**前言:**最近在复习 Linux 网络编程,重点梳理了 UDP 协议的实现细节。虽然 UDP 是无连接、不可靠的协议,但其简单高效的特性在很多场景下(如实时音视频、DNS)依然是首选。从最简单的 Echo Server 出发,逐步重构为支持业务解耦的字典服务器,最后实现一个支持多线程的全双工聊天室,并探讨其中涉及的地址转换陷阱。
一、UDP 编程的核心套路
与 TCP 不同,UDP 不需要维护连接状态(没有三次握手),因此其系统调用更加精简。
核心 API 概览
- socket() : 创建套接字,参数需指定
SOCK_DGRAM。 - bind() : 服务器必须显式绑定 IP 和 Port;客户端通常不需要显式绑定,由 OS 在首次发送数据时自动分配随机端口 。
- recvfrom() : 核心读取函数。因为没有连接,必须通过参数(
src_addr)获取发送方的地址信息(IP+Port),否则无法回信 。 - sendto() : 核心发送函数。必须指定目标地址(
dest_addr)。
为什么服务器推荐绑定
INADDR_ANY?
在云服务器或多网卡机器上,直接绑定公网 IP 可能会失败(因为公网 IP 通常是在云厂商的 NAT 网关上)。 最佳实践是绑定 INADDR_ANY (0.0.0.0)。
含义:服务器愿意接收本机所有网卡(任意 IP)转发到该端口的数据 。
优势:通用性强,无需关心具体 IP 变动。
二、不同版本的UDP服务器
V1 版本:Echo Server(最简模型)
这是 UDP 的"Hello World"。逻辑非常简单:收到什么,就发回什么。
关键点 在于使用 recvfrom 获取客户端的 sockaddr,利用这个地址直接 sendto 返回数据。
不足在于网络逻辑和业务逻辑耦合在一起,无法扩展。
服务端由以下几个文件组成:
UdpServer.hpp:
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include "Logger.hpp"
static const int gdefaultsockfd = -1;
class UdpServer
{
public:
UdpServer(uint16_t port) : _sockfd(gdefaultsockfd), _port(port), _isrunning(false)
{
}
void Init()
{
// 1.创建套接字
_sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0); // 把网络在文件系统中展开
if (_sockfd < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::FATAL) << "create socket error";
exit(1);
}
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "create socket success: " << _sockfd;
// 2.bind套接字
// 2.1 填充IP和Port
struct sockaddr_in local;
bzero(&local, sizeof(local));
local.sin_family = AF_INET;
local.sin_port = htons(_port); // 统一大端
// local.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(_ip.c_str()); // inet_addr 1. 字符串转整数ip 2. 整数ip是网络序列的
local.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY); // 任意IPbind 不明确具体IP,只要发给对应的主机,对应的port,全都能收到
// 2.2 和socketfd进行bind
int n = bind(_sockfd, (const sockaddr *)&local, sizeof(local));
if (n < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::FATAL) << "bind socket error";
exit(2);
}
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "bind socket success : " << _sockfd;
}
void Start()
{
_isrunning = true;
while (_isrunning)
{
// 读取数据
char buffer[1024];
buffer[0] = 0; // O(1) 清空数据
struct sockaddr_in peer;
socklen_t len = sizeof(peer);
ssize_t n = recvfrom(_sockfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&peer, &len); // flag == 0 , 阻塞模式
if (n > 0)
{
uint16_t clientport = ntohs(peer.sin_port);
std::string clientip = inet_ntoa(peer.sin_addr);
buffer[n] = 0;
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "[" << clientip << " : " << clientport << "]#" << buffer;
std::string echo_string = "server echo# ";
echo_string += buffer;
sendto(_sockfd, echo_string.c_str(), echo_string.size(), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&peer, len);
}
}
_isrunning = false;
}
void Stop()
{
_isrunning = false;
}
~UdpServer()
{
}
private:
int _sockfd;
uint16_t _port;
// std::string _ip; // 不建议绑定固定ip
bool _isrunning;
};
cpp
#include "UdpServer.hpp"
#include <memory>
void Usage(std::string proc)
{
std::cerr << "Usage :" << proc << "loaclport" << std::endl;
}
// ./udp_server serverport
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 2)
{
Usage(argv[0]);
exit(0);
}
uint16_t localport = std::stoi(argv[1]);
EnableConsoleLogStrategy();
std::unique_ptr<UdpServer> ptr = std::make_unique<UdpServer>(localport);
ptr->Init();
ptr->Start();
return 0;
