摘要
本文将通过解析 binder 驱动代码探究 IBinder 对象的跨进程传递和跨进程调用 IBinder 对象的机制流程,并找出 Binder IPC 发起函数和 Binder 回调跑在同一个线程里导致的线程同步问题。
问题: Binder IPC 发起函数和 Binder 回调跑在同一个线程里
笔者在实现 nfc hal 层服务(使用 INfc.aidl) android.hardware.nfc-service.example (源码路径:hardware/interfaces/nfc/aidl/default) 的过程中遇到了个多线程问题, 问题现象如下:
在 NFC 功能关闭的情况下,系统开机时段 com.android.nfc 中的 NfcAdaptation::DownloadFirmware 会有卡死问题。
走读代码:
system/nfc/src/adaptation/NfcAdaptation.cc
cpp
ThreadCondVar NfcAdaptation::mHalOpenCompletedEvent;
bool NfcAdaptation::DownloadFirmware() {
mHalOpenCompletedEvent.lock();
DLOG_IF(INFO, nfc_debug_enabled) << StringPrintf("%s: try open HAL", func);
HalOpen(HalDownloadFirmwareCallback, HalDownloadFirmwareDataCallback);
mHalOpenCompletedEvent.wait();
}
void NfcAdaptation::HalDownloadFirmwareCallback(nfc_event_t event,
__attribute__((unused))
nfc_status_t event_status) {
case HAL_NFC_POST_INIT_CPLT_EVT:
DLOG_IF(INFO, nfc_debug_enabled)
<< StringPrintf("%s: HAL_NFC_INIT_CPLT_EVT", func);
if (event_status == HAL_NFC_STATUS_OK) isDownloadFirmwareCompleted = true;
mHalOpenCompletedEvent.signal();
break;
}正常逻辑是在 DownloadFirmware() 中调用 HalOpen() 后,接着调用 mHalOpenCompletedEvent.wait() 阻塞住线程,等待 HalDownloadFirmwareCallback 调用 mHalOpenCompletedEvent.signal() 将其唤醒。
通过 log 发现,HalDownloadFirmwareCallback 已经有被调用, 但 mHalOpenCompletedEvent.signal() 还是没有成功唤醒 DownloadFirmware() 的等待。
log如下:
less
07-07 15:59:28.849 2429 2759 I libnfc_nci: [INFO:NfcAdaptation.cc(550)] NfcAdaptation::Initialize: exit
07-07 15:59:28.849 2429 2759 I libnfc_nci: [INFO:NfcAdaptation.cc(988)] NfcAdaptation::DownloadFirmware: enter
07-07 15:59:28.849 2429 2759 I libnfc_nci: [INFO:NfcAdaptation.cc(770)] NfcAdaptation::HalInitialize
07-07 15:59:28.849 2429 2759 I libnfc_nci: [INFO:NfcAdaptation.cc(992)] NfcAdaptation::DownloadFirmware: try open HAL
07-07 15:59:28.849 2429 2759 I libnfc_nci: [INFO:NfcAdaptation.cc(800)] NfcAdaptation::HalOpen
07-07 15:59:28.871 2429 2759 I libnfc_nci: [INFO:NfcAdaptation.cc(1023)] NfcAdaptation::HalDownloadFirmwareCallback: event=0x2, event_status=0x00
07-07 15:59:28.871 2429 2759 I libnfc_nci: [INFO:NfcAdaptation.cc(1038)] NfcAdaptation::HalDownloadFirmwareCallback: HAL_NFC_INIT_CPLT_EVT怀疑是 DownloadFirmware() 和 HalDownloadFirmwareCallback() 跑在在同一个线程导致的问题,mHalOpenCompletedEvent.signal() 不能唤醒同一线程中 mHalOpenCompletedEvent.wait()。
其它机器正常流程的log:
ruby
07-11 10:46:45.223 8689 8848 I libnfc_nci: [INFO:NfcAdaptation.cc(489)] NfcAdaptation::Initialize: exit
07-11 10:46:45.223 8689 8848 I libnfc_nci: [INFO:NfcAdaptation.cc(886)] NfcAdaptation::DownloadFirmware: enter
07-11 10:46:45.223 8689 8848 I libnfc_nci: [INFO:NfcAdaptation.cc(677)] NfcAdaptation::HalInitialize
07-11 10:46:45.224 8689 8848 I libnfc_nci: [INFO:NfcAdaptation.cc(890)] NfcAdaptation::DownloadFirmware: try open HAL
07-11 10:46:45.224 8689 8848 I libnfc_nci: [INFO:NfcAdaptation.cc(707)] NfcAdaptation::HalOpen
07-11 10:46:45.225 786 786 D android.hardware.nfc@1.2-impl: Nfc::open Enter
07-11 10:46:45.225 786 786 D android.hardware.nfc@1.2-impl: Nfc::open Exit
07-11 10:46:45.226 8689 8732 I libnfc_nci: [INFO:NfcAdaptation.cc(916)] NfcAdaptation::HalDownloadFirmwareCallback: event=0x0
07-11 10:46:45.227 8689 8732 I libnfc_nci: [INFO:NfcAdaptation.cc(920)] NfcAdaptation::HalDownloadFirmwareCallback: HAL_NFC_OPEN_CPLT_EVT
07-11 10:46:45.227 8689 8848 I libnfc_nci: [INFO:NfcAdaptation.cc(894)] NfcAdaptation::DownloadFirmware: try close HAL
07-11 10:46:45.227 8689 8848 I libnfc_nci: [INFO:NfcAdaptation.cc(727)] NfcAdaptation::HalClose正常的流程中,DownloadFirmware() 和 HalDownloadFirmwareCallback() 不在同一个线程。
那就在 HalDownloadFirmwareCallback() 中另起一个线程来执行 mHalOpenCompletedEvent.signal() 试试:
system/nfc/src/adaptation/NfcAdaptation.cc
diff
@@ -1006,7 +1006,14 @@ bool NfcAdaptation::DownloadFirmware() {
return isDownloadFirmwareCompleted;
}
-
+void* NfcAdaptation::HalOpenCompletedThread(void *ptr)
+{
+ (void)ptr;
+ DLOG_IF(INFO, nfc_debug_enabled)
+ << StringPrintf("enter %s", __func__);
+ mHalOpenCompletedEvent.signal();
+ return nullptr;
+}
/*******************************************************************************
**
** Function: NfcAdaptation::HalDownloadFirmwareCallback
@@ -1020,8 +1027,9 @@ void NfcAdaptation::HalDownloadFirmwareCallback(nfc_event_t event,
__attribute__((unused))
nfc_status_t event_status) {
const char* func = "NfcAdaptation::HalDownloadFirmwareCallback";
+ pthread_t thread_open_completed;
DLOG_IF(INFO, nfc_debug_enabled)
- << StringPrintf("%s: event=0x%X", func, event);
+ << StringPrintf("%s: event=0x%X, event_status=0x%02X", func, event, event_status);
switch (event) {
/* START_SLSI [S14111804] Patch for prcoessing the first core_init response */
#if (NFC_SEC_NOT_OPEN_INCLUDED == TRUE)
@@ -1038,7 +1046,8 @@ void NfcAdaptation::HalDownloadFirmwareCallback(nfc_event_t event,
DLOG_IF(INFO, nfc_debug_enabled)
<< StringPrintf("%s: HAL_NFC_INIT_CPLT_EVT", func);
if (event_status == HAL_NFC_STATUS_OK) isDownloadFirmwareCompleted = true;
- mHalOpenCompletedEvent.signal();
+ pthread_create(&thread_open_completed, NULL, HalOpenCompletedThread, NULL);
+ //mHalOpenCompletedEvent.signal();
break;system/nfc/src/include/NfcAdaptation.h
diff
@@ -155,6 +155,7 @@ class NfcAdaptation {
static void HalControlGranted();
static void HalPowerCycle();
static uint8_t HalGetMaxNfcee();
+ static void* HalOpenCompletedThread(void *ptr);做以上修改,可以规避问题, log如下:
yaml
07-07 19:35:20.352 2449 2777 I libnfc_nci: [INFO:NfcAdaptation.cc(1031)] NfcAdaptation::HalDownloadFirmwareCallback: event=0x2, event_status=0x00
07-07 19:35:20.352 2449 2777 I libnfc_nci: [INFO:NfcAdaptation.cc(1046)] NfcAdaptation::HalDownloadFirmwareCallback: HAL_NFC_INIT_CPLT_EVT
07-07 19:35:20.354 650 2783 D nfc-service.example: reset_nfc_thread: fd = 7
07-07 19:35:20.354 650 2783 D nfc-service.example: reset_nfc_thread: send rest_nfc data succ!
