文章目录
-
- [1. 基本使用](#1. 基本使用)
- [2. fixture嵌套](#2. fixture嵌套)
- [3. 请求多个fixture](#3. 请求多个fixture)
- [4. yield fiture](#4. yield fiture)
- [5. fixture参数](#5. fixture参数)
-
- [5.1 scope](#5.1 scope)
- [5.2 autouse](#5.2 autouse)
- [5.3 params](#5.3 params)
- [5.4 ids](#5.4 ids)
- [5.5 name](#5.5 name)
pytest 中的 fixture 是一种强大的机制,用于提供测试函数所需的资源或上下文。它可以用于设置测试环境、准备数据等。以下是 fixture 的⼀些核心概念和使用场景。
1. 基本使用
没有使用fixture标记方法:
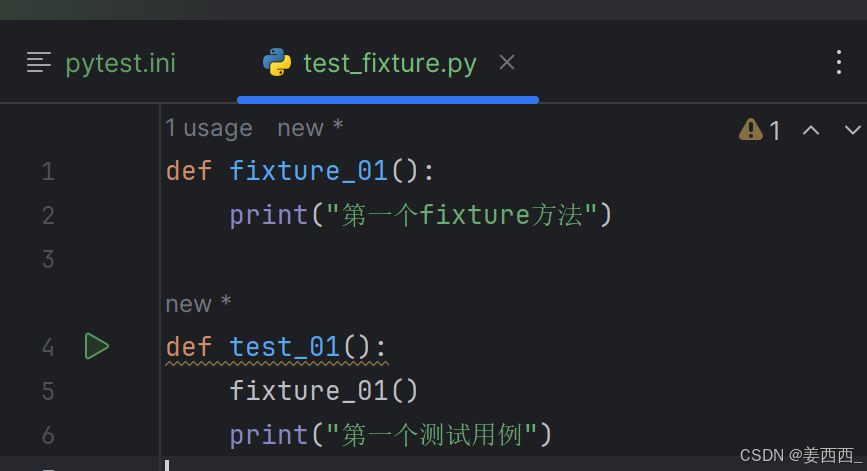
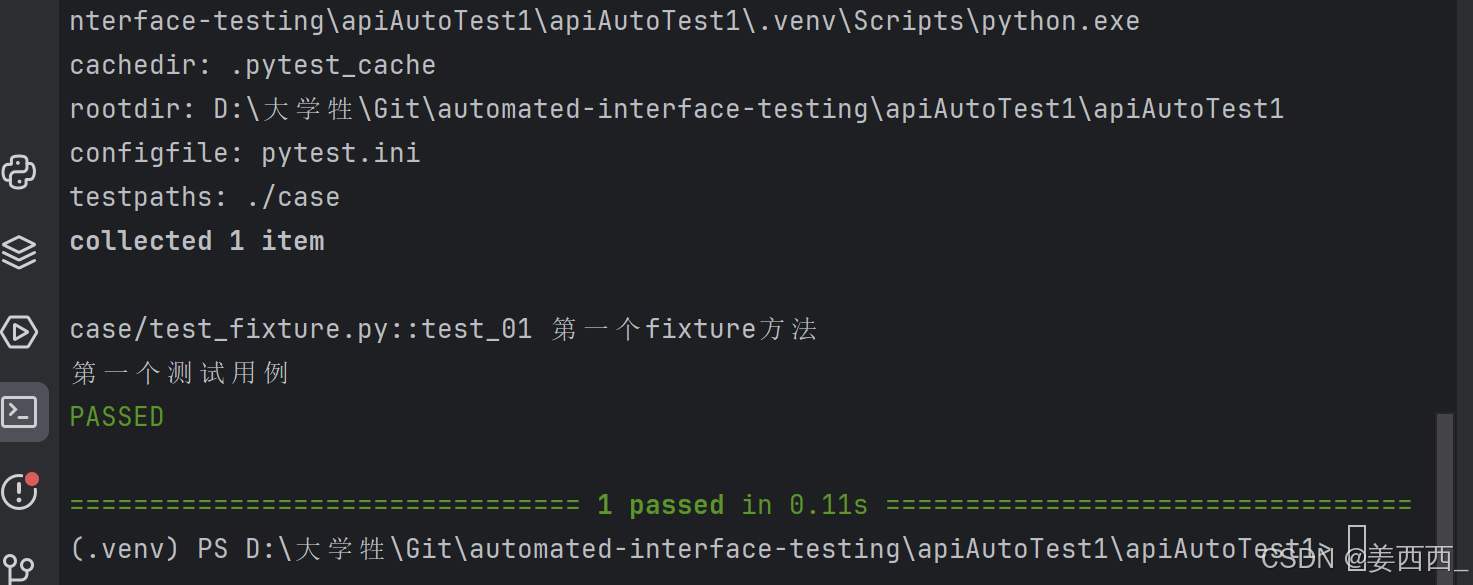
使用fixture标记方法:
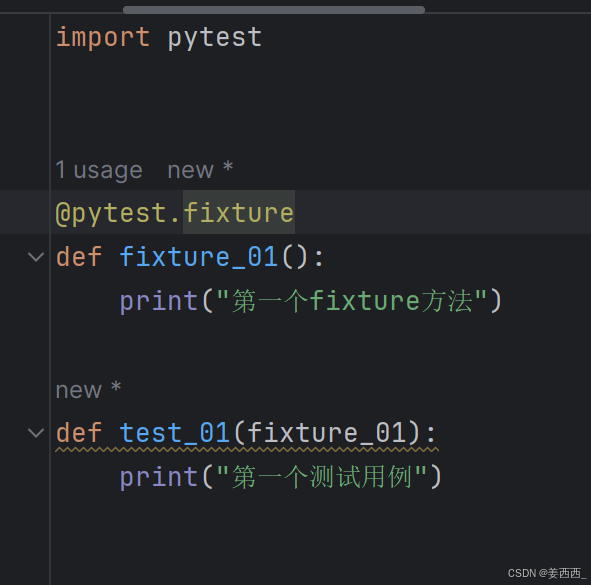
未标记 fixture 方法的调用与 fixture 标记的方法调用完全不⼀样,前者需要在方法体中调用,而后者可以将函数名作为参数进行调用。