}客户端文件为:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <string>
void Usage(std::string proc)
{
std::cerr << "Usage :" << proc << "serverip serverport" << std::endl;
}
// ./udp_client serverip serverport
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 3)
{
Usage(argv[0]);
exit(0);
}
int sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
if (sockfd < 0)
{
std::cout << "create socket error" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
std::string serverip = argv[1];
uint16_t serverport = std::stoi(argv[2]);
struct sockaddr_in server;
bzero(&server, sizeof(server));
server.sin_family = AF_INET;
server.sin_port = htons(serverport);
server.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(serverip.c_str());
socklen_t len = sizeof(server);
while (true)
{
std::cout << "Please Enter@ ";
std::string line;
std::getline(std::cin, line);
sendto(sockfd, line.c_str(), line.size(), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&server, len);
char buffer[1024];
struct sockaddr_in temp;
socklen_t len = sizeof(temp);
ssize_t m = recvfrom(sockfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&temp, &len);
if(m > 0)
{
buffer[m] = 0;
std::cout << buffer << std::endl;
}
}
return 0;
}V2 版本:Dict Server(业务解耦)
为了让服务器能处理不同业务(如英译汉、查数据),我们需要将"网络收发"与"业务处理"分离。
设计模式:策略模式 / 回调函数。
实现 :定义一个 callback_t 类型(利用 C++11 std::function):
cpp
using callback_t = std::function<std::string(const std::string &word, const std::string &whoip, uint16_t whoport)>;服务器类 UdpServer 持有一个 func_t 成员。在 Recv 之后,调用回调函数处理业务,获取结果后再 Send 。
服务端文件为:
DictServer.hpp:
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <functional>
#include "Logger.hpp"
using callback_t = std::function<std::string(const std::string &word, const std::string &whoip, uint16_t whoport)>;
static const int gdefaultsockfd = -1;
class DictServer
{
public:
DictServer(uint16_t port, callback_t func)
: _sockfd(gdefaultsockfd), _port(port), _cb(func), _isrunning(false)
{
}
void Init()
{
// 1.创建套接字
_sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0); // 把网络在文件系统中展开
if (_sockfd < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::FATAL) << "create socket error";
exit(1);
}
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "create socket success: " << _sockfd;
// 2.bind套接字
// 2.1 填充IP和Port
struct sockaddr_in local;
bzero(&local, sizeof(local));
local.sin_family = AF_INET;
local.sin_port = htons(_port); // 统一大端
// local.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(_ip.c_str()); // inet_addr 1. 字符串转整数ip 2. 整数ip是网络序列的
local.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY); // 任意IPbind 不明确具体IP,只要发给对应的主机,对应的port,全都能收到
// 2.2 和socketfd进行bind
int n = bind(_sockfd, (const sockaddr *)&local, sizeof(local));
if (n < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::FATAL) << "bind socket error";
exit(2);
}
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "bind socket success : " << _sockfd;
}
void Start()
{
_isrunning = true;
while (_isrunning)
{
// 读取数据
char buffer[1024];
buffer[0] = 0; // O(1) 清空数据
struct sockaddr_in peer;
socklen_t len = sizeof(peer);
ssize_t n = recvfrom(_sockfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&peer, &len); // flag == 0 , 阻塞模式
if (n > 0)
{
uint16_t clientport = ntohs(peer.sin_port);
std::string clientip = inet_ntoa(peer.sin_addr);
buffer[n] = 0;
// buffer[n] = 0;
// LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "[" << clientip << " : " << clientport << "]#" << buffer;
// std::string echo_string = "server echo# ";
// echo_string += buffer;
std::string word = buffer;
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "用户查找: " << word;
std::string result = _cb(word, clientip, clientport);
sendto(_sockfd, result.c_str(), result.size(), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&peer, len);
}
}
_isrunning = false;
}
void Stop()
{
_isrunning = false;
}
~DictServer()
{
}
private:
int _sockfd;
uint16_t _port;
// std::string _ip; // 不建议绑定固定ip
callback_t _cb;
bool _isrunning;
};Dictionary.hpp:
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <string>
#include <filesystem>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include "Logger.hpp"
static const std::string sep = ": ";
class Dictionary
{
private:
void LoadConf()
{
std::ifstream in(_path);
if (!in.is_open())
{
LOG(LogLevel::ERROR) << "open file error" << _path;
return;
}
std::string line;
while (std::getline(in, line))
{
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "load dict message: " << line;
auto pos = line.find(sep);
if (pos == std::string::npos)
{
LOG(LogLevel::WARNING) << "format error: " << line;
continue;
}
std::string word = line.substr(0, pos);
std::string value = line.substr(pos + sep.size());
if (word.empty() || value.empty())
{
LOG(LogLevel::WARNING) << "format error, word or value is empty";
}
_dict.insert({word, value});
}
in.close();
}
public:
Dictionary(const std::string &path) : _path(path)
{
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "construct Dictionary obj";
LoadConf();
}
std::string Translate(const std::string &word, const std::string &whoip, uint16_t whoport)
{
(void)whoip,(void)whoport;
auto iter = _dict.find(word);
if(iter == _dict.end())
{
return "unknown";
}
return iter->first + " -> " + iter->second;
}
~Dictionary()
{
}
private:
std::string _path;
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _dict;
};
cpp
#include "DictServer.hpp"
#include "Dictionary.hpp"
#include <memory>
void Usage(std::string proc)
{
std::cerr << "Usage :" << proc << " loaclport" << std::endl;
}
// ./udp_server serverport
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 2)
{
Usage(argv[0]);
exit(0);
}
EnableConsoleLogStrategy();
Dictionary dict("./dict.txt");
uint16_t localport = std::stoi(argv[1]);
std::unique_ptr<DictServer> ptr = std::make_unique<DictServer>(localport,
[&dict](const std::string &word, const std::string &whoip, uint16_t whoport) -> std::string
{
return dict.Translate(word, whoip, whoport);
});
ptr->Init();
ptr->Start();
return 0;
}客户端文件为:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <string>
void Usage(std::string proc)
{
std::cerr << "Usage :" << proc << "serverip serverport" << std::endl;
}
// ./udp_client serverip serverport
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 3)
{
Usage(argv[0]);
exit(0);
}
int sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
if (sockfd < 0)
{
std::cout << "create socket error" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
std::string serverip = argv[1];
uint16_t serverport = std::stoi(argv[2]);
struct sockaddr_in server;
bzero(&server, sizeof(server));
server.sin_family = AF_INET;
server.sin_port = htons(serverport);
