文章目录
- 前言
- [一、QPainter 在 QPixmap 上绘图](#一、QPainter 在 QPixmap 上绘图)
-
- 1.方法一:离屏绘制
- [2.方法二:自定义 QLabel 子类(paintEvent 中绘制)](#2.方法二:自定义 QLabel 子类(paintEvent 中绘制))
- 3.两种方法对比
- [二、QPainter 创建遮罩和光标](#二、QPainter 创建遮罩和光标)
- [三、QPicture 绘图命令的记录器和回放器](#三、QPicture 绘图命令的记录器和回放器)
- 总结
前言
本节主要讲解 QPainter 类在 QPixmap、QBitmap、QPicture 上的 基础操作 和 常规应用 。
一、QPainter 在 QPixmap 上绘图
在 QLabel 上显示 QPixmap 并在其上进行绘图有两种主要方法:离屏绘制 和 直接在 QLabel 的 paintEvent 中绘制。
1.方法一:离屏绘制
先在一个临时的 QPixmap 上绘制,然后将结果设置到 QLabel,该方式简单易懂,还易操作。
python
# QPainter 在 QPixmap 上绘图
self.pixmap = QPixmap("Resources/image/jd.png") # 加载图像文件
self.current_pixmap = self.pixmap.copy()
self.update_label_image()
# 方法一:离屏绘制 先在一个临时的 QPixmap 上绘制,然后将结果设置到 QLabel
# 对齐方式
self.ui.lab_Show.setAlignment(Qt.AlignmentFlag.AlignCenter) # 图片在Label中居中显示
# 槽函数
self.ui.btn_Rect.clicked.connect(self.draw_rectangle)
self.ui.btn_Circle.clicked.connect(self.draw_circle)
self.ui.btn_Text.clicked.connect(self.draw_text)
self.ui.btn_Line.clicked.connect(self.draw_line)
self.ui.btn_Reset.clicked.connect(self.reset_image)
self.ui.btn_Save.clicked.connect(self.save_image)
def draw_rectangle(self):
"""绘制矩形"""
painter = QPainter(self.current_pixmap)
painter.setRenderHint(QPainter.RenderHint.Antialiasing)
# 设置画笔和画刷
painter.setPen(QPen(QColor(0, 0, 255), 3))
painter.setBrush(QBrush(QColor(0, 0, 255).lighter(150)))
# 随机位置绘制矩形
x = random.randint(50, self.current_pixmap.width() - 150)
y = random.randint(50, self.current_pixmap.height() - 150)
width = random.randint(50, 150)
height = random.randint(50, 150)
painter.drawRect(x, y, width, height)
painter.end()
self.update_label_image()
self.statusBar().showMessage(f"绘制矩形: ({x}, {y}, {width}, {height})", 3000)
def draw_circle(self):
"""绘制圆形"""
painter = QPainter(self.current_pixmap)
painter.setRenderHint(QPainter.RenderHint.Antialiasing)
painter.setPen(QPen(QColor(255, 255, 0), 3))
painter.setBrush(Qt.BrushStyle.NoBrush) # 设置"无填充"画刷
#painter.setBrush(QBrush(QColor(255, 255, 0).lighter(200)))
x = random.randint(50, self.current_pixmap.width() - 150)
y = random.randint(50, self.current_pixmap.height() - 150)
diameter = random.randint(100, 150)
painter.drawEllipse(x, y, diameter, diameter)
painter.end()
self.update_label_image()
self.statusBar().showMessage(f"绘制圆形: ({x}, {y}, {diameter})", 3000)
def draw_text(self):
"""绘制文字"""
painter = QPainter(self.current_pixmap)
painter.setRenderHint(QPainter.RenderHint.Antialiasing)
painter.setPen(QPen(QColor(255, 0, 0)))
# 设置字体
font = QFont()
font.setPointSize(random.randint(24, 36))
font.setBold(random.choice([True, False]))
painter.setFont(font)
texts = ["Hello!", "PySide6", "绘图演示", "QLabel", "QPixmap", "QPainter"]
