IOC(Inversion of Control,控制反转)容器 是 Spring 的核心,也称为 DI(Dependency Injection,依赖注入)容器。它的主要职责是:①创建对象:管理应用中所有对象(Bean)的生命周期;②维护依赖关系:自动装配对象之间的依赖;③提供配置方式:支持多种配置方式(XML、注解、Java配置)。IoC 容器工作的基础是Bean 的扫描(组件扫描)。
一、bean对象的扫描
在传统的xml文件中,扫描包写法:<context:component-scan base-package="com.test"/>;而对于springboot来说,我们只需要注解@ComponentScan(basePackages="com.test")即可,举例如下:(启动类路径是com/test/springbootquickstart/SpringbootQuickstartApplication)
java
//启动类
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootQuickstartApplication{
public static voic main(String[] args){
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootQuickstartApplication.class,args);
}
}
//SpringBoot默认扫描启动类所在的包及其子包,具体如下图,启动类在springbootquickstart包下,如果使用的文件不在该包里面,那么运行启动类也不会扫描到使用的文件
其中的注解@SpringBootApplication相当于以下三个注解:
@SpringBootConfiguration //启动文件也相当于配置文件
@EnableAutoConfiguration //自动配置
@ComponentScan //ComponentScan自动扫描包
public @interface SpringBootApplication{
}SpringBoot默认扫描启动类所在的包及其子包,如果想要扫描的包不在这个范围,可以在启动类文件上加扫描注解。举例:如果使用的包不在com.test.springbootquickstart,而在com.test文件下,只需要在@SpringBootApplication注解上面添加扫描注解即可。
java
//添加ComponentScan注解
@ComponentScan(basePackages="com.test")二、注解
1.声明 Bean 的注解
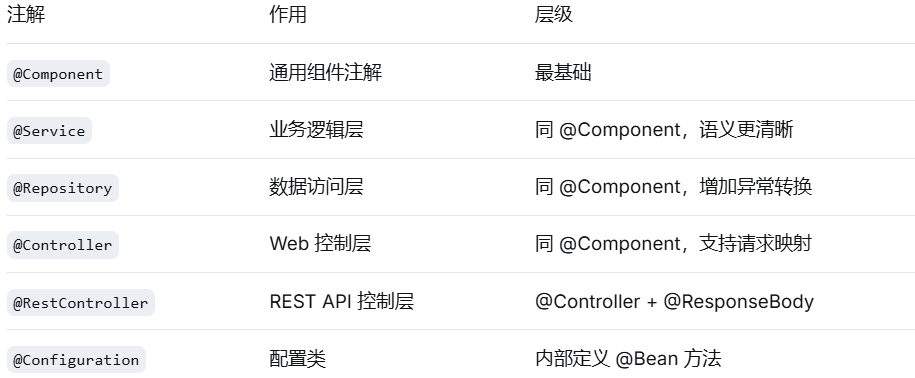
java
@Service // 声明这是一个 Service Bean
public class UserService {
public void saveUser(User user) {
// 业务逻辑
}
}
@Repository // 声明这是一个 Repository Bean
public class UserRepository {
public User findById(Long id) {
// 数据访问逻辑
return null;
}
}
@RestController // REST API 控制器
@RequestMapping("/api/users")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public User getUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userService.findById(id);
}
}2.依赖注入相关注解
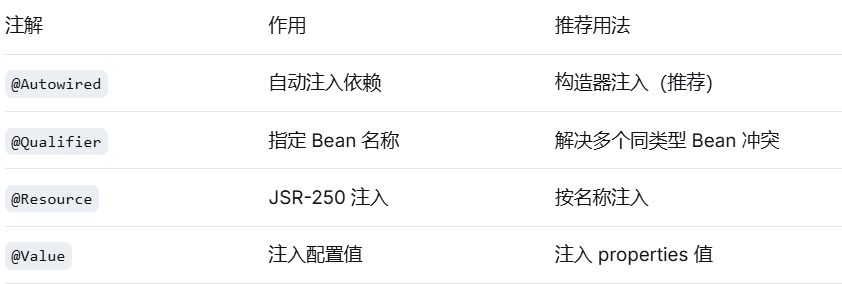
java
@Component
public class OrderService {
// 1. 构造器注入
private final UserService userService;
private final ProductService productService;
@Autowired
public OrderService(UserService userService,ProductService productService) {
this.userService = userService;
this.productService = productService;
}
// 2. 字段注入
@Autowired
private PaymentService paymentService;
// 3. Setter 注入
private NotificationService notificationService;
@Autowired
public void setNotificationService(NotificationService service) {
this.notificationService = service;
}
// 4. 使用 @Value 注入配置
@Value("${app.order.max-items:10}") // 默认值 10
private int maxItems;
// 5. 使用 @Qualifier 解决冲突
@Autowired
@Qualifier("emailNotification") // 指定 Bean 名称
private NotificationService emailNotification;
}
// 定义多个同类型 Bean
@Configuration
class NotificationConfig {
@Bean
@Qualifier("emailNotification")
public NotificationService emailNotification() {
return new EmailNotification();
}
@Bean
@Qualifier("smsNotification")
public NotificationService smsNotification() {
return new SmsNotification();
}
}3.配置相关注解

4.Spring Boot 特有注解
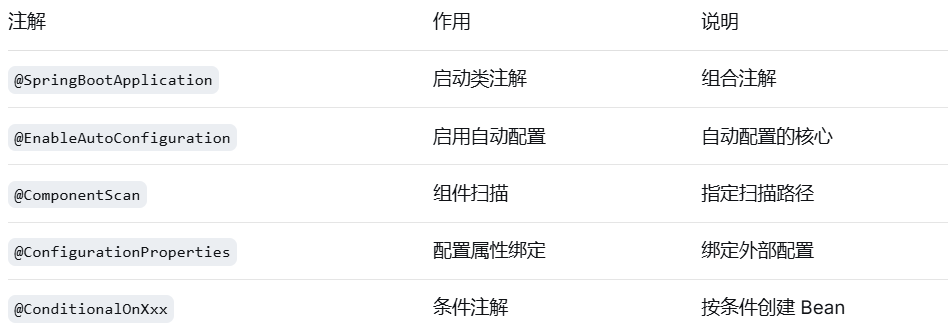
java
// @SpringBootApplication 相当于下面五种注解组合:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@SpringBootConfiguration // ← @Configuration 的变体
@EnableAutoConfiguration // ← 启用自动配置
@ComponentScan // ← 组件扫描
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
// ...
