信息
Logger &_logger; // 引用外部logger类, 方便使用策略进行刷新
};
// 故意拷贝,形成LogMessage临时对象,后续在被<<时,会被持续引用,
// 直到完成输入,才会自动析构临时LogMessage,至此也完成了日志的显示或者刷新
// 同时,形成的临时对象内包含独立日志数据
// 未来采用宏替换,进行文件名和代码行数的获取
LogMessage operator()(LogLevel level, std::string filename, int line)
{
return LogMessage(level, filename, line, *this);
}
~Logger()
{
}
private:
// 写入日志的策略
std::unique_ptr<LogStrategy> _strategy;
};
// 定义全局的logger对象
Logger logger;
// 使用宏,可以进行代码插入,方便随时获取文件名和行号
#define LOG(level) logger(level, __FILE__, __LINE__)
// 提供选择使用何种日志策略的方法
#define EnableConsoleLogStrategy() logger.EnableConsoleLogStrategy()
#define EnableFileLogStrategy() logger.EnableFileLogStrategy()
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <functional>
#include <sys/syscall.h> /* For SYS_xxx definitions */
#include "Logger.hpp"
#define get_lwp_id() syscall(SYS_gettid)
using func_t = std::function<void(const std::string&name)>;
const std::string threadnamedefault = "None-Name";
class Thread
{
public:
Thread(func_t func, const std::string &name = threadnamedefault)
: _name(name),
_func(func),
_isrunning(false)
{
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << _name << " create thread obj success";
}
static void *start_routine(void *args)
{
Thread *self = static_cast<Thread *>(args);
self->_isrunning = true;
self->_lwpid = get_lwp_id();
self->_func(self->_name);
pthread_exit((void *)0);
}
void Start()
{
int n = pthread_create(&_tid, nullptr, start_routine, this);
if (n == 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << _name << " running success";
}
}
void Stop()
{
int n = pthread_cancel(_tid); // 太简单粗暴了
(void)n;
}
// void Die()
// {
// pthread_cancel(_tid);
// }
// 检测线程结束并且回收的功能
void Join()
{
if (!_isrunning)
return;
int n = pthread_join(_tid, nullptr);
if (n == 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << _name << " pthread_join success";
}
}
~Thread()
{
// LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << _name << " destory thread obj success";
}
private:
bool _isrunning;
pthread_t _tid;
pid_t _lwpid;
std::string _name;
func_t _func;
};
cpp
#pragma once
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include "Thread.hpp"
#include "Cond.hpp"
#include "Logger.hpp"
using namespace std;
// 单例线程池 - 懒汉模式
const static int default_thread_num = 3;
template <typename T>
class ThreadPool
{
void Routine(string name)
{
while (true)
{
T t;
{
LockGuard lock(&_mutex);
// 如果线程池正在运行且任务队列为空
// 注意,一定要使用while,防止出错
while (_is_running && QueueIsEmpty())
{
_wait_thread_num++;
_cond.Wait(_mutex); // 线程唤醒后执行的是这里的逻辑 如果队列为空了 就要离开循环了
_wait_thread_num--;
}
// 如果线程池要退出且任务队列为空
if (!_is_running && QueueIsEmpty())
{
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "线程池准备退出&&任务队列为空 " << name.c_str() << "退出";
break;
}
// 此时任务队列一定不为空,存在两种情况
// 1. 线程池准备退出 -- 消耗历史任务
// 2. 线程池没有准备退出 -- 正常工作
t = _task_queue.front();
_task_queue.pop();
// LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << name << "::::" <<_task_queue.size();
// if (!QueueIsEmpty())
// {