text = random.choice(texts)
x = random.randint(50, self.current_pixmap.width() - 150)
y = random.randint(50, self.current_pixmap.height() - 50)
painter.drawText(x, y, text)
painter.end()
self.update_label_image()
self.statusBar().showMessage(f"绘制文字: '{text}' 位置: ({x}, {y})", 3000)
def draw_line(self):
"""绘制线条"""
painter = QPainter(self.current_pixmap)
painter.setRenderHint(QPainter.RenderHint.Antialiasing)
painter.setPen(QPen(QColor(255, 0, 255), random.randint(3, 6)))
x1 = random.randint(50, self.current_pixmap.width() - 50)
y1 = random.randint(50, self.current_pixmap.height() - 50)
x2 = random.randint(50, self.current_pixmap.width() - 50)
y2 = random.randint(50, self.current_pixmap.height() - 50)
painter.drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2)
painter.end()
self.update_label_image()
self.statusBar().showMessage(f"绘制线条: ({x1}, {y1}) -> ({x2}, {y2})", 3000)
def reset_image(self):
"""重置图像"""
self.current_pixmap = self.pixmap.copy()
self.update_label_image()
self.statusBar().showMessage("图像已重置", 3000)
def save_image(self):
"""保存图像"""
file_path, _ = QFileDialog.getSaveFileName(self, "保存图像", "", "PNG图像 (*.png);;JPEG图像 (*.jpg)")
if file_path:
if self.current_pixmap.save(file_path):
self.statusBar().showMessage(f"图像已保存到: {file_path}", 3000)
else:
self.statusBar().showMessage("保存失败", 3000)
def update_label_image(self):
"""更新QLabel显示的图像"""
# 保持宽高比缩放
scaled_pixmap = self.current_pixmap.scaled(self.ui.lab_Show.geometry().width(),
self.ui.lab_Show.geometry().height(),
Qt.AspectRatioMode.KeepAspectRatio, # 保持宽高比
Qt.TransformationMode.SmoothTransformation) # 平滑变换
self.ui.lab_Show.setPixmap(scaled_pixmap)
① 大体逻辑是 copy() 函数复制一张 QPixmap 图像,然后在这张图进行 QPainter 各图形绘制操作,然后将绘制完的图显示在 QLabel 上;
② 绘制矩形时,矩形内部有填充,但是绘制的圆形图形内部没有填充,通过 painter.setBrush(Qt.BrushStyle.NoBrush) 进行"无填充"画刷的设置;
2.方法二:自定义 QLabel 子类(paintEvent 中绘制)
通过继承 QLabel 并重写 paintEvent 方法,在绘制时叠加图形的方式,较难理解,但能进行丰富的交互功能,并且能对多层 / 多对象进行管理。
主函数程序:
python
# 方法二:自定义 QLabel 子类(paintEvent 中绘制) 通过继承 QLabel 并重写 paintEvent 方法,在绘制时叠加图形
# 加载或创建基础图像
pixmap2 = QPixmap("Resources/image/110.jpg") # 加载图像文件
self.ui.add_Show.set_base_pixmap(pixmap2)
# 槽函数
self.ui.spin_R.valueChanged.connect(self.update_color_preview)
self.ui.spin_G.valueChanged.connect(self.update_color_preview)
self.ui.spin_B.valueChanged.connect(self.update_color_preview)
self.ui.add_Rect.clicked.connect(self.add_rectangle)
self.ui.add_Circle.clicked.connect(self.add_circle)
self.ui.add_Text.clicked.connect(self.add_text)
self.ui.add_clear.clicked.connect(self.clear_overlay)
self.ui.add_save.clicked.connect(self.save_result)
self.ui.spin_R.setValue(255)
#方法二函数
def get_current_color(self):
"""获取当前设置的颜色"""
m_R = self.ui.spin_R.value()