测试脚本中存在的很多重复的代码、公共的数据对象时,使用 fixture 最为合适
2. fixture嵌套
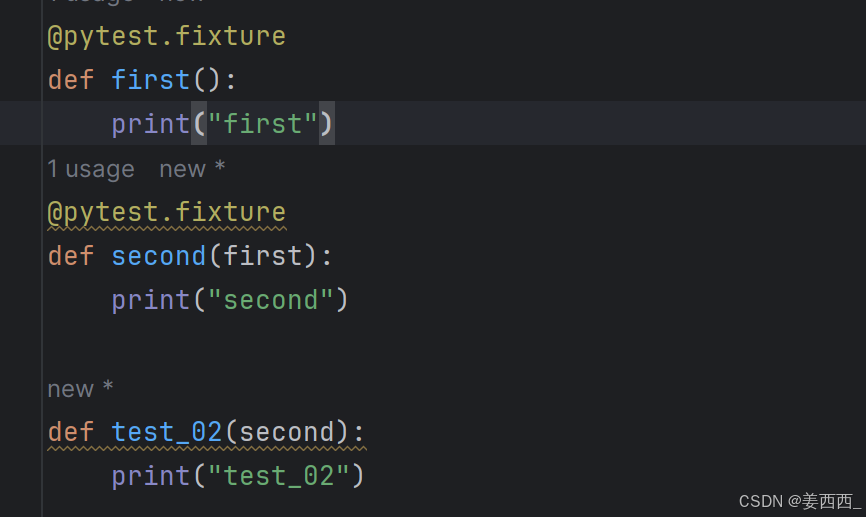
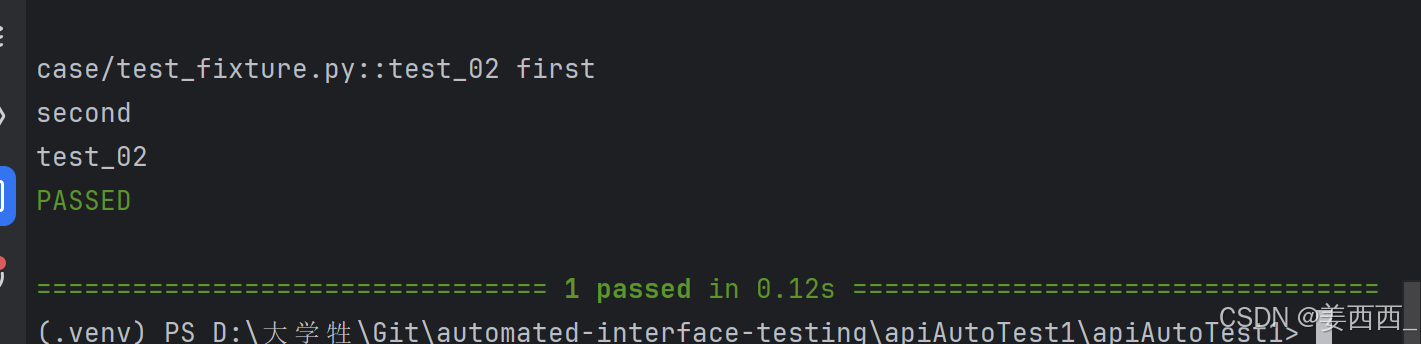
测试不必局限于单个 fixture ,它们可以依赖于您想要的任意数量的 fixture ,并且fixture 也可以使用其他 fixture 。 pytest 最伟大的优势之一是其极其灵活的 fixture 系统,它允许我们将测试的复杂需求简化为更简单和有组织的函数,我们只需要每个函数描述它们所依赖的事物
3. 请求多个fixture
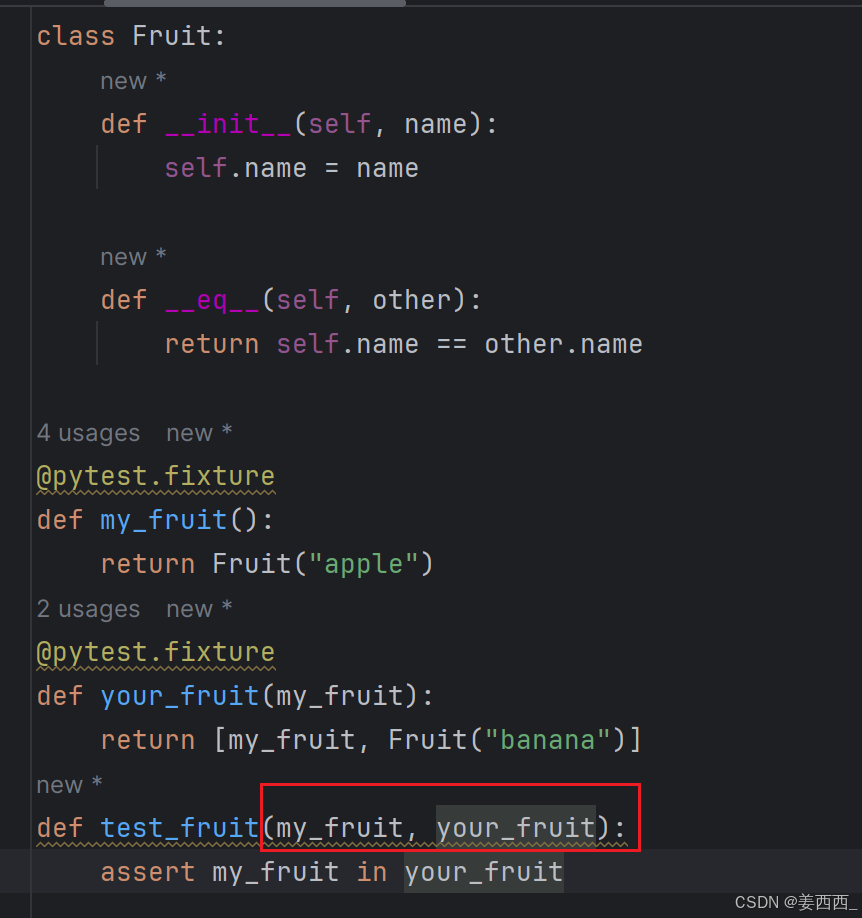
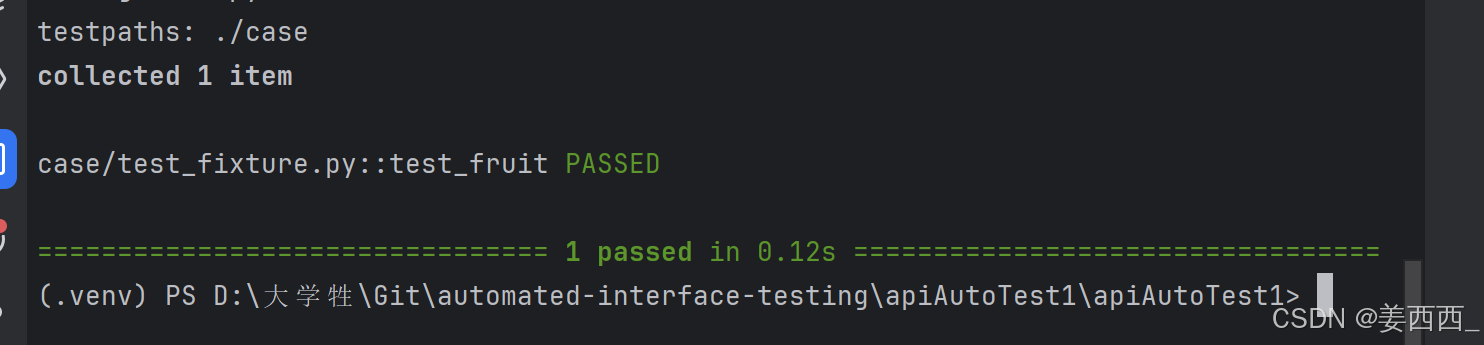
测试和 fixture 不仅限于一次请求单个 fixture ,它们可以请求任意多个。
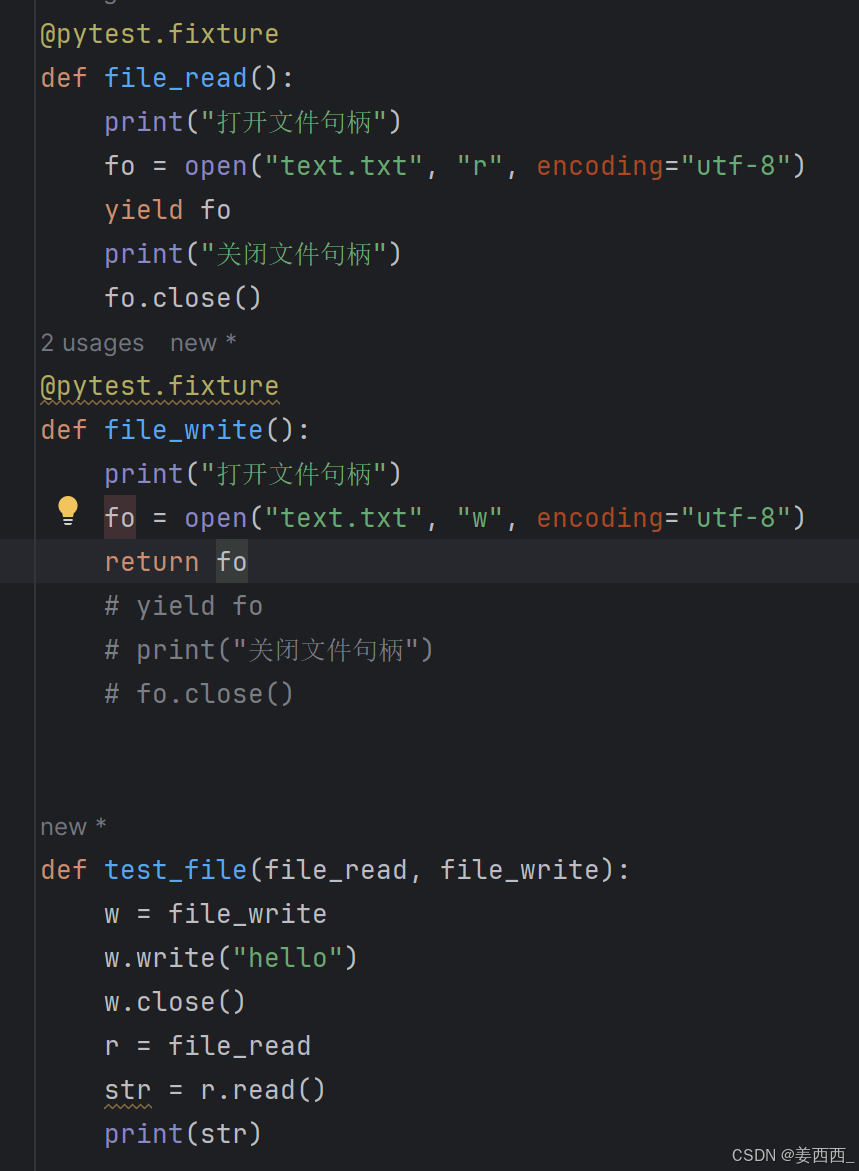
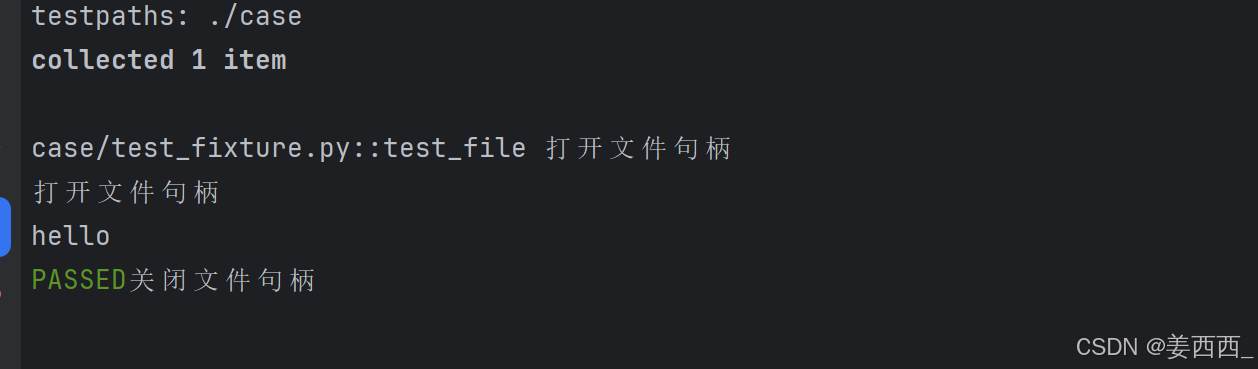
4. yield fiture
当我们运行测试时,我们希望确保它们能够自我清理,以便它们不会干扰其他测试(同时也避免留下大量测试数据来膨胀系统)。pytest中的 fixture 提供了⼀个非常有用拆卸系统,它允许我们为每个 fixture 定义具体的清理步骤。