}5.Web 相关注解
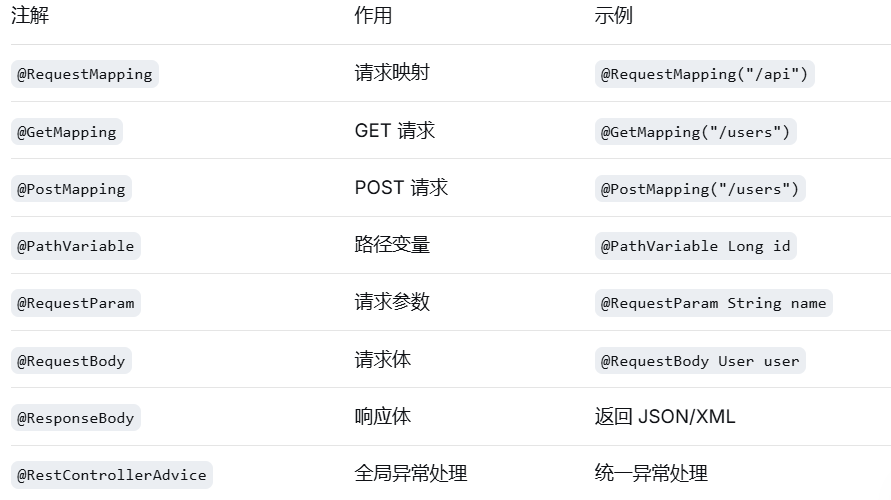
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/users")
public class UserController {
@GetMapping("/{id}") //get请求方法,与RequestMapping映射内容做拼接
public User getUser(@PathVariable Long id,
@RequestParam(required = false) String detail) {
// 处理 GET /api/v1/users/123?detail=true
return userService.findById(id);
}
@PostMapping //post请求方法,与RequestMapping映射内容做拼接
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public User createUser(@Valid @RequestBody UserDto userDto) {
// @Valid 会触发数据校验
return userService.create(userDto);
}
@PutMapping("/{id}") //put请求方法,与RequestMapping映射内容做拼接
public User updateUser(@PathVariable Long id,
@RequestBody UserDto userDto) {
return userService.update(id, userDto);
}
@DeleteMapping("/{id}") //delete请求方法,与RequestMapping映射内容做拼接
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT)
public void deleteUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
userService.delete(id);
}
}
// 全局异常处理
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(ResourceNotFoundException.class)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
public ErrorResponse handleNotFound(ResourceNotFoundException ex) {
return new ErrorResponse("NOT_FOUND", ex.getMessage());
}
@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
public ErrorResponse handleValidation(MethodArgumentNotValidException ex) {
// 处理参数校验失败
return new ErrorResponse("VALIDATION_ERROR", "参数校验失败");
}
}6.事务相关注解
java
@Service
@Transactional // 类级别:所有方法都开启事务
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
// 方法级别的事务配置
@Transactional(
readOnly = true, // 只读事务,性能优化
timeout = 5, // 超时时间(秒)
rollbackFor = Exception.class, // 对哪些异常回滚
noRollbackFor = RuntimeException.class // 对哪些异常不回滚
)
public User findUser(Long id) {
return userRepository.findById(id).orElse(null);
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED) // 事务传播行为
public User createUser(User user) {
// 默认 REQUIRED:如果当前有事务就加入,没有就新建
return userRepository.save(user);
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void updateLog(Long userId) {
// REQUIRES_NEW:总是新建事务,挂起当前事务
logRepository.save(new Log("用户更新", userId));
}
}总结:
