模型架构图:
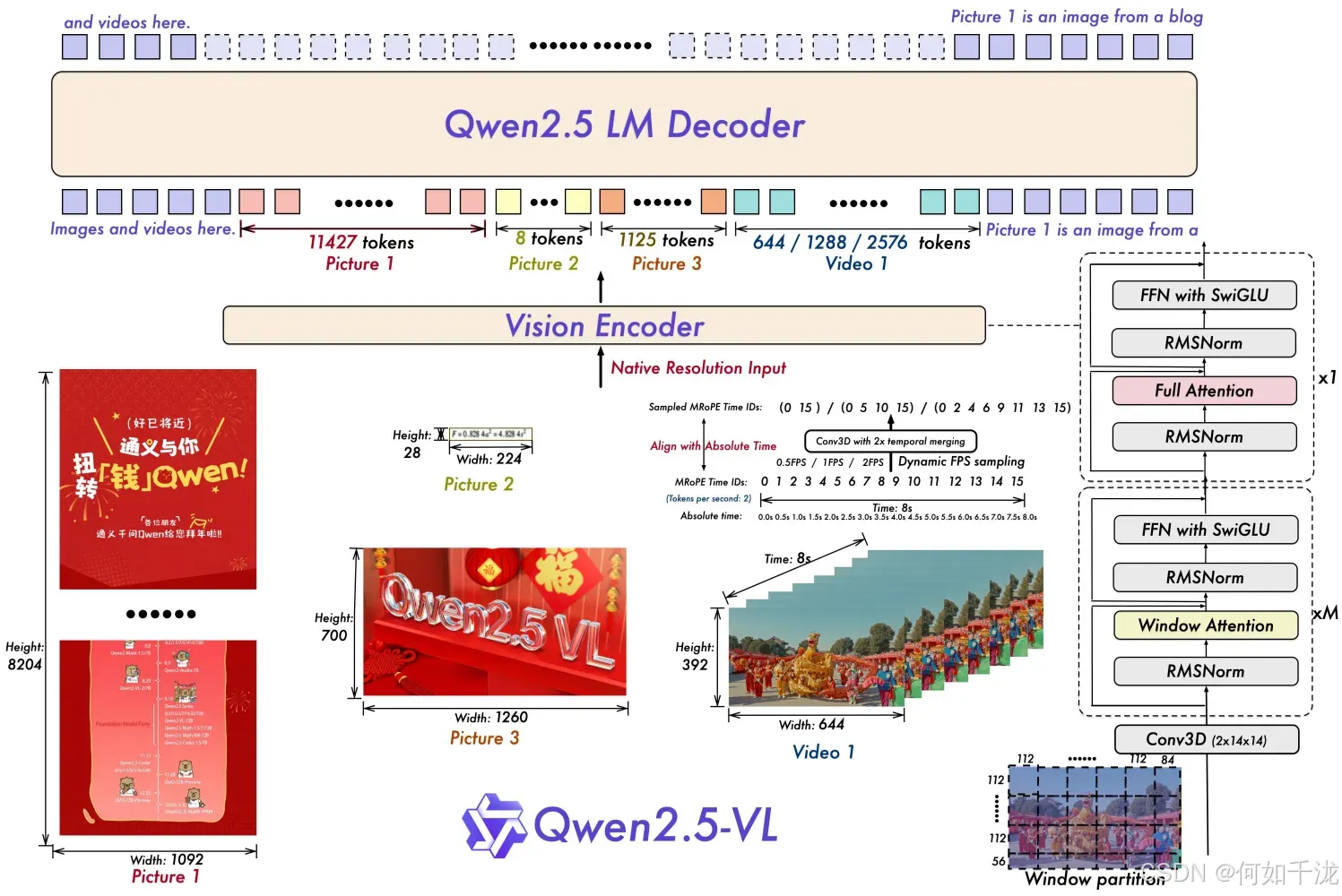
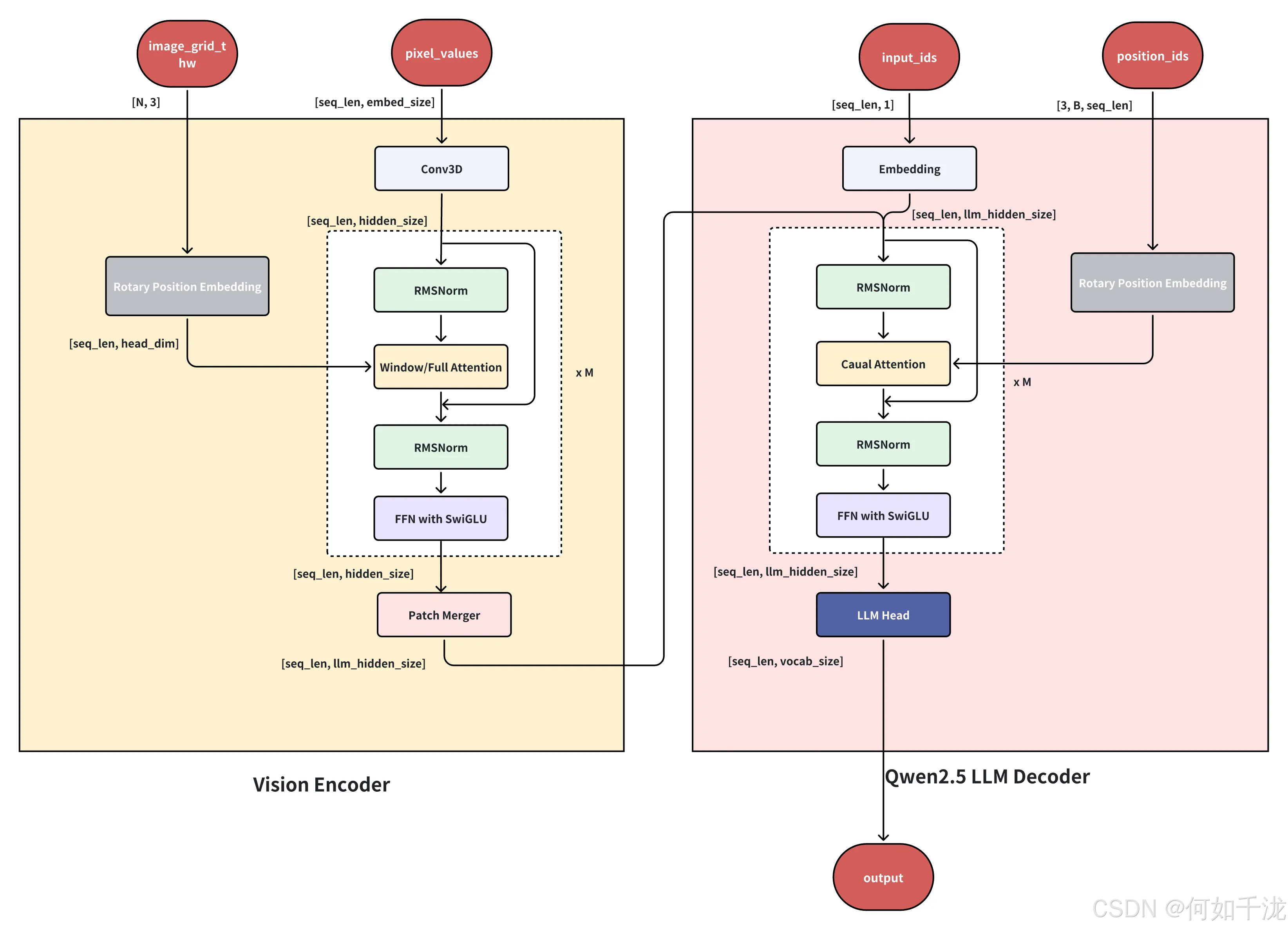
Visual Encoder
python
class Qwen2_5_VisionTransformerPretrainedModel(Qwen2_5_VLPreTrainedModel):
config: Qwen2_5_VLVisionConfig
_no_split_modules = ["Qwen2_5_VLVisionBlock"]
def __init__(self, config, *inputs, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(config, *inputs, **kwargs)
self.spatial_merge_size = config.spatial_merge_size
self.patch_size = config.patch_size
self.fullatt_block_indexes = config.fullatt_block_indexes
self.window_size = config.window_size
self.spatial_merge_unit = self.spatial_merge_size * self.spatial_merge_size
self.patch_embed = Qwen2_5_VisionPatchEmbed(
patch_size=config.patch_size,
temporal_patch_size=config.temporal_patch_size,
in_channels=config.in_channels,
embed_dim=config.hidden_size,
)
head_dim = config.hidden_size // config.num_heads
self.rotary_pos_emb = Qwen2_5_VisionRotaryEmbedding(head_dim // 2)
self.blocks = nn.ModuleList([Qwen2_5_VLVisionBlock(config) for _ in range(config.depth)])
self.merger = Qwen2_5_VLPatchMerger(
dim=config.out_hidden_size,
context_dim=config.hidden_size,
spatial_merge_size=config.spatial_merge_size,
)
self.gradient_checkpointing = False
def rot_pos_emb(self, grid_thw):
pos_ids = []
for t, h, w in grid_thw:
hpos_ids = torch.arange(h).unsqueeze(1).expand(-1, w)
hpos_ids = hpos_ids.reshape(
h // self.spatial_merge_size,
self.spatial_merge_size,
w // self.spatial_merge_size,
self.spatial_merge_size,
)
hpos_ids = hpos_ids.permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
hpos_ids = hpos_ids.flatten()
wpos_ids = torch.arange(w).unsqueeze(0).expand(h, -1)
wpos_ids = wpos_ids.reshape(
h // self.spatial_merge_size,
self.spatial_merge_size,
w // self.spatial_merge_size,
self.spatial_merge_size,
)
wpos_ids = wpos_ids.permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
wpos_ids = wpos_ids.flatten()
pos_ids.append(torch.stack([hpos_ids, wpos_ids], dim=-1).repeat(t, 1))
pos_ids = torch.cat(pos_ids, dim=0)
max_grid_size = grid_thw[:, 1:].max()
rotary_pos_emb_full = self.rotary_pos_emb(max_grid_size)
rotary_pos_emb = rotary_pos_emb_full[pos_ids].flatten(1)
return rotary_pos_emb
def get_window_index(self, grid_thw):
window_index: list = []
cu_window_seqlens: list = [0]
window_index_id = 0
vit_merger_window_size = self.window_size // self.spatial_merge_size // self.patch_size
for grid_t, grid_h, grid_w in grid_thw:
llm_grid_h, llm_grid_w = (
grid_h // self.spatial_merge_size,
grid_w // self.spatial_merge_size,
)
index = torch.arange(grid_t * llm_grid_h * llm_grid_w).reshape(grid_t, llm_grid_h, llm_grid_w)
pad_h = vit_merger_window_size - llm_grid_h % vit_merger_window_size
pad_w = vit_merger_window_size - llm_grid_w % vit_merger_window_size
num_windows_h = (llm_grid_h + pad_h) // vit_merger_window_size
num_windows_w = (llm_grid_w + pad_w) // vit_merger_window_size
index_padded = F.pad(index, (0, pad_w, 0, pad_h), "constant", -100)
index_padded = index_padded.reshape(
grid_t,
num_windows_h,
vit_merger_window_size,
num_windows_w,
vit_merger_window_size,
)
index_padded = index_padded.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4).reshape(
grid_t,
num_windows_h * num_windows_w,
vit_merger_window_size,
vit_merger_window_size,
)
seqlens = (index_padded != -100).sum([2, 3]).reshape(-1)
index_padded = index_padded.reshape(-1)
index_new = index_padded[index_padded != -100]
window_index.append(index_new + window_index_id)
cu_seqlens_tmp = seqlens.cumsum(0) * self.spatial_merge_unit + cu_window_seqlens[-1]
cu_window_seqlens.extend(cu_seqlens_tmp.tolist())
window_index_id += (grid_t * llm_grid_h * llm_grid_w).item()
window_index = torch.cat(window_index, dim=0)
return window_index, cu_window_seqlens
def forward(self, hidden_states: torch.Tensor, grid_thw: torch.Tensor, **kwargs) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
Args:
hidden_states (`torch.Tensor` of shape `(seq_len, hidden_size)`):
The final hidden states of the model.
