目标
实现的功能:
- 使用YOLOv8模型检测视频中的人物
- 计算人物之间的距离(基于检测框中心点的欧氏距离)
- 当人物之间距离小于设定的安全阈值时,标记为红色并绘制连接线
- 显示人物之间的实时距离值
- 显示当前的安全距离阈值
程序特点:
- 从摄像头实时获取视频流进行处理
- 使用绿色框标记安全距离内的人物,红色框标记距离过近的人物
- 通过红色线条连接距离过近的人物,并显示距离数值
- 按'q'键可退出程序
测试结果: 程序运行正常,可以成功检测人物并计算距离,当人物距离过近时会进行适当标记。
看效果
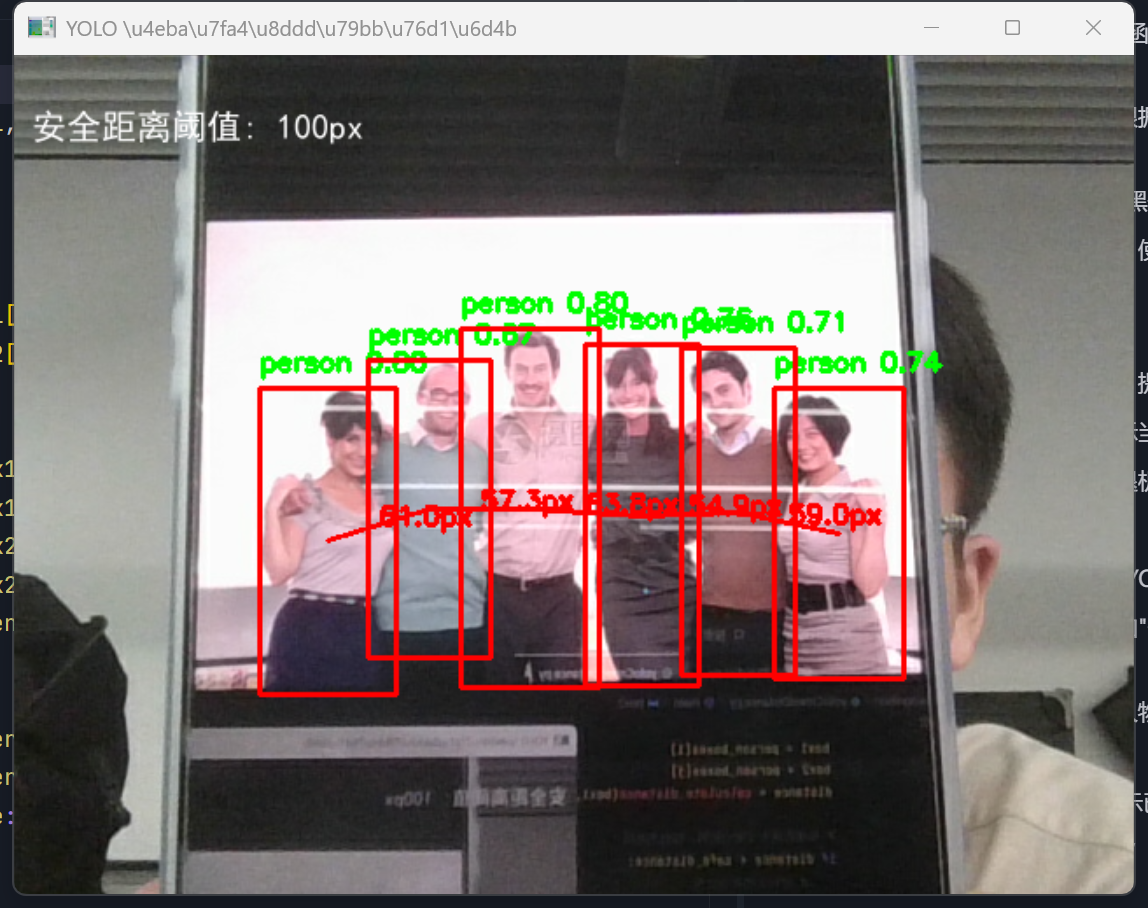
实现思路
- 创建新的Python文件yoloCrowdDistance.py
- 复制yoloUltralytics.py的基本结构
- 添加距离计算功能
- 添加过近人物标记功能
- 测试程序
贴源码
python
import cv2
from ultralytics import YOLO
import numpy as np
import os
import platform
from PIL import ImageFont, ImageDraw, Image
def draw_chinese_text(image, text, position, font_size, color):
"""
使用PIL在图像上绘制中文文本
"""
try:
# 将OpenCV图像转换为PIL图像
pil_image = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(pil_image)
# 选择字体
font_path = None
system = platform.system()
if system == "Windows":
# Windows系统默认字体路径(使用原始字符串)
font_path = r"C:\Windows\Fonts\simhei.ttf" # 黑体
if not os.path.exists(font_path):
font_path = r"C:\Windows\Fonts\simsun.ttc" # 宋体
if not os.path.exists(font_path):
font_path = r"C:\Windows\Fonts\msyh.ttc" # 微软雅黑
elif system == "Darwin": # macOS
font_path = "/Library/Fonts/PingFang.ttc"
elif system == "Linux":
font_path = "/usr/share/fonts/truetype/wqy/wqy-zenhei.ttc"
if font_path and os.path.exists(font_path):
font = ImageFont.truetype(font_path, font_size)
print(f"✅ 使用字体: {font_path}")
else:
font = ImageFont.load_default()
print("⚠️ 使用默认字体,中文可能无法正常显示")
# 绘制文本
draw.text(position, text, font=font, fill=color)
# 将PIL图像转换回OpenCV图像
return cv2.cvtColor(np.array(pil_image), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
except Exception as e:
print(f"⚠️ 绘制中文文本时出错: {e}")
# 如果绘制中文失败,使用OpenCV的putText(可能显示为方框)
cv2.putText(image, text, position, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, font_size/20, color, 2)
return image
def calculate_distance(box1, box2):
"""
计算两个检测框之间的距离(使用中心点之间的欧氏距离)
box1, box2: 检测框坐标 (x1, y1, x2, y2)
"""
# 计算两个检测框的中心点
center1_x = (box1[0] + box1[2]) / 2
center1_y = (box1[1] + box1[3]) / 2
center2_x = (box2[0] + box2[2]) / 2
center2_y = (box2[1] + box2[3]) / 2
# 计算欧氏距离
distance = np.sqrt((center1_x - center2_x) ** 2 + (center1_y - center2_y) ** 2)
return distance
def main():
print("开始加载YOLO模型进行人群距离监测...")
try:
# 加载YOLOv8模型
model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
print("✅ 模型加载成功!")