// t = _task_queue.front();
// //Linux上面实现的stl库,队列为空的时候(size==0)还可以去数据导致(size--)
// //拿到了一个0+0 = 0的任务
// //然后size(size_t类型的数据没有负数)就变成了一个非常大的正数,队列就不为空了
// //这里段错误和数组的越界访问类似 然后一直拿去数据 触发了段错误
// _task_queue.pop();
// }
}
// 此时,线程已经把任务从临界资源获取到线程私有!临界区 -> 线程私有的栈
// 处理任务时不需要再临界区内部进行,并发进行效率更高
t(); // 规定,未来的任务必须这样处理!operate()重载
//LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << name << " handler task: " << t.Result2String();
}
}
private:
// 将构造函数设为私有,不允许用户直接创建对象
ThreadPool(int threadnum = default_thread_num)
: _thread_num(threadnum),
_wait_thread_num(0),
_is_running(false)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= _thread_num; i++)
{
// 方法1:
// auto f = std::bind(hello, this);
// 方法2
string name = "thread-" + to_string(i);
// emplace_back()是STL容器(如vector、deque、list)的成员函数,
// 用于在容器尾部直接构造元素,避免不必要的拷贝或移动。
_threads.emplace_back([this](const string &name)
{ this->Routine(name); }, name);
}
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "thread pool obj create success";
}
// 禁掉拷贝构造和赋值重载
ThreadPool<T> &operator=(const ThreadPool<T> &) = delete;
ThreadPool(const ThreadPool<T> &) = delete;
public:
void Start()
{
if (_is_running)
return;
_is_running = true;
for (auto &t : _threads)
t.Start();
}
void Stop()
{
// 线程池要退出,不是立刻就能退出的,它要把任务队列中的任务处理完后才能退出
if (!_is_running)
return;
_is_running = false;
// 线程池都要退出了,那些休眠的线程还休眠什么,赶紧把他们全部唤醒
// 处理完任务后线程池好退出
if (_wait_thread_num)
_cond.NotifyAll();
}
void Enqueue(const T &task)
{
// 如果线程池准备退出,任务就不要入队列了
if (!_is_running)
return;
{
LockGuard lock(&_mutex);
_task_queue.push(task);
// LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "一个任务入队列了";
if (_wait_thread_num)
_cond.NotifyOne();
}
}
void Wait()
{
for (auto &t : _threads)
{
t.Join();
}
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "thread pool wait success";
}
bool QueueIsEmpty()
{
return _task_queue.empty();
}
// 用static修饰的成员函数,称之为静态成员函数,静态成员函数没有this指针
// 静态成员函数中可以访问其他的静态成员,但是不能访问非静态的,因为没有this指针
// 静态成员函数只能访问静态成员,非静态的成员函数,可以访问任意的静态成员变量和静态成员函数
// 地址转字符串,证明多线程申请的单例都是同一个
static std::string ToHex(ThreadPool<T> *addr)
{
char buffer[64];
snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "%p", addr);
return buffer;
}
// 获取单例
static ThreadPool<T> *GetInstance()
{
// A, B, c
// 线程安全,提高效率式的获取单例
// 双重 if 判定, 避免不必要的锁竞争
if (!_instance)
{
// 外层if是为了防止获取单例后多线程申请单例时判断前还要申请锁,降低效率
// 保证第二次之后,所有线程,不用在加锁,直接返回_instance单例对象
LockGuard lockguard(&_singleton_lock);
if (!_instance)
{
_instance = new ThreadPool<T>();
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "线程池单例首次被使用,创建并初始化, addr: " << ToHex(_instance);
_instance->Start();
}
}
else
{
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "线程池单例已经存在,直接获取, addr: " << ToHex(_instance);
}
return _instance;
}
~ThreadPool()
{
}
private:
// 任务队列
queue<T> _task_queue; // 整体使用的临界资源
vector<Thread> _threads;
int _thread_num; // 线程池中线程个数
int _wait_thread_num; // 线程池正在等待的线程个数
// 保护线程池安全
Mutex _mutex;
Cond _cond;
// 检测线程池是否在运行
bool _is_running;
// 单例中静态指针
// 需要设置 volatile 关键字, 防止被编译器优化.
