文章目录
MOE基础版本
原理
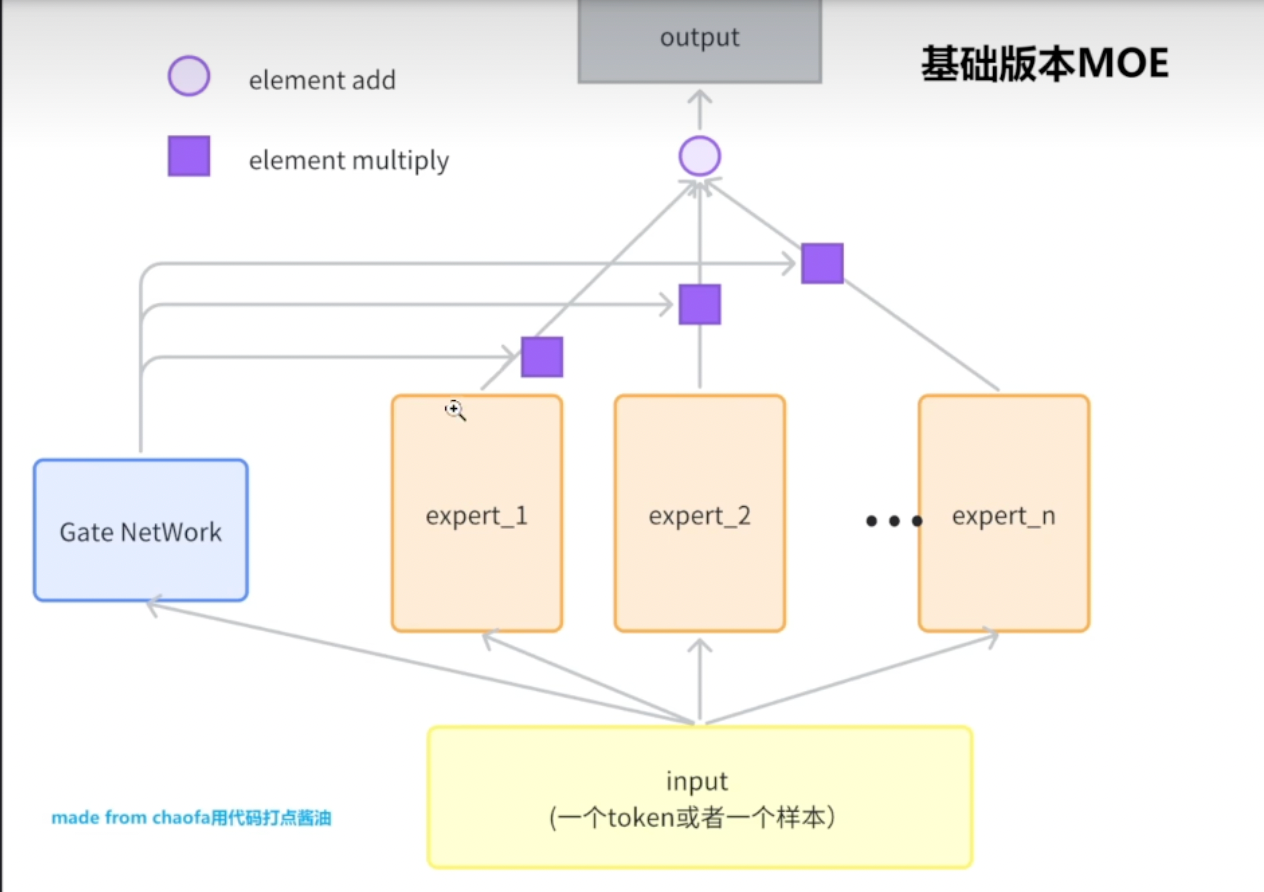
代码
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
## 用一个全连接层表示FFN层
class BasicExpert(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, feature_in, feature_out):
super().__init__()
self.fc = nn.Linear(feature_in, feature_out)
def forward(self, x):
return self.fc(x)
class BasicMoE(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, feature_in, feature_out,num_experts):
super().__init__()
self.gate = nn.Linear(feature_in, num_experts) # [batch_size, num_experts]
self.experts = nn.ModuleList([BasicExpert(feature_in, feature_out) for _ in range(num_experts)])
def forward(self, x):
gates = self.gate(x)
gates = F.softmax(gates, dim=1) #[batch_size, num_experts]
## 方式1:逐个相乘
outputs = []
for i, expert in enumerate(self.experts):
output = gates.squeeze(0)[i] * expert(x)
outputs.append(output)
output = torch.stack(outputs).sum(dim=0).squeeze()
print(output)
## 方式2:矩阵
# num_experts 个 [batch_size, 1, feature_out]
expert_outputs = [expert(x).unsqueeze(dim=1) for i, expert in enumerate(self.experts)]
expert_outputs = torch.concat(expert_outputs, dim=1) # [batch_size, num_experts, feature_out]
output2 = torch.bmm(gates.unsqueeze(1), expert_outputs).squeeze() # [batch_size, feature_out]
print(output2)
return output
moe = BasicMoE(10, 5, 2)
moe2 = BasicMoE2(10,5,2)
x = torch.randn(1, 10)
outputs1 = moe(x)Sparse MOE
原理
输入的token不再经过每一个专家处理, 而是选择topk个专家处理,其他专家不处理这个token;
