9. Redis 客户端
前面文字中 redis 的操作都是在 redis 命令行客户端,手动进行的
日常开发中,则是基于 redis 的 api 实现定制化的 redis 客户端程序,来操作redis ,即在代码中操作 redis。(redis 提供的 命令行客户端 / 第三方的图形化客户端,本质上都是 "通用的客户程序)
9.1 RESP 协议
RESP协议 是 redis 的应用层协议,全称 Redis serialization protocol
优点:
- 简单好实现
- 快速解析
- 肉眼可读
请求和响应之间的通信模型是一问一答的形式
客户端给服务器发送的是 redis 命令,(bulk string 数组形式发送)
服务器根据命令返回不同的结果,有的返回 ok,有的返一个整数或数组,且通过第一字节告诉客户端怎么解析。

simple string 只能用来传输文本,bulk string 可以传输二进制数据
后文,就要使用代码操作 redis 了,redis 支持 50+ 种语言,几乎包含了所有的常用语言,后面以 Java 进行
10. Redis 在 Java 中的使用
10.1 引入依赖
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
<version>4.3.2</version>
</dependency>10.2 配置端口转发
由于 redis 是部署在 云服务器 上的,没办法之间访问,若是开发 redis 的 6379 端口,则很有可能被黑客攻击,造成损失。
解决办法:配置 ssh 端口转发,将服务器上的 redis 端口映射到本地。
ssh 是一个程序,默认走 22 端口,功能强大,端口转发就是它的一项功能,即通过 ssh 的 22 端口,来传递其他端口的数据。
ssh 会监听本地映射的端口,将本地端口数据发送到服务器端口,服务器上的数据发送到本地。
右击图标,选择属性
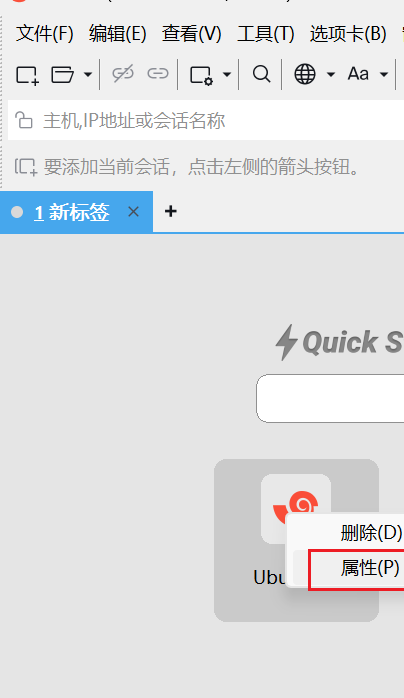
点击 ssh 下的隧道,添加新隧道
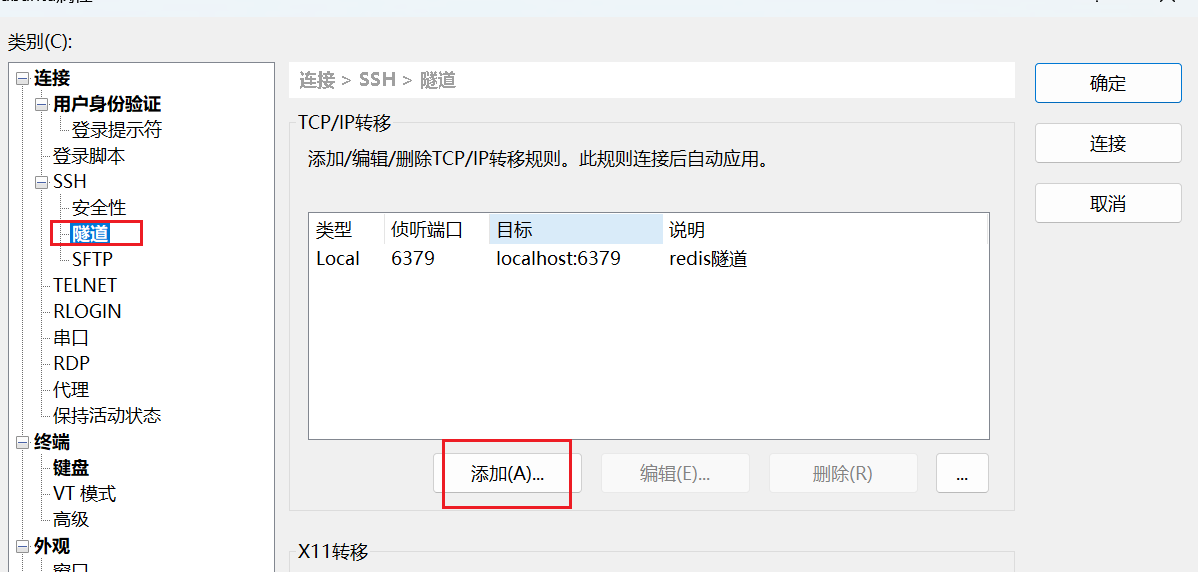
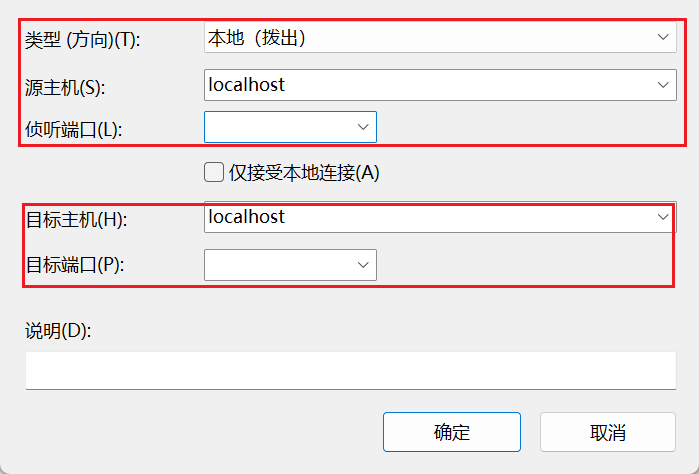
上面的端口填要映射到的本地端口,下边填服务器上 redis 的端口
除此之外,最开始按照 redis 时要配置绑定的 ip 并关闭保护模式。
默认绑定 ip 是 127.0.0.1 只能本机访问,跨机无法访问。
保护模式默认是 yes,即开启保护模式,此时跨主机也无法访问。
具体配置,见之前的文章。
10.3 部分基本操作
java
package com.example.demo;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool;
import redis.clients.jedis.params.SetParams;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class RedisDemo {
public static void test1(Jedis jedis) {
System.out.println("get, set 使用");
jedis.flushDB();
jedis.set("key1","111");
jedis.set("key2","222");
SetParams setParams = new SetParams();
setParams.ex(10);
setParams.xx();
jedis.set("key1","333",setParams);
System.out.println(jedis.get("key1"));
System.out.println(jedis.get("key2"));
}
public static void test2(Jedis jedis) {
System.out.println("exist, del 使用");
jedis.flushDB();
jedis.set("key1","111");
jedis.set("key2","222");
boolean key1 = jedis.exists("key1");
System.out.println(key1);
long del = jedis.del("key1", "key2");
System.out.println(del);
long exists = jedis.exists("key1", "key2");
System.out.println(exists);
}
public static void test3(Jedis jedis) {
System.out.println("keys 使用");
jedis.flushDB();
jedis.set("key1","111");
jedis.set("key2","222");
Set<String> keys = jedis.keys("*");
System.out.println(keys);
}
public static void test4(Jedis jedis) {
System.out.println("expire, ttl 使用");
jedis.flushDB();
jedis.set("key1","111");
jedis.expire("key1",10);
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
long ttl = jedis.ttl("key1");
System.out.println(ttl);
}
public static void test5(Jedis jedis) {
System.out.println("type 使用");
jedis.flushDB();
jedis.set("key1","111");
jedis.hset("key2", "field", "123");
jedis.lpush("key3", "123456");
jedis.sadd("key4","12346","123");
jedis.zadd("key5",99.9,"789");
Set<String> keys = jedis.keys("*");
Iterator<String> iterator = keys.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
String next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(next);
System.out.println(jedis.type(next));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
JedisPool jedisPool = new JedisPool("tcp://127.0.0.1:6379");
try (Jedis jedis = jedisPool.getResource()){
// System.out.println(jedis.ping());
// test1(jedis);
// test2(jedis);
// test3(jedis);
// test4(jedis);
test5(jedis);
}
}
}操作很简单,和 redis 命令行时的命令基本一致,无非是多加了一个 jedis,这里不再赘述其他的命令。
11. Redis 在 Spring Boot 中的使用
11.1 引入依赖
创建项目时,在 NoSQL 下选择 Spring Data Redis 加入。
或在 pom 文件中添加:
xm
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>11.2 配置文件配置
yml
spring:
data:
redis:
port: 6379
host: localhost因为在 10.2 小节中,我们已经进行了端口配置,这里就填 本机 IP 和 映射到本地的端口
11.3 部分基本操作
Spring 中 string,hash,list,set,zset 的命令都封装到了 opsForXXX 下。如果想用原命令则在 execute 下
Spring 中通过 RedisTemplate 接口操作 Redis,下面的 StringRedisTemplate 是针对 文本内容的接口实现
java
