Qt6 在 QFutureInterface 基础上进一步封装出了 QPromise 类,搭配 QFuture 使用,逻辑类似 std::promise + std::future,线程内使用 promise 设置进度和结果,外部通过关联的 future 判断状态和获取结果。
cpp
#include <future>
std::promise<T> p;
// 获取与 promise 关联的 future
std::future<T> f = p.get_future();
// 线程 A 中设置值
p.set_value(value);
// 线程 B 中阻塞获取 promise 设置的值
T result = f.get();使用 QFuture 的优势在于,搭配 QFutureWatcher 使用时可以获取 started / finished 等相关信号,这是 QFutureInterface 内部生成的事件被 QFutureWatcher 接收后发出的。
当需要后台执行任务时,界面上一般会有相应的进度提示,借助 QPromise / QFuture 相关接口可以很容易的实现这个功能。在此基础上做一点小小的封装,就得到了一个简易的任务管理类。
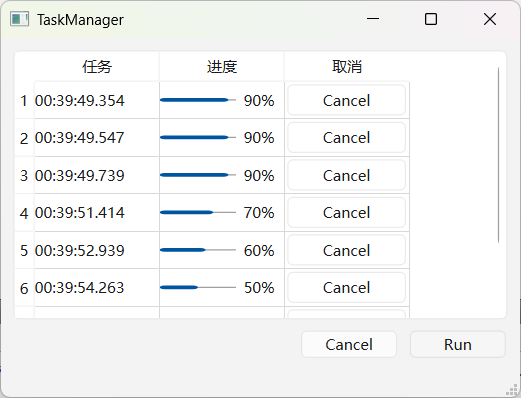
封装时一个麻烦的地方是,QFutureWatcher 需要在关联 QFuture 之前关联信号槽,这样我们的 run / start 开始任务接口就需要把所有的槽和槽接收者作为参数。不过这样写起来有点麻烦,就干脆拆成了两部分,先生成 QFutureWatcher,关联好信号槽后再开始任务。
另一个问题是 QPromise / QFuture 的模板类型参数我使用了 QObject*(懒得自定义基类),主要还是考虑到后续进行 QML 版封装用模板不方便,子类化任务返回类型实现起来更顺手一点。
后续扩展:如果要在 QML 中使用,任务接口和返回的 future 对象就需要封装。
TaskManager 实现代码:
cpp
#pragma once
#include <QThreadPool>
#include <QFuture>
#include <QFutureWatcher>
#include <QPromise>
#include <functional>
#include <list>
// 任务管理
class TaskManager : public QObject
{
Q_OBJECT
Q_DISABLE_COPY_MOVE(TaskManager)
private:
explicit TaskManager(QObject *parent = nullptr);
public:
~TaskManager();
static TaskManager *instance();
// 任务结果暂时为QObject*,可以用一个自定义基类,包含type判断类型
using TPromise = QPromise<QObject*>;
using TWatcher = QFutureWatcher<QObject*>;
// 创建任务future watcher
// 如果将槽函数作为run参数传入,代码有点乱,拆分为两步,先创建watcher关联信号槽,再run任务
auto create() -> std::shared_ptr<TWatcher>;
// 执行任务,繁忙时任务排队
void run(const std::function<void (TPromise &)> &task, std::shared_ptr<TWatcher> watcher);
// 判断是否繁忙
bool busy() const;
// 取消所有任务
void cancel();
// 等待全部任务结束
void wait();
signals:
void taskStarted();
void taskFinished();
private:
// 任务线程池
QThreadPool taskPool;
// 内部管理任务列表
std::list<std::shared_ptr<TWatcher>> taskList;
// 任务列表锁
std::mutex listMutex;
};
TaskManager::TaskManager(QObject *parent)
: QObject{parent}
{
// 线程池最大线程数
taskPool.setMaxThreadCount(QThread::idealThreadCount());
// 线程空闲时,销毁判定时间,单位ms,默认半分钟
taskPool.setExpiryTimeout(1000 * 60);
}
TaskManager::~TaskManager()
{
cancel();
wait();
}
TaskManager *TaskManager::instance()
{
static TaskManager manager;
return &manager;
}
auto TaskManager::create() -> std::shared_ptr<TWatcher>
{
return std::make_shared<TWatcher>();
}
void TaskManager::run(const std::function<void (TPromise &)> &task, std::shared_ptr<TWatcher> watcher)
{
if (!task || !watcher)
return;
TPromise promise{};
auto future = promise.future();
watcher->setFuture(future);
{
// 添加到任务列表
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> guard(listMutex); Q_UNUSED(guard)
taskList.push_back(watcher);
// qDebug() << "push task";
}
// 丢进线程池泡澡
taskPool.start([this, task, watcher, promise = std::move(promise)]() mutable {
promise.start();
task(promise);
promise.finish();
{
// 任务结束从列表移除
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> guard(listMutex); Q_UNUSED(guard)
taskList.remove(watcher);
