背景:
最近项目用到了一种看着比较奇怪的写法,起初感觉非常不解,通过在网上学习后,逐渐理解了这些,将这块的实战跟各位同学做个分享。
上图:
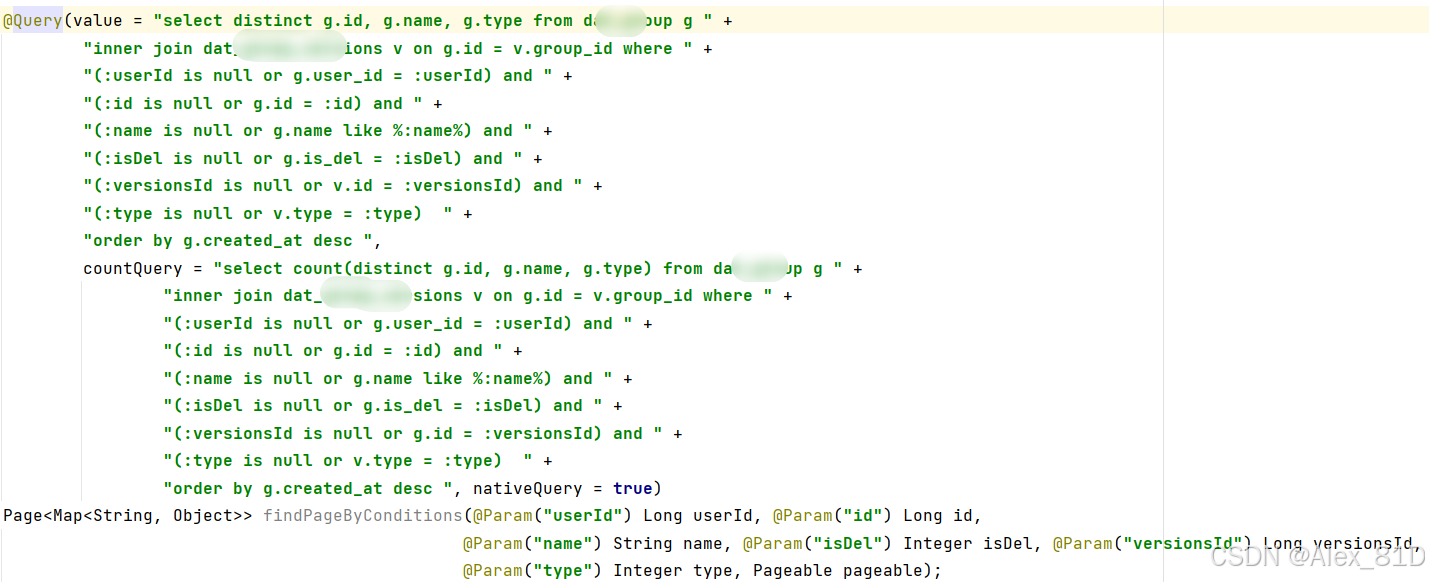
接下来,我们就揭开这个神秘的面纱。
一、Spring Data JPA概述
Spring Data JPA 是 Spring Data 家族的一部分,旨在简化数据访问层(DAO)的开发。它基于 JPA(Java Persistence API) 规范,并通过提供 Repository 抽象,大幅减少样板代码。
- 底层实现通常使用 Hibernate。
- 支持声明式查询(方法名推导)、JPQL、原生 SQL。
- 提供分页、排序、审计、事务等开箱即用的功能
1.实战Demo
1.1添加依赖(Maven)
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Boot Starter Data JPA -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 数据库驱动(以 MySQL 为例) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>1.2 配置数据库(application.yml)
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/testdb?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: root
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: update # 自动建表策略:create, create-drop, update, validate, none
show-sql: true
properties:
hibernate:
format_sql: true1.3.实体类
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "users")
@Data
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false, unique = true)
private String email;
@Column(name = "full_name")
private String fullName;
}1.4.Repository 接口
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
}JpaRepository<T, ID> 提供了丰富的 CRUD 和分页方法。
或者这么写:
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaSpecificationExecutor;
import org.springframework.data.repository.NoRepositoryBean;
@NoRepositoryBean
public interface BaseRepository<T> extends JpaRepository<T, Long>, JpaSpecificationExecutor<T> {
default T getById(Long id) {
//立即查询,而不是返回代理
return findById(id).orElse(null);
}
}
@Repository
public interface UserRepository extends BaseRepository<User> {
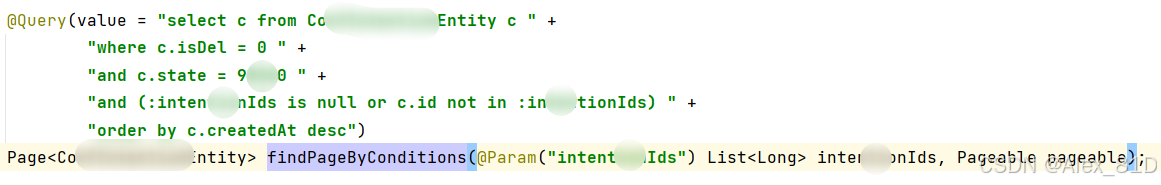
@Query(value = "select c from test c " +
"where c.isDel = 0 " +
"and c.state = 98360 " +
"and (:colis null or c.id not in :col) " +
"order by c.createdAt desc")
Page<User> findPageByConditions(@Param("col") List<Long> intentionIds, Pageable pageable);
}2. 基本用法
2.1 常用方法(继承自 JpaRepository)
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
save(T entity) |
保存或更新实体 |
findById(ID id) |
根据主键查找 |
findAll() |
查询所有 |
deleteById(ID id) |
删除 |
count() |
统计总数 |
existsById(ID id) |
判断是否存在 |
2.2 分页与排序
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(0, 10, Sort.by("email").ascending());
Page<User> users = userRepository.findAll(pageable);二、JPQL