python
@pytest.fixture
def setup():
# 前置操作
yield
# 后置操作yield不返回数据:
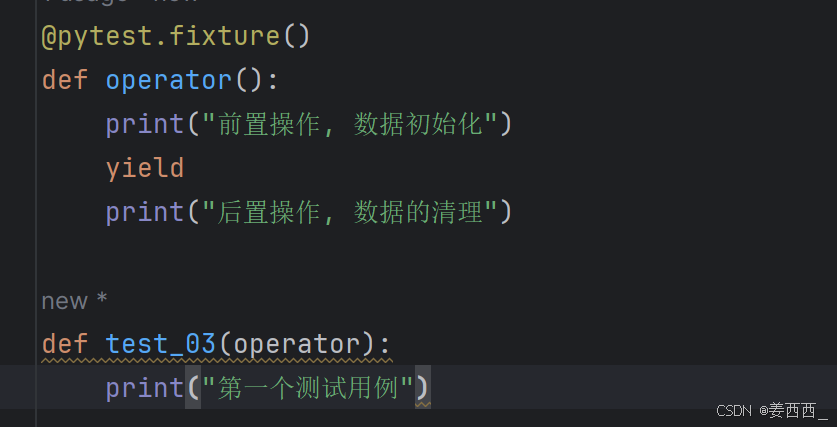
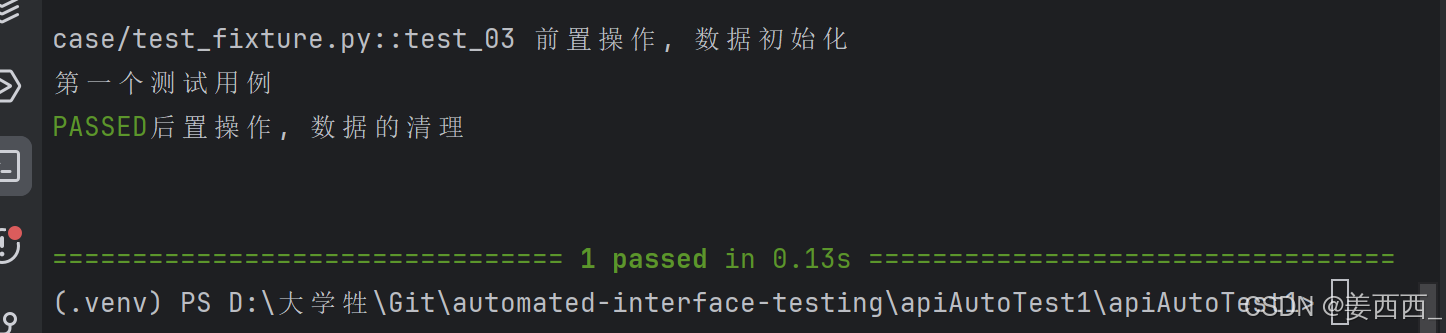
"Yield" fixture 使用 yield 而不是 return 。有了这些 fixture ,我们可以运行一些代码,并将对象返回给请求的 fixture/test ,就像其他 fixture ⼀样。唯⼀的不同是:
- return 被替换为 yield 。
- 该 fixture 的任何拆卸代码放置在 yield 之后。
yield返回数据:
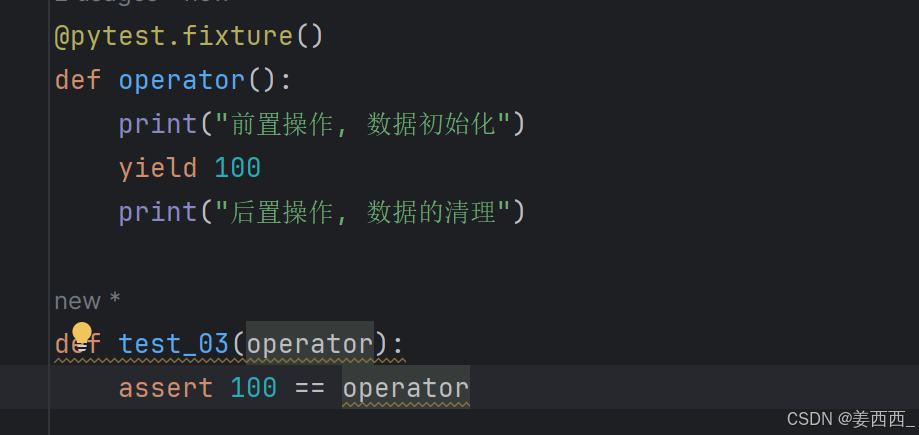
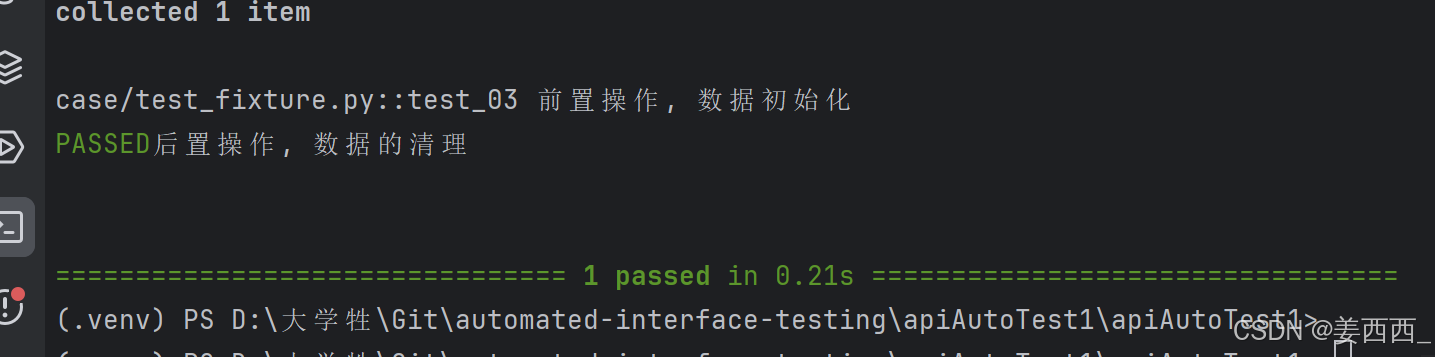
⼀旦 pytest 确定了 fixture 的线性顺序,它将运行每个 fixture 直到它返回或 yield ,然后继续执行列表中的下⼀个 fixture 做同样的事情。
测试完成后, pytest 将逆向遍历 fixture 列表,对于每个 yield 的 fixture ,运行 yield语句之后的代码。
5. fixture参数