package com.example.demo.springredis.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnection;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RequestMapping("/redis")
@RestController
public class RedisController {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@RequestMapping("/string")
public String set() {
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("key1","1");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("key2","2");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("key3","3");
String key1 = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("key1");
System.out.println(key1);
return "OK";
}
@RequestMapping("/list")
public String testList() {
stringRedisTemplate.execute((RedisConnection connection) ->{
connection.flushAll();
return null;
});
stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush("key1","111");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush("key1","222");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush("key1","333");
System.out.println(stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().range("key1", 0, -1));
System.out.println(stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().rightPop("key1"));
System.out.println(stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().rightPop("key1"));
System.out.println(stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().rightPop("key1"));
return null;
}
@RequestMapping("/set")
public String testSet() {
stringRedisTemplate.execute((RedisConnection connection) ->{
connection.flushAll();
return null;
});
stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().add("key1","111","222","333");
System.out.println(stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().members("key1"));
System.out.println(stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().isMember("key1","111"));
System.out.println(stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().size("key1"));
stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().remove("key1","111");
System.out.println(stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().members("key1"));
return null;
}
@RequestMapping("/hash")
public String testHash() {
stringRedisTemplate.execute((RedisConnection connection) ->{
connection.flushAll();
return null;
});
stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().put("key1","111","1");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().put("key1","222","2");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().put("key1","333","3");
System.out.println(stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().entries("key1"));
System.out.println(stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().hasKey("key1","111"));
System.out.println(stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().size("key1"));
System.out.println((String) stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().get("key1", "111"));
return null;
}
@RequestMapping("/zset")
public String testZset() {
stringRedisTemplate.execute((RedisConnection connection) ->{
connection.flushAll();
return null;
});
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().add("key1","111",1);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().add("key1","222",2);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().add("key1","333",3);
System.out.println(stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().rangeWithScores("key1", 0, -1));
System.out.println(stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().score("key1","111"));
System.out.println(stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().size("key1"));
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().remove("key1","111");
System.out.println(stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().rangeWithScores("key1", 0, -1));
return null;
}
}