安卓在开机后,会加载一个开机动画,本文将介绍开机动画是如何被加载的
| 安卓版本 | API版本 |
|---|---|
| Android 8.1 | API 27 |
Init 初始化
众所周知,一个软件总归是有一个入口的,基于AOSP的架构,Android系统的启动入口一定也是Linux系统的启动入口。在 Linux 内核加载完成后,会启动用户空间的第一个进程 ------ init 进程(PID 为 1),该进程的启动位置为 system/core/init/init.cpp中的main方法。
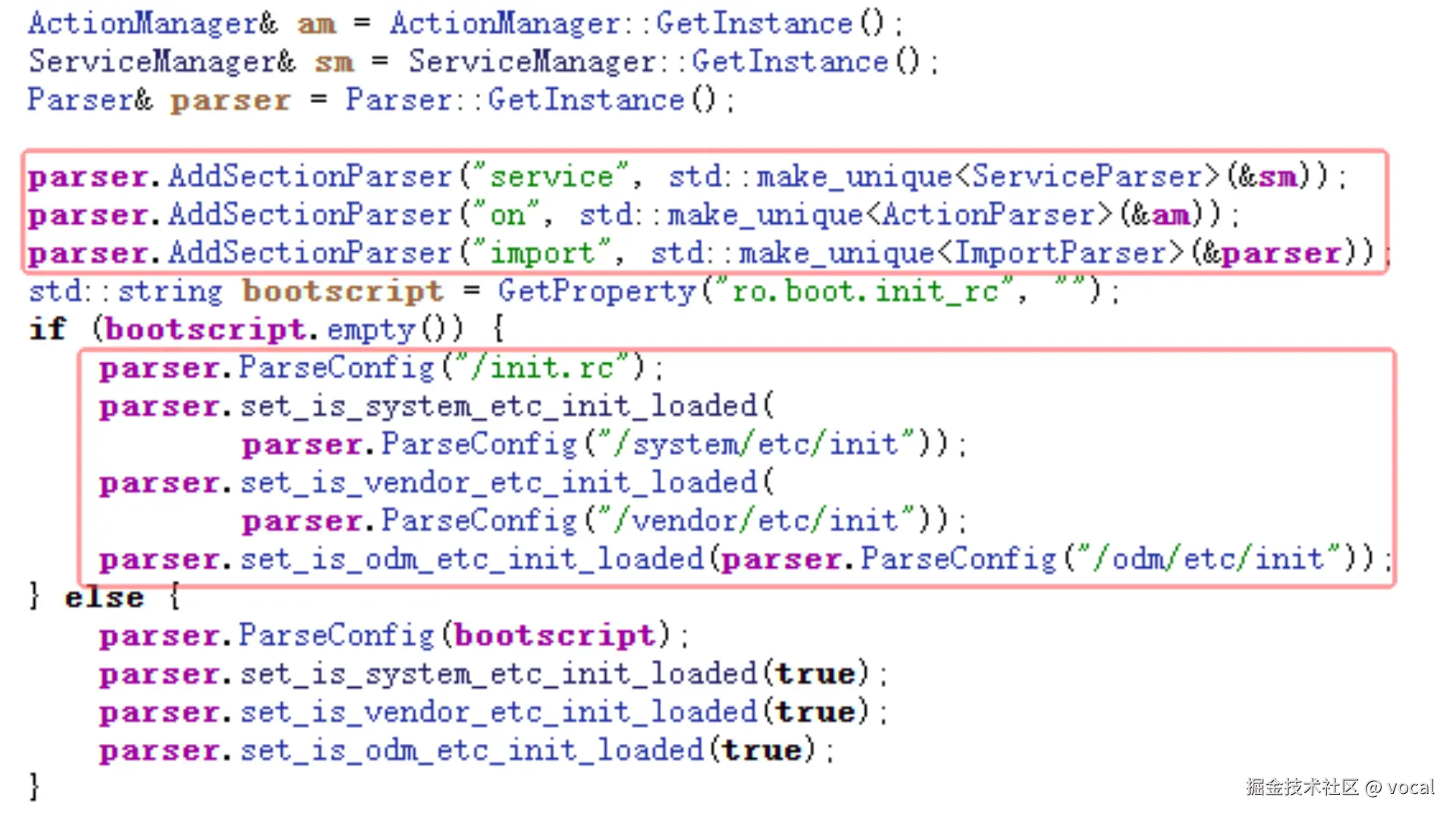 在上一文中,我们认识了
在上一文中,我们认识了rc文件的主要构成,图中可以看到,main函数创建了Service、Action以及Import的解析器,并加载了init.rc、system/ect/init/*、vendor/ect/init/*、odm/etc/init/*下的 rc文件。
如果解析到Action会将其加入ActionManager,解析到Service会将其加入ServiceManager。
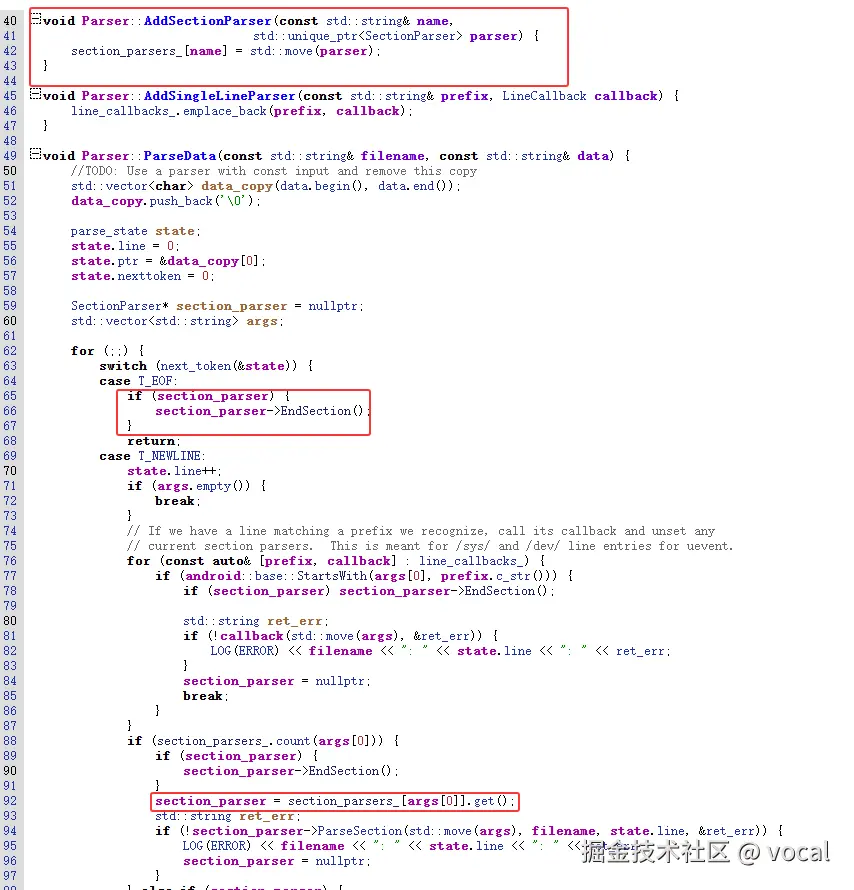
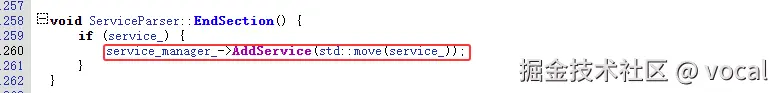
其中,init.rc的位置:
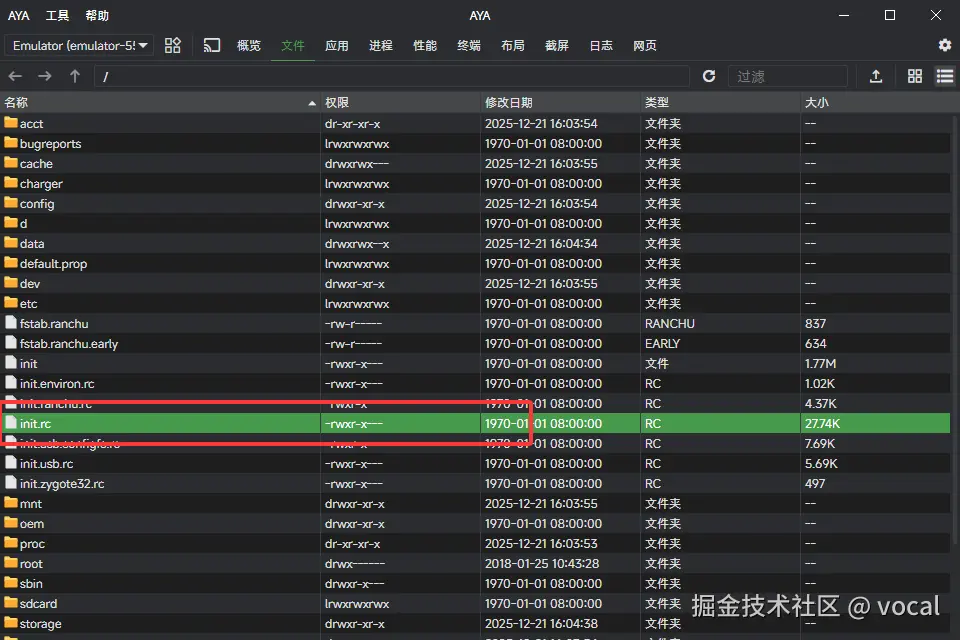
其中,和开机动画有关的rc文件就位于system/ect/init/下
rc
service bootanim /system/bin/bootanimation
class core animation
user graphics
group graphics audio
disabled
oneshot
writepid /dev/stune/top-app/tasks根据上一文的内容,我们可以这样描述该文件:
| 指令 | 说明 |
|---|---|
service bootanim /system/bin/bootanimation |
定义bootanim服务,对应程序为/system/bin/bootanimation |
class core animation |
该服务归类为 core 和 animation 两个类。当系统启动这些类时,会尝试启动该服务 |
user graphics |
指定运行该服务的用户为graphics,该用户拥有访问图形缓冲区的权限 |
group graphics audio |
指定运行该服务的用户组。除了图形权限,还赋予了 audio 权限 |
disabled |
非常关键 。表示该服务不会在类启动时自动运行。它必须由其他进程手动启动 |
oneshot |
表示该服务只运行一次 |
writepid /dev/stune/top-app/tasks |
将该进程的 PID 写入文件/dev/stune/top-app/tasks |