python
@pytest.fixture(scope='', params='', autouse=False/True, ids='', name='')5.1 scope
scope 参数用于控制fixture的作用范围,决定了fixture的生命周期。可选值有:
- function (默认):每个测试函数都会调用一次fixture。
python
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(scope="function")
def fixture_01():
print("初始化")
yield
print("清理")
class TestCase():
def test_01(self,fixture_01):
print("第⼀个测试⽤例")
def test_02(self,fixture_01):
print("第⼆个测试⽤例")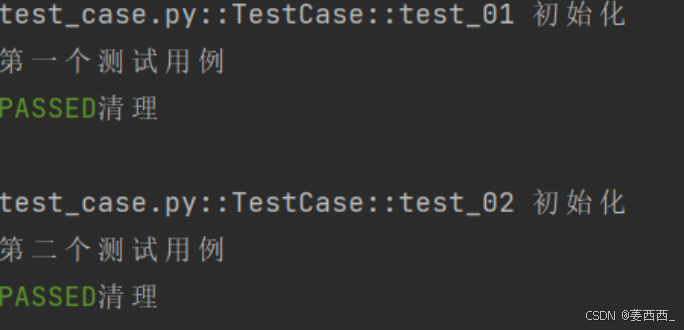
- class :在同一个测试类中共享这个fixture。
python
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(scope="class")
def fixture_01():
print("初始化")
yield
print("清理")