07-07 19:35:20.363 2449 2785 I libnfc_nci: [INFO:NfcAdaptation.cc(1012)] enter HalOpenCompletedThread
07-07 19:35:20.363 2449 2777 E libnfc_nci: [ERROR:NfcAdaptation.cc(996)] NfcAdaptation::DownloadFirmware: try close HAL
07-07 19:35:20.363 2449 2777 I libnfc_nci: [INFO:NfcAdaptation.cc(832)] NfcAdaptation::HalClose在这里引出一个问题,我的系统中 DownloadFirmware() 和 HalDownloadFirmwareCallback() 为什么会跑到同一个线程里?
源码分析
NfcAdaptation::HalDownloadFirmwareCallback() 的调用总流程
system/nfc/src/adaptation/NfcAdaptation.cc
cpp
bool NfcAdaptation::DownloadFirmware() {
HalOpen(HalDownloadFirmwareCallback, HalDownloadFirmwareDataCallback);
}
void NfcAdaptation::HalOpen(tHAL_NFC_CBACK* p_hal_cback,
tHAL_NFC_DATA_CBACK* p_data_cback) {
mAidlCallback = ::ndk::SharedRefBase::make<NfcAidlClientCallback>(
p_hal_cback, p_data_cback);
Status status = mAidlHal->open(mAidlCallback);
}
class NfcAidlClientCallback
: public ::aidl::android::hardware::nfc::BnNfcClientCallback {
public:
NfcAidlClientCallback(tHAL_NFC_CBACK* eventCallback,
tHAL_NFC_DATA_CBACK dataCallback) {
mEventCallback = eventCallback;
mDataCallback = dataCallback;
};
}如上代码所示,HalDownloadFirmwareCallback() 经由 HalOpen() 赋值给 mAidlCallback.mEventCallback, mAidlCallback 再经由 mAidlHal->open(mAidlCallback) 传递给 android.hardware.nfc-service.example,
android.hardware.nfc-service.example 的代码:
hardware/interfaces/nfc/aidl/default/Nfc.cpp
cpp
::ndk::ScopedAStatus Nfc::open(const std::shared_ptr<INfcClientCallback>& clientCallback) {
Nfc::mCallback = clientCallback;
int ret = Vendor_hal_open(eventCallback, dataCallback);
}hardware/interfaces/nfc/aidl/default/Nfc.h
cpp
struct Nfc : public BnNfc {
public:
static void eventCallback(uint8_t event, uint8_t status) {
if (mCallback != nullptr) {
auto ret = mCallback->sendEvent((NfcEvent)event, (NfcStatus)status);
if (!ret.isOk()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to send event!";
}
}
}
static void dataCallback(uint16_t data_len, uint8_t* p_data) {
std::vector<uint8_t> data(p_data, p_data + data_len);
if (mCallback != nullptr) {
auto ret = mCallback->sendData(data);
if (!ret.isOk()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to send data!";
}
}
}
}hardware/interfaces/nfc/aidl/default/Vendor_hal_api.cpp
cpp
static nfc_stack_callback_t* p_nfc_stack_cback;
static nfc_stack_data_callback_t* p_nfc_stack_data_cback;
int Vendor_hal_open(nfc_stack_callback_t* p_cback, nfc_stack_data_callback_t* p_data_cback) {
p_nfc_stack_cback = p_cback;
p_nfc_stack_data_cback = p_data_cback;
p_nfc_stack_cback(HAL_NFC_OPEN_CPLT_EVT, HAL_NFC_STATUS_OK);
}1.android.hardware.nfc-service.example 接到 NfcAdaptation 发起的 mAidlHal->open(mAidlCallback) ipc调用请求后,进入 Nfc::open();
2.Nfc::open() 中将 NfcAdaptation.mAidlCallback 的 Binder 对象赋值给Nfc::mCallback;
3.Nfc::open() 中把 Nfc.eventCallback() 和 Nfc.dataCallback() 传给Vendor_hal_open();
4.Vendor_hal_api.cpp 在有事件或数据要上报给 com.android.nfc 的话就会调用 Nfc.eventCallback()[p_nfc_stack_cback] 和 Nfc.dataCallback()[p_nfc_stack_data_cback] 传递事件和数据,最终会通过 binder 机制调用到 NfcAdaptation 中的 mAidlCallback.mEventCallback 和 mAidlCallback.mDataCallback,也就是 HalDownloadFirmwareCallback, HalDownloadFirmwareDataCallback。
IBinder 对象的跨进程传递
本文将以 NfcAdaptation.mAidlCallback 的传递流程为例来描述 IBinder 对象的跨进程传递。
传递之前的准备
传递 NfcAdaptation.mAidlCallback 在进入驱动之前的调用链
cpp
NfcAdaptation::HalOpen()
mAidlHal->open(mAidlCallback)
INfcAidl::open(INfcAidlClientCallback in_clientCallback)
aidl::android::hardware::nfc::BpNfc::open(INfcClientCallback& in_clientCallback)
BpBinder::transact(unsigned int, android::Parcel const&, android::Parcel*, unsigned int)
IPCThreadState::transact(int32_t handle, uint32_t code, const Parcel& data, Parcel* reply, uint32_t flags)
IPCThreadState::writeTransactionData(int32_t cmd, uint32_t binderFlags, int32_t handle, uint32_t code, const Parcel& data, status_t* statusBuffer)
IPCThreadState::waitForResponse()
IPCThreadState::talkWithDriver()
ioctl(mProcess->mDriverFD, BINDER_WRITE_READ, &bwr)out/soong/.intermediates/hardware/interfaces/nfc/aidl/android.hardware.nfc-V1-ndk-source/gen/android/hardware/nfc/INfc.cpp
cpp
::ndk::ScopedAStatus BpNfc::open(const std::shared_ptr<::aidl::android::hardware::nfc::INfcClientCallback>& in_clientCallback) {
_aidl_ret_status = ::ndk::AParcel_writeData(_aidl_in.get(), in_clientCallback);
}AParcel_writeData的调用链如下:
cpp
AParcel_writeData()
AParcel_writeData(_aidl_in.get(), in_clientCallback)
AParcel_writeStrongBinder()
Parcel::writeStrongBinder(const sp<IBinder>& val)
Parcel::flattenBinder(const sp<IBinder>& binder)
if (binder) local = binder->localBinder();
flat_binder_object obj;
obj.hdr.type = BINDER_TYPE_BINDER;
obj.binder = reinterpret_cast<uintptr_t>(local->getWeakRefs());
obj.cookie = reinterpret_cast<uintptr_t>(local);
writeObject(obj, false)在这里,NfcAdaptation.mAidlCallback 被赋值给 flat_binder_object.cookie, flat_binder_object 被打包进一个 Parcel 对象中,并往下传给 BpBinder::transact() ---> IPCThreadState::transact().
