一、原型模式
1.1、定义
原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并通过拷贝这些原型,创建新的对象。即克隆,细胞分裂等。
1.2、核心思想
通过复制现有对象(原型)来创建新对象,而不是通过new新建实例
1.3、为什么需要原型模式
问题场景
创建角色,以孙悟空为例
cpp
// 装备类
class Equipment {
private:
std::string name;
int power;
public:
Equipment(std::string name, int power) : name(name), power(power) {}
Equipment* clone() const {
return new Equipment(name, power);
}
std::string getName() const { return name; }
int getPower() const { return power; }
void display() const {
std::cout << " " << name << " (威力:" << power << ")" << std::endl;
}
};
cpp
class SunWuKong {
private:
std::string name;
int health;
int attack;
std::vector<std::string> skills;
std::vector<Equipment*> equipment;
public:
SunWuKong(std::string name, int health, int attack)
: name(name), health(health), attack(attack)
{
// 初始化技能
skills.push_back("七十二变");
skills.push_back("筋斗云");
skills.push_back("火眼金睛");
skills.push_back("法天象地");
skills.push_back("身外身");
// 初始化装备
equipment.push_back(new Equipment("金箍棒", 1000));
equipment.push_back(new Equipment("锁子黄金甲", 500));
equipment.push_back(new Equipment("凤翅紫静", 300));
equipment.push_back(new Equipment("藕丝步云履", 200));
}
// 复制构造函数
SunWuKong(const SunWuKong& other)
: name(other.name), health(other.health), attack(other.attack), skills(other.skills), equipment(other.equipment)
{
}
// 拷贝赋值运算符
SunWuKong& operator=(const SunWuKong& other)
{
if (this != &other) {
name = other.name;
health = other.health;
attack = other.attack;
skills = other.skills;
equipment = other.equipment;
}
return *this;
}
~SunWuKong()
{
for (auto& eq : equipment) {
delete eq;
}
}
};
// 创建分身
void createCloneMonkey()
{
// 创建本体
SunWuKong* original = new SunWuKong("齐天大圣", 1000, 100);
// 吹毛化兵,创建分身
vector<SunWuKong*> clones;
for(int i = 0; i < 100000; ++i){
std::count<<"创建第 "<< i << " 个分身\n";
SunWuKong* clone = new SunWuKong(*original);
clones.push_back(clone);
}
delete original;
// 删除分身
for (auto& clone : clones) {
delete clone;
}
}问题点:
- 性能上:每次创建分身时,都需要初始化技能和装备,效率低下
- 灵活性差,如果修改了本体,分身不会自动进行更新
- 浅拷贝问题,容易导致双重释放或访问已释放内存
解决方案
使用原型模式之后
- 创建原型抽象类
cpp
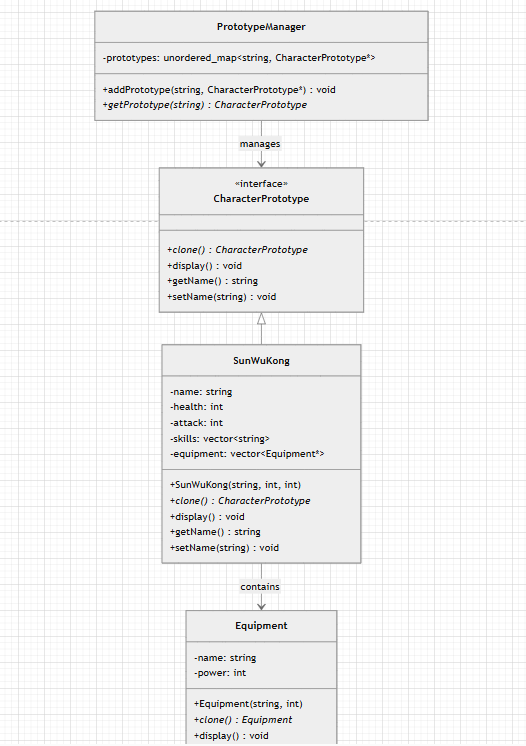
class CharacterPrototype
{
public:
virtual ~CharacterPrototype() {} = default;
virtual CharacterPrototype* clone() const = 0;
virtual void display() const = 0;
virtual std::string getName() const = 0;
virtual void setName(std::string name) = 0;
};- 具体原型类
cpp
class SunWuKong : public CharacterPrototype
{
private:
std::string name;
int health;
int attack;
std::vector<std::string> skills;
std::vector<Equipment*> equipment;
public:
SunWuKong(std::string name, int health, int attack)
: name(name), health(health), attack(attack)
{
// 初始化技能
skills.push_back("七十二变");
skills.push_back("筋斗云");
skills.push_back("火眼金睛");
skills.push_back("法天象地");
// 初始化装备
equipment.push_back(new Equipment("金箍棒", 1000));