class TestCase():
def test_01(self,fixture_01):
print("第⼀个测试⽤例")
def test_02(self,fixture_01):
print("第⼆个测试⽤例")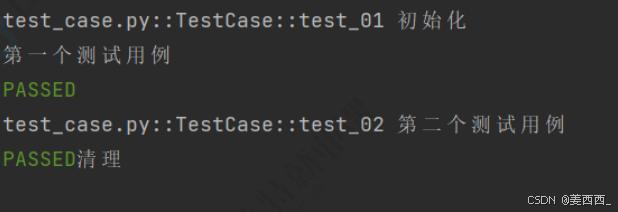
conftest.py和@pytest.fixture结合使用实现全局的前后置应用
@pytest.fixture 与 conftest.py 文件结合使用,可以实现在多个测试模块( .py )文件中共享前后置操作,这种结合的方式使得可以在整个测试项目中定义和维护通用的前后置逻辑,使测试代码更加模块化和可维护。- module :在同⼀个测试模块中共享这个fixture。(⼀个文件里)
python
//conftest.py
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(scope="module",
autouse=True)
def fixture_01():
print("初始化")
yield
print("清理")
//test_case_01.py
def test_case01():
print("单独放出来的测试⽤例01")
class TestCase01():
def test_01(self):
print("第⼀个测试⽤例")