1.方法命名查询(Query Derivation)
Spring Data JPA 支持通过 方法名自动解析查询逻辑。
1.1命名规则
格式:find[Distinct]...By[PropertyExpression][And|Or][PropertyExpression]...
findFirstByServerNameAndIsDel(...)| 关键词 | 含义 |
|---|---|
findBy |
查询条件(必须以 find 开头) |
first |
只返回第一条记录(类似 LIMIT 1) |
By |
分隔符,后面接字段名 |
And |
多个条件连接(AND) |
| 字段名 | 实体类中的属性名(如 serverName, isDel) |
比如:
// 根据 email 查找
User findByEmail(String email);
// 根据 email 或 fullName 查找(模糊)
List<User> findByEmailContainingOrFullNameContaining(String email, String name);
// 大于某个创建时间
List<User> findByCreatedAtAfter(LocalDateTime time);
// 分页 + 排序
Page<User> findByFullNameStartingWith(String prefix, Pageable pageable);1.2 支持的关键字
| 关键字 | 示例 | 对应 JPQL |
|---|---|---|
And / Or |
findByAgeAndName |
where x.age = ?1 and x.name = ?2 |
Between |
findByAgeBetween |
where x.age between ?1 and ?2 |
LessThan / GreaterThan |
findByAgeLessThan |
where x.age < ?1 |
Like / Containing |
findByNameContaining |
where x.name like %?1% |
IsNull / IsNotNull |
findByEmailIsNull |
where x.email is null |
OrderBy |
findByAgeOrderByCreateTimeDesc |
order by x.createTime desc |
https://docs.spring.io/spring-data/jpa/docs/current/reference/html/#jpa.query-methods.query-creation
放个官方的文档,可以查看学习一下
写一个关于findByServerName的一系列方法
| 方法名 | 对应 SQL |
|---|---|
findByServerName(String name) |
WHERE server_name = ? |
findByServerNameAndIsDel(String name, Integer isDel) |
WHERE server_name = ? AND is_del = ? |
findFirstByServerName(String name) |
SELECT ... WHERE server_name = ? ORDER BY id LIMIT 1 |
findByServerNameLike(String name) |
WHERE server_name LIKE ? (%name%) |
findByServerNameContaining(String name) |
WHERE server_name LIKE %?% |
findByServerNameIgnoreCase(String name) |
WHERE UPPER(server_name) = UPPER(?) |
findByServerNameIn(List<String> names) |
WHERE server_name IN (?, ?, ...) |
Spring Data JPA 通过"方法名命名规则"自动帮你生成 SQL,所以你不需要写 SQL 也能查数据!这是一种强大的约定式编程方式。
2.更新/删除操作(需加 @Modifying)
@Modifying
@Query("UPDATE User u SET u.email = :newEmail WHERE u.id = :id")
int updateUserEmail(@Param("id") Long id, @Param("newEmail") String newEmail);3.原生 SQL 查询
使用 nativeQuery = true 可执行原生 SQL:
@Query(value = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE email = ?", nativeQuery = true)
User findUserByEmailNative(String email);原生 SQL 返回的字段需与实体类属性匹配
4.如果要查看自动生成的 SQL
logging:
level:
org.hibernate.SQL: DEBUG
org.hibernate.type.descriptor.sql.BasicBinder: TRACE
org.hibernate.type.descriptor.sql.BasicExtractor: TRACE运行后就能发现sql了
三、事务管理
Spring Data JPA 默认在 Repository 方法上启用事务(只读事务用于查询,读写事务用于修改),如果需要自定义:
@Service
@Transactional
public class UserService {
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public List<User> getAllUsers() {
return userRepository.findAll();
}
@Transactional
public User saveUser(User user) {
return userRepository.save(user);
}
}总结:
- 优先使用 方法命名查询,简洁清晰。
- 复杂逻辑使用 JPQL,避免原生 SQL(除非必要)。
- 使用 DTO/Projection 避免暴露整个实体。
- 所有修改操作确保在 事务 中执行。
- 合理使用 分页 避免内存溢出。
- 开启
show-sql和format_sql便于调试。
先到这里,如有补充接着写。
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_32953079/article/details/79493541
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_32953079/article/details/79494955
隐藏问题处理:
今天发现在调用 userRepository.getById(id) 方法时,传了一个 不存在的 ID, 调试时发现:所有字段都是 null,但对象不为空,导致进了我的if了,经过排查,发现了如下情况:
UserEntity userEntity = userRepository.getById(id);
if (userEntity!= null) {
// 修改字段并保存
chatEntity.setIsDel(1);
chatRepository.save(userEntity);
}核心原因:Hibernate 使用了代理对象(Proxy)机制
当你调用getById(id) 时,即使数据库里没有这个 ID 对应的数据,Hibernate 也会返回一个 代理对象(Proxy) ,它是一个"空壳"对象,看起来像实体,但实际上它的所有字段都为 null,但它本身不是 null,所以 != null 成立
这不是普通的 Java 对象,而是 Hibernate 的 懒加载代理(Lazy Loading Proxy)
正确处理方法:
Optional<UseerEntity> optional = userRepository.findById(id);
if (optional.isPresent()) {
UseerEntity entity = optional.get();
entity.setIsDel(1);
userRepository.save(entity);
} else {
// 不存在,不做任何操作
log.warn("ChatEntity not found for id: " + id);
}findById() 返回的是 Optional<T>,如果查不到就返回 Optional.empty(),不会返回代理对象
我是因为代码里面写了好多这个getById(id)查询,我封装了一下,可供大家参考
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaSpecificationExecutor;
import org.springframework.data.repository.NoRepositoryBean;
@NoRepositoryBean
public interface BaseRepository<T> extends JpaRepository<T, Long>, JpaSpecificationExecutor<T> {
default T getById(Long id) {
//立即查询,而不是返回代理
return findById(id).orElse(null);
}
}补充getById() vs findById()
| 方法 | 返回类型 | 是否返回代理对象 | 是否能判断"不存在" |
|---|---|---|---|
getById() |
T |
是(代理) | 不能(永远不为 null) |
findById() |
Optional<T> |
否 | 可以(isPresent()) |
放几个官方文档学习一下:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-data/jpa/reference/#jpa.query-methods.query-creation
https://docs.spring.io/spring-data/jpa/reference/