在 IPCThreadState::transact()中:
cpp
status_t IPCThreadState::transact(int32_t handle,
uint32_t code, const Parcel& data,
Parcel* reply, uint32_t flags)
{
err = writeTransactionData(BC_TRANSACTION, flags, handle, code, data, nullptr);
}
status_t IPCThreadState::writeTransactionData(int32_t cmd, uint32_t binderFlags,
int32_t handle, uint32_t code, const Parcel& data, status_t* statusBuffer)
{
binder_transaction_data tr;
tr.target.handle = handle;
tr.code = code;
tr.data_size = data.ipcDataSize();
tr.data.ptr.buffer = data.ipcData();
tr.offsets_size = data.ipcObjectsCount()*sizeof(binder_size_t);
tr.data.ptr.offsets = data.ipcObjects();
mOut.writeInt32(cmd);
mOut.write(&tr, sizeof(tr));
}IPCThreadState::writeTransactionData() 的作用如下:
1.创建 binder_transaction_data, 把 handle,code,data 赋值到binder_transaction_data;
2.将命令号 cmd(如 IPCThreadState::transact() 给的 BC_TRANSACTION) 和binder_transaction_data 写到 Parcel 类型的 mOut。
至此,代表 NfcAdaptation.mAidlCallback 的 cookie 也被打包进binder_transaction_data,并在 IPCThreadState::talkWithDriver() 中通过ioctl(mProcess->mDriverFD, BINDER_WRITE_READ, &bwr) 传给了 binder 驱动。
关注这个 cookie, 后续我们将跟踪这个 cookie 的传递和最终调用。
IBinder 对象在驱动中的传递
发送 IBinder 对象
binder_ioctl()
随着系统调用 ioctl(), 程序进入了内核驱动层 binder_ioctl():
kernel5.4/drivers/android/binder.c
cpp
static long binder_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
struct binder_proc *proc = filp->private_data;
struct binder_thread *thread;
thread = binder_get_thread(proc);
switch (cmd) {
case BINDER_WRITE_READ:
ret = binder_ioctl_write_read(filp, cmd, arg, thread);
if (ret)
goto err;
break;
}
}binder_ioctl() 首先出现的是 struct binder_proc *proc 和 struct binder_thread *thread 两个变量。
struct binder_proc *proc 代表的是进程,由 binder_open() 创建, binder_open() 又是在什么地方被调用呢,请看以下代码:
每个 app 在启动时会运行 app_process, 并走 AppRuntime::onZygoteInit(): frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp
cpp
virtual void onZygoteInit()
{
sp<ProcessState> proc = ProcessState::self();
ALOGV("App process: starting thread pool.\n");
proc->startThreadPool();
}接着走
cpp
ProcessState::self()
ProcessState::init()
ProcessState::ProcessState()
ProcessState::open_driver()在 ProcessState::open_driver() 中打开了 binder 的驱动节点文件 "/dev/binder":
frameworks/native/libs/binder/ProcessState.cpp
cpp
const char* kDefaultDriver = "/dev/binder";
sp<ProcessState> ProcessState::self()
{
return init(kDefaultDriver, false /*requireDefault*/);
}
sp<ProcessState> ProcessState::init(const char *driver, bool requireDefault)
{
gProcess = sp<ProcessState>::make(driver);
}
ProcessState::ProcessState(const char* driver)
: mDriverName(String8(driver)),
mDriverFD(-1) {
base::Result<int> opened = open_driver(driver);
if (opened.ok()) {
mDriverFD = opened.value();
}
}
static base::Result<int> open_driver(const char* driver) {
int fd = open(driver, O_RDWR | O_CLOEXEC);
return fd;
}然后在驱动的 binder_open() 函数中创建了 struct binder_proc *proc, 用于在内核空间代表当前进程,每个使用了 binder 通信机制的进程在内核空间中有个唯一的 struct binder_proc *proc
kernel5.4/drivers/android/binder.c
cpp
static int binder_open(struct inode *nodp, struct file *filp)
{
struct binder_proc *proc, *itr;
eproc = kzalloc(sizeof(*eproc), GFP_KERNEL);
proc = &eproc->proc;
proc->tsk = current->group_leader;
proc->context = &binder_dev->context;
proc->pid = current->group_leader->pid;
filp->private_data = proc;
}struct binder_thread *thread 代表着当前线程,怎么来的呢
kernel5.4/drivers/android/binder.c
cpp
static long binder_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
thread = binder_get_thread(proc);
}
static struct binder_thread *binder_get_thread(struct binder_proc *proc)
{
thread = binder_get_thread_ilocked(proc, NULL);
if (!thread) {
new_thread = kzalloc(sizeof(*thread), GFP_KERNEL);
thread = binder_get_thread_ilocked(proc, new_thread);
}
return thread;
}
static struct binder_thread *binder_get_thread_ilocked(
struct binder_proc *proc, struct binder_thread *new_thread)
{
struct binder_thread *thread = NULL;
struct rb_node *parent = NULL;
struct rb_node **p = &proc->threads.rb_node;
while (*p) {
parent = *p;
thread = rb_entry(parent, struct binder_thread, rb_node);
if (current->pid < thread->pid)
p = &(*p)->rb_left;
else if (current->pid > thread->pid)
p = &(*p)->rb_right;
else
return thread;
}
if (!new_thread)
return NULL;
thread = new_thread;
binder_stats_created(BINDER_STAT_THREAD);
thread->proc = proc;
thread->pid = current->pid;
rb_link_node(&thread->rb_node, parent, p);
rb_insert_color(&thread->rb_node, &proc->threads);
......
return thread;
}如上代码所示,binder_get_thread_ilocked() 先在当前 binder_proc.threads 中查找有没有为当前线程创建过的 binder_thread, 线程第一次调用 binder_ioctl() 的话,是没有对应binder_thread 的,那就返回 binder_get_thread() 新创一个,再传入binder_get_thread_ilocked(), 并 "rb_insert_color(&thread->rb_node, &proc->threads);" 给加到 binder_proc.threads 的红黑树中。
binder_ioctl_write_read()
说完 binder_proc 和 binder_thread, 接着来到了写读流程 binder_ioctl_write_read(),为什么是写读呢?
frameworks/native/libs/binder/IPCThreadState.cpp
cpp
status_t IPCThreadState::waitForResponse(Parcel *reply, status_t *acquireResult)
{
while (1) {
if ((err=talkWithDriver()) < NO_ERROR) break;
}
}
status_t IPCThreadState::talkWithDriver(bool doReceive)
{
// Is the read buffer empty?
const bool needRead = mIn.dataPosition() >= mIn.dataSize();
const size_t outAvail = (!doReceive || needRead) ? mOut.dataSize() : 0;
bwr.write_size = outAvail;
bwr.write_buffer = (uintptr_t)mOut.data();
if (doReceive && needRead) {
bwr.read_size = mIn.dataCapacity();
bwr.read_buffer = (uintptr_t)mIn.data();
} else {
bwr.read_size = 0;
bwr.read_buffer = 0;
}
ALOGD("%s: Size of receive buffer: %llu, write_size: %llu, needRead: %d, doReceive: %d", __func__, bwr.read_size, bwr.write_size, needRead, doReceive)
do {
if (ioctl(mProcess->mDriverFD, BINDER_WRITE_READ, &bwr) >= 0)
err = NO_ERROR;
else
err = -errno;
}
}IPCThreadState::waitForResponse() 中不带参数地调用了 talkWithDriver(),
查看 talkWithDriver() 的定义
frameworks/native/libs/binder/include/binder/IPCThreadState.h
cpp
class IPCThreadState
{
private:
status_t talkWithDriver(bool doReceive=true);
}不带参数的 talkWithDriver() 等于 talkWithDriver(true),也就是要等待接收数据的。除非 mIn 的数据空间不为空。
看 log:
yaml
D ipc : Size of receive buffer: 256, write_size: 68, needRead: 1, doReceive: 1传给 ioctl() 的 write_size 和 read_size 都是大于 0。
接着在驱动中,通过 write_size 和 read_size 来判断是否要走 binder_thread_write() 或 binder_thread_read()
kernel5.4/drivers/android/binder.c
cpp
static int binder_ioctl_write_read(struct file *filp,
unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg,
struct binder_thread *thread)
{
if (bwr.write_size > 0) {
ret = binder_thread_write(proc, thread,
bwr.write_buffer,
bwr.write_size,
&bwr.write_consumed);
}
if (bwr.read_size > 0) {
ret = binder_thread_read(proc, thread, bwr.read_buffer,
bwr.read_size,
&bwr.read_consumed,
filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK);
}
}所以会先 binder_thread_write() 写入要传输的命令,然后再调用 binder_thread_read() 等待应答。
binder_thread_write()
kernel5.4/drivers/android/binder.c
cpp
static int binder_thread_write(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_thread *thread,
binder_uintptr_t binder_buffer, size_t size,
binder_size_t *consumed)
{
uint32_t cmd;
while (ptr < end && thread->return_error.cmd == BR_OK) {
int ret;
if (get_user(cmd, (uint32_t __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
switch (cmd) {
case BC_TRANSACTION:
case BC_REPLY: {
struct binder_transaction_data tr;
if (copy_from_user(&tr, ptr, sizeof(tr)))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(tr);
binder_transaction(proc, thread, &tr,
cmd == BC_REPLY, 0);
break;
}
}
}