// qDebug() << "remove task";
}
});
}
bool TaskManager::busy() const
{
// 活跃线程数达到上限
return (taskPool.activeThreadCount() >= taskPool.maxThreadCount());
}
void TaskManager::cancel()
{
// 移除未启动的任务
taskPool.clear();
// 取消所有任务
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> guard(listMutex); Q_UNUSED(guard)
for (auto &handle : taskList) {
handle->cancel();
}
}
void TaskManager::wait()
{
// 等待最后一个线程开始
taskPool.waitForDone(-1);
}测试代码:
cpp
void MainWindow::onRun()
{
// 先创建future watcher关联信号槽
auto pwatcher = TaskManager::instance()->create();
auto watcher = pwatcher.get();
// 列表更新
auto table = ui->tableWidget;
int row = table->rowCount();
table->insertRow(row);
QString time = QTime::currentTime().toString("hh:mm:ss.zzz");
auto title = new QLabel(time);
table->setCellWidget(row, 0, title);
auto bar = new QProgressBar();
table->setCellWidget(row, 1, bar);
auto btn = new QPushButton("Cancel");
table->setCellWidget(row, 2, btn);
connect(btn, &QPushButton::clicked, [pwatcher]{ pwatcher->cancel(); });
// 测试对象释放
connect(btn, &QPushButton::destroyed, this, [time]{ qDebug() << "free" << time; });
// 状态更新
connect(watcher, &TaskManager::TWatcher::progressTextChanged,
this, [](const QString &text){
// qDebug() << "progress text changed" << text;
});
connect(watcher, &TaskManager::TWatcher::progressRangeChanged,
this, [this, bar](int min, int max){
// qDebug() << "progress range changed" << min << max;
bar->setRange(min, max);
bar->setValue(min);
});
connect(watcher, &TaskManager::TWatcher::progressValueChanged,
this, [this, bar](int value){
// qDebug() << "progress changed" << value;
bar->setValue(value);
});
connect(watcher, &TaskManager::TWatcher::started,
this, [time](){
qDebug() << "started" << time;
});
connect(watcher, &TaskManager::TWatcher::finished,
this, [this, table, time, btn, pwatcher](){
qDebug() << "finished" << time;
int index = -1;
for (int row = 0; row < table->rowCount(); ++row) {
QPushButton *item = static_cast<QPushButton *>(table->cellWidget(row, 2));
if (item && item == btn) {
index = row;
break;
}
}
if (index < 0) return;
ui->tableWidget->removeRow(index);
});
connect(watcher, &TaskManager::TWatcher::canceled,
this, [this, time](){
qDebug() << "canceled" << time;
});
connect(watcher, &TaskManager::TWatcher::resultReadyAt,
this, [this, time, pwatcher](int index){
qDebug() << "result" << time << index << pwatcher->resultAt(index);
});
// 执行任务,并通过关联的future watcher更新ui
auto task = [](TaskManager::TPromise &promise){
promise.setProgressRange(0, 10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10 && !promise.isCanceled(); ++i)
{
promise.setProgressValue(i);
QThread::sleep(1);
}
if (promise.isCanceled())
return;
promise.setProgressValue(10);
promise.addResult(nullptr);
};
TaskManager::instance()->run(task, pwatcher);
}
void MainWindow::onCancel()
{
TaskManager::instance()->cancel();
}完整代码:https://github.com/gongjianbo/MyTestCode/tree/master/Qt6/TestQt_20251220_Future