server.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(serverip.c_str());
socklen_t len = sizeof(server);
// client 不需要显示bind自己的ip和端口
// client会在os的帮助下,随机bind端口号,防止端口冲突
while (true)
{
std::cout << "Please Enter@ ";
std::string line;
std::getline(std::cin, line);
sendto(sockfd, line.c_str(), line.size(), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&server, len);
char buffer[1024];
buffer[0] = 0;
struct sockaddr_in temp;
socklen_t len = sizeof(temp);
ssize_t m = recvfrom(sockfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&temp, &len);
if(m > 0)
{
buffer[m] = 0;
std::cout << buffer << std::endl;
}
}
return 0;
}效果 :UdpServer 变成了通用的网络底层,具体的查字典逻辑(加载 dict.txt 到 unordered_map)封装在外部模块中 。
V3 版本:多人聊天室(状态管理与多线程)
这是最复杂的场景,实现了类似群聊的功能。
服务端设计: 消息路由,服务端不再是简单的"请求-响应"模型,而是变成了消息分发中心。
用户管理 :维护一个在线用户列表 std::vector<InetAddr>。
核心逻辑:
- 接收消息。
- 检查发送者是否在用户列表中。如果不在,视为新用户上线,加入列表 。
- 广播 :遍历用户列表,将消息
sendto给除了发送者之外的所有人(或所有人)。- 处理指令(如 "QUIT"):从列表中移除用户 。
服务端由以下几个文件组成:
ChatServer.hpp:
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <functional>
#include "Logger.hpp"
#include "InetAddr.hpp"
using callback_t = std::function<void(int socket, const std::string message, InetAddr inetaddr)>; // 不要设为引用
static const int gdefaultsockfd = -1;
class ChatServer
{
public:
ChatServer(uint16_t port, callback_t func)
: _sockfd(gdefaultsockfd), _port(port), _cb(func), _isrunning(false)
{
}
void Init()
{
// 1.创建套接字
_sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0); // 把网络在文件系统中展开
if (_sockfd < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::FATAL) << "create socket error";
exit(1);
}
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "create socket success: " << _sockfd;
InetAddr local(_port);
int n = bind(_sockfd, local.Addr(), local.Length());
if (n < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::FATAL) << "bind socket error";
exit(2);
}
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "bind socket success : " << _sockfd;
}
void Start()
{
_isrunning = true;
while (_isrunning)
{
// 读取数据
char buffer[1024];
buffer[0] = 0; // O(1) 清空数据
struct sockaddr_in peer;
socklen_t len = sizeof(peer);
ssize_t n = recvfrom(_sockfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&peer, &len); // flag == 0 , 阻塞模式
if (n > 0)
{
buffer[n] = 0;
InetAddr clinetaddr(peer);
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "get a client info# " << clinetaddr.Ip() << " - " << clinetaddr.Port() << ": " << buffer;
std::string message = buffer;
// 回调
_cb(_sockfd, message, clinetaddr);
}
}
_isrunning = false;
}
void Stop()
{
_isrunning = false;
}
~ChatServer()
{
}
private:
int _sockfd;
uint16_t _port;
// std::string _ip; // 不建议绑定固定ip
callback_t _cb;
bool _isrunning;
};Route.hpp:
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include "InetAddr.hpp"
class Route
{
private:
bool IsExists(const InetAddr &addr)
{
for (auto &e : _online_user)
{
if (e == addr)
return true;
}
return false;
}
void AddUser(const InetAddr &addr)
{
if (!IsExists(addr))
_online_user.push_back(addr);
}
void SendMessageToAll(int sockfd, std::string &message, InetAddr &addr)
{
for (auto &e : _online_user)
{
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "route [" << message << "] to: " << e.ToString();
std::string info = addr.ToString();
info += "# ";
info += message;