}binder_thread_write() 取到应用层下传的 BC_TRANSACTION 的命令号和 binder_transaction_data 数据后, 进入 binder_transaction()。
binder_transaction()
kernel5.4/drivers/android/binder.c
cpp
static void binder_transaction(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_thread *thread,
struct binder_transaction_data *tr, int reply,
binder_size_t extra_buffers_size)
{
struct binder_transaction *t;
binder_size_t buffer_offset = 0;
binder_size_t off_start_offset, off_end_offset;
const void __user *user_buffer = (const void __user *)
(uintptr_t)tr->data.ptr.buffer;
if (reply) {
} else {
if (!(tr->flags & TF_ONE_WAY) && thread->transaction_stack) {
struct binder_transaction *tmp;
tmp = thread->transaction_stack;
while (tmp) {
struct binder_thread *from;
spin_lock(&tmp->lock);
from = tmp->from;
if (from && from->proc == target_proc) {
atomic_inc(&from->tmp_ref);
target_thread = from;
spin_unlock(&tmp->lock);
is_nested = true;
break;
}
spin_unlock(&tmp->lock);
tmp = tmp->from_parent;
}
}
}
off_start_offset = ALIGN(tr->data_size, sizeof(void *));
buffer_offset = off_start_offset;
off_end_offset = off_start_offset + tr->offsets_size;
for (buffer_offset = off_start_offset; buffer_offset < off_end_offset;
buffer_offset += sizeof(binder_size_t)) {
struct binder_object_header *hdr;
size_t object_size;
struct binder_object object;
binder_size_t object_offset;
binder_size_t copy_size;
object_size = binder_get_object(target_proc, user_buffer,
t->buffer, object_offset, &object);
hdr = &object.hdr;
off_min = object_offset + object_size;
switch (hdr->type) {
case BINDER_TYPE_BINDER:
case BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_BINDER: {
struct flat_binder_object *fp;
fp = to_flat_binder_object(hdr);
ret = binder_translate_binder(fp, t, thread);
break;
} break;
}
}
binder_alloc_copy_user_to_buffer(
&target_proc->alloc,
t->buffer, user_offset,
user_buffer + user_offset,
tr->data_size - user_offset)
if (reply) {
} else if (!(t->flags & TF_ONE_WAY)) {
t->need_reply = 1;
t->from_parent = thread->transaction_stack;
thread->transaction_stack = t;
return_error = binder_proc_transaction(t,
target_proc, target_thread);
}
}binder_transaction() 做了这几个事:
-
判断 thread->transaction_stack 是否为空, 不为空的话, 从中取得 target_thread , 因为在 NfcAdaptation::HalOpen() 中这是第一次发起 transact(), thread 是新创的, thread->transaction_stack 为空, 所以 target_thread 也为空, 需要在 binder_proc_transaction() 里选择合适的线程做 target_thread
-
遍历 binder_transaction_data.data.ptr.buffer 里的数据,调用binder_get_object() 找出 BINDER_TYPE_BINDER, BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE, BINDER_TYPE_FD 等对象的数据, 并将数据拷贝给 binder_transaction.buffer
-
找到 BINDER_TYPE_BINDER 类型数据后,调用 binder_translate_binder() 做处理
-
调用 binder_alloc_copy_user_to_buffer() 将 binder_transaction_data.data.ptr.buffer 里剩余的数据拷贝给 binder_transaction.buffer
-
调用 binder_proc_transaction() 将打包好的 binder_transaction 数据发送给 target_proc, 并唤醒 target_proc 来读取和处理 binder_transaction
binder_translate_binder()
我们现在来分析一下, binder_translate_binder() 函数会对 NfcAdaptation.mAidlCallback 这个 BINDER_TYPE_BINDER 对象做什么处理
BINDER_TYPE_BINDER 对象数据在传入 binder_translate_binder() 之前,先被转化为 flat_binder_object 数据结构,与用户层下发之前在 Parcel::flattenBinder() 里把 IBinder 转化为 flat_binder_object 对应上了。
kernel5.4/drivers/android/binder.c
cpp
static void binder_transaction(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_thread *thread,
struct binder_transaction_data *tr, int reply,
binder_size_t extra_buffers_size)
{
switch (hdr->type) {
case BINDER_TYPE_BINDER:
case BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_BINDER: {
struct flat_binder_object *fp;
fp = to_flat_binder_object(hdr);
ret = binder_translate_binder(fp, t, thread);
break;
} break;
}
}kernel5.4/drivers/android/binder.c
cpp
static int binder_translate_binder(struct flat_binder_object *fp,
struct binder_transaction *t,
struct binder_thread *thread)
{
struct binder_proc *proc = thread->proc;
struct binder_proc *target_proc = t->to_proc;
struct binder_ref_data rdata;
node = binder_get_node(proc, fp->binder);
if (!node) {
node = binder_new_node(proc, fp);
if (!node)
return -ENOMEM;
}
ret = binder_inc_ref_for_node(target_proc, node,
fp->hdr.type == BINDER_TYPE_BINDER,
&thread->todo, &rdata);
if (fp->hdr.type == BINDER_TYPE_BINDER)
fp->hdr.type = BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE;
else
fp->hdr.type = BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_HANDLE;
fp->binder = 0;
fp->handle = rdata.desc;
fp->cookie = 0;
}
static struct binder_node *binder_new_node(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct flat_binder_object *fp)
{
struct binder_node *node;
struct binder_node *new_node = kzalloc(sizeof(*node), GFP_KERNEL);
node = binder_init_node_ilocked(proc, new_node, fp);
}
static struct binder_node *binder_init_node_ilocked(
struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_node *new_node,
struct flat_binder_object *fp)
{
binder_uintptr_t ptr = fp ? fp->binder : 0;
binder_uintptr_t cookie = fp ? fp->cookie : 0;
rb_link_node(&node->rb_node, parent, p);
rb_insert_color(&node->rb_node, &proc->nodes);
node->proc = proc;
node->ptr = ptr;
node->cookie = cookie;
}在 binder_translate_binder() 中,又出现了个新的数据结构 struct binder_node, struct binder_node 用于在内核中代表 IBinder 实例。
binder_translate_binder() 主要做了这些事:
-
在当前进程中查找 flat_binder_object 对应的 binder_node, 没找到的话就调用 binder_new_node() 新创一个
1.1. binder_new_node() 创建新的 binder_node 后就调用 binder_init_node_ilocked() 将 flat_binder_object.cookie 赋值给 binder_node.cookie, 并将新的 binder_node 添加到红黑树 binder_proc.nodes中
-
在 binder_inc_ref_for_node() 查找或创建一个跟 binder_node 关联的 binder_ref, 并且将这个 binder_ref 跟 target_proc 关联
发送端 binder_proc, binder_node, binder_ref, 接收端 target_proc:binder_proc 四者之间的关系可看下图:
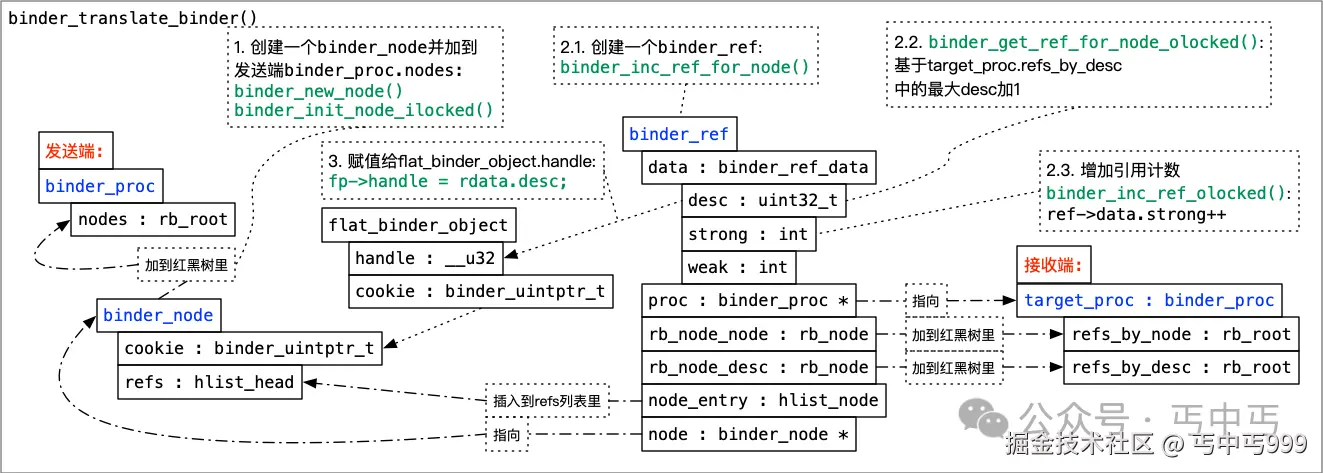
go
`binder_ref` 在内核中代表一个 binder\_node 也就是应用层 IBinder 的引用对象。每个 `binder_ref` 都包含强引用计数(binder\_ref.data.strong)和弱引用计数(binder\_ref.data.weak)字段,用于跟踪有多少个引用指向该对象。- 将 fp->hdr.type 由 BINDER_TYPE_BINDER 转为 BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_HANDLE , 将上面创建的 binder_ref.data.desc 赋值给 fp->handle (flat_binder_object.handle) , fp->handle 最终会传到接收端应用层程序, 接收端应用层程序要调用 NfcAdaptation.mAidlCallback 的话,就会向 binder 驱动传入该 handle, binder 驱动再根据该 handle 查找对应的 binder_ref 和 binder_node , 然后将 binder_node.cookie 传给 NfcAdaptation, 这个 binder_node.cookie 的值就是 NfcAdaptation.mAidlCallback 的指针。
binder_proc_transaction()
该函数将一个事务排队到指定的进程中。它会尝试在目标进程中找到一个线程来处理该事务并唤醒它。如果找不到可用的线程,则将此项工作排队到进程的等待队列中。
因为第一次 transact() 在 binder_transaction() 里传给 binder_proc_transaction() 的 target_thread 为 NULL, 所以在 binder_proc_transaction() 会走 binder_select_thread_ilocked() 去查找 target_proc 中可用于接收 binder_transaction 的线程 binder_thread
kernel5.4/drivers/android/binder.c
cpp
static int binder_proc_transaction(struct binder_transaction *t,
struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_thread *thread)
{
if (!thread && !pending_async)
thread = binder_select_thread_ilocked(proc);
if (thread) {
binder_transaction_priority(thread, t, node);
binder_enqueue_thread_work_ilocked(thread, &t->work);
}
if (!pending_async)
binder_wakeup_thread_ilocked(proc, thread, !oneway /* sync */);
}binder_select_thread_ilocked() 代码如下:
cpp
static struct binder_thread *
binder_select_thread_ilocked(struct binder_proc *proc)
{
struct binder_thread *thread;
assert_spin_locked(&proc->inner_lock);
thread = list_first_entry_or_null(&proc->waiting_threads,
struct binder_thread,
waiting_thread_node);
if (thread)
list_del_init(&thread->waiting_thread_node);
return thread;
}是从 proc->waiting_threads 列表中取出一个 binder_thread,那等待的 binder_thread 是在什么时候加到 waiting_threads 的呢?