所以说,此时开机动画相关的服务已经定义好了,但处于禁用状态,需要重新启用 ;根据前文的内容,我们已经了解到了两种启用方式enable (解除禁用,但不一定立即执行,除非该服务的class已经执行完毕)与start (启动服务)。不过除了用rc文件的方式再启用,还有一种使用系统属性的方式ctl.start bootanim,可以在代码中的ServiceManager中看到。
cpp
// The length of a service name should not exceed SERVICE_NAME_MAX. Starting
// a service is done by writing its name to the "ctl.start" system property
// and stopping a service is done by writing its name to "ctl.stop". If a
// service name is too long to fit in a property, you won't be able to start
// or stop it.propertyService 初始化
在安卓中,system property 的修改也是靠对应的服务来完成的;比如,在解析rc文件前,可以看到 start_property_service();。
cpp
void start_property_service() {
property_set("ro.property_service.version", "2");
property_set_fd = CreateSocket(PROP_SERVICE_NAME, SOCK_STREAM | SOCK_CLOEXEC | SOCK_NONBLOCK,
false, 0666, 0, 0, nullptr, sehandle);
if (property_set_fd == -1) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "start_property_service socket creation failed";
exit(1);
}
listen(property_set_fd, 8);
register_epoll_handler(property_set_fd, handle_property_set_fd);
}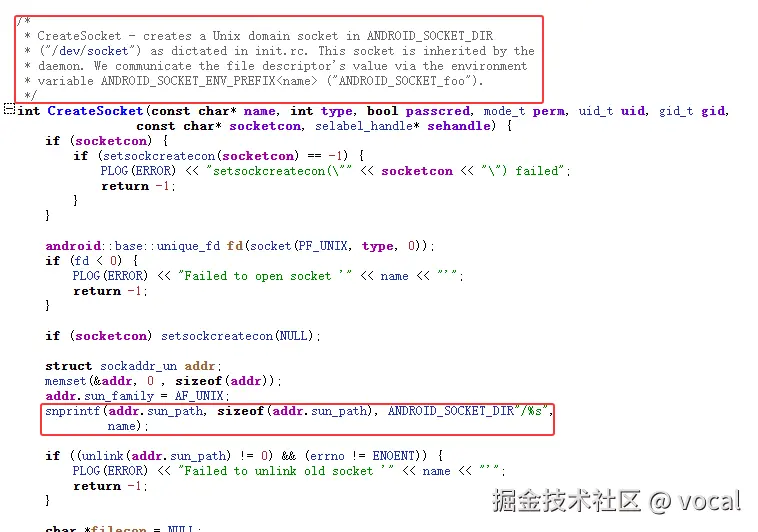
在这段代码中,我们创建了一个Unix Domain Socket,以供外部进程使用,其监听/dev/socket/property_service,其使用handle_property_set_fd处理请求
cpp
static void handle_property_set_fd() {