grid_thw (`torch.Tensor` of shape `(num_images_or_videos, 3)`):
The temporal, height and width of feature shape of each image in LLM.
Returns:
`torch.Tensor`: hidden_states.
"""
hidden_states = self.patch_embed(hidden_states)
rotary_pos_emb = self.rot_pos_emb(grid_thw)
window_index, cu_window_seqlens = self.get_window_index(grid_thw)
cu_window_seqlens = torch.tensor(
cu_window_seqlens,
device=hidden_states.device,
dtype=grid_thw.dtype if torch.jit.is_tracing() else torch.int32,
)
cu_window_seqlens = torch.unique_consecutive(cu_window_seqlens)
seq_len, _ = hidden_states.size()
hidden_states = hidden_states.reshape(seq_len // self.spatial_merge_unit, self.spatial_merge_unit, -1)
hidden_states = hidden_states[window_index, :, :]
hidden_states = hidden_states.reshape(seq_len, -1)
rotary_pos_emb = rotary_pos_emb.reshape(seq_len // self.spatial_merge_unit, self.spatial_merge_unit, -1)
rotary_pos_emb = rotary_pos_emb[window_index, :, :]
rotary_pos_emb = rotary_pos_emb.reshape(seq_len, -1)
emb = torch.cat((rotary_pos_emb, rotary_pos_emb), dim=-1)
position_embeddings = (emb.cos(), emb.sin())
cu_seqlens = torch.repeat_interleave(grid_thw[:, 1] * grid_thw[:, 2], grid_thw[:, 0]).cumsum(
dim=0,
# Select dtype based on the following factors:
# - FA2 requires that cu_seqlens_q must have dtype int32
# - torch.onnx.export requires that cu_seqlens_q must have same dtype as grid_thw
# See https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/34852 for more information
dtype=grid_thw.dtype if torch.jit.is_tracing() else torch.int32,
)
cu_seqlens = F.pad(cu_seqlens, (1, 0), value=0)
for layer_num, blk in enumerate(self.blocks):
if layer_num in self.fullatt_block_indexes:
cu_seqlens_now = cu_seqlens
else:
cu_seqlens_now = cu_window_seqlens
hidden_states = blk(
hidden_states,
cu_seqlens=cu_seqlens_now,
position_embeddings=position_embeddings,
**kwargs,
)
hidden_states = self.merger(hidden_states)
reverse_indices = torch.argsort(window_index)
hidden_states = hidden_states[reverse_indices, :]
return hidden_statesStep1:Patch Embedding
将输入的图像或视频帧(已预切成固定大小的时空 patch)线性投影为统一维度的 token。
python
class Qwen2_5_VisionPatchEmbed(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
patch_size: int = 14,
temporal_patch_size: int = 2,
in_channels: int = 3,
embed_dim: int = 1280,
) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.patch_size = patch_size
self.temporal_patch_size = temporal_patch_size
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
kernel_size = [temporal_patch_size, patch_size, patch_size]
self.proj = nn.Conv3d(in_channels, embed_dim, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=kernel_size, bias=False)
def forward(self, hidden_states: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
target_dtype = self.proj.weight.dtype
hidden_states = hidden_states.view(
-1, self.in_channels, self.temporal_patch_size, self.patch_size, self.patch_size
)
hidden_states = self.proj(hidden_states.to(dtype=target_dtype)).view(-1, self.embed_dim)
return hidden_states- input shape:
[num_images*grid_w*grid_h, channel * temporal_patch_size * patch_size * patch_size] - output shape:
[num_images*grid_h*grid_w, embed_dim]
Step2: 旋转位置编码(RoPE, Rotary Position Embedding)
Qwen2.5-VL 模型中的旋转位置编码(RoPE, Rotary Position Embedding),用于为视觉 token 提供空间位置信息。它包含两个部分:
Qwen2_5_VisionRotaryEmbedding:生成基础的 RoPE 频率表(freqs)。rot_pos_emb方法 (属于某个视觉编码器类):根据图像/视频的网格布局(grid_thw)和空间合并策略(spatial_merge_size),为每个视觉 patch 构建对应的 RoPE,并从预计算的 RoPE 表中索引出实际位置编码。
Qwen2_5_VisionRotaryEmbedding 类:
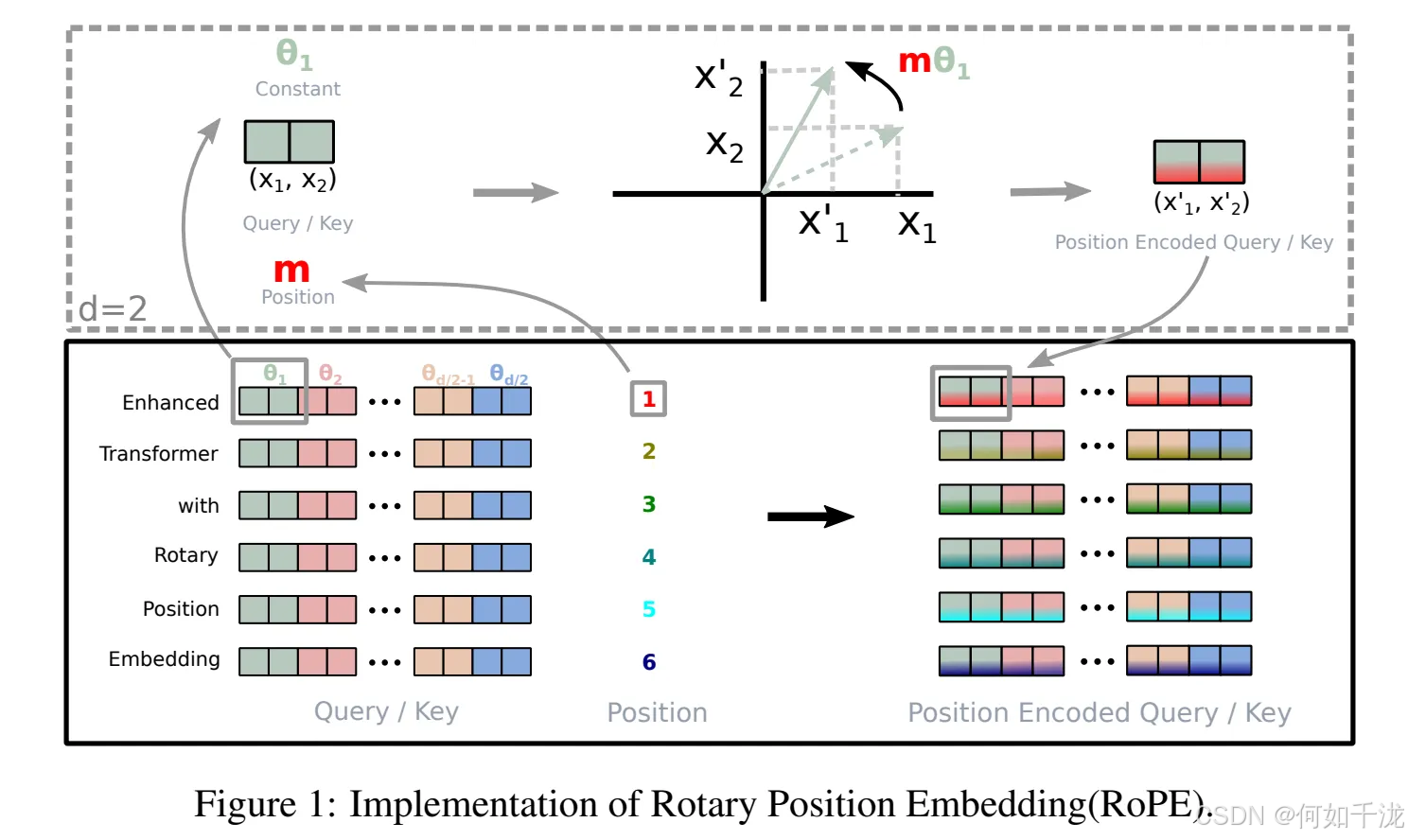
RoPE 的数学构造(关键公式)
对维度为 d d d的向量(通常 d d d为偶数),将其分成 d / 2 d/2 d/2 个二维子空间。对于位置 m m m,在第 i i i个子空间(对应维度 2 i 2i 2i 和 2 i + 1 2i+1 2i+1)上,定义旋转角度:
θ i = m ⋅ 1 θ 2 i / d , 其中 θ = 10000 θ_i=m⋅\frac {1} {θ^{2i/d}}, 其中 θ=10000 θi=m⋅θ2i/d1,其中θ=10000
则 RoPE 将向量 ( x 2 i , x 2 i + 1 ) (x_{2i},x_{2i+1}) (x2i,x2i+1) 变换为:
( c o s θ i − s i n θ i s i n θ i c o s θ i ) ( x 2 i x 2 i + 1 ) (\begin{matrix} cos \theta_i&-sin\theta_i\\ sin\theta_i&cos \theta_i \end{matrix})(\begin{matrix} x_{2i}\\ x_{2i+1} \end{matrix}) (cosθisinθi−sinθicosθi)(x2ix2i+1)
为了高效计算,通常预计算:
- freqs= [ m ⋅ θ 0 , m ⋅ θ 1 , ... , m ⋅ θ d / 2 − 1 ] [m⋅θ_0,m⋅θ_1,...,m⋅θ_{d/2−1}] [m⋅θ0,m⋅θ1,...,m⋅θd/2−1]
- 然后在运行时用
torch.cos(freqs)和torch.sin(freqs)构造旋转。
python
class Qwen2_5_VisionRotaryEmbedding(nn.Module):
inv_freq: torch.Tensor # fix linting for `register_buffer`
def __init__(self, dim: int, theta: float = 10000.0) -> None:
super().__init__()
inv_freq = 1.0 / (theta ** (torch.arange(0, dim, 2, dtype=torch.float) / dim))
self.register_buffer("inv_freq", inv_freq, persistent=False)
def forward(self, seqlen: int) -> torch.Tensor:
seq = torch.arange(seqlen, device=self.inv_freq.device, dtype=self.inv_freq.dtype)
freqs = torch.outer(seq, self.inv_freq)
return freqs标准的 2D 旋转位置编码的频率生成器 ,但这里只生成一维序列的 RoPE 基础频率(后续通过 (x, y) 坐标组合实现 2D)。
dim:RoPE 的维度(通常是head_dim的一半,因为 RoPE 作用于复数形式,每两个维度组成一个旋转对)。theta=10000.0:RoPE 的基频缩放因子(与原始 Transformer 一致)。
rot_pos_emb(self, grid_thw) 方法:
python
def rot_pos_emb(self, grid_thw):
pos_ids = []
for t, h, w in grid_thw:
# 1. 构建高度方向位置 ID
hpos_ids = torch.arange(h).unsqueeze(1).expand(-1, w)
hpos_ids = hpos_ids.reshape(
h // self.spatial_merge_size,
self.spatial_merge_size,
w // self.spatial_merge_size,
self.spatial_merge_size,
)
hpos_ids = hpos_ids.permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
hpos_ids = hpos_ids.flatten()
# 2. 构建宽度方向位置 ID
wpos_ids = torch.arange(w).unsqueeze(0).expand(h, -1)
wpos_ids = wpos_ids.reshape(
h // self.spatial_merge_size,
self.spatial_merge_size,
w // self.spatial_merge_size,
self.spatial_merge_size,
)
wpos_ids = wpos_ids.permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
wpos_ids = wpos_ids.flatten()
# 3. 合并 h/w,重复 t 次(处理时间维度)
pos_ids.append(torch.stack([hpos_ids, wpos_ids], dim=-1).repeat(t, 1))
pos_ids = torch.cat(pos_ids, dim=0)
# 4. 预计算最大 RoPE 表
max_grid_size = grid_thw[:, 1:].max()
rotary_pos_emb_full = self.rotary_pos_emb(max_grid_size)
# 5. 根据 pos_ids 索引 RoPE
rotary_pos_emb = rotary_pos_emb_full[pos_ids].flatten(1)
return rotary_pos_emb输入:grid_thw
- 形状为
(B, 3)或(num_images, 3),每一行[t, h, w]表示一个图像/视频片段被划分成h × w个空间 patch,共t帧(时间维度)。
关键参数:self.spatial_merge_size
- 用于 空间合并(spatial merging) ,例如
spatial_merge_size=2表示每2×2个原始 patch 被合并为一个 token。 - 因此,实际 token 数量 = (h // merge) × (w // merge) × t
步骤详解:
- 1. 构建高度位置 ID(
hpos_ids)torch.arange(h).unsqueeze(1).expand(-1, w):生成h × w的网格,每行是[0, 0, ..., 0], [1, 1, ..., 1], ...reshape(h//M, M, w//M, M):将网格划分为(h//M × w//M)个M×M块(M = spatial_merge_size)permute(0, 2, 1, 3):调整顺序为[block_row, block_col, in_block_h, in_block_w]flatten():展平后,顺序变为:先遍历每个 block,再遍历 block 内部的行和列,得到每个合并 token 的"代表高度位置"。
- 2. 宽度位置 ID(
wpos_ids)同理- 生成
h × w的列索引网格。 - 同样 reshape + permute + flatten,得到每个合并 token 的"代表宽度位置"。
- 生成
- 3. 合并
h和w,并复制t次torch.stack([hpos_ids, wpos_ids], dim=-1):每个 token 对应一个(h_id, w_id)坐标。.repeat(t, 1):因为时间维度有t帧,每帧共享相同的空间位置
- 4. 预计算 RoPE 表
max_grid_size = max(h, w):取所有图像中最大边长。self.rotary_pos_emb(max_grid_size):调用Qwen2_5_VisionRotaryEmbedding的forward,生成(max_grid_size, dim//2)的频率表。
- 5. 索引并展平
rotary_pos_emb_full[pos_ids]:pos_ids形状为(N, 2),其中N = total tokens- 索引后得到
(N, 2, dim//2):每个 token 有两个 RoPE 向量(一个来自 h,一个来自 w)
.flatten(1):展平为(N, dim),拼接h和w的 RoPE,形成完整的 2D 位置编码。
Step3: 构建窗口注意力(windowed attention)的索引
Qwen2.5-VL 视觉编码器中用于构建窗口注意力(windowed attention)的索引机制 ,尤其用于支持 可变分辨率图像 和 稀疏/分块注意力(例如在 ViT-Merger 或 FlashAttention-2 的变体中)。其核心目标是:
将不规则大小的视觉 token 网格(来自不同图像)按固定窗口大小分组,并生成:
window_index:全局 token 索引,表示每个窗口内包含哪些 token;cu_window_seqlens:每个窗口的累计 token 长度(用于高效 attention 计算,如 FlashAttention 的cu_seqlens接口)。
python
def get_window_index(self, grid_thw):
window_index: list = []
cu_window_seqlens: list = [0]
window_index_id = 0
vit_merger_window_size = self.window_size // self.spatial_merge_size // self.patch_size
for grid_t, grid_h, grid_w in grid_thw:
llm_grid_h, llm_grid_w = (
grid_h // self.spatial_merge_size,
grid_w // self.spatial_merge_size,
)
index = torch.arange(grid_t * llm_grid_h * llm_grid_w).reshape(grid_t, llm_grid_h, llm_grid_w)
pad_h = vit_merger_window_size - llm_grid_h % vit_merger_window_size
pad_w = vit_merger_window_size - llm_grid_w % vit_merger_window_size
num_windows_h = (llm_grid_h + pad_h) // vit_merger_window_size
num_windows_w = (llm_grid_w + pad_w) // vit_merger_window_size
index_padded = F.pad(index, (0, pad_w, 0, pad_h), "constant", -100)
index_padded = index_padded.reshape(
grid_t,
num_windows_h,
vit_merger_window_size,
num_windows_w,
vit_merger_window_size,
)
index_padded = index_padded.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4).reshape(
grid_t,
num_windows_h * num_windows_w,
vit_merger_window_size,
vit_merger_window_size,
)
seqlens = (index_padded != -100).sum([2, 3]).reshape(-1)
index_padded = index_padded.reshape(-1)
index_new = index_padded[index_padded != -100]
window_index.append(index_new + window_index_id)
cu_seqlens_tmp = seqlens.cumsum(0) * self.spatial_merge_unit + cu_window_seqlens[-1]
cu_window_seqlens.extend(cu_seqlens_tmp.tolist())
window_index_id += (grid_t * llm_grid_h * llm_grid_w).item()
window_index = torch.cat(window_index, dim=0)
return window_index, cu_window_seqlens输入:grid_thw
- 形状为
(B, 3)或(num_images, 3),每一行[t, h, w]表示一个图像/视频片段被划分成h × w个空间 patch,共t帧(时间维度)。
关键参数说明:
python
vit_merger_window_size = self.window_size // self.spatial_merge_size // self.patch_sizeself.patch_size:原始图像被划分的 patch 尺寸(如 14)。self.spatial_merge_size:空间合并因子(如 2),表示每M×M个原始 patch 合并为 1 个 token。self.window_size:原始像素尺度下的窗口大小(如 112 像素)。
因此:
vit_merger_window_size= 在合并后的 token 网格中,每个窗口应包含的 token 数量(边长)。
步骤详解:
-
1. 计算合并后的 token 网格尺寸
pythonllm_grid_h, llm_grid_w = grid_h // self.spatial_merge_size, grid_w // self.spatial_merge_size- 经过空间合并后,每张图像变为
t × llm_grid_h × llm_grid_w个 视觉 token。
- 经过空间合并后,每张图像变为
-
2. 为当前图像生成全局 token 索引(局部)
pythonindex = torch.arange(grid_t * llm_grid_h * llm_grid_w).reshape(grid_t, llm_grid_h, llm_grid_w)index是一个(t, H, W)张量,每个位置的值是该 token 在 当前图像内的局部索引(从 0 开始)。
-
3. 计算 padding 以对齐窗口边界
pythonpad_h = vit_merger_window_size - llm_grid_h % vit_merger_window_size pad_w = vit_merger_window_size - llm_grid_w % vit_merger_window_size- 目的:将
H × Wtoken 网格 补零到能被vit_merger_window_size整除,以便划分为完整窗口。 - 使用
100作为 padding 值(后续用于 mask 掉无效 token)。
- 目的:将
-
4. 计算窗口数量
pythonnum_windows_h = (llm_grid_h + pad_h) // vit_merger_window_size num_windows_w = (llm_grid_w + pad_w) // vit_merger_window_size- 总窗口数 =
t × num_windows_h × num_windows_w
- 总窗口数 =
-
5. 填充并重排为窗口格式
pythonindex_padded = F.pad(index, (0, pad_w, 0, pad_h), "constant", -100) index_padded = index_padded.reshape( grid_t, num_windows_h, vit_merger_window_size, num_windows_w, vit_merger_window_size, ) index_padded = index_padded.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4).reshape( grid_t, num_windows_h * num_windows_w, vit_merger_window_size, vit_merger_window_size, )reshape + permute:将(t, H, W)重排为(t, num_win_h, win_h, num_win_w, win_w),再合并窗口维度。- 最终形状:
(t, num_windows, win_h, win_w)
-
6. 计算每个窗口的实际 token 数量(非 padding)
pythonseqlens = (index_padded != -100).sum([2, 3]).reshape(-1)seqlens:长度为t × num_windows,每个元素是该窗口中 有效 token 的数量。
-
7. 提取有效 token 的全局索引
pythonindex_padded = index_padded.reshape(-1) index_new = index_padded[index_padded != -100] window_index.append(index_new + window_index_id)window_index_id在每张图像后累加,确保索引不冲突。+ window_index_id:将其转换为 全局 token 索引(跨所有图像)。index_new:当前图像所有窗口中 有效 token 的局部索引列表。
-
8. 构建累计长度(cu_seqlens)
pythoncu_seqlens_tmp = seqlens.cumsum(0) * self.spatial_merge_unit + cu_window_seqlens[-1] cu_window_seqlens.extend(cu_seqlens_tmp.tolist()) -
9. 更新全局索引偏移
pythonwindow_index_id += (grid_t * llm_grid_h * llm_grid_w).item()- 为下一张图像的 token 索引做准备。
Step4: VisionBlock
python
class Qwen2_5_VLVisionBlock(GradientCheckpointingLayer):
def __init__(self, config, attn_implementation: str = "sdpa") -> None:
super().__init__()
self.norm1 = Qwen2RMSNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=1e-6)
self.norm2 = Qwen2RMSNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=1e-6)
self.attn = Qwen2_5_VLVisionAttention(config=config)