接收端线程进入 binder_thread_read() 然后调用 binder_wait_for_work() 将 binder_thread 加到 proc->waiting_threads 列表里的。然后调用 schedule() 让线程进入睡眠等待发送端准备好数据后唤醒。
kernel5.4/drivers/android/binder.c
c
static int binder_thread_read() {
if (non_block) {
if (!binder_has_work(thread, wait_for_proc_work))
ret = -EAGAIN;
} else {
ret = binder_wait_for_work(thread, wait_for_proc_work);
}
}
static int binder_wait_for_work(struct binder_thread *thread,
bool do_proc_work)
{
for (;;) {
prepare_to_wait(&thread->wait, &wait, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
if (do_proc_work)
list_add(&thread->waiting_thread_node,
&proc->waiting_threads);
schedule();
}
}回到 binder_proc_transaction() 找到目标线程后:
-
通过 binder_transaction_priority() 临时提升接收端线程的优先级,以匹配发送端线程的优先级,从而避免因为接收端线程优先级较低而导致的高优先级发送端线程被长时间阻塞的问题。
-
binder_enqueue_thread_work_ilocked() 将 t->work 添加到目标线程的待办事项列表binder_thread.todo中,并启用待处理队列的处理。
-
binder_wakeup_thread_ilocked() 唤醒目标线程来接收 binder_transaction 。
接收 IBinder 对象
接收准备
android.hardware.nfc-service.example 的启动
hardware/interfaces/nfc/aidl/default/main.cpp
cpp
using ::aidl::android::hardware::nfc::Nfc;
int main() {
LOG(INFO) << "NFC HAL starting up";
if (!ABinderProcess_setThreadPoolMaxThreadCount(1)) {
LOG(INFO) << "failed to set thread pool max thread count";
return 1;
}
std::shared_ptr<Nfc> nfc_service = ndk::SharedRefBase::make<Nfc>();
const std::string instance = std::string() + Nfc::descriptor + "/default";
binder_status_t status =
AServiceManager_addService(nfc_service->asBinder().get(), instance.c_str());
CHECK(status == STATUS_OK);
ABinderProcess_joinThreadPool();
return 0;
}-
先创建一个 Nfc 类的服务 nfc_service, Nfc 继承于 BnNfc, 也就是 INfc 的服务端
-
AServiceManager_addService() 将 nfc_service 注册到 binder 服务中
-
ABinderProcess_joinThreadPool() 让当前线程加入 Binder 线程池,进入循环以处理传入的 Binder 事务
ABinderProcess_joinThreadPool() 源码如下:
frameworks/native/libs/binder/ndk/process.cpp
cpp
void ABinderProcess_joinThreadPool() {
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
}frameworks/native/libs/binder/IPCThreadState.cpp
cpp
IPCThreadState* IPCThreadState::self()
{
return new IPCThreadState;
}
IPCThreadState::IPCThreadState()
: mProcess(ProcessState::self()),
....... ) {
pthread_setspecific(gTLS, this);
clearCaller();
mIn.setDataCapacity(256);
mOut.setDataCapacity(256);
}上面代码:
-
在 IPCThreadState::self() 中创建一个代表当前线程的 IPCThreadState
-
IPCThreadState::IPCThreadState() 中调用了 ProcessState::self() , ProcessState::self() 的代码我们在前面分析过,是创建代表当前进程的 ProcessState , 并打开 binder 的驱动节点文件 "/dev/binder" 用来做 binder 通信。
接着是 joinThreadPool 的代码:
frameworks/native/libs/binder/IPCThreadState.cpp
cpp
void IPCThreadState::joinThreadPool(bool isMain)
{
LOG_THREADPOOL("**** THREAD %p (PID %d) IS JOINING THE THREAD POOL\n", (void*)pthread_self(), getpid());
mOut.writeInt32(isMain ? BC_ENTER_LOOPER : BC_REGISTER_LOOPER);
do {
processPendingDerefs();
// now get the next command to be processed, waiting if necessary
result = getAndExecuteCommand();
} while (result != -ECONNREFUSED && result != -EBADF);
}
status_t IPCThreadState::getAndExecuteCommand()
{
status_t result;
int32_t cmd;
result = talkWithDriver();
if (result >= NO_ERROR) {
cmd = mIn.readInt32();
result = executeCommand(cmd);
}
}
status_t IPCThreadState::executeCommand(int32_t cmd)
{
switch ((uint32_t)cmd) {
case BR_TRANSACTION:
{
binder_transaction_data_secctx tr_secctx;
binder_transaction_data& tr = tr_secctx.transaction_data;
if (tr.target.ptr) {
// We only have a weak reference on the target object, so we must first try to
// safely acquire a strong reference before doing anything else with it.