sendto(sockfd, message.c_str(), message.size(), 0, e.Addr(), e.Length());
}
}
void DeleteUser(const std::string &message, const InetAddr &addr)
{
if (message == "QUIT")
{
auto iter = _online_user.begin();
for (; iter < _online_user.end(); iter++)
{
if (*iter == addr)
{
_online_user.erase(iter);
}
break;
}
}
}
public:
Route()
{
}
void RouteMessageToAll(int sockfd, std::string &message, InetAddr &addr)
{
AddUser(addr);
SendMessageToAll(sockfd, message,addr);
DeleteUser(message, addr);
}
~Route()
{
}
private:
// 临界资源
// 1. 锁
std::vector<InetAddr> _online_user;
// 2. 锁 + 拷贝
// std::vector<InetAddr> _send_lint;
};
cpp
#include "ChatServer.hpp"
#include "ThreadPool.hpp"
#include "Route.hpp"
#include <memory>
void Usage(std::string proc)
{
std::cerr << "Usage :" << proc << " loaclport" << std::endl;
}
using task_t = std::function<void()>;
// ./udp_server serverport
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 2)
{
Usage(argv[0]);
exit(0);
}
EnableConsoleLogStrategy();
uint16_t localport = std::stoi(argv[1]);
// 1.消息转发功能
std::unique_ptr<Route> r = std::make_unique<Route>();
// 2.线程池对象
auto tp = ThreadPool<task_t>::GetInstance();
// 3.服务器对象
std::unique_ptr<ChatServer> ptr = std::make_unique<ChatServer>(localport,
[&r, &tp](int sockfd, std::string message, InetAddr addr)
{
task_t task = std::bind(&Route::RouteMessageToAll, r.get(), sockfd, message, addr);
tp->Enqueue(task);
});
ptr->Init();
ptr->Start();
return 0;
}V3代码中为了使IP、端口号看起来更具体,定义了InetAddr类:
cpp
#pragma once
// 描述client socket信息的类
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <functional>
#include <string>
#include "Logger.hpp"
class InetAddr
{
private:
void Net2Host()
{
_port = ntohs(_addr.sin_port);
_ip = inet_ntoa(_addr.sin_addr);
}
void Host2Net()
{
bzero(&_addr, sizeof(_addr));
_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
_addr.sin_port = htons(_port);
_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(_ip.c_str());
}
public:
InetAddr(const struct sockaddr_in &client) : _addr(client)
{
Net2Host();
}
InetAddr(uint16_t port,const std::string &ip = "0.0.0.0") : _port(port), _ip(ip)
{
Host2Net();
}
uint16_t Port()
{
return _port;
}
std::string Ip()
{
return _ip;
}
struct sockaddr *Addr()
{
return (sockaddr *)&_addr;
}
socklen_t Length()
{
socklen_t len = sizeof(_addr);
return len;
}
std::string ToString()
{
return _ip + std::to_string(_port);
}
bool operator==(const InetAddr &addr)
{
return _ip == addr._ip && _port == addr._port;
}
~InetAddr()
{
}
private:
struct sockaddr_in _addr; // 网络风格地址
std::string _ip; // 主机风格地址
uint16_t _port;
};以及单例线程池代码:
Thread.hpp:
cpp
#ifndef __THREAD_HPP__
#define __THREAD_HPP__
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <functional>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include "Logger.hpp"
#define get_lwp_id() syscall(SYS_gettid);
using func_t = std::function<void(const std::string& name)>;
const std::string threadnamedefault = "None - name";
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
class Thread
{
private:
/* data */
pthread_t _tid;
pid_t lwpid;
std::string _name;
func_t _func;
bool _isrunning;
public:
Thread(func_t func, const std::string &name = threadnamedefault) : _name(name), _func(func), _isrunning(false)
{
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << _name << " create thread success";
}
~Thread()
{
// LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << _name << "thread destory";
}
static void *start_routine(void *args) // 取消this指针
{
Thread *self = static_cast<Thread *>(args);
self->_isrunning = true;
self->lwpid = get_lwp_id();
self->_func(self->_name);
pthread_exit((void *)0);
}
void Start()
{
int n = pthread_create(&_tid, nullptr, start_routine, this);
if (n == 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << _name << " run thread success";
}
}
void Join()
{
if (!_isrunning)
return;
int n = pthread_join(_tid, nullptr);
if (n == 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << _name << " pthread join success";
}
}
void Stop()
{
if(!_isrunning)
return;
_isrunning = false;
int n = pthread_cancel(_tid);
}
};
#endifThreadPool.hpp:
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include "Thread.hpp"
#include "Mutex.hpp"
#include "Cond.hpp"
const static int threadnum_default = 3; // for debug
// 单例线程池
template <typename T>
class ThreadPool
{
private:
bool QueueIsEmpty()
{
return _q.empty();
}
void Routine(const std::string &name)
{
// LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << name << " hello world";
while (true) // 死循环
{
// 把任务从线程获取到线程私有 临界区 -> 私有栈
T t;
{
LockGuard lockguard(&_lock);
while (QueueIsEmpty() && _isrunning)
{
_thread_wait_num++;
_cond.Wait(_lock);
_thread_wait_num--;
}
// T t = _q.front(); // 处理任务不需要再临界区,只需把取任务保护好就行
if (!_isrunning && QueueIsEmpty()) // 退出情况设计
{
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "线程池退出 && 任务队列为空, " << name << "退出";
break;
}
t = _q.front();
_q.pop();
// t();
}
t(); // 处理任务
}
}
ThreadPool(int threadnum = threadnum_default) : _threadnum(threadnum), _thread_wait_num(0), _isrunning(false) // 对象先创建(存在),再初始化
{
for (int i = 0; i < threadnum; i++)
{
// 方法1
// auto f = std::bind(hello, this);
// 方法2
std::string name = "thread-" + std::to_string(i + 1);
_threads.emplace_back(Thread([this](const std::string &name)
{ this->Routine(name); }, name));
// Thread t([this]() {
// }, name);
// _threads.push_back(std::move(t));
}
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << " threadpool cerate success";
}
// 复制拷⻉禁⽤
ThreadPool<T> &operator=(const ThreadPool<T> &) = delete;
ThreadPool(const ThreadPool<T> &) = delete;
public:
void Start()
{
if (_isrunning)
return;
_isrunning = true;
for (auto &t : _threads)
{
t.Start();
}
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << " threadpool start success";
}
// 退出逻辑设计
// 1.如果被唤醒 && 队列没有任务 = 让线程退出
// 2.如果被唤醒 && 队列有任务 = 线程不能立即退出 而应该让线程把任务处理完,再退出
// 3.线程本身没有休眠 我们应该让他把能处理的任务全处理完成,再退出
void Stop()
{
// 这种做法太简单粗暴
// if (!_isrunning)
// return;
// _isrunning = false;
// for (auto &t : _threads)
// {
// t.Stop();
// }
// LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << " threadpool stop success";
if (!_isrunning)
return;
_isrunning = false;
if (_thread_wait_num > 0)
_cond.NotifyAll();
}
void Wait()
{
for (auto &t : _threads)
{
t.Join();
}
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << " threadpool wait success";
}
void Enqueue(const T &in)
{
if (!_isrunning)
return;
{
LockGuard lockguard(&_lock);
_q.push(in);
if (_thread_wait_num > 0)
_cond.NotifyOne();
}
}
// 获取单例 // 让用户以类的方式访问构造单例,不需要自己构造
static ThreadPool<T> *GetInstance()
{
if(!_instance)
{
LockGuard LockGuard(&_singleton_lock);
if (!_instance)
{