static constexpr uint32_t kDefaultSocketTimeout = 2000; /* ms */
int s = accept4(property_set_fd, nullptr, nullptr, SOCK_CLOEXEC);
if (s == -1) {
return;
}
struct ucred cr;
socklen_t cr_size = sizeof(cr);
if (getsockopt(s, SOL_SOCKET, SO_PEERCRED, &cr, &cr_size) < 0) {
close(s);
PLOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop: unable to get SO_PEERCRED";
return;
}
SocketConnection socket(s, cr);
uint32_t timeout_ms = kDefaultSocketTimeout;
uint32_t cmd = 0;
if (!socket.RecvUint32(&cmd, &timeout_ms)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop: error while reading command from the socket";
socket.SendUint32(PROP_ERROR_READ_CMD);
return;
}
switch (cmd) {
case PROP_MSG_SETPROP: {
char prop_name[PROP_NAME_MAX];
char prop_value[PROP_VALUE_MAX];
if (!socket.RecvChars(prop_name, PROP_NAME_MAX, &timeout_ms) ||
!socket.RecvChars(prop_value, PROP_VALUE_MAX, &timeout_ms)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop(PROP_MSG_SETPROP): error while reading name/value from the socket";
return;
}
prop_name[PROP_NAME_MAX-1] = 0;
prop_value[PROP_VALUE_MAX-1] = 0;
handle_property_set(socket, prop_value, prop_value, true);
break;
}
case PROP_MSG_SETPROP2: {
std::string name;
std::string value;
if (!socket.RecvString(&name, &timeout_ms) ||