if (reinterpret_cast<RefBase::weakref_type*>(
tr.target.ptr)->attemptIncStrong(this)) {
error = reinterpret_cast<BBinder*>(tr.cookie)->transact(tr.code, buffer,
&reply, tr.flags);
reinterpret_cast<BBinder*>(tr.cookie)->decStrong(this);
} else {
error = UNKNOWN_TRANSACTION;
}
} else {
error = the_context_object->transact(tr.code, buffer, &reply, tr.flags);
}
}
}
}joinThreadPool() 里的关键调用链是:
cpp
joinThreadPool()
getAndExecuteCommand()
talkWithDriver()
executeCommand()当进入 talkWithDriver() 后,也会跟发送端一样,调用 ioctl() 进入内核态
因为 getAndExecuteCommand() 前有一句:
cpp
mOut.writeInt32(isMain ? BC_ENTER_LOOPER : BC_REGISTER_LOOPER);所以在内核驱动中先会走到:
kernel5.4/drivers/android/binder.c
cpp
static int binder_thread_write(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_thread *thread,
binder_uintptr_t binder_buffer, size_t size,
binder_size_t *consumed)
{
switch (cmd) {
case BC_ENTER_LOOPER:
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_THREADS,
"%d:%d BC_ENTER_LOOPER\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
if (thread->looper & BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_REGISTERED) {
thread->looper |= BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_INVALID;
binder_user_error("%d:%d ERROR: BC_ENTER_LOOPER called after BC_REGISTER_LOOPER\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
}
thread->looper |= BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_ENTERED;
break;
}
}标识 android.hardware.nfc-service.example 主线程已经成功进入了 Binder 的主循环,正在等待和处理来自 Binder 驱动的事务(Transaction) 。
binder_thread_read()
接着驱动进入 binder_thread_read() 然后如之前所述,调用 binder_wait_for_work() 将当前线程的 binder_thread 加到 proc->waiting_threads 列表里的。然后调用 schedule() 让线程进入睡眠等待发送端准备好数据后唤醒。
kernel5.4/drivers/android/binder.c
cpp
static int binder_thread_read() {
if (non_block) {
if (!binder_has_work(thread, wait_for_proc_work))
ret = -EAGAIN;
} else {
ret = binder_wait_for_work(thread, wait_for_proc_work);
}
thread->looper &= ~BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_WAITING;
while (1) {
uint32_t cmd;
struct binder_transaction_data_secctx tr;
struct binder_transaction_data *trd = &tr.transaction_data;
struct binder_work *w = NULL;
struct list_head *list = NULL;
struct binder_transaction *t = NULL;
if (!binder_worklist_empty_ilocked(&thread->todo)) {
list = &thread->todo;
if (nfc_hal_pid == proc->pid || nfc_pid == proc->pid) {
pr_err("%s: get thread->todo\n", __func__);
}
}
w = binder_dequeue_work_head_ilocked(list);
switch (w->type) {
case BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION: {
binder_inner_proc_unlock(proc);
t = container_of(w, struct binder_transaction, work);
} break;
if (t->buffer->target_node) {
struct binder_node *target_node = t->buffer->target_node;
trd->target.ptr = target_node->ptr;
trd->cookie = target_node->cookie;
binder_transaction_priority(thread, t, target_node);
cmd = BR_TRANSACTION;
}
trd->code = t->code;
trd->data_size = t->buffer->data_size;
trd->offsets_size = t->buffer->offsets_size;
trd->data.ptr.buffer = (uintptr_t)t->buffer->user_data;
put_user(cmd, (uint32_t __user *)ptr);
copy_to_user(ptr, &tr, trsize);
}
}
static int binder_wait_for_work(struct binder_thread *thread,
bool do_proc_work)
{
for (;;) {
prepare_to_wait(&thread->wait, &wait, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
if (do_proc_work)
list_add(&thread->waiting_thread_node,
&proc->waiting_threads);
schedule();
}
}接收端线程被发送端在 binder_proc_transaction() 函数中唤醒后,就从 binder_wait_for_work() 退出,走到 while (1) 循环中, 通过
cpp
list = &thread->todo;
binder_dequeue_work_head_ilocked(list);从 thread->todo 取出在 binder_proc_transaction() 中添加的 binder_work , 再通过 container_of(w, struct binder_transaction, work) 取到 w 的所属 binder_transaction 结构体。
取到 binder_transaction 后,就将 binder_transaction 的数据打包到 struct binder_transaction_data *trd, 然后通过 copy_to_user() 传给应用层。
cpp
trd->code = t->code;
trd->data_size = t->buffer->data_size;
trd->offsets_size = t->buffer->offsets_size;
put_user(cmd, (uint32_t __user *)ptr);
copy_to_user(ptr, &tr, trsize);struct binder_transaction_data_secctx tr 的数据结构定义如下:
cpp
struct binder_transaction_data_secctx {
struct binder_transaction_data transaction_data;
binder_uintptr_t secctx;
};所以, copy_to_user(ptr, &tr, trsize) 中 &tr 也就是 trd 的地址。
返回应用层
收到数据应用层也从 IPCThreadState::talkWithDriver() 中的 ioctl() 醒来,退出 IPCThreadState::talkWithDriver() 来到 IPCThreadState::executeCommand() 走
cpp
reinterpret_cast<BBinder*>(tr.cookie)->transact(tr.code, buffer,
&reply, tr.flags)最终来到
out/soong/.intermediates/hardware/interfaces/nfc/aidl/android.hardware.nfc-V1-ndk-source/gen/android/hardware/nfc/INfc.cpp
cpp
namespace aidl {
namespace android {
namespace hardware {
namespace nfc {
static binder_status_t _aidl_android_hardware_nfc_INfc_onTransact(AIBinder* _aidl_binder, transaction_code_t _aidl_code, const AParcel* _aidl_in, AParcel* _aidl_out) {
(void)_aidl_in;
(void)_aidl_out;
binder_status_t _aidl_ret_status = STATUS_UNKNOWN_TRANSACTION;
std::shared_ptr<BnNfc> _aidl_impl = std::static_pointer_cast<BnNfc>(::ndk::ICInterface::asInterface(_aidl_binder));
switch (_aidl_code) {
case (FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 0 /*open*/): {
std::shared_ptr<::aidl::android::hardware::nfc::INfcClientCallback> in_clientCallback;
_aidl_ret_status = ::ndk::AParcel_readData(_aidl_in, &in_clientCallback);
if (_aidl_ret_status != STATUS_OK) break;
::ndk::ScopedAStatus _aidl_status = _aidl_impl->open(in_clientCallback);
_aidl_ret_status = AParcel_writeStatusHeader(_aidl_out, _aidl_status.get());
if (_aidl_ret_status != STATUS_OK) break;
if (!AStatus_isOk(_aidl_status.get())) break;
break;
}
}经过以下调用链,代码来到了 Parcel::unflattenBinder()
cpp
AParcel_readData()
AParcel_readRequiredStrongBinder()
AParcel_readStrongBinder()
Parcel::readNullableStrongBinder()
Parcel::unflattenBinder()代码:
frameworks/native/libs/binder/ndk/include_cpp/android/binder_parcel_utils.h
cpp
static inline binder_status_t AParcel_readData(const AParcel* parcel, T* value) {
} else if constexpr (std::is_same_v<SpAIBinder, T>) {
return AParcel_readRequiredStrongBinder(parcel, value);
}
static inline binder_status_t AParcel_readRequiredStrongBinder(const AParcel* parcel,
SpAIBinder* binder) {
AIBinder* readBinder;
binder_status_t ret = AParcel_readStrongBinder(parcel, &readBinder);
if (ret == STATUS_OK) {
if (readBinder == nullptr) {
return STATUS_UNEXPECTED_NULL;
}
binder->set(readBinder);
}
return ret;
}frameworks/native/libs/binder/ndk/parcel.cpp
cpp
binder_status_t AParcel_readStrongBinder(const AParcel* parcel, AIBinder** binder) {
sp<IBinder> readBinder = nullptr;
status_t status = parcel->get()->readNullableStrongBinder(&readBinder);
if (status != STATUS_OK) {
return PruneStatusT(status);
}
sp<AIBinder> ret = ABpBinder::lookupOrCreateFromBinder(readBinder);
AIBinder_incStrong(ret.get());
*binder = ret.get();
return PruneStatusT(status);
}
status_t Parcel::readNullableStrongBinder(sp<IBinder>* val) const
{
return unflattenBinder(val);
}
status_t Parcel::unflattenBinder(sp<IBinder>* out) const
{
const flat_binder_object* flat = readObject(false);
if (flat) {
switch (flat->hdr.type) {
case BINDER_TYPE_BINDER: {
sp<IBinder> binder =
sp<IBinder>::fromExisting(reinterpret_cast<IBinder*>(flat->cookie));
return finishUnflattenBinder(binder, out);
}
case BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE: {