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "线程池首次被使用,创建并初始化";
_instance = new ThreadPool<T>();
_instance->Start();
}
// else
// {
// LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "线程池单例已经存在,直接获取";
// }
}
return _instance;
}
~ThreadPool()
{
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << " threadpool destory success";
}
private:
// 任务队列
std::queue<T> _q; // 整体使用的临界资源
// 多个线程
std::vector<Thread> _threads;
int _threadnum;
int _thread_wait_num;
// 锁
Mutex _lock;
// 条件变量
Cond _cond;
bool _isrunning; // 防止线程池重复启动
// 单例中静态指针 // 懒汉模式设计
static ThreadPool<T> *_instance;
static Mutex _singleton_lock;
};
template <class T>
ThreadPool<T> *ThreadPool<T>::_instance = nullptr;
template <class T>
Mutex ThreadPool<T>::_singleton_lock;线程池中的Cond、Mutex都是对库函数的封装,不难理解。
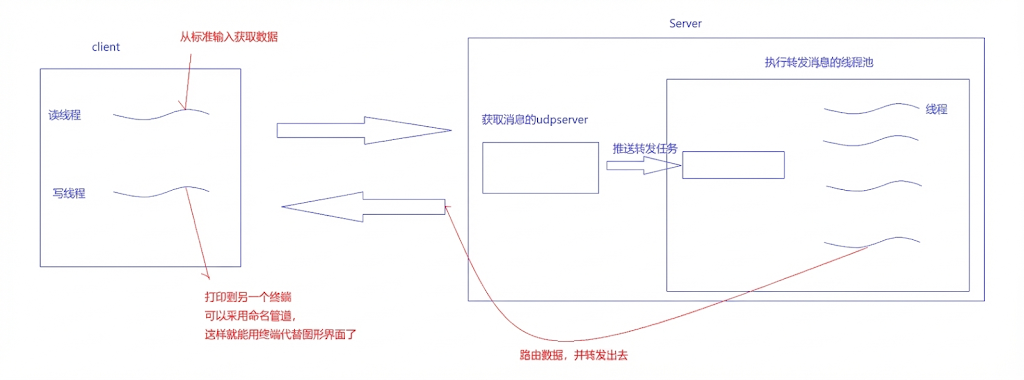
而UDP 协议本身是全双工的(可以同时读写)。在聊天室场景下,客户端不能阻塞在 cin 等待输入,否则无法及时接收别人发来的消息。
于是采用多线程来解决该问题。
主线程 :负责从标准输入读取数据,调用 sendto。
接收线程 :负责死循环调用 recvfrom,将收到的消息打印到屏幕 。
于是客户端文件为:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <string>
#include <thread>
void Usage(std::string proc)
{
std::cerr << "Usage :" << proc << "serverip serverport" << std::endl;
}
int sockfd = -1;
uint16_t serverport;
std::string serverip;
void InitClient(const std::string &serverip, uint16_t serverport)
{
sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
if (sockfd < 0)
{
std::cout << "create socket error" << std::endl;
exit(2);
}
}
void recver()
{
while (true)
{
char buffer[1024];
buffer[0] = 0;
struct sockaddr_in temp;
socklen_t len = sizeof(temp);
ssize_t m = recvfrom(sockfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&temp, &len);
if (m > 0)
{
buffer[m] = 0;
std::cout << buffer << std::endl;
}
}
}
void sender()
{
struct sockaddr_in server;
bzero(&server, sizeof(server));
server.sin_family = AF_INET;
server.sin_port = htons(serverport);
server.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(serverip.c_str());
socklen_t len = sizeof(server);
while (true)
{
std::cout << "Please Enter@ ";
std::string line;
std::getline(std::cin, line);
sendto(sockfd, line.c_str(), line.size(), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&server, len);
}
}
// ./udp_client serverip serverport
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 3)
{
Usage(argv[0]);
exit(0);
}
serverip = argv[1];
serverport = std::stoi(argv[2]);
InitClient(serverip, serverport);
std::thread tsend(sender);
std::thread trecv(recver);
trecv.join();
tsend.join();
return 0;
}上述的聊天逻辑使用图片来进行如下总结:
三、地址转换与线程安全
在网络编程中,我们经常需要将 sockaddr_in 中的 IP 地址(32位整数)转换为点分十进制字符串(如 "192.168.1.1")。
而使用in_addr转字符串函数 inet_ntoa 需要注意一些情况。
接口原型:
cpp
char *inet_ntoa(struct in_addr in);该函数会将转换结果存放在内部的一个静态缓冲区 (static buffer) 中,并返回该缓冲区的指针 。
会出现如下问题:
覆盖问题 :如果在一行代码中连续调用两次 inet_ntoa,第二次的结果会覆盖第一次。
cpp
// 错误示例
printf("ptr1: %s, ptr2: %s\n", inet_ntoa(addr1), inet_ntoa(addr2));
// 输出结果可能是一样的,都是 addr2 的值线程不安全:在多线程环境下,如果两个线程同时调用该函数,缓冲区内容会被竞争覆盖,导致乱码或逻辑错误 。
解决方案
推荐使用**inet_ntop** : 这是一个现代的、线程安全的函数。它要求调用者提供缓冲区,从而避免了内部静态缓冲区。
函数原型:
cpp
const char *inet_ntop(int af, const void *restrict src,
char dst[restrict .size], socklen_t size);使用示例:
cpp
char ip_buf[INET_ADDRSTRLEN];
inet_ntop(AF_INET, &addr.sin_addr, ip_buf, sizeof(ip_buf));总结
关键知识点在于:
- 客户端不需要显式 Bind,服务端建议 Bind
INADDR_ANY。- 网络层与业务层必须解耦(Function/Callback)。
- 实现即时通讯类应用时,客户端必须通过多线程实现收发分离。
- 严禁在多线程环境使用
inet_ntoa,请认准inet_ntop。