// volatile static ThreadPool<T> *_instance;
// 用static修饰的成员变量,称之为静态成员变量,静态成员变量一定要在类外进行初始化。
// 类内定义,类外初始化
// 添加单例模式
static ThreadPool<T> *_instance;
static Mutex _singleton_lock;
};
template <class T>
ThreadPool<T> *ThreadPool<T>::_instance = nullptr;
template <class T>
Mutex ThreadPool<T>::_singleton_lock;聊天室主体
cpp
#pragma once
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include "Logger.hpp"
using namespace std;
#define Conv(addr) ((struct sockaddr *)&addr)
class InetAddr
{
private:
void Net2Host()
{
_port = ntohs(_addr.sin_port);
_ip = inet_ntoa(_addr.sin_addr);
//LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << _ip << _port;
}
void Host2Net()
{
memset(&_addr, 0, sizeof(_addr));
_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
_addr.sin_port = htons(_port);
_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(_ip.c_str());
}
public:
InetAddr(uint16_t port,string ip)
: _ip(ip),
_port(port)
{
Host2Net();
}
InetAddr(struct sockaddr_in &addr)
{
_addr = addr;
Net2Host();
}
struct sockaddr *Addr()
{
return Conv(_addr);
}
string IP()
{
return _ip;
}
uint16_t Port()
{
return _port;
}
bool operator==(const InetAddr &addr)
{
return _ip == addr._ip && _port == addr._port;
}
socklen_t Length()
{
return sizeof(_addr);
}
string ToString()
{
return _ip + "-" + to_string(_port);
}
~InetAddr()
{
}
private:
// 网络风格地址
struct sockaddr_in _addr;
// 主机风格地址
string _ip;
uint16_t _port;
};
cpp
#pragma once
#include "InetAddr.hpp"
#include <vector>
#include "Logger.hpp"
class Routine
{
private:
bool IsExist(const InetAddr &addr)
{
for (auto &user : _online_user)
{
if (user == addr)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void AddUser(const InetAddr &user)
{
if (!IsExist(user))
_online_user.push_back(user);
return;
}
void DeleteUser(const string &message, const InetAddr &addr)
{
// 权宜之计, 自定义协议部分
if (message == "QUIT")
{
auto iter = _online_user.begin();
for (; iter != _online_user.end(); iter++)
{
if (*iter == addr)
{
_online_user.erase(iter);
break;
}
}
}
}
void SendMessageToAll(int sockfd, string message, InetAddr &addr)
{
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << " [" << message << "] from : " << addr.ToString();
string s = addr.ToString();
s += "# ";
s += message;
// LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "--------------: " << _online_user.size();
for (auto &user : _online_user)
{
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "route [" << message << "] to : " << user.ToString();
sendto(sockfd, s.c_str(), s.size(), 0, user.Addr(), user.Length());
}
}
public:
Routine()
{
}
void RoutineToAll(int sockfd, string message, InetAddr &addr)
{
AddUser(addr);
SendMessageToAll(sockfd, message, addr);
DeleteUser(message, addr);
}
~Routine()
{
}
private:
// 在线用户列表
vector<InetAddr> _online_user;
};
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include "InetAddr.hpp"
#include "Route.hpp"
using callback_t = std::function<void(int sockfd, std::string message, InetAddr addr)>;
class UdpServer
{
public:
UdpServer(uint16_t port, callback_t cb)
: _port(port),
_cb(cb),
_socketfd(-1),
_isrunning(false)
{
}
void Init()
{
// 1. 创建socket fd
_socketfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
if (_socketfd < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::FATAL) << "create socket error";
exit(1);
}
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "create socket success : " << _socketfd;
InetAddr local(_port,"0.0.0.0");
// 2.2 和socketfd进行bind
int n = bind(_socketfd, local.Addr(), local.Length());
if (n < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::FATAL) << "bind socket error";
exit(2);
}
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "bind socket success : " << _socketfd;
}
void Start()
{
// 所有的服务器都是死循环,一直在运行
_isrunning = true;
while (_isrunning)
{
// 定义一个缓冲区从 socket 接收数据
char buffer[1024];
// 缓冲区清零
buffer[0] = 0;
// 当我们收到消息时我们也应该知道消息的发送方是谁以便之后给它回消息
struct sockaddr_in peer;
socklen_t len = sizeof(peer);
// 1. 读取数据
ssize_t n = recvfrom(_socketfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&peer, &len);
// 没有加字符串的结束标志\0
buffer[n] = '\0';
if (n < 0)
{
cout << "recvfrom fail" << endl;
_isrunning = false;
exit(1);
}
//LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "get a client info # " << inet_ntoa(peer.sin_addr) << "- " << ntohs(peer.sin_port);
InetAddr client(peer);
// LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "get a client info # "
// << client.IP() << "-" << client.Port() << ": "
// << buffer;
std::string message = buffer;
// 回调!