sp<IBinder> binder =
ProcessState::self()->getStrongProxyForHandle(flat->handle);
return finishUnflattenBinder(binder, out);
}
}
}
}因为在 binder_translate_binder() 中,flat_binder_object.hdr.type 已经由 BINDER_TYPE_BINDER 转为 BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_HANDLE , 所以 Parcel::unflattenBinder() 里走的 case BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE 分支。
ProcessState::self()->getStrongProxyForHandle(flat->handle) 以 flat->handle 为标识创建了一个 BpBinder 对象,用来在 android.hardware.nfc-service.example 里代表 NfcAdaptation.mAidlCallback 。
getStrongProxyForHandle()源码如下:
frameworks/native/libs/binder/ProcessState.cpp
cpp
sp<IBinder> ProcessState::getStrongProxyForHandle(int32_t handle)
{
sp<IBinder> result;
handle_entry* e = lookupHandleLocked(handle);
if (e != nullptr) {
IBinder* b = e->binder;
if (b == nullptr || !e->refs->attemptIncWeak(this)) {
sp<BpBinder> b = BpBinder::PrivateAccessor::create(handle);
e->binder = b.get();
if (b) e->refs = b->getWeakRefs();
result = b;
}
return result;
}从 Parcel::unflattenBinder() 返回后,再经过
cpp
Parcel::readNullableStrongBinder()
AParcel_readStrongBinder()
AParcel_readRequiredStrongBinder()
AParcel_readData()的层层包装,将 BpBinder 对象包装成 SpAIBinder。
最后来到 _aidl_android_hardware_nfc_INfc_onTransact 的 _aidl_impl->open(in_clientCallback) 也就是 hardware/interfaces/nfc/aidl/default/Nfc.cpp
cpp
::ndk::ScopedAStatus Nfc::open(const std::shared_ptr<INfcClientCallback>& clientCallback) {
Nfc::mCallback = clientCallback;
}将 NfcAdaptation.mAidlCallback 的替身赋值给 Nfc::mCallback 。
将来 android.hardware.nfc-service.example 调用 Nfc::mCallback 也就是 NfcAdaptation.mAidlCallback 时,会往在 SpAIBinder 里查找 BpBinder , 再获取 BpBinder 的handle, 然后往 binder 驱动传入该 handle, binder 驱动再根据该 handle 查找对应的 binder_ref 和 binder_node , 然后将 binder_node.cookie 传给 NfcAdaptation, 这个 binder_node.cookie 的值就是 NfcAdaptation.mAidlCallback 的真实指针, 通过这个指针,就可以调用 NfcAdaptation.mAidlCallback 的方法。
至此,我们完成了 binder 传递 一个 IBinder 对象 (NfcAdaptation.mAidlCallback) 的流程分析。
使用回调类 IBinder 对象
以 android.hardware.nfc-service.example 调用 INfcClientCallback 为例解析调用 IBinder 对象的详细流程。
回调前的准备
hardware/interfaces/nfc/aidl/default/Nfc.cpp Nfc::open 将 NfcAdaptation.mAidlCallback 的替身赋值给 Nfc::mCallback 后,接着将 Nfc::eventCallback() Nfc::dataCallback() 两个函数传给 Vendor_hal_open():
cpp
::ndk::ScopedAStatus Nfc::open(const std::shared_ptr<INfcClientCallback>& clientCallback) {
Nfc::mCallback = clientCallback;
int ret = Vendor_hal_open(eventCallback, dataCallback);
}Nfc::eventCallback() Nfc::dataCallback() 两个函数的定义如下:
hardware/interfaces/nfc/aidl/default/Nfc.h
cpp
struct Nfc : public BnNfc {
static void eventCallback(uint8_t event, uint8_t status) {
if (mCallback != nullptr) {
auto ret = mCallback->sendEvent((NfcEvent)event, (NfcStatus)status);
if (!ret.isOk()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to send event!";
}
}
}
static void dataCallback(uint16_t data_len, uint8_t* p_data) {
std::vector<uint8_t> data(p_data, p_data + data_len);
if (mCallback != nullptr) {
auto ret = mCallback->sendData(data);
if (!ret.isOk()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to send data!";
}
}
}
}Nfc::eventCallback()、 Nfc::dataCallback() 分别调用了 mCallback->sendEvent() 和 mCallback->sendData() 给 NfcAdaptation 上发事件和数据。
Vendor_hal_open() 的实现如下:
hardware/interfaces/nfc/aidl/default/Vendor_hal_api.cpp
cpp
static nfc_stack_callback_t* p_nfc_stack_cback;
static nfc_stack_data_callback_t* p_nfc_stack_data_cback;
int Vendor_hal_open(nfc_stack_callback_t* p_cback, nfc_stack_data_callback_t* p_data_cback) {
p_nfc_stack_cback = p_cback;
p_nfc_stack_data_cback = p_data_cback;
p_nfc_stack_cback(HAL_NFC_OPEN_CPLT_EVT, HAL_NFC_STATUS_OK);
return HAL_NFC_STATUS_OK;
}Vendor_hal_open() 里分别将 Nfc::eventCallback()、 Nfc::dataCallback() 赋值给了 p_nfc_stack_cback, p_nfc_stack_data_cback 这两个函数指针。
Vendor_hal_open() 在返回前, 通过 p_nfc_stack_cback(HAL_NFC_OPEN_CPLT_EVT, HAL_NFC_STATUS_OK) 给 NfcAdaptation 发送了 HAL_NFC_OPEN_CPLT_EVT 事件。
进入驱动之前的处理流程
p_nfc_stack_cback 指向 Nfc::eventCallback() 所以调用链如下:
cpp
p_nfc_stack_cback(HAL_NFC_OPEN_CPLT_EVT, HAL_NFC_STATUS_OK)
Nfc::eventCallback()
INfcClientCallback::sendEvent()
BpNfcClientCallback::sendEvent(NfcEvent in_event, NfcStatus in_status)
::ndk::ScopedAParcel _aidl_in;
/* 为 Binder 调用准备一个 Parcel 对象 */
AIBinder_prepareTransaction(asBinder().get(), _aidl_in.getR())
/* 将事件号写入 _aidl_in */
AParcel_writeData(_aidl_in.get(), in_event)
/* 将事件返回状态写入 _aidl_in */
AParcel_writeData(_aidl_in.get(), in_status)
/* 执行 Binder 调用 */
AIBinder_transact(asBinder().get(), (FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 1 /*sendEvent*/),
_aidl_in.getR(),
_aidl_out.getR(),
0
#ifdef BINDER_STABILITY_SUPPORT
| FLAG_PRIVATE_LOCAL
#endif // BINDER_STABILITY_SUPPORT
);
/* 从 Binder 调用的返回值里读出所要的信息 */
AParcel_readStatusHeader(_aidl_out.get(), _aidl_status.getR())AIBinder_transact() 的调用链如下:
cpp
AIBinder_transact()
BpBinder::transact()
IPCThreadState::self()->transact(binderHandle(), code, data, reply, flags)
IPCThreadState::transact()
IPCThreadState::writeTransactionData()
IPCThreadState::waitForResponse()
IPCThreadState::talkWithDriver()
ioctl(mProcess->mDriverFD, BINDER_WRITE_READ, &bwr)其中 binderHandle() 对应的就是在
cpp
sp<IBinder> ProcessState::getStrongProxyForHandle(int32_t handle)
{
sp<IBinder> result;
handle_entry* e = lookupHandleLocked(handle);
if (e != nullptr) {
IBinder* b = e->binder;
if (b == nullptr || !e->refs->attemptIncWeak(this)) {
sp<BpBinder> b = BpBinder::PrivateAccessor::create(handle);
e->binder = b.get();
if (b) e->refs = b->getWeakRefs();
result = b;
}
return result;
}里用来创建 Nfc::mCallback 用到的 handle 。
接着用来到了 IPCThreadState::transact()
cpp
status_t IPCThreadState::transact(int32_t handle,
uint32_t code, const Parcel& data,
Parcel* reply, uint32_t flags)
{
err = writeTransactionData(BC_TRANSACTION, flags, handle, code, data, nullptr);
}
status_t IPCThreadState::writeTransactionData(int32_t cmd, uint32_t binderFlags,
int32_t handle, uint32_t code, const Parcel& data, status_t* statusBuffer)
{
binder_transaction_data tr;
tr.target.handle = handle;
tr.code = code;
tr.data_size = data.ipcDataSize();
tr.data.ptr.buffer = data.ipcData();
tr.offsets_size = data.ipcObjectsCount()*sizeof(binder_size_t);
tr.data.ptr.offsets = data.ipcObjects();
mOut.writeInt32(cmd);
mOut.write(&tr, sizeof(tr));
}我们现在重点关注 handle 和 code 的传递。如上 IPCThreadState::writeTransactionData() 代码所示, handle 和 code 都被打包进了 binder_transaction_data 数据结构中, binder_transaction_data 将通过 IPCThreadState::waitForResponse() --> IPCThreadState::talkWithDriver() --> ioctl() 传到 binder 驱动里。
进入驱动
发起端
binder_transaction()
经过
cpp
//用户层:
ioctl()
//内核驱动:
binder_ioctl()
binder_ioctl_write_read()
binder_thread_write()
binder_transaction()我们又来到了 binder_transaction() 函数。这次我们来看看驱动里如何根据 handle 找到目标 Binder 执行对象。
cpp
static void binder_transaction(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_thread *thread,
struct binder_transaction_data *tr, int reply,
binder_size_t extra_buffers_size)
{
int ret;
struct binder_transaction *t;
struct binder_work *w;
struct binder_proc *target_proc = NULL;
struct binder_thread *target_thread = NULL;
struct binder_node *target_node = NULL;
if (reply) {
} else {
struct binder_ref *ref;
/*
* There must already be a strong ref
* on this node. If so, do a strong
* increment on the node to ensure it
* stays alive until the transaction is
* done.