self.mlp = Qwen2_5_VLMLP(config, bias=True)
def forward(
self,
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
cu_seqlens: torch.Tensor,
rotary_pos_emb: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
position_embeddings: Optional[tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None,
**kwargs,
) -> torch.Tensor:
hidden_states = hidden_states + self.attn(
self.norm1(hidden_states),
cu_seqlens=cu_seqlens,
rotary_pos_emb=rotary_pos_emb,
position_embeddings=position_embeddings,
**kwargs,
)
hidden_states = hidden_states + self.mlp(self.norm2(hidden_states))
return hidden_statesRMSNorm(Root Mean Square Layer Normalization)
RMSNorm(Root Mean Square Layer Normalization),用于替代标准 LayerNorm 的归一化方法。它在结构上比传统 LayerNorm 更简单、计算更高效,且在大语言模型中表现良好。
python
class Qwen2RMSNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, eps: float = 1e-6) -> None:
"""
Qwen2RMSNorm is equivalent to T5LayerNorm
"""
super().__init__()
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(hidden_size))
self.variance_epsilon = eps
def forward(self, hidden_states: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
input_dtype = hidden_states.dtype
hidden_states = hidden_states.to(torch.float32)
variance = hidden_states.pow(2).mean(-1, keepdim=True)
hidden_states = hidden_states * torch.rsqrt(variance + self.variance_epsilon)
return self.weight * hidden_states.to(input_dtype)RMSNorm 的数学原理
RMSNorm 的核心思想是:只对激活值进行缩放(scale),不进行平移(no bias/centering)。
对于一个向量 x ∈ R d x∈R^d x∈Rd,RMSNorm 定义为:
R M S N o r m ( x ) = x R M S ( x ) ⊙ γ RMSNorm(x)=\frac {x} {RMS(x)}⊙γ RMSNorm(x)=RMS(x)x⊙γ
其中:
- R M S ( x ) = 1 d ∑ i = 1 d x i 2 RMS(x)=\sqrt {\frac {1} {d}∑_{i=1}^d x_i^2} RMS(x)=d1∑i=1dxi2 是 均方根(Root Mean Square)
- γ ∈ R d γ∈R^d γ∈Rd是可学习的缩放参数(即
self.weight) - ⊙ ⊙ ⊙表示逐元素相乘(Hadamard product)
注意:没有减去均值(no centering),这是与标准 LayerNorm 的主要区别。
自注意力机制(Vision Attention)
Qwen2.5-VL 多模态大模型中视觉编码器的自注意力机制(Vision Attention) ,其设计专门用于高效处理变长、高分辨率图像 (或视频帧)产生的视觉 token 序列。它支持多种注意力后端(如 Eager、FlashAttention-2),并集成了旋转位置编码(RoPE)。
python
class Qwen2_5_VLVisionAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config: Qwen2_5_VLVisionConfig) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.dim = config.hidden_size
self.num_heads = config.num_heads
self.head_dim = self.dim // self.num_heads
self.num_key_value_groups = 1 # needed for eager attention
self.qkv = nn.Linear(self.dim, self.dim * 3, bias=True)
self.proj = nn.Linear(self.dim, self.dim)
self.scaling = self.head_dim**-0.5
self.config = config
self.attention_dropout = 0.0
self.is_causal = False
def forward(
self,
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
cu_seqlens: torch.Tensor,
rotary_pos_emb: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
position_embeddings: Optional[tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None,
**kwargs,
) -> torch.Tensor:
seq_length = hidden_states.shape[0]
query_states, key_states, value_states = (
self.qkv(hidden_states).reshape(seq_length, 3, self.num_heads, -1).permute(1, 0, 2, 3).unbind(0)
)
cos, sin = position_embeddings
query_states, key_states = apply_rotary_pos_emb_vision(query_states, key_states, cos, sin)
query_states = query_states.transpose(0, 1).unsqueeze(0)
key_states = key_states.transpose(0, 1).unsqueeze(0)
value_states = value_states.transpose(0, 1).unsqueeze(0)
attention_interface: Callable = eager_attention_forward
if self.config._attn_implementation != "eager":
attention_interface = ALL_ATTENTION_FUNCTIONS[self.config._attn_implementation]
if self.config._attn_implementation == "flash_attention_2":
# Flash Attention 2: Use cu_seqlens for variable length attention
max_seqlen = (cu_seqlens[1:] - cu_seqlens[:-1]).max()
attn_output, _ = attention_interface(
self,
query_states,
key_states,
value_states,
attention_mask=None,
scaling=self.scaling,
dropout=0.0 if not self.training else self.attention_dropout,
cu_seq_lens_q=cu_seqlens,
cu_seq_lens_k=cu_seqlens,
max_length_q=max_seqlen,
max_length_k=max_seqlen,
is_causal=False,
**kwargs,
)
else:
# Other implementations: Process each chunk separately
lengths = cu_seqlens[1:] - cu_seqlens[:-1]
splits = [
torch.split(tensor, lengths.tolist(), dim=2) for tensor in (query_states, key_states, value_states)
]
attn_outputs = [
attention_interface(
self,
q,
k,
v,
attention_mask=None,
scaling=self.scaling,
dropout=0.0 if not self.training else self.attention_dropout,
is_causal=False,
**kwargs,
)[0]
for q, k, v in zip(*splits)
]
attn_output = torch.cat(attn_outputs, dim=1)
attn_output = attn_output.reshape(seq_length, -1).contiguous()
attn_output = self.proj(attn_output)
return attn_output-
步骤 1:QKV 投影 + 分头
pythonquery_states, key_states, value_states = ( self.qkv(hidden_states) .reshape(seq_length, 3, self.num_heads, -1) .permute(1, 0, 2, 3) .unbind(0) )self.qkv(hidden_states):(N, 3*D)reshape(N, 3, H, D/H):(N, 3, num_heads, head_dim)permute(1, 0, 2, 3):(3, N, H, head_dim)unbind(0): 拆分为三个(N, H, head_dim)张量
-
步骤 2:应用旋转位置编码(RoPE)
pythoncos, sin = position_embeddings query_states, key_states = apply_rotary_pos_emb_vision(query_states, key_states, cos, sin)旋转位置编码(Rotary Position Embedding, RoPE)在视觉模型中的应用 ,核心思想是通过 向量旋转 将位置信息注入到注意力机制的
query和key向量中。pythondef apply_rotary_pos_emb_vision( q: torch.Tensor, k: torch.Tensor, cos: torch.Tensor, sin: torch.Tensor ) -> tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]: orig_q_dtype = q.dtype orig_k_dtype = k.dtype q, k = q.float(), k.float() cos, sin = cos.unsqueeze(-2).float(), sin.unsqueeze(-2).float() q_embed = (q * cos) + (rotate_half(q) * sin) k_embed = (k * cos) + (rotate_half(k) * sin) q_embed = q_embed.to(orig_q_dtype) k_embed = k_embed.to(orig_k_dtype) return q_embed, k_embedpythondef rotate_half(x): """Rotates half the hidden dims of the input.""" x1 = x[..., : x.shape[-1] // 2] x2 = x[..., x.shape[-1] // 2 :] return torch.cat((-x2, x1), dim=-1)RoPE 的目标是:让 attention 能感知 token 的相对位置。
对于两个位置 m m m 和 n n n,RoPE 保证:
A t t e n t i o n ( q m , k n ) = f ( q , k , m − n ) Attention(q_m,k_n)=f(q,k,m−n) Attention(qm,kn)=f(q,k,m−n)