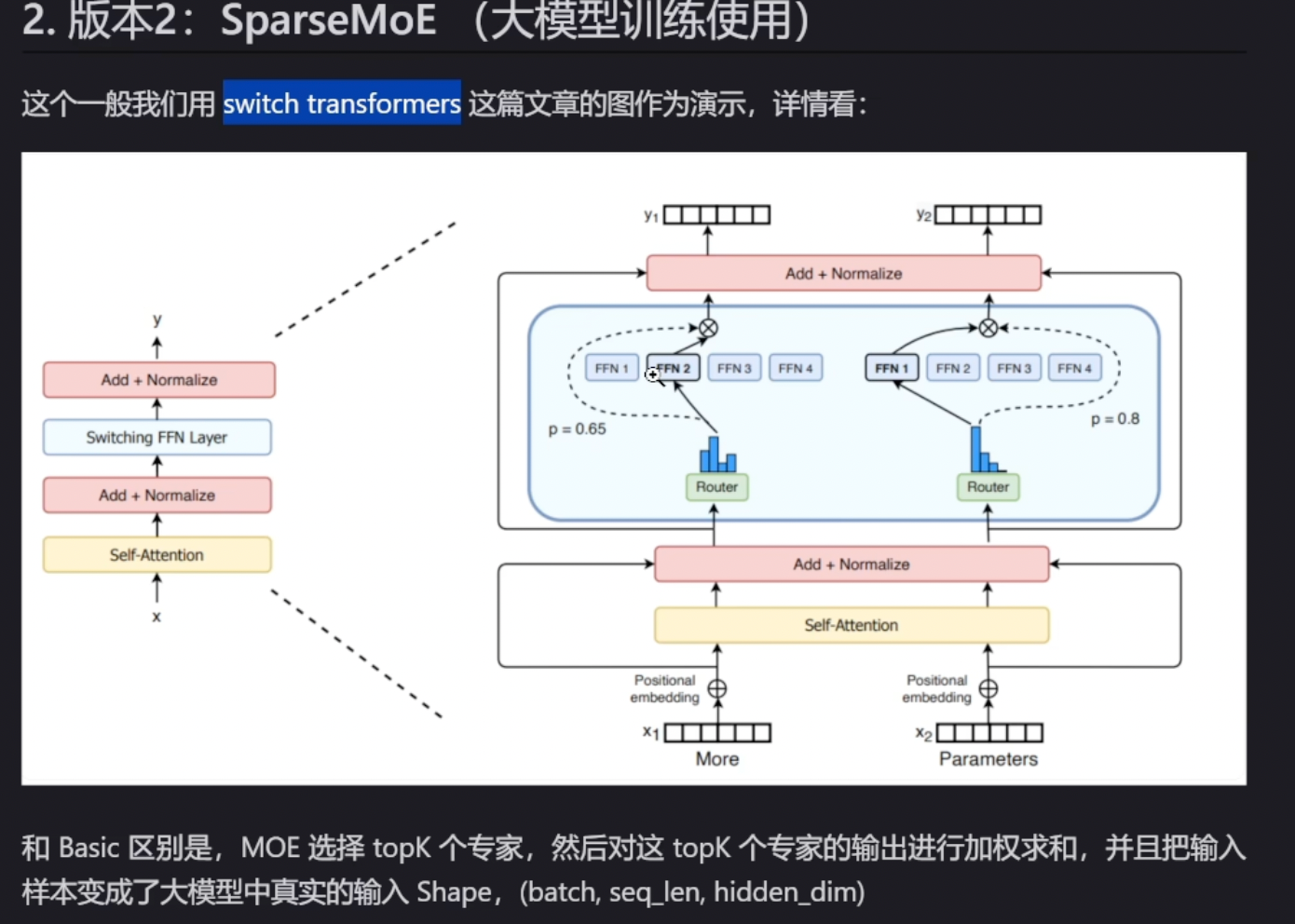
代码
python
# 主要参考自 mistral MOE 的实现
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class BasicExpert(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, feature_in, feature_out):
super().__init__()
self.fc = nn.Linear(feature_in, feature_out)
def forward(self, x):
return self.fc(x)
class MOERouter(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_dim, expert_number, top_k):
super().__init__()
self.gate = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, expert_number)
self.expert_number = expert_number
self.top_k = top_k
def forward(self, hidden_states):
# 计算路由logits
router_logits = self.gate(hidden_states) # shape is (b * s, expert_number) 8*4
# 计算专家经过softmax之后的概率
routing_probs = F.softmax(router_logits, dim=-1, dtype=torch.float)
# 计算topk的专家的输出
router_weights, selected_experts = torch.topk(
routing_probs, self.top_k, dim=-1
) # shape都是 (b * s, top_k)
# 专家权重归一化
router_weights = router_weights / router_weights.sum(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
router_weights = router_weights.to(hidden_states.dtype)
# 生成专家掩码
expert_mask = F.one_hot(
selected_experts,
num_classes=self.expert_number
) # shape是 (b * s, top_k, expert_number)
expert_mask = expert_mask.permute(2, 1, 0) # (expert_number, top_k, b * s)
return router_logits, router_weights, selected_experts, expert_mask
class MOEConfig:
def __init__(
self,
hidden_dim,
expert_number,
top_k,
shared_experts_number=2,