*/
binder_proc_lock(proc);
ref = binder_get_ref_olocked(proc, tr->target.handle,
true);
if (ref) {
target_node = binder_get_node_refs_for_txn(
ref->node, &target_proc,
&return_error);
} else {
binder_user_error("%d:%d got transaction to invalid handle\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
}
binder_proc_unlock(proc);
}
}根据 IPCThreadState::transact() 传下来的 tr->target.handle 在当前 binder_proc 中查找 binder_ref
cpp
static struct binder_ref *binder_get_ref_olocked(struct binder_proc *proc,
u32 desc, bool need_strong_ref)
{
struct rb_node *n = proc->refs_by_desc.rb_node;
struct binder_ref *ref;
while (n) {
ref = rb_entry(n, struct binder_ref, rb_node_desc);
if (desc < ref->data.desc) {
n = n->rb_left;
} else if (desc > ref->data.desc) {
n = n->rb_right;
} else if (need_strong_ref && !ref->data.strong) {
binder_user_error("tried to use weak ref as strong ref\n");
return NULL;
} else {
return ref;
}
}
return NULL;
}binder_get_ref_olocked() 就是遍历 binder_proc.refs_by_desc 红黑树里的 binder_ref 节点, 然后将 binder_ref.data.desc 与要查找的 desc 也就是 tr->target.handle 比较, 当两者相等时,该 binder_ref 节点就是所要找的目标 binder_ref 。
这时候,我们再来看看分析 binder_translate_binder() 时画的图:

图中的 target_pro 就是我们现在的当前 binder_proc , binder_get_ref_olocked() 根据 tr->target.handle 找到了传递 IBinder 对象时在内核中创建的 binder_ref 。
从 binder_ref.node 中可以获取 binder_ref 代表的 binder_node , 然后根据 binder_node 取得 target_node 和 target_proc:
cpp
static struct binder_node *binder_get_node_refs_for_txn(
struct binder_node *node,
struct binder_proc **procp,
uint32_t *error)
{
struct binder_node *target_node = NULL;
binder_node_inner_lock(node);
if (node->proc) {
target_node = node;
binder_inc_node_nilocked(node, 1, 0, NULL);
binder_inc_node_tmpref_ilocked(node);
node->proc->tmp_ref++;
*procp = node->proc;
} else
*error = BR_DEAD_REPLY;
binder_node_inner_unlock(node);
return target_node;
}target_node 就是传递 NfcAdaptation.mAidlCallback 时在 binder_translate_binder() 创建的代表 NfcAdaptation.mAidlCallback 的 binder_node , 现在的 target_proc 就是图中的发送端 binder_proc, 也就是 NfcAdaptation 所在的 "com.android.nfc" 进程。
找到了 target_node 和 target_proc , 接下来又到了找 target_thread 的流程:
cpp
static void binder_transaction(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_thread *thread,
struct binder_transaction_data *tr, int reply,
binder_size_t extra_buffers_size)
{
if (reply) {
} else {
if (!(tr->flags & TF_ONE_WAY) && thread->transaction_stack) {
struct binder_transaction *tmp;
tmp = thread->transaction_stack;
while (tmp) {
struct binder_thread *from;
spin_lock(&tmp->lock);
from = tmp->from;
if (from && from->proc == target_proc) {
atomic_inc(&from->tmp_ref);
target_thread = from;
spin_unlock(&tmp->lock);
is_nested = true;
break;
}
spin_unlock(&tmp->lock);
tmp = tmp->from_parent;
}
}
}
}因为调用栈
cpp
Nfc::open()
Vendor_hal_open()
p_nfc_stack_cback(HAL_NFC_OPEN_CPLT_EVT, HAL_NFC_STATUS_OK)
Nfc::eventCallback()
INfcClientCallback::sendEvent()运行在同一个线程里, 也就是接收 Nfc::open() 调用和发起 INfcClientCallback::sendEvent() 调用的是同一个 binder_thread, 所以 binder_transaction() 里的 thread->transaction_stack 不为空了, thread->transaction_stack 为 Nfc::open() 发起端创建的 binder_transaction ,最后获取到的 target_thread = from 也就是发起 Nfc::open() 调用的线程, 即 com.android.nfc 中 NfcAdaptation::DownloadFirmware() 所在的线程。至此, 文首所说的 NfcAdaptation::DownloadFirmware()和 NfcAdaptation::HalDownloadFirmwareCallback() 跑在同一个线程的根本原因终于找到了。
还有一个解决 NfcAdaptation::DownloadFirmware() 和 NfcAdaptation::HalDownloadFirmwareCallback() 跑在同一个线程的方法是在 INfc 服务端 android.hardware.nfc-service.example 中另起一个线程来发起 INfcClientCallback 回调,另起一个线程就会新创一个 binder_transaction 来做 thread->transaction_stack, 不会用到 Nfc::open() 发起端创建的 binder_transaction, 此时 target_thread 为 NULL, 就会在 binder_proc_transaction() 走 binder_select_thread_ilocked() 去找 com.android.nfc 的另一个 binder 线程来接收调用。 该方法也是 nxp 等厂家的 INfc 服务端实现代码里所使用的,所以主线 NfcAdaptation 代码可以正常适配现有的 nxp 等厂家的 INfc 服务端实现。
再往下就是创建新的 binder_transaction, 把 target_proc, target_thread, code, target_node 等关键数据打包进 binder_transaction:
cpp
static void binder_transaction(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_thread *thread,
struct binder_transaction_data *tr, int reply,
binder_size_t extra_buffers_size)
{
struct binder_transaction *t;
t = kzalloc(sizeof(*t), GFP_KERNEL);
t->to_proc = target_proc;
t->to_thread = target_thread;
t->code = tr->code;
t->flags = tr->flags;
t->buffer->debug_id = t->debug_id;
t->buffer->transaction = t;
t->buffer->target_node = target_node;
}然后又是 binder_proc_transaction() 把打包好 binder_transaction 发给 target_proc target_thread。
接收端
binder_thread_read()
com.android.nfc 中 NfcAdaptation::DownloadFirmware() 所在的线程被 binder_proc_transaction() 唤醒后, 在 binder_wait_for_work() 中醒来, 退出到 binder_thread_read():
cpp
static int binder_thread_read(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_thread *thread,
binder_uintptr_t binder_buffer, size_t size,
binder_size_t *consumed, int non_block)
{
if (non_block) {
if (!binder_has_work(thread, wait_for_proc_work))
ret = -EAGAIN;
} else {
ret = binder_wait_for_work(thread, wait_for_proc_work);
}
if (t->buffer->target_node) {
struct binder_node *target_node = t->buffer->target_node;
trd->target.ptr = target_node->ptr;
trd->cookie = target_node->cookie;
binder_transaction_priority(thread, t, target_node);
cmd = BR_TRANSACTION;
}
}然后取出 binder_proc_transaction() 填入的 t->buffer->target_node, 把 target_node->cookie 赋值给 trd->cookie, 最后通过 copy_to_user() 传给应用层代码。这个 cookie 的值就是 NfcAdaptation::HalOpen() 调用 mAidlHal->open(mAidlCallback) 往 binder 驱动传递的最原始的 NfcAdaptation.mAidlCallback 指针,现在回传给 NfcAdaptation, 表示要调用 NfcAdaptation.mAidlCallback 里的成员函数了。
返回应用层
com.android.nfc 中 NfcAdaptation::DownloadFirmware() 所在的线程收到数据后, 应用层代码也从 IPCThreadState::talkWithDriver() 中的 ioctl() 醒来,退出 IPCThreadState::talkWithDriver() 来到 IPCThreadState::executeCommand() 走
cpp
reinterpret_cast<BBinder*>(tr.cookie)->transact(tr.code, buffer,
&reply, tr.flags)接着按一下调用链走向 NfcAdaptation::HalDownloadFirmwareCallback():
cpp
BBinder::transact()
ABBinder::onTransact()
aidl::android::hardware::nfc::_aidl_android_hardware_nfc_INfcClientCallback_onTransact()
NfcAidlClientCallback::sendEvent()
NfcAdaptation::HalDownloadFirmwareCallback()总结
至此, 我们分析了 NfcAdaptation::DownloadFirmware() 到 INfc::open() 服务端实现, 再从 INfc 服务端回调 INfcClientCallback 最终走到 NfcAdaptation::HalDownloadFirmwareCallback() 的整个 binder 通信流程,也弄清楚了 NfcAdaptation::DownloadFirmware()和 NfcAdaptation::HalDownloadFirmwareCallback() 跑在同一个线程的根本原因。