!socket.RecvString(&value, &timeout_ms)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop(PROP_MSG_SETPROP2): error while reading name/value from the socket";
socket.SendUint32(PROP_ERROR_READ_DATA);
return;
}
handle_property_set(socket, name, value, false);
break;
}
default:
LOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop: invalid command " << cmd;
socket.SendUint32(PROP_ERROR_INVALID_CMD);
break;
}
}最终真正执行处理的是下面的函数
cpp
static void handle_property_set(SocketConnection& socket,
const std::string& name,
const std::string& value,
bool legacy_protocol) {
const char* cmd_name = legacy_protocol ? "PROP_MSG_SETPROP" : "PROP_MSG_SETPROP2";
if (!is_legal_property_name(name)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop(" << cmd_name << "): illegal property name "" << name << """;
socket.SendUint32(PROP_ERROR_INVALID_NAME);
return;
}
struct ucred cr = socket.cred();
char* source_ctx = nullptr;
getpeercon(socket.socket(), &source_ctx);
if (android::base::StartsWith(name, "ctl.")) {
if (check_control_mac_perms(value.c_str(), source_ctx, &cr)) {
handle_control_message(name.c_str() + 4, value.c_str());
if (!legacy_protocol) {
socket.SendUint32(PROP_SUCCESS);
}
} else {
LOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop(" << cmd_name << "): Unable to " << (name.c_str() + 4)