m_G = self.ui.spin_G.value()
m_B = self.ui.spin_B.value()
return QColor(m_R, m_G, m_B)
def update_color_preview(self):
"""更新颜色预览"""
color = self.get_current_color()
self.ui.add_Color.setStyleSheet(f"background-color: {color.name()}; border: 1px solid black;")
self.ui.add_Color.setText(f"RGB({color.red()},{color.green()},{color.blue()})")
def add_rectangle(self):
"""添加矩形"""
color = self.get_current_color()
x = random.randint(50, 500)
y = random.randint(50, 300)
w = random.randint(50, 150)
h = random.randint(50, 150)
self.ui.add_Show.add_shape("rectangle", color, x, y, w, h)
print(f"添加矩形: ({x}, {y}, {w}, {h}) 颜色: {color.name()}")
def add_circle(self):
"""添加圆形"""
color = self.get_current_color()
x = random.randint(50, 500)
y = random.randint(50, 300)
diameter = random.randint(50, 150)
self.ui.add_Show.add_shape("circle", color, x, y, diameter)
print(f"添加圆形: ({x}, {y}, {diameter}) 颜色: {color.name()}")
def add_text(self):
"""添加文字"""
color = self.get_current_color()
x = random.randint(50, 500)
y = random.randint(50, 300)
texts = ["Hello", "World", "PySide6", "绘图", "QLabel", "叠加"]
text = random.choice(texts)
font_size = random.randint(12, 24)
self.ui.add_Show.add_shape("text", color, x, y, text, font_size)
print(f"添加文字: '{text}' 位置: ({x}, {y}) 大小: {font_size}")
def clear_overlay(self):
"""清除叠加层"""
self.ui.add_Show.clear_overlay()
print("已清除所有叠加图形")
def save_result(self):
"""保存最终结果(基础图像+叠加图形)"""
# 创建临时QPixmap来绘制最终结果
final_pixmap = QPixmap(self.ui.add_Show.base_pixmap.size())
final_pixmap.fill(Qt.GlobalColor.transparent)
# 绘制基础图像
painter = QPainter(final_pixmap)
painter.drawPixmap(0, 0, self.ui.add_Show.base_pixmap)
# 绘制所有叠加图形
for shape_type, args in self.ui.add_Show.overlay_shapes:
self.draw_shape_on_pixmap(painter, shape_type, *args)
painter.end()
# 保存文件
file_path, _ = QFileDialog.getSaveFileName(self, "保存结果图像", "", "PNG图像 (*.png);;JPEG图像 (*.jpg)")
if file_path:
if final_pixmap.save(file_path):
print(f"结果已保存到: {file_path}")
else:
print("保存失败")
def draw_shape_on_pixmap(self, painter, shape_type, *args):
"""在QPixmap上绘制图形"""
if shape_type == "rectangle":
color, x, y, w, h = args
painter.setPen(QPen(color, 3))
painter.setBrush(QBrush(color.lighter(150)))
painter.drawRect(x, y, w, h)
elif shape_type == "circle":
color, x, y, diameter = args
painter.setPen(QPen(color, 3))
painter.setBrush(QBrush(color.lighter(200)))
painter.drawEllipse(x, y, diameter, diameter)
elif shape_type == "text":
color, x, y, text, font_size = args
painter.setPen(QPen(color))
font = QFont()
font.setPointSize(font_size)
painter.setFont(font)
painter.drawText(x, y, text)DrawableLabel(QLabel) 可绘制的 QLabel 子类程序:
python
class DrawableLabel(QLabel):