_cb(_socketfd, message, client);
}
}
~UdpServer() {}
void Stop()
{
_isrunning = false;
}
private:
int _socketfd;
uint16_t _port;
callback_t _cb;
// 设一个标志看服务器是否在运行
bool _isrunning;
};
cpp
#include"UdpServer.hpp"
#include"ThreadPool.hpp"
#include<memory>
// ./udp_server serverport
using task_t=function<void()>;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if(argc != 2)
{
cout<<"格式错误"<<endl;
cout<<argv[0]<<" server port"<<endl;
exit(1);
}
uint16_t port =stoi(argv[1]);
EnableConsoleLogStrategy();
//1.消息转发功能
unique_ptr<Routine> r=make_unique<Routine>();
//2.线程池对象
auto tp=ThreadPool<task_t>::GetInstance();
//服务器对象
std::unique_ptr<UdpServer> usvr = std::make_unique<UdpServer>(port,
[&r, &tp](int sockfd, std::string message, InetAddr addr){
// 包装普通成员函数
// 普通成员函数还有一个隐含的this指针参数,所以绑定时传对象或者对象的指针过去都可以
task_t task = bind(&Routine::RoutineToAll, r.get(), sockfd, message, addr); //成员函数第一个参数是隐藏的this指针
tp->Enqueue(task); //这个是回调函数,每当客户端发消息时服务器都会回调这个函数
//所以说不会有只入了一个任务就不入了的情况
}
);
usvr->Init();
usvr->Start();
return 0;
}
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <thread>
using namespace std;
void Usage(std::string proc)
{
std::cout << "Usage: " << proc << " serverip serverport" << std::endl;
}
int sockfd = -1;
std::string serverip;
uint16_t serverport;
void InitClient(const std::string &serverip, uint16_t serverport)
{
sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
if (sockfd < 0)
{
std::cout << "create socket errror" << std::endl;
}
}
void recver()
{
while (true)
{
struct sockaddr_in temp;
socklen_t len = sizeof(temp);
char buffer[1024];
int m = recvfrom(sockfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&temp, &len);
if (m > 0)
{
buffer[m] = 0;
cerr << buffer << std::endl; // 1->2
}
}
}
void sender()
{
struct sockaddr_in server;
memset(&server, 0, sizeof(server));
server.sin_family = AF_INET;
server.sin_port = htons(serverport);
server.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(serverip.c_str());
while (true)
{
std::cout << "my input:"; //1
std::string line;
std::getline(std::cin, line); //0
// 写
sendto(sockfd, line.c_str(), line.size(), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&server, sizeof(server));
}
}
// ./udp_client server_ip server_port
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 3)
{
Usage(argv[0]);
exit(0);
}
serverip = argv[1];
serverport = std::stoi(argv[2]);
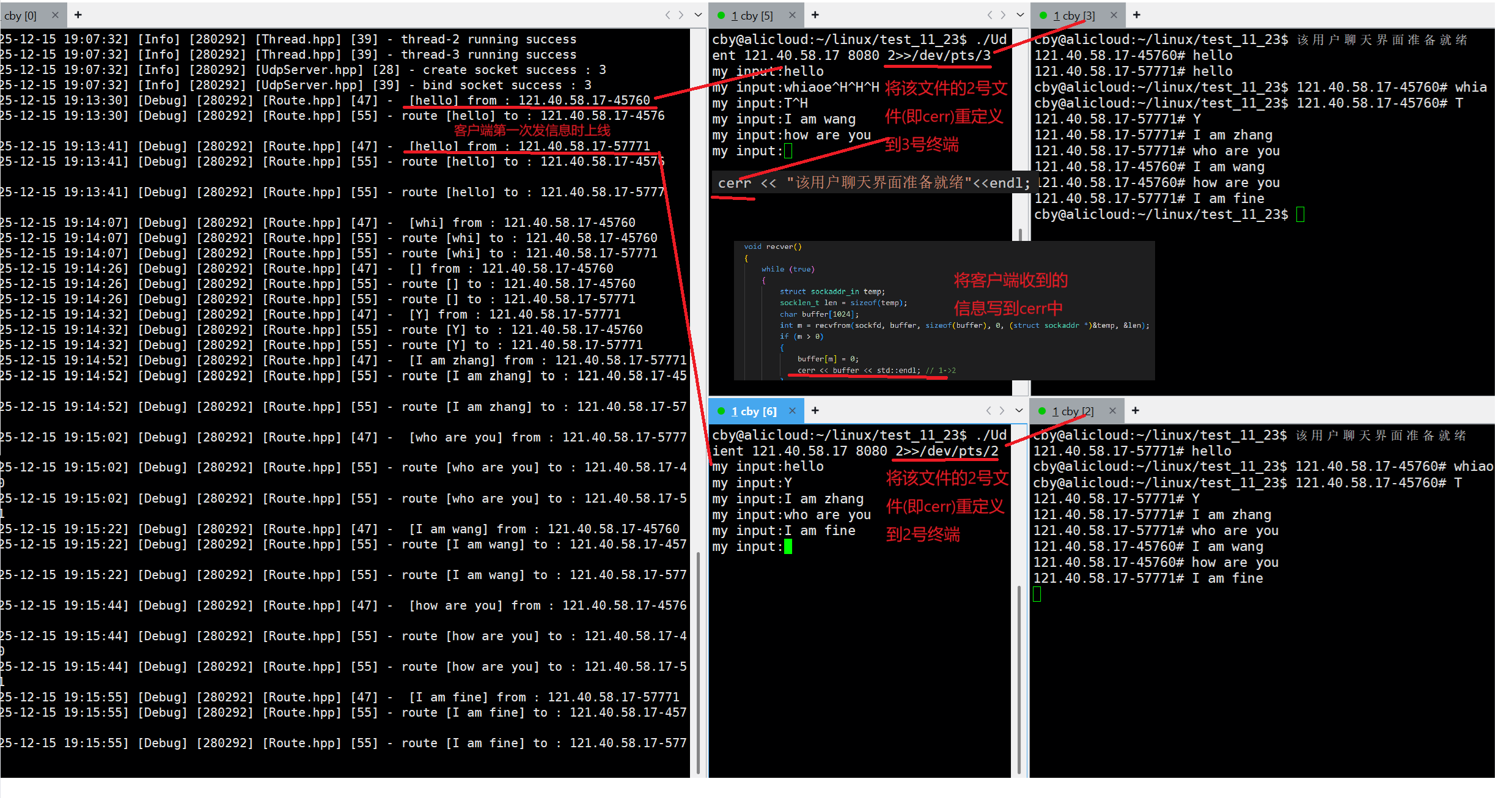
cerr << "该用户聊天界面准备就绪"<<endl;
InitClient(serverip, serverport);
std::thread trecv(recver);
std::thread tsend(sender);
trecv.join();
tsend.join();
return 0;
}结果展示
cpp
tty示例输出
/dev/pts/2
说明你现在正在 /dev/pts/2 这个终端里打字,它就是"你在输入的显示器文件"。