即只依赖相对位置 m − n m−n m−n,这在视觉和语言任务中都非常重要。
实现方式:复数旋转
- 将向量 x ∈ R d x∈R^d x∈Rd( ∗ d ∗ *d* ∗d∗ 为偶数)视为 d / 2 d/2 d/2 个复数:
x c o m p l e x = ( x 0 + i x d / 2 , x 1 + i x d / 2 + 1 , ... , x d / 2 − 1 + i x d − 1 ) x_{complex}=(x_0+ix_{d/2}, x_1+ix_{d/2+1}, ..., x_{d/2−1}+ix_{d−1}) xcomplex=(x0+ixd/2, x1+ixd/2+1, ..., xd/2−1+ixd−1)
- 对位置 ∗ m ∗ *m* ∗m∗,旋转角度 ∗ θ i = m ⋅ θ − 2 i / d ∗ *θ_i=m⋅θ^{−2i/d}* ∗θi=m⋅θ−2i/d∗。
- 旋转操作: ∗ x r o t = x ⋅ e i θ = x ⋅ ( c o s θ + i s i n θ ) ∗ *x_{rot}=x⋅e^{iθ}=x⋅(cosθ+isinθ)* ∗xrot=x⋅eiθ=x⋅(cosθ+isinθ)∗
- 展开为实部和虚部:
x i n e w x i + d / 2 n e w \] = \[ c o s θ i − s i n θ i s i n θ i c o s θ i \] \[ x i x i + d / 2 \] \[\\begin{matrix} x_{i}\^{new}\\\\ x_{i+d/2}\^{new} \\end{matrix}\]=\[\\begin{matrix} cos \\theta_i\&-sin\\theta_i\\\\ sin\\theta_i\&cos \\theta_i \\end{matrix}\]\[\\begin{matrix} x_{i}\\\\ x_{i+d/2} \\end{matrix}\] \[xinewxi+d/2new\]=\[cosθisinθi−sinθicosθi\]\[xixi+d/2
rotate_half:实现 90° 旋转的向量操作pythondef rotate_half(x): x1 = x[..., : x.shape[-1] // 2] # 前半部分:x0, x1, ..., x_{d/2-1} x2 = x[..., x.shape[-1] // 2 :] # 后半部分:x_{d/2}, ..., x_{d-1} return torch.cat((-x2, x1), dim=-1) # 拼接为 [-x_{d/2}, ..., -x_{d-1}, x0, ..., x_{d/2-1}]应用 RoPE 公式
pythonq_embed = (q * cos) + (rotate_half(q) * sin) k_embed = (k * cos) + (rotate_half(k) * sin)- 前半部分( i i i):
q i n e w = q i ⋅ c o s θ i − q i + d / 2 ⋅ s i n θ i q_i^{new}=qi⋅cosθ_i−q_{i+d/2}⋅sinθ_i qinew=qi⋅cosθi−qi+d/2⋅sinθi
- 后半部分( i + d / 2 i+d/2 i+d/2):
q i + d / 2 n e w = q i ⋅ s i n θ i + q i + d / 2 ⋅ c o s θ i q_{i+d/2}^{new}=q_i⋅sinθ_i+q_{i+d/2}⋅cosθ_i qi+d/2new=qi⋅sinθi+qi+d/2⋅cosθi
-
步骤 3:调整维度以适配 attention 接口
pythonquery_states = query_states.transpose(0, 1).unsqueeze(0) # (1, H, N, head_dim) key_states = key_states.transpose(0, 1).unsqueeze(0) # (1, H, N, head_dim) value_states = value_states.transpose(0, 1).unsqueeze(0) # (1, H, N, head_dim) -
步骤 4:分路径处理注意力(关键!)
-
路径 A:FlashAttention-2(推荐)
pythonif self.config._attn_implementation == "flash_attention_2": max_seqlen = (cu_seqlens[1:] - cu_seqlens[:-1]).max() attn_output, _ = attention_interface( self, query_states, key_states, value_states, cu_seq_lens_q=cu_seqlens, cu_seq_lens_k=cu_seqlens, max_length_q=max_seqlen, max_length_k=max_seqlen, is_causal=False, ... )cu_seqlens:告诉 FlashAttention 每张图像的 token 边界max_seqlen:最长子序列长度(用于 kernel 显存分配)- 优势 :
- O(1) 显存复杂度(不存储 attention 矩阵)
- 支持变长序列
- 极速计算
-
路径 B:Eager / 其他实现(fallback)
pythonelse: lengths = cu_seqlens[1:] - cu_seqlens[:-1] splits = [torch.split(tensor, lengths.tolist(), dim=2) for tensor in (q, k, v)] attn_outputs = [ attention_interface(self, q_i, k_i, v_i, is_causal=False, ...)[0] for q_i, k_i, v_i in zip(*splits) ] attn_output = torch.cat(attn_outputs, dim=1)- 手动拆分 :按
lengths将(1, H, N, D)拆分为多个(1, H, L_i, D) - 对每张图像单独做 attention
- 拼接结果 →
(1, H, N, D) - 缺点:显存占用高(需存储 full attention matrix),速度慢
- 手动拆分 :按
-
-
步骤 5:输出投影
pythonattn_output = attn_output.reshape(seq_length, -1).contiguous() # (N, D) attn_output = self.proj(attn_output) # (N, D)reshape(seq_length, -1):(N, H * head_dim) = (N, D)contiguous(): 确保内存连续,提升后续操作效率
多层感知机(MLP)模块
Qwen2.5-VL 模型中的多层感知机(MLP)模块 ,采用的是现代大语言模型(如 LLaMA、Qwen、Mistral 等)中广泛使用的 Gated MLP(或称 SwiGLU 激活结构)。
python
class Qwen2_5_VLMLP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config, bias: bool = False):
super().__init__()
self.hidden_size = config.hidden_size
self.intermediate_size = config.intermediate_size
self.gate_proj = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.intermediate_size, bias=bias)
self.up_proj = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.intermediate_size, bias=bias)
self.down_proj = nn.Linear(self.intermediate_size, self.hidden_size, bias=bias)
self.act_fn = ACT2FN[config.hidden_act]
def forward(self, hidden_state):
return self.down_proj(self.act_fn(self.gate_proj(hidden_state)) * self.up_proj(hidden_state))Qwen2.5 LM Decoder
python
class Qwen2_5_VLTextModel(Qwen2_5_VLPreTrainedModel):
config: Qwen2_5_VLTextConfig
def __init__(self, config: Qwen2_5_VLTextConfig):
super().__init__(config)
self.padding_idx = config.pad_token_id
self.vocab_size = config.vocab_size
self.embed_tokens = nn.Embedding(config.vocab_size, config.hidden_size, self.padding_idx)
self.layers = nn.ModuleList(
[Qwen2_5_VLDecoderLayer(config, layer_idx) for layer_idx in range(config.num_hidden_layers)]
)
self._attn_implementation = config._attn_implementation
self.norm = Qwen2RMSNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=config.rms_norm_eps)
self.rotary_emb = Qwen2_5_VLRotaryEmbedding(config=config)
self.has_sliding_layers = "sliding_attention" in self.config.layer_types
self.gradient_checkpointing = False
# Initialize weights and apply final processing
self.post_init()
@auto_docstring
def forward(
self,
input_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
position_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
past_key_values: Optional[Cache] = None,
inputs_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
use_cache: Optional[bool] = None,
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = None,
output_hidden_states: Optional[bool] = None,
return_dict: Optional[bool] = None,
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
**kwargs: Unpack[FlashAttentionKwargs],
) -> Union[tuple, BaseModelOutputWithPast]:
output_attentions = output_attentions if output_attentions is not None else self.config.output_attentions
output_hidden_states = (
output_hidden_states if output_hidden_states is not None else self.config.output_hidden_states
)
use_cache = use_cache if use_cache is not None else self.config.use_cache
return_dict = return_dict if return_dict is not None else self.config.use_return_dict
if (input_ids is None) ^ (inputs_embeds is not None):
raise ValueError("You must specify exactly one of input_ids or inputs_embeds")
if self.gradient_checkpointing and self.training:
if use_cache:
logger.warning_once(
"`use_cache=True` is incompatible with gradient checkpointing. Setting `use_cache=False`..."