"""可绘制的QLabel子类"""
def __init__(self, parent=None):
super().__init__(parent)
self.overlay_shapes = [] # 存储叠加的图形
self.base_pixmap = None
def set_base_pixmap(self, pixmap):
"""设置基础图像"""
self.base_pixmap = pixmap
# 保持宽高比缩放
scaled_pixmap = pixmap.scaled(self.geometry().width(),
self.geometry().height(),
Qt.AspectRatioMode.KeepAspectRatio, # 保持宽高比
Qt.TransformationMode.SmoothTransformation) # 平滑变换
self.setPixmap(scaled_pixmap)
def add_shape(self, shape_type, *args):
"""添加一个图形到叠加层"""
self.overlay_shapes.append((shape_type, args))
self.update() # 触发重绘
def clear_overlay(self):
"""清除所有叠加图形"""
self.overlay_shapes.clear()
self.update()
def paintEvent(self, event: QPaintEvent):
"""重写绘制事件"""
# 先调用父类的绘制,显示基础图像
super().paintEvent(event)
# 创建QPainter在QLabel上绘制
painter = QPainter(self)
painter.setRenderHint(QPainter.RenderHint.Antialiasing)
# 绘制所有叠加图形
for shape_type, args in self.overlay_shapes:
self.draw_shape(painter, shape_type, *args)
painter.end()
def draw_shape(self, painter, shape_type, *args):
"""根据类型绘制图形"""
if shape_type == "rectangle":
color, x, y, w, h = args
painter.setPen(QPen(color, 3))
#painter.setBrush(QBrush(color.lighter(150)))
painter.setBrush(Qt.BrushStyle.NoBrush) # 设置"无填充"画刷
painter.drawRect(x, y, w, h)
elif shape_type == "circle":
color, x, y, diameter = args
painter.setPen(QPen(color, 3))
painter.setBrush(QBrush(color.lighter(200)))
painter.drawEllipse(x, y, diameter, diameter)
elif shape_type == "text":
color, x, y, text, font_size = args
painter.setPen(QPen(color))
font = QFont()
font.setPointSize(font_size)
painter.setFont(font)
painter.drawText(x, y, text)
elif shape_type == "line":
color, x1, y1, x2, y2, width = args
painter.setPen(QPen(color, width))
painter.drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2)然后进行组件提升:
最终效果:
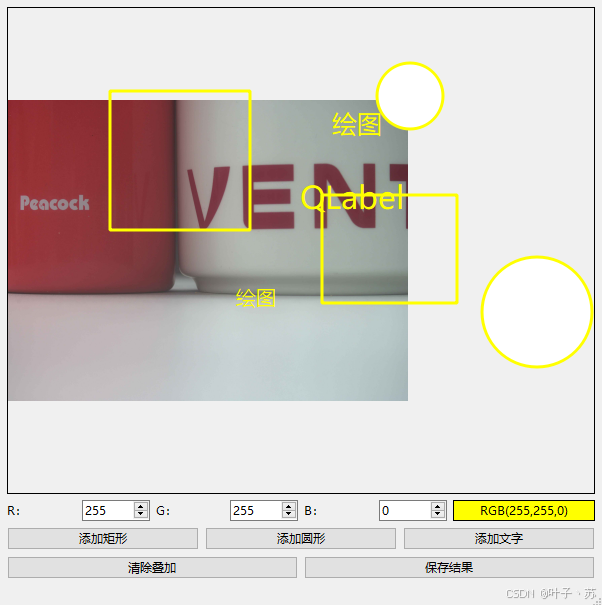
①创建一个继承自QLabel的类;
②重写paintEvent方法,在其中先调用基类的paintEvent,然后使用QPainter在QLabel上绘制图形(注意:绘制图形时,需要考虑到QPixmap的缩放和位置,因为QLabel可能会根据其sizePolicy和缩放设置来调整显示的图像);
③基类的paintEvent会绘制QLabel的内容,包括文本和图像。如果我们已经设置了Pixmap,那么基类会绘制这个Pixmap。然后我们再在上面绘制矩形;
④从上述例程中可以看到使用的常值去进行图形的位置绘制,绘制出的各种图形可能会落在图形的外侧,这里读者可以根据上面缩放设置来优化该代码,让所绘制的图形都落在图像中,实践是最快速的学习方式。
注意点:
DrawableLabel 类中所定义的 self.overlay_shapes = [] # 存储叠加的图形,通过改列表可以对所画的图像进行撤销、重画、删除部分图形的操作,能更好的管控所绘画的对象。
3.两种方法对比
| 特性 | 方法一:离屏绘制 | 方法二:自定义QLabel子类 |
|---|---|---|
| 实现复杂度 | 简单,直接操作QPixmap | 中等,需要继承并重写paintEvent |
| 性能 | 较高,一次绘制完成 | 每次重绘都需要重新绘制叠加层 |
| 内存使用 | 需要保持两份图像(原始和当前) | 只需原始图像,叠加层是动态绘制的 |
| 交互性 | 绘制后图像固定,修改需重绘 | 叠加层可独立管理,方便单独清除或修改 |
| 适用场景 | 需要保存绘制结果的场景 | 需要频繁修改叠加层或实时预览的场景 |
| 图像保存 | 直接保存当前QPixmap | 需要重新合成图像再保存 |
基本原则:如果绘制操作本身的计算成本高于复制图像的成本,用方法一;如果绘制操作简单但需要频繁更新和交互,用方法二。
二、QPainter 创建遮罩和光标
python