equipment.push_back(new Equipment("锁子黄金甲", 500));
equipment.push_back(new Equipment("凤翅紫金冠", 300));
equipment.push_back(new Equipment("藕丝步云履", 200));
}
// 拷贝构造函数(采用深拷贝)
SunWuKong(const SunWuKong& other)
{
name = other.name;
health = other.health;
attack = other.attack;
skills = other.skills;
equipment.clear();
for(auto& eq : other.equipment){
equipment.push_back(eq->clone());
}
}
// 拷贝赋值运算符(采用深拷贝)
SunWuKong& operator=(const SunWuKong& other)
{
if (this != &other) {
name = other.name;
health = other.health;
attack = other.attack;
skills = other.skills;
equipment.clear();
for(auto& eq : other.equipment){
equipment.push_back(eq->clone());
}
}
}
// 克隆方法(核心)
CharacterPrototype* clone() const override
{
return new SunWuKong(*this); // 调用拷贝构造函数
}
void setName(std::string name) override
{
this->name = name;
}
std::string getName() const override
{
return name;
}
void display() const override
{
std::cout<<"name: "<< this->name <<" , "
<<"health: "<< this->health <<" , "
<<"attack: "<< this->attack <<" , "
<<"skills: \n";
for(const auto& skill : skills){
std::cout<< skill << " ";
}
std::cout<<"\n";
std::cout<<"equipment:\n";
for(const auto& eq : equipment){
eq->display();
}
}
~SunWuKong()
{
for (auto& eq : equipment) {
delete eq;
}
}
};- 原型管理器
cpp
class PrototypeManager {
private:
std::unordered_map<std::string, CharacterPrototype*> prototypes;
public:
~PrototypeManager() {
for (auto& pair : prototypes) {
delete pair.second;
}
}
void addPrototype(std::string key, CharacterPrototype* prototype) {
prototypes[key] = prototype;
}
CharacterPrototype* getPrototype(std::string key) {
if (prototypes.find(key) != prototypes.end()) {
return prototypes[key]->clone();
}
return nullptr;
}
};- 使用
cpp
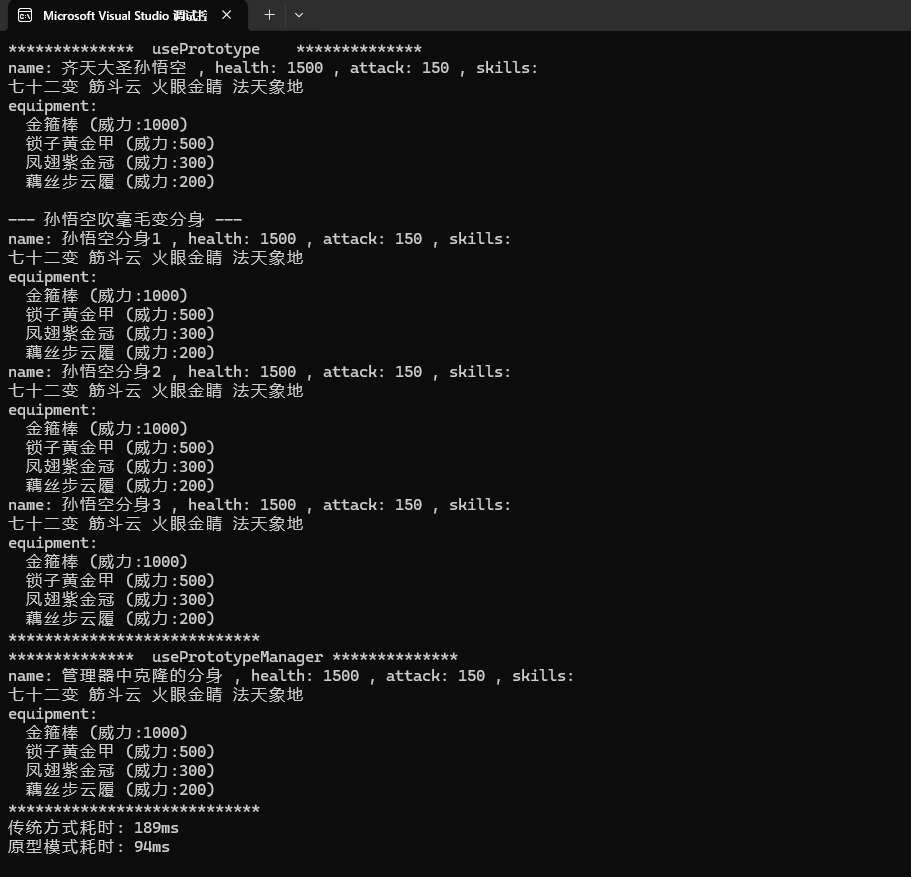
void usePrototype()
{
// 1. 创建原型
SunWukong* original = new SunWukong("齐天大圣孙悟空", 1500, 150);
original->display();
std::cout << "\n--- 孙悟空吹毫毛变分身 ---\n";
// 2. 创建多个分身
std::vector<CharacterPrototype*> clones;
for (int i = 1; i <= 30; i++) {
// 使用克隆方法创建分身
CharacterPrototype* clone = original->clone();
clone->setName("孙悟空分身" + to_string(i));
clones.push_back(clone);
}
// 3. 分身展示
for (auto& clone : clones) {
clone->display();
}
// 4. 清理内存
for (auto& clone : clones) {
delete clone;
}
delete original;
}
void usePrototypeManager()
{
PrototypeManager manager;
manager.addPrototype("孙悟空", new SunWuKong("齐天大圣孙悟空", 1500, 150));
// 从管理器获取原型并克隆
auto cloneFromManager = manager.getPrototype("sunwukong");
if (cloneFromManager) {
cloneFromManager->setName("管理器中克隆的分身");
cloneFromManager->display();
delete cloneFromManager;
}
}
void comparison() {
auto start1 = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
// 传统方式创建10000个分身
std::vector<SunWuKong*> clones1;
SunWuKong* original = new SunWuKong("齐天大圣", 1000, 100);