)
use_cache = False
# torch.jit.trace() doesn't support cache objects in the output
if use_cache and past_key_values is None and not torch.jit.is_tracing():
past_key_values = DynamicCache(config=self.config)
if inputs_embeds is None:
inputs_embeds = self.embed_tokens(input_ids)
if cache_position is None:
past_seen_tokens = past_key_values.get_seq_length() if past_key_values is not None else 0
cache_position = torch.arange(
past_seen_tokens, past_seen_tokens + inputs_embeds.shape[1], device=inputs_embeds.device
)
# the hard coded `3` is for temporal, height and width.
if position_ids is None:
position_ids = cache_position.view(1, 1, -1).expand(3, inputs_embeds.shape[0], -1)
elif position_ids.ndim == 2:
position_ids = position_ids[None, ...].expand(3, position_ids.shape[0], -1)
# NOTE: we need to pass text position ids for packing. Qwen2-VL uses 3D positions
# where each dim indicates visual spatial positions for temporal/height/width grids.
# There are two scenarios when FA2-like packed masking might be activated.
# 1. User specifically passed packed `position_ids` and no attention mask.
# In this case we expect the useer to create correct position ids for all 3 grids
# and prepend text-only position ids to it. The final tensor will be [4, bs, seq-len]
# 2. User runs forward with no attention mask and no position ids. In this case, position ids
# are prepared by the model (`get_rope_index`) as `[4, bs, seq-len]` tensor. Text-only positions are
# prepended by us when creating positions so that the mask is constructed correctly. NOTE: failing to pass
# text-only positions will cause incorrect mask construction, do not change `prepare_input_for_generation`
if position_ids.ndim == 3 and position_ids.shape[0] == 4:
text_position_ids = position_ids[0]
position_ids = position_ids[1:]
else:
# If inputs are not packed (usual 3D positions), do not prepare mask from position_ids
text_position_ids = None
# It may already have been prepared by e.g. `generate`
if not isinstance(causal_mask_mapping := attention_mask, dict):
# Prepare mask arguments
mask_kwargs = {
"config": self.config,
"input_embeds": inputs_embeds,
"attention_mask": attention_mask,
"cache_position": cache_position,
"past_key_values": past_key_values,
"position_ids": text_position_ids,
}
# Create the masks
causal_mask_mapping = {
"full_attention": create_causal_mask(**mask_kwargs),
}
# The sliding window alternating layers are not always activated depending on the config
if self.has_sliding_layers:
causal_mask_mapping["sliding_attention"] = create_sliding_window_causal_mask(**mask_kwargs)
hidden_states = inputs_embeds
# create position embeddings to be shared across the decoder layers
position_embeddings = self.rotary_emb(hidden_states, position_ids)
# decoder layers
all_hidden_states = () if output_hidden_states else None
all_self_attns = () if output_attentions else None
for decoder_layer in self.layers:
if output_hidden_states:
all_hidden_states += (hidden_states,)
layer_outputs = decoder_layer(
hidden_states,
attention_mask=causal_mask_mapping[decoder_layer.attention_type],
position_ids=text_position_ids,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
output_attentions=output_attentions,
use_cache=use_cache,
cache_position=cache_position,
position_embeddings=position_embeddings,
**kwargs,
)
hidden_states = layer_outputs[0]
if output_attentions:
all_self_attns += (layer_outputs[1],)
hidden_states = self.norm(hidden_states)
# add hidden states from the last decoder layer
if output_hidden_states:
all_hidden_states += (hidden_states,)
if not return_dict:
return tuple(
v for v in [hidden_states, past_key_values, all_hidden_states, all_self_attns] if v is not None
)
return BaseModelOutputWithPast(
last_hidden_state=hidden_states,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
hidden_states=all_hidden_states,
attentions=all_self_attns,
)Step1: Embedding
用于将离散的整数索引 (如 token ID)映射为稠密的连续向量(即嵌入向量)
python
nn.Embedding(config.vocab_size, config.hidden_size, self.padding_idx)config.vocab_size- 作用:词汇表大小,即模型能识别的不同 token 的总数。
- 示例 :如果词汇表有 151,936 个词(如 Qwen 系列),则
vocab_size = 151936。 - 嵌入矩阵形状 :第一维为
vocab_size,每个 token 对应一行向量。
config.hidden_size- 作用:每个 token 嵌入向量的维度(也称为 embedding dimension 或 hidden size)。
- 示例 :若
hidden_size = 4096,则每个 token 被映射为一个 4096 维的向量。 - 与模型一致 :这个维度通常等于 Transformer 层的隐藏层大小(即
d_model
Step2: 旋转位置编码(RoPE, Rotary Position Embedding)模块
Qwen2.5-VL (多模态大语言模型)中的 旋转位置编码 (RoPE, Rotary Position Embedding)模块,专门用于处理视觉-语言模型中 非标准的位置 ID
python
class Qwen2_5_VLRotaryEmbedding(nn.Module):
inv_freq: torch.Tensor # fix linting for `register_buffer`
def __init__(self, config: Qwen2_5_VLTextConfig, device=None):
super().__init__()
# BC: "rope_type" was originally "type"
if hasattr(config, "rope_scaling") and config.rope_scaling is not None:
self.rope_type = config.rope_scaling.get("rope_type", config.rope_scaling.get("type"))
else:
self.rope_type = "default"
self.max_seq_len_cached = config.max_position_embeddings
self.original_max_seq_len = config.max_position_embeddings
self.config = config
self.rope_init_fn = ROPE_INIT_FUNCTIONS[self.rope_type]
inv_freq, self.attention_scaling = self.rope_init_fn(self.config, device)
self.register_buffer("inv_freq", inv_freq, persistent=False)
self.original_inv_freq = self.inv_freq
@torch.no_grad()
@dynamic_rope_update # power user: used with advanced RoPE types (e.g. dynamic rope)
def forward(self, x, position_ids):
# In contrast to other models, Qwen2_5_VL has different position ids for the grids
# So we expand the inv_freq to shape (3, ...)
inv_freq_expanded = self.inv_freq[None, None, :, None].float().expand(3, position_ids.shape[1], -1, 1)
position_ids_expanded = position_ids[:, :, None, :].float() # shape (3, bs, 1, positions)
device_type = x.device.type if isinstance(x.device.type, str) and x.device.type != "mps" else "cpu"
with torch.autocast(device_type=device_type, enabled=False): # Force float32
freqs = (inv_freq_expanded.float() @ position_ids_expanded.float()).transpose(2, 3)
emb = torch.cat((freqs, freqs), dim=-1)
cos = emb.cos() * self.attention_scaling
sin = emb.sin() * self.attention_scaling
return cos.to(dtype=x.dtype), sin.to(dtype=x.dtype)-
1. 扩展
inv_freq以匹配多维位置编码pythoninv_freq_expanded = self.inv_freq[None, None, :, None].float().expand(3, position_ids.shape[1], -1, 1)self.inv_freq: 原始形状(dim // 2,)- 经过索引
[None, None, :, None]→(1, 1, dim//2, 1) .expand(3, position_ids.shape[1], -1, 1)→ 形状变为(3, bs, dim//2, 1)
-
2. 处理
position_idspythonposition_ids_expanded = position_ids[:, :, None, :].float() # shape (3, bs, 1, positions)- 经过索引
[:, :, None, :]→(3, bs, 1, seq_len)
- 经过索引
-
3. 计算频率
freqspythondevice_type = x.device.type if isinstance(x.device.type, str) and x.device.type != "mps" else "cpu" with torch.autocast(device_type=device_type, enabled=False): # Force float32 freqs = (inv_freq_expanded.float() @ position_ids_expanded.float()).transpose(2, 3)- 禁用
autocast:确保 RoPE 计算在float32下进行,避免精度损失(尤其在bfloat16训练时)。 - 矩阵乘法:
inv_freq_expanded @ position_ids_expanded(3, bs, dim//2, 1) @ (3, bs, 1, seq_len)→ 广播后得到(3, bs, dim//2, seq_len).transpose(2, 3)→(3, bs, seq_len, dim//2)
- 每个坐标维度(3 个)独立计算 RoPE 频率。
- 禁用
-
4. 构建
cos和sinpythonemb = torch.cat((freqs, freqs), dim=-1) # (3, bs, seq_len, dim) cos = emb.cos() * self.attention_scaling sin = emb.sin() * self.attention_scaling- 将
freqs拼接两次,得到完整维度dim(因为 RoPE 假设维度成对出现:[cos θ, sin θ])。 - 应用
attention_scaling - 最终
cos和sin形状:(3, bs, seq_len, dim)
- 将
Setp3: 解码器层 (Qwen2_5_VLDecoderLayer)
Qwen2.5-VL 模型中的一个解码器层 (Qwen2_5_VLDecoderLayer),并实现了标准的 Transformer 解码器结构 ,但针对 多模态输入 (文本 + 图像/视频)和 长上下文处理 进行了专门优化。
python
class Qwen2_5_VLDecoderLayer(GradientCheckpointingLayer):
def __init__(self, config: Qwen2_5_VLTextConfig, layer_idx: int):
super().__init__()
self.hidden_size = config.hidden_size
if config.use_sliding_window and config._attn_implementation != "flash_attention_2":
logger.warning_once(
f"Sliding Window Attention is enabled but not implemented for `{config._attn_implementation}`; "
"unexpected results may be encountered."