# 打开摄像头
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
if not cap.isOpened():
print("❌ 无法打开摄像头")
return
print("🎥 摄像头已开启,按 'q' 键退出...")
# 设定安全距离阈值(像素单位)
safe_distance = 100
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
print("❌ 无法读取视频帧")
break
# 使用模型进行预测
results = model(frame)
person_boxes = []
# 遍历每一帧的检测结果
for r in results:
# 获取检测框的坐标、置信度和类别ID
boxes = r.boxes
if boxes is not None and len(boxes) > 0:
for box in boxes:
# 获取坐标
x1, y1, x2, y2 = box.xyxy[0].tolist()
conf = box.conf[0].item() # 置信度
cls_id = int(box.cls[0].item()) # 类别ID
class_name = model.names[cls_id] # 类别名称
# 只关注人物类别(COCO数据集中类别ID为0)
if cls_id == 0 and conf > 0.5:
# 保存人物检测框
person_boxes.append((x1, y1, x2, y2))
# 绘制人物边界框
cv2.rectangle(frame, (int(x1), int(y1)), (int(x2), int(y2)), (0, 255, 0), 2)
# 绘制标签
label = f"{class_name} {conf:.2f}"
cv2.putText(frame, label, (int(x1), int(y1) - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5,
(0, 255, 0), 2)
# 检测过近距离的人物对
if len(person_boxes) > 1:
for i in range(len(person_boxes)):
for j in range(i + 1, len(person_boxes)):
box1 = person_boxes[i]
box2 = person_boxes[j]
distance = calculate_distance(box1, box2)
# 如果距离小于安全阈值,标记为危险
if distance < safe_distance:
# 绘制人物框为红色
cv2.rectangle(frame, (int(box1[0]), int(box1[1])), (int(box1[2]), int(box1[3])), (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.rectangle(frame, (int(box2[0]), int(box2[1])), (int(box2[2]), int(box2[3])), (0, 0, 255), 2)
# 绘制连接线
center1_x = int((box1[0] + box1[2]) / 2)
center1_y = int((box1[1] + box1[3]) / 2)
center2_x = int((box2[0] + box2[2]) / 2)
center2_y = int((box2[1] + box2[3]) / 2)
cv2.line(frame, (center1_x, center1_y), (center2_x, center2_y), (0, 0, 255), 2)
# 显示距离
mid_x = int((center1_x + center2_x) / 2)
mid_y = int((center1_y + center2_y) / 2)
cv2.putText(frame, f"{distance:.1f}px", (mid_x, mid_y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5,
(0, 0, 255), 2)
# 显示安全距离阈值信息
frame = draw_chinese_text(frame, f"安全距离阈值: {safe_distance}px", (10, 30), 20, (255, 255, 255))
# 显示视频帧
cv2.imshow('YOLO 人群距离监测', frame)
# 按'q'键退出
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
# 释放资源
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
print("✅ 程序正常退出")
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ 程序执行出错: {e}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()