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
clones1.push_back(new SunWuKong("分身", 1000, 100));
}
auto end1 = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto start2 = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
// 原型模式创建10000个分身
std::vector<CharacterPrototype*> clones2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
clones2.push_back(original->clone());
}
auto end2 = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
std::cout << "传统方式耗时: "
<< std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end1 - start1).count()
<< "ms\n";
std::cout << "原型模式耗时: "
<< std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end2 - start2).count()
<< "ms\n";
}
附上UML图:
二、总结
2.1、与传统方式进行对比
| 特点 | 传统创建方式 | 原型模式 |
|---|---|---|
| 性能 | 低,每次都要执行完整初始化 | 高,一次初始化,多次复制 |
| 内存 | 每个对象独立内存 | 可共享不变部分 |
| 代码复杂度 | 低 | 高,需要实现clone |
| 灵活性 | 低 | 高,可动态修改原型 |
| 适用场景 | 对象创建简单 | 对象创建复杂,批量创建 |
2.2、深拷贝 VS 浅拷贝
- 浅拷贝:亦可称为值拷贝。将源对象的值拷贝到目标对象中,如果对象中某个成员是指针类型数据,并且是在堆上创建的,那么源对象和目标对象都指向同一块内存区域,此时如果其中一个对象释放了内存,那么另一个对象的指针就会变成野指针。
- 深拷贝:在拷贝的时候,先开辟出与源对象大小一样的空间,然后将源对象的内容拷贝到新开辟的空间中。这样无论哪个对象释放内存,都不会影响另一个对象的正常使用。
2.3、原型模式 VS 工厂模式
- 原型模式:通过克隆原型对象来创建新的对象,适用于创建复杂对象,特别是当对象的创建过程较为耗时或复杂时。
- 工厂模式:通过工厂方法来创建对象,适用于创建不同类型的对象,特别是当对象的创建逻辑较为复杂时。
三、附加
由于C++语法的灵活性,原型模式实现可以有多种方式
1. 结合智能指针版--原型模式
cpp
// 使用智能指针和移动语义
class SunWuKong1 : public CharacterPrototype
{
private:
string name;
int health;
int attack;
vector<string> skills;
vector<unique_ptr<Equipment>> equipment; // 使用unique_ptr
public:
SunWuKong1(string name, int health, int attack)
: name(name), health(health), attack(attack)
{
// 初始化技能
skills.push_back("七十二变");
skills.push_back("筋斗云");
skills.push_back("火眼金睛");
skills.push_back("法天象地");
// 初始化装备
equipment.push_back(new Equipment("金箍棒", 1000));
equipment.push_back(new Equipment("锁子黄金甲", 500));
equipment.push_back(new Equipment("凤翅紫金冠", 300));
equipment.push_back(new Equipment("藕丝步云履", 200));
}
// 使用移动构造函数提高效率
SunWuKong1(SunWuKong1&& other) noexcept
: name(move(other.name)), health(other.health), attack(other.attack),
skills(move(other.skills)), equipment(move(other.equipment))
{}
CharacterPrototype* clone() const override
{
// 先创建一个副本
auto clone = make_unique<SunWuKong1>(name, health, attack);
// 深拷贝equipment
for (const auto& eq : equipment) {
clone->equipment.push_back(make_unique<Equipment>(*eq));
}
return clone.release();
}
};2. 结合函数模板,通过注册的方式--原型模式
cpp
class PrototypeRegistry {
private:
static unordered_map<string, function<unique_ptr<CharacterPrototype>()>> registry;
public:
static void registerPrototype(const string& key,
function<unique_ptr<CharacterPrototype>()> creator)
{
registry[key] = move(creator);
}
static unique_ptr<CharacterPrototype> clone(const string& key)
{
if (auto it = registry.find(key); it != registry.end()) {
return it->second();
}
return nullptr;
}
};