# 对齐方式
self.ui.lab_Show.setAlignment(Qt.AlignmentFlag.AlignCenter) # 图片在Label中居中显示
#创建自定义光标(结合遮罩)
self.pixmap01 = QPixmap("Resources/image/3.jpeg")
self.update_label_image()
# 创建光标图像(彩色)
pixmap = QPixmap(64, 64)
pixmap.fill(Qt.GlobalColor.transparent) # 透明背景
painter = QPainter(pixmap)
painter.setRenderHint(QPainter.RenderHint.Antialiasing)
# 绘制一个简单的十字光标
painter.setPen(QPen(QColor(255, 255, 0), 5)) # 红色十字
painter.drawLine(32, 0, 32, 64) # 垂直线
painter.drawLine(0, 32, 64, 32) # 水平线
# 绘制中心点
painter.setBrush(QBrush(QColor(255, 255, 0)))
painter.drawEllipse(28, 28, 8, 8)
painter.end()
# 从彩色图像创建遮罩位图(会自动抖动)
mask = QBitmap.fromPixmap(pixmap)
# 创建自定义光标(需要图像和遮罩)
cursor = QCursor(mask, mask, 16, 16) # 热点在中心(16,16)
#彩色光标显示
#cursor = QCursor(pixmap, 16, 16) # 热点在中心(16,16)
# 设置光标
self.ui.lab_Show.setCursor(cursor)
def update_label_image(self):
"""更新QLabel显示的图像"""
# 保持宽高比缩放
scaled_pixmap = self.pixmap01.scaled(self.ui.lab_Show.geometry().width(),
self.ui.lab_Show.geometry().height(),
Qt.AspectRatioMode.KeepAspectRatio, # 保持宽高比
Qt.TransformationMode.SmoothTransformation) # 平滑变换
self.ui.lab_Show.setPixmap(scaled_pixmap)
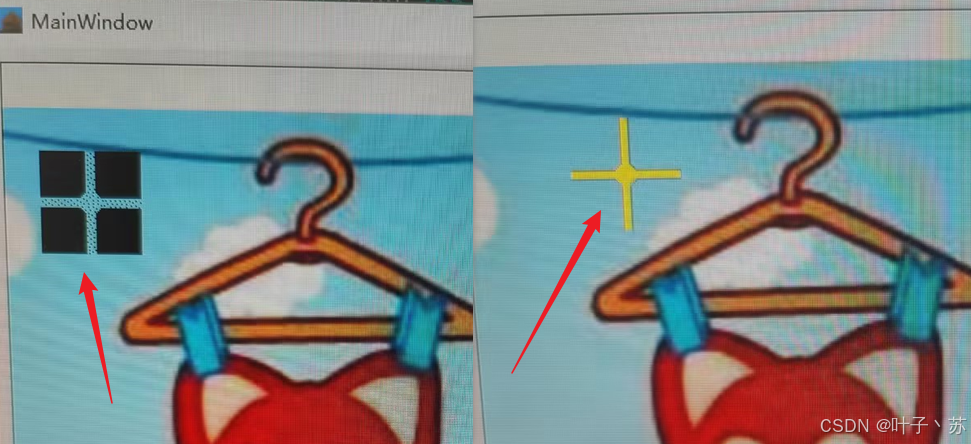

上面例程展示了通过 QPixmap 图形如何制作光标和遮罩,并通过 mask = QBitmap.fromPixmap(pixmap) 操作从彩色图像创建遮罩位图,应用起来简单高效。
三、QPicture 绘图命令的记录器和回放器
1.工作原理:记录与回放
QPicture 的核心工作流程分为两个阶段:
① 记录阶段:创建一个 QPicture,用 QPainter 在上面"录制"所有绘图命令;
②回放阶段:在任意绘图设备(如窗口、打印机、另一张图片)上,用 QPainter "播放"录制的命令。
2.实践应用
python
#QPicture 保存和加载绘图文件
self.picture = QPicture()
self.current_file = None
self.ui.lab_Show2.setAlignment(Qt.AlignmentFlag.AlignCenter) # 图片在Label中居中显示
#槽函数
self.ui.btn_create.clicked.connect(self.create_sample_picture)
self.ui.btn_clear.clicked.connect(self.picture_clear)
self.ui.btn_save.clicked.connect(self.save_picture)
self.ui.btn_load.clicked.connect(self.load_picture)
self.ui.lab_Show2.setStyleSheet("border: 2px solid gray; background-color: white;")
def create_sample_picture(self):
"""创建一个示例图形"""
self.picture = QPicture()
painter = QPainter(self.picture)
painter.setRenderHint(QPainter.RenderHint.Antialiasing)
# 绘制一个笑脸
# 脸
painter.setBrush(QColor(255, 255, 200))
painter.setPen(QPen(Qt.GlobalColor.black, 2))
painter.drawEllipse(50, 50, 200, 200)
# 眼睛
painter.setBrush(Qt.GlobalColor.white)
painter.drawEllipse(100, 100, 30, 30)
painter.drawEllipse(170, 100, 30, 30)
painter.setBrush(Qt.GlobalColor.black)
painter.drawEllipse(110, 110, 10, 10)
painter.drawEllipse(180, 110, 10, 10)
# 嘴巴
painter.setBrush(Qt.GlobalColor.red)
painter.drawChord(80, 120, 140, 80, 30 * 16, 120 * 16)
# 添加文字
painter.setPen(Qt.GlobalColor.blue)
painter.drawText(60, 280, "这是一个保存到 QPicture 的笑脸")
painter.end()
self.current_file = None
self.statusBar().showMessage("状态: 已创建新图形", 3000)