)
self.self_attn = Qwen2_5_VLAttention(config, layer_idx)
self.mlp = Qwen2MLP(config)
self.input_layernorm = Qwen2RMSNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=config.rms_norm_eps)
self.post_attention_layernorm = Qwen2RMSNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=config.rms_norm_eps)
self.attention_type = config.layer_types[layer_idx]
@deprecate_kwarg("past_key_value", new_name="past_key_values", version="4.58")
def forward(
self,
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
position_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
past_key_values: Optional[Cache] = None,
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = False,
use_cache: Optional[bool] = False,
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
position_embeddings: Optional[tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None, # necessary, but kept here for BC
**kwargs: Unpack[FlashAttentionKwargs],
) -> tuple[torch.FloatTensor, Optional[tuple[torch.FloatTensor, torch.FloatTensor]]]:
"""
Args:
hidden_states (`torch.FloatTensor`): input to the layer of shape `(batch, seq_len, embed_dim)`
attention_mask (`torch.FloatTensor`, *optional*): attention mask of size
`(batch, sequence_length)` where padding elements are indicated by 0.
output_attentions (`bool`, *optional*):
Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. See `attentions` under
returned tensors for more detail.
use_cache (`bool`, *optional*):
If set to `True`, `past_key_values` key value states are returned and can be used to speed up decoding
(see `past_key_values`).
past_key_values (`Cache`, *optional*): cached past key and value projection states
cache_position (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(sequence_length)`, *optional*):
Indices depicting the position of the input sequence tokens in the sequence.
position_embeddings (`tuple[torch.FloatTensor, torch.FloatTensor]`, *optional*):
Tuple containing the cosine and sine positional embeddings of shape `(batch_size, seq_len, head_dim)`,
with `head_dim` being the embedding dimension of each attention head.
kwargs (`dict`, *optional*):
Arbitrary kwargs to be ignored, used for FSDP and other methods that injects code
into the model
"""
residual = hidden_states
hidden_states = self.input_layernorm(hidden_states)
# Self Attention
hidden_states, self_attn_weights = self.self_attn(
hidden_states=hidden_states,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
position_ids=position_ids,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
output_attentions=output_attentions,
use_cache=use_cache,
cache_position=cache_position,
position_embeddings=position_embeddings,
**kwargs,
)
hidden_states = residual + hidden_states
# Fully Connected
residual = hidden_states
hidden_states = self.post_attention_layernorm(hidden_states)
hidden_states = self.mlp(hidden_states)
hidden_states = residual + hidden_states
outputs = (hidden_states,)
if output_attentions:
outputs += (self_attn_weights,)
return outputs-
1、Attention 子层(Pre-Norm + Residual)
pythonresidual = hidden_states hidden_states = self.input_layernorm(hidden_states) # Self Attention hidden_states, self_attn_weights = self.self_attn( hidden_states=hidden_states, attention_mask=attention_mask, position_ids=position_ids, past_key_values=past_key_values, output_attentions=output_attentions, use_cache=use_cache, cache_position=cache_position, position_embeddings=position_embeddings, **kwargs, ) hidden_states = residual + hidden_states- 先 LayerNorm :
input_layernorm对输入做 RMS 归一化 - 调用多模态注意力:内部使用 M-ROPE 处理 3D 位置,GQA 降低 KV 显存,滑动窗口限制注意力范围
- 残差连接:将原始输入加回注意力输出
- 先 LayerNorm :
-
2、MLP 子层(Pre-Norm + Residual)
pythonresidual = hidden_states hidden_states = self.post_attention_layernorm(hidden_states) hidden_states = self.mlp(hidden_states) hidden_states = residual + hidden_states- 第二个 LayerNorm :
post_attention_layernorm对 attention 输出归一化 - MLP 结构 :Qwen2 使用 SwiGLU 激活(比 ReLU/GELU 更强)
- 残差连接:将 attention 输出加回 MLP 输出
- 第二个 LayerNorm :
-
3、 输出
pythonoutputs = (hidden_states,) if output_attentions: outputs += (self_attn_weights,) return outputs
RMSNorm(Root Mean Square Layer Normalization)
RMSNorm(Root Mean Square Layer Normalization),用于替代标准 LayerNorm 的归一化方法。它在结构上比传统 LayerNorm 更简单、计算更高效,且在大语言模型中表现良好。
python
class Qwen2RMSNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, eps: float = 1e-6) -> None:
"""
Qwen2RMSNorm is equivalent to T5LayerNorm
"""
super().__init__()
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(hidden_size))
self.variance_epsilon = eps
def forward(self, hidden_states: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
input_dtype = hidden_states.dtype
hidden_states = hidden_states.to(torch.float32)
variance = hidden_states.pow(2).mean(-1, keepdim=True)
hidden_states = hidden_states * torch.rsqrt(variance + self.variance_epsilon)
return self.weight * hidden_states.to(input_dtype)RMSNorm 的数学原理
RMSNorm 的核心思想是:只对激活值进行缩放(scale),不进行平移(no bias/centering)。
对于一个向量 x ∈ R d x∈R^d x∈Rd,RMSNorm 定义为:
R M S N o r m ( x ) = x R M S ( x ) ⊙ γ RMSNorm(x)=\frac {x} {RMS(x)}⊙γ RMSNorm(x)=RMS(x)x⊙γ
其中:
- R M S ( x ) = 1 d ∑ i = 1 d x i 2 RMS(x)=\sqrt {\frac {1} {d}∑_{i=1}^d x_i^2} RMS(x)=d1∑i=1dxi2 是 均方根(Root Mean Square)
- γ ∈ R d γ∈R^d γ∈Rd是可学习的缩放参数(即
self.weight) - ⊙ ⊙ ⊙表示逐元素相乘(Hadamard product)
注意:没有减去均值(no centering),这是与标准 LayerNorm 的主要区别。
多头注意力模块 (Qwen2_5_VLAttention)
Qwen2.5-VL 模型中的多头注意力模块 (Qwen2_5_VLAttention),它针对 多模态输入 (文本 + 图像/视频)进行了专门设计,融合了 多模态旋转位置编码(M-ROPE)
python
class Qwen2_5_VLAttention(nn.Module):
"""
Multi-headed attention from 'Attention Is All You Need' paper. Modified to use sliding window attention: Longformer
and "Generating Long Sequences with Sparse Transformers".
"""
def __init__(self, config: Qwen2_5_VLTextConfig, layer_idx: Optional[int] = None):
super().__init__()
self.config = config
self.layer_idx = layer_idx
if layer_idx is None:
logger.warning_once(
f"Instantiating {self.__class__.__name__} without passing `layer_idx` is not recommended and will "
"to errors during the forward call, if caching is used. Please make sure to provide a `layer_idx` "
"when creating this class."
)
self.hidden_size = config.hidden_size
self.num_heads = config.num_attention_heads
self.head_dim = self.hidden_size // self.num_heads
self.num_key_value_heads = config.num_key_value_heads
self.num_key_value_groups = self.num_heads // self.num_key_value_heads
self.is_causal = True
self.attention_dropout = config.attention_dropout
self.rope_scaling = config.rope_scaling
self.scaling = self.head_dim**-0.5
if (self.head_dim * self.num_heads) != self.hidden_size:
raise ValueError(
f"hidden_size must be divisible by num_heads (got `hidden_size`: {self.hidden_size}"
f" and `num_heads`: {self.num_heads})."