def test_02(self):
print("第⼆个测试⽤例")
//test_case_02.py
def test_case02():
print("单独放出来的测试⽤例02")
class TestCase02():
def test_01(self):
print("第⼀个测试⽤例")
def test_02(self):
print("第⼆个测试⽤例")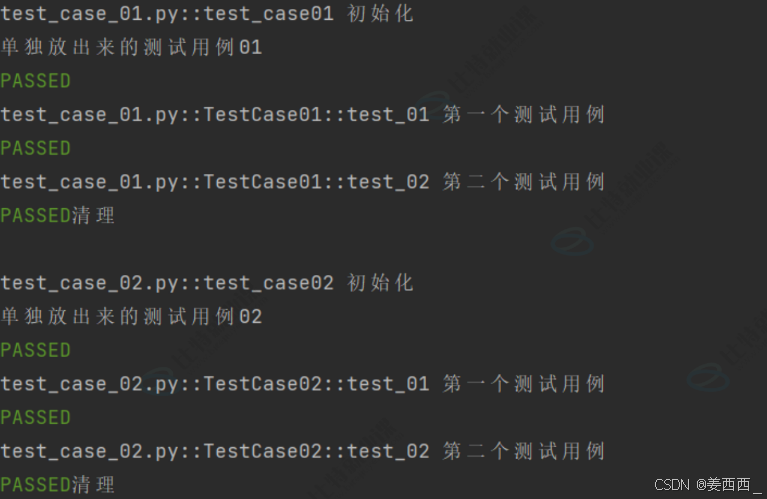
- session :整个测试会话中共享这个fixture。
python
//conftest.py
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(scope="session",
autouse=True)
def fixture_01():
print("初始化")
yield
print("清理")
//test_case_01.py
def test_case01():
print("单独放出来的测试⽤例01")
class TestCase01():
def test_01(self):
print("第⼀个测试⽤例")
def test_02(self):
print("第⼆个测试⽤例")
//test_case_02.py
def test_case02():