self.update_preview()
def picture_clear(self):
self.ui.lab_Show2.clear()
def save_picture(self):
"""将 QPicture 保存到文件"""
if self.picture.isNull():
QMessageBox.warning(self, "错误", "没有可保存的图形")
return
file_path, _ = QFileDialog.getSaveFileName(self, "保存 QPicture", "", "Picture Files (*.pic);;All Files (*)")
if file_path:
# 确保文件扩展名
if not file_path.endswith('.pic'):
file_path += '.pic'
if self.picture.save(file_path):
self.current_file = file_path
self.statusBar().showMessage(f"状态: 已保存到 {os.path.basename(file_path)}", 3000)
# 显示文件大小
file_size = os.path.getsize(file_path)
else:
QMessageBox.warning(self, "错误", "保存失败")
def load_picture(self):
"""从文件加载 QPicture"""
file_path, _ = QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(self, "加载 QPicture", "", "Picture Files (*.pic);;All Files (*)")
if file_path and os.path.exists(file_path):
loaded_picture = QPicture()
if loaded_picture.load(file_path):
self.picture = loaded_picture
self.current_file = file_path
# 显示文件信息
file_size = os.path.getsize(file_path)
self.statusBar().showMessage(f"状态: 已加载 ({file_size} 字节) - {os.path.basename(file_path)}", 3000)
self.update_preview()
else:
QMessageBox.warning(self, "错误", "加载失败,可能不是有效的 QPicture 文件")
def update_preview(self):
"""更新预览区域的显示"""
if self.picture.isNull():
self.ui.lab_Show2.setText("无图形可显示")
return
# 创建一个临时的 QPixmap 用于预览
pixmap = QPixmap(400, 300)
pixmap.fill(Qt.GlobalColor.white)
painter = QPainter(pixmap)
# 获取 QPicture 的边界矩形,以便居中显示
picture_rect = self.picture.boundingRect()
if not picture_rect.isEmpty():
# 计算缩放比例以适应预览区域
scale_x = 380 / picture_rect.width()
scale_y = 280 / picture_rect.height()
scale = min(scale_x, scale_y, 1.0) # 不超过1倍,防止放大
# 计算居中位置
offset_x = (300 - picture_rect.width() * scale) / 2
offset_y = (160 - picture_rect.height() * scale) / 2
painter.translate(offset_x, offset_y)
painter.scale(scale, scale)
# 绘制 QPicture
painter.drawPicture(0, 0, self.picture)
painter.end()
self.ui.lab_Show2.setPixmap(pixmap)
① 先进行 self.picture = QPicture() 、 painter = QPainter(self.picture) 记录器的创建,当笑脸图形绘制完成后,painter 的绘制流程和命令都已被记录并存储在 QPicture 类中,此时可以进行保存或者显示;
② update_preview 函数中 pixmap = QPixmap(400, 300) 创建一个临时的 QPixmap 用于预览,然后 painter.drawPicture(0, 0, self.picture) 进行 保存在 QPicture 类中数据的绘制,并绘制在 pixmap 上,显示于 QLabel 控件上;
③ 通过 self.picture.save(file_path) 函数进行保存 QPicture 类中的绘制数据,后缀为 pic ;
④ 通过 loaded_picture.load(file_path) 函数可以对 QPicture 文件进行加载并进行显示。
总结
设备选择策略
① QWidget:实时交互界面、动画、自定义控件;
② QImage:图像处理、滤镜、像素分析、文件I/O;
③ QPixmap:界面元素、图标、缓存图像、图像合成;
④ QBitmap:遮罩、光标、简单形状、内存敏感场景;
⑤ QPicture:矢量图形、重复绘制、模板化绘图。
本节示例展示了 QPainter 在不同设备上的强大能力。理解每种设备的特性和适用场景,可以让你在 PySide6 开发中选择最合适的绘图方式。
本节源码路径为:PySide6基本窗口控件深度补充_窗口绘图类