)
self.q_proj = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.num_heads * self.head_dim, bias=True)
self.k_proj = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.num_key_value_heads * self.head_dim, bias=True)
self.v_proj = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.num_key_value_heads * self.head_dim, bias=True)
self.o_proj = nn.Linear(self.num_heads * self.head_dim, self.hidden_size, bias=False)
self.sliding_window = config.sliding_window if config.layer_types[layer_idx] == "sliding_attention" else None
self.rotary_emb = Qwen2_5_VLRotaryEmbedding(config=config)
@deprecate_kwarg("past_key_value", new_name="past_key_values", version="4.58")
def forward(
self,
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
position_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
past_key_values: Optional[Cache] = None,
output_attentions: bool = False,
use_cache: bool = False,
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
position_embeddings: Optional[tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None, # necessary, but kept here for BC
**kwargs: Unpack[FlashAttentionKwargs],
) -> tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor], Optional[tuple[torch.Tensor]]]:
bsz, q_len, _ = hidden_states.size()
query_states = self.q_proj(hidden_states)
key_states = self.k_proj(hidden_states)
value_states = self.v_proj(hidden_states)
query_states = query_states.view(bsz, q_len, -1, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
key_states = key_states.view(bsz, q_len, -1, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
value_states = value_states.view(bsz, q_len, -1, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
cos, sin = position_embeddings
query_states, key_states = apply_multimodal_rotary_pos_emb(
query_states, key_states, cos, sin, self.rope_scaling["mrope_section"]
)
if past_key_values is not None:
cache_kwargs = {"sin": sin, "cos": cos, "cache_position": cache_position} # Specific to RoPE models
key_states, value_states = past_key_values.update(key_states, value_states, self.layer_idx, cache_kwargs)
attention_interface: Callable = eager_attention_forward
if self.config._attn_implementation != "eager":
attention_interface = ALL_ATTENTION_FUNCTIONS[self.config._attn_implementation]
attn_output, attn_weights = attention_interface(
self,
query_states,
key_states,
value_states,
attention_mask,
dropout=0.0 if not self.training else self.attention_dropout,
scaling=self.scaling,
sliding_window=self.sliding_window,
position_ids=position_ids, # pass positions for FA2
**kwargs,
)
attn_output = attn_output.reshape(bsz, q_len, -1).contiguous()
attn_output = self.o_proj(attn_output)
return attn_output, attn_weights步骤一、线性投影 Q/K/V
python
query_states = self.q_proj(hidden_states) # (B, L, num_heads * head_dim)
key_states = self.k_proj(hidden_states) # (B, L, num_kv_heads * head_dim)
value_states = self.v_proj(hidden_states)步骤二、reshape 为多头格式
python
query_states = query_states.view(bsz, q_len, -1, self.head_prot).transpose(1, 2) # (B, H, L, D_h)
key_states = key_states.view(...).transpose(1, 2) # (B, KV_H, L, D_h)
value_states = ... # (B, KV_H, L, D_h)- 标准 BHSD 格式
(Batch, Head, Seq_Len, HeadDim)
步骤三、应用多模态 RoPE
python
cos, sin = position_embeddings
query_states, key_states = apply_multimodal_rotary_pos_emb(
query_states, key_states, cos, sin, self.rope_scaling["mrope_section"]
)Qwen2.5-VL 中用于多模态输入(文本 + 图像/视频)的 多模态旋转位置编码 (Multimodal Rotary Position Embedding, M-ROPE)
python
def apply_multimodal_rotary_pos_emb(q, k, cos, sin, mrope_section, unsqueeze_dim=1):
"""Applies Rotary Position Embedding with Multimodal Sections to the query and key tensors (https://qwenlm.github.io/blog/qwen2-vl/).
Explanation:
Multimodal 3D rotary position embedding is an extension to 1D rotary position embedding. The input embedding
sequence contains vision (images / videos) embedding and text embedding or just contains text embedding. For
vision embedding part, we apply rotary position embedding on temporal, height and width dimension separately.
Here we split the channel dimension to 3 chunks for the temporal, height and width rotary position embedding.
For text embedding part, we just apply 1D rotary position embedding. The three rotary position index (temporal,
height and width) of text embedding is always the same, so the text embedding rotary position embedding has no
difference with modern LLMs.
Args:
q (`torch.Tensor`): The query tensor.
k (`torch.Tensor`): The key tensor.
cos (`torch.Tensor`): The cosine part of the rotary embedding.
sin (`torch.Tensor`): The sine part of the rotary embedding.
position_ids (`torch.Tensor`):
The position indices of the tokens corresponding to the query and key tensors. For example, this can be
used to pass offsetted position ids when working with a KV-cache.
mrope_section(`List(int)`):
Multimodal rope section is for channel dimension of temporal, height and width in rope calculation.
unsqueeze_dim (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 1):
The 'unsqueeze_dim' argument specifies the dimension along which to unsqueeze cos[position_ids] and
sin[position_ids] so that they can be properly broadcasted to the dimensions of q and k. For example, note
that cos[position_ids] and sin[position_ids] have the shape [batch_size, seq_len, head_dim]. Then, if q and
k have the shape [batch_size, heads, seq_len, head_dim], then setting unsqueeze_dim=1 makes
cos[position_ids] and sin[position_ids] broadcastable to the shapes of q and k. Similarly, if q and k have
the shape [batch_size, seq_len, heads, head_dim], then set unsqueeze_dim=2.
Returns:
`tuple(torch.Tensor)` comprising of the query and key tensors rotated using the Rotary Position Embedding.
"""
mrope_section = mrope_section * 2
cos = torch.cat([m[i % 3] for i, m in enumerate(cos.split(mrope_section, dim=-1))], dim=-1).unsqueeze(
unsqueeze_dim
)
sin = torch.cat([m[i % 3] for i, m in enumerate(sin.split(mrope_section, dim=-1))], dim=-1).unsqueeze(
unsqueeze_dim
)
q_embed = (q * cos) + (rotate_half(q) * sin)
k_embed = (k * cos) + (rotate_half(k) * sin)
return q_embed, k_embed-
1. 扩展
mrope_sectionpythonmrope_section = mrope_section * 2 # [T_dim, H_dim, W_dim] → [T_dim, H_dim, W_dim, T_dim, H_dim, W_dim]将
head_dim切分为 6 段,对应:Temporal 前半段、Height 前半段、Width 前半段、Temporal 后半段、Height 后半段、Width 后半段
-
2. 对
cos和sin沿head_dim切分并重组pythoncos = torch.cat([m[i % 3] for i, m in enumerate(cos.split(mrope_section, dim=-1))], dim=-1).unsqueeze(unsqueeze_dim)- **
cos.split(mrope_section, dim=-1):**将cos(形状[3, B, L, D])沿head_dim(D)切分为 6 块:- 块0:Temporal RoPE 的前
T_dim对通道(即2*T_dim个浮点) - 块1:Height RoPE 的前
H_dim对 - 块2:Width RoPE 的前
W_dim对 - 块3:Temporal RoPE 的后
T_dim对 - 块4:Height RoPE 的后
H_dim对 - 块5:Width RoPE 的后
W_dim对
- 块0:Temporal RoPE 的前
m[i % 3]:分- 块0和块3对应 Temporal(时间)维度 的 RoPE 通道(前半段和后半段)
- 块1和块4应 Height(高度)维度 的 RoPE 通道(前半段和后半段)
- 块2和块5对应 Width(宽度)维度的 RoPE 通道(前半段和后半段)
- **
-
3. 对 Query 和 Key 应用旋转
pythonq_embed = (q * cos) + (rotate_half(q) * sin) k_embed = (k * cos) + (rotate_half(k) * sin)
步骤四、KV 缓存更新(推理时)
python
if past_key_values is not None:
cache_kwargs = {"sin": sin, "cos": cos, "cache_position": cache_position}
key_states, value_states = past_key_values.update(key_states, value_states, self.layer_idx, cache_kwargs)- 将当前 K/V 拼接到缓存中,用于下一次生成。
- 传递
cos/sin是为了支持 动态 RoPE (如YaRN在缓存扩展时更新位置编码)。
步骤五、选择注意力实现后端
python
attention_interface = eager_attention_forward # 默认 PyTorch 实现
if self.config._attn_implementation != "eager":
attention_interface = ALL_ATTENTION_FUNCTIONS[self.config._attn_implementation]- 支持多种后端:
"eager":标准实现(O(L²) 显存)"sdpa":torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention(自动选 FlashAttention / Mem-Efficient)"flash_attention_2":强制使用 FlashAttention-2(最快)
- 通过配置
config._attn_implementation切换。
步骤六、调用注意力函数
python
attn_output, attn_weights = attention_interface(
self,
query_states,
key_states,
value_states,
attention_mask,
dropout=...,
scaling=self.scaling,
sliding_window=self.sliding_window,
position_ids=position_ids,
**kwargs,
)
python
# "sdpa":torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention
attn_output = torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention(
query,
key,
value,
attn_mask=attention_mask,
dropout_p=dropout,
scale=scaling,
is_causal=is_causal,
**sdpa_kwargs,
)- **
is_causal(布尔值):**自动应用 下三角 causal mask(即只允许 token 关注自身及之前的位置)
步骤七、输出投影
python
attn_output = attn_output.reshape(bsz, q_len, -1).contiguous() # (B, L, H * D_h)
attn_output = self.o_proj(attn_output) # (B, L, D)- 合并头维度,投影回
hidden_size
多层感知机(MLP)模块
Qwen2.5-VL 模型中的多层感知机(MLP)模块 ,采用的是现代大语言模型(如 LLaMA、Qwen、Mistral 等)中广泛使用的 Gated MLP(或称 SwiGLU 激活结构)。
python
class Qwen2_5_VLMLP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config, bias: bool = False):
super().__init__()
self.hidden_size = config.hidden_size
self.intermediate_size = config.intermediate_size
self.gate_proj = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.intermediate_size, bias=bias)
self.up_proj = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.intermediate_size, bias=bias)
self.down_proj = nn.Linear(self.intermediate_size, self.hidden_size, bias=bias)
self.act_fn = ACT2FN[config.hidden_act]
def forward(self, hidden_state):
return self.down_proj(self.act_fn(self.gate_proj(hidden_state)) * self.up_proj(hidden_state))