print("单独放出来的测试⽤例02")
class TestCase02():
def test_01(self):
print("第⼀个测试⽤例")
def test_02(self):
print("第⼆个测试⽤例")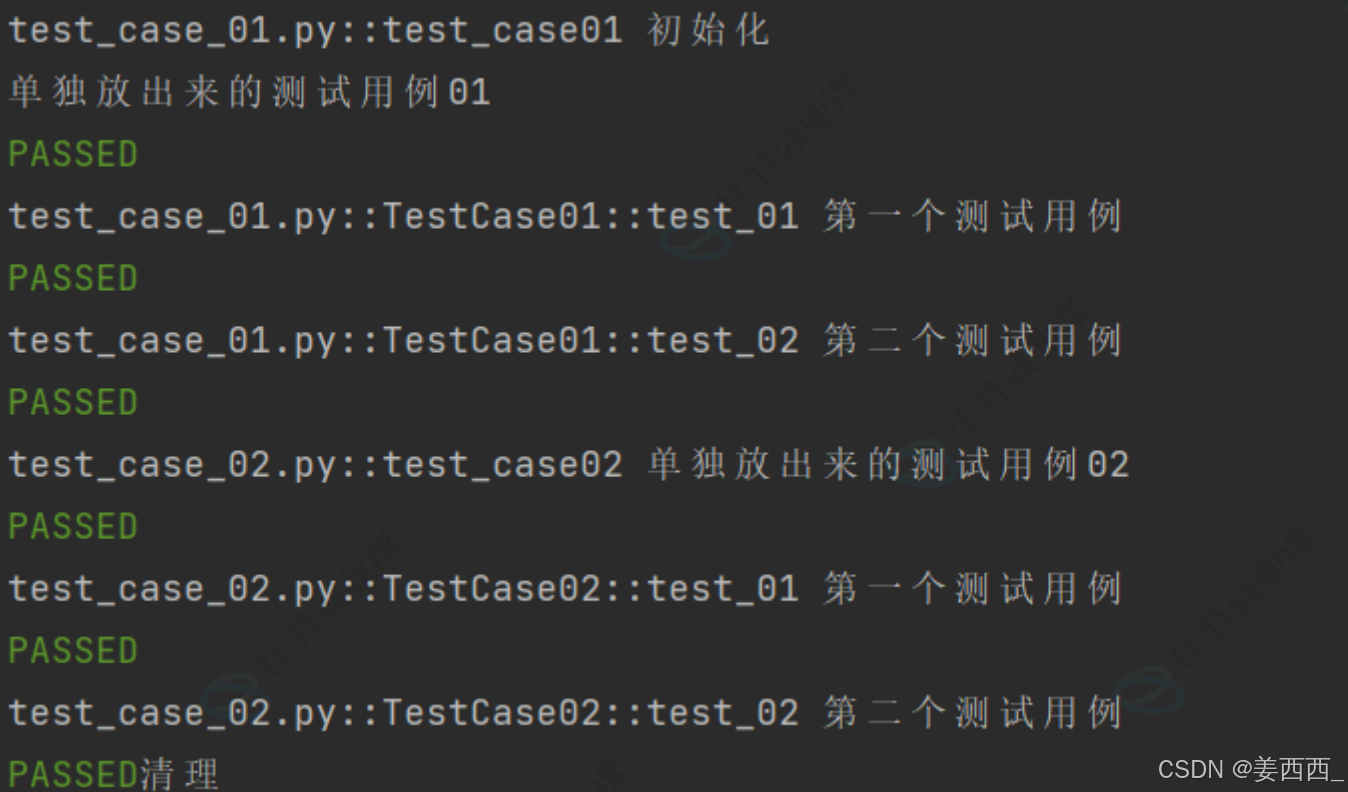
5.2 autouse
autouse 参数默认为 False 。如果设置为 True ,则每个测试函数都会自动调用该fixture,无需显式传入
python
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(scope="class", autouse=True)
def fixture_01():
print("初始化")
yield
print("清理")
class TestCase():
def test_01(self):
print("第⼀个测试⽤例")
def test_02(self):
print("第⼆个测试⽤例")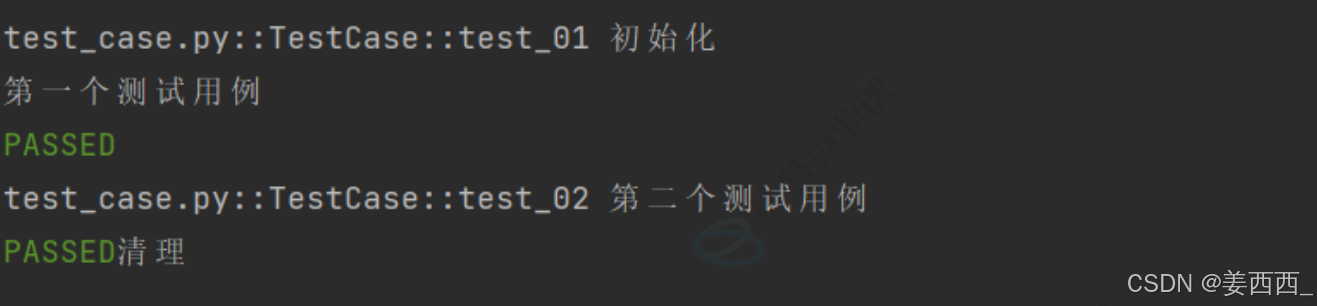
5.3 params
参数用于参数化fixture,支持列表传入。每个参数值都会使fixture执行⼀次,类似于for循环
python
# 定义⼀个参数化的 fixture
@pytest.fixture(params=["a", "b"])
def data_provider(request):
return request.param
# 定义⼀个测试函数,它依赖于上⾯的参数化 fixture
def test_data(data_provider):
assert data_provider != None
print(f"Testing with data provider: {data_provider}")前面我们已经学过pytest中通过 @pytest.mark.parametrize 实现参数化,通过 fixture 也可以实现参数化,如果测试场景主要涉及简单的参数传递,且不需要复杂的资源管理,建议使用 parametrize,因为它更简单直接;如果测试需要动态加载外部数据,或者需要管理复杂的测试资源(如数据库连接、文件操作等),建议使用 fixture,在某些情况下,也可以结合使用 parametrize 和 fixture,以充分利用两者的优点。总结来说,parametrize 更适合简单场景,而 fixture 更适合需要动态数据和资源管理的复杂场景。
5.4 ids
ids参数与 params 配合使用,为每个参数化实例指定可读的标识符(给参数取名字)
5.5 name
name 参数用于为fixture显式设置⼀个名称。如果使用了 name ,则在测试函数中需要使用这个
名称来引用 fixture (给fixture取名字)