<< " service ctl [" << value << "]"
<< " uid:" << cr.uid
<< " gid:" << cr.gid
<< " pid:" << cr.pid;
if (!legacy_protocol) {
socket.SendUint32(PROP_ERROR_HANDLE_CONTROL_MESSAGE);
}
}
} else {
if (check_mac_perms(name, source_ctx, &cr)) {
uint32_t result = property_set(name, value);
if (!legacy_protocol) {
socket.SendUint32(result);
}
} else {
LOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop(" << cmd_name << "): permission denied uid:" << cr.uid << " name:" << name;
if (!legacy_protocol) {
socket.SendUint32(PROP_ERROR_PERMISSION_DENIED);
}
}
}
freecon(source_ctx);
}该方法中,主要的逻辑如红框下所示: 
最终,会去根据name (name为service的名称,比如 bootanim),从ServiceManager 中查找对应的Service,根据 ctl.后的内容执行 start,stop或restart。
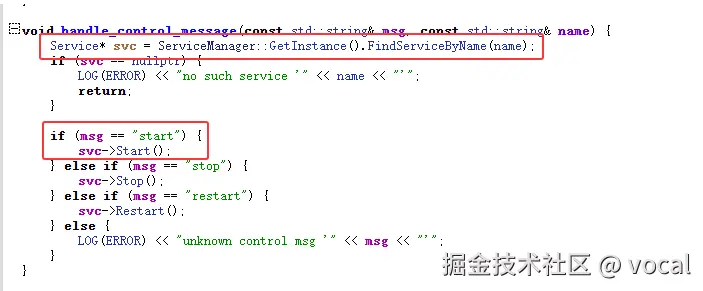
至此,/system/bin/bootanimation 正式开始执行。我们也可以使用setprop ctl.start bootanim,直接查看效果。
property_set
根据前面的介绍,我们得知,想要执行开机动画,一定有一个地方设置了系统属性 ctl.start bootanim。所以我们现在需要在 propertyService 里找到用于设置系统属性的方法,不过观察 init.cpp 中的 main 已经可以发现对应的方法了
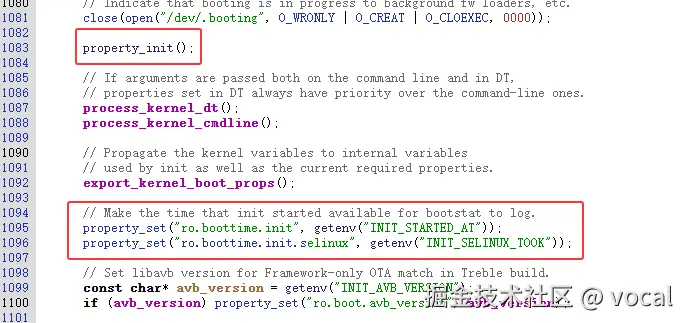
搜索一下property_set("ctl.start", "bootanim"),发现在存在于frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/StartPropertySetThread.cpp
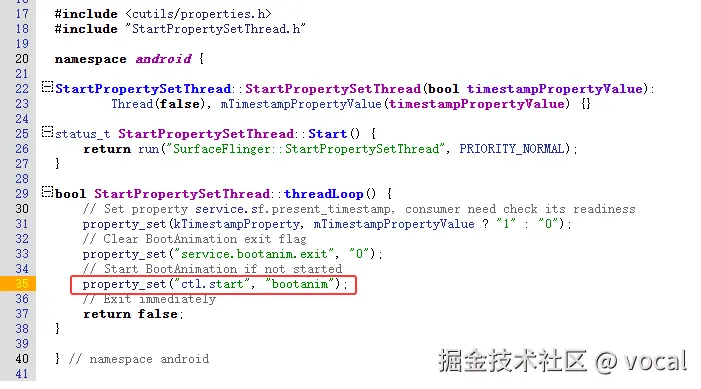
所以说,很明显,surfaceflinger启动后,此时系统具备了图像渲染能力,随后由surfaceflinger修改系统属性,来触发bootanim的启动