):
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.expert_number = expert_number
self.top_k = top_k
self.shared_experts_number = shared_experts_number
class SparseMOE(nn.Module):
# 稀疏 MOE 模型,这里每一个 token 都会过 topk 个专家,得到对应token 的 hidden_embeddings
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.hidden_dim = config.hidden_dim
self.expert_number = config.expert_number
self.top_k = config.top_k
self.experts = nn.ModuleList(
[
BasicExpert(self.hidden_dim, self.hidden_dim) for _ in range(self.expert_number)
]
)
self.router = MOERouter(self.hidden_dim, self.expert_number, self.top_k)
def forward(self, x):
# x shape is (b, s, hidden_dim)
batch_size, seq_len, hidden_dim = x.size()
# 合并前两个维度,因为不是 Sample 维度了,而是 token 维度, b * s 可以理解为总token数
hidden_states = x.view(-1, hidden_dim) # shape is(b * s, hidden_dim)
router_logits, router_weights, selected_experts_indices, expert_mask = self.router(hidden_states)
# 其中 selected_experts_indices shape 是 (b * s, top_k)
# 其中 expert_mask shape 是 (expert_number, top_k, b * s)
final_hidden_states = torch.zeros(
(batch_size * seq_len, hidden_dim),
dtype=hidden_states.dtype,
device=hidden_states.device
) # shape is (b * s, hidden_dim)
# 写代码的时候是 循环每个专家, 每个专家处理指定的token
for expert_idx in range(self.expert_number):
expert_layer = self.experts[expert_idx]
# expert_mask[expert_idx] shape 是 (top_k, b * s)
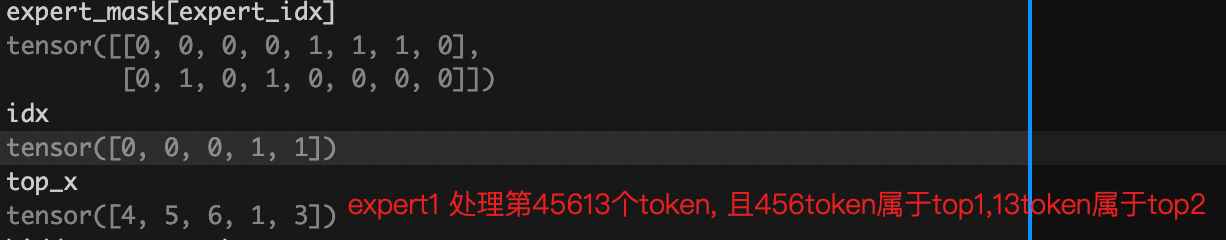
idx, top_x = torch.where(expert_mask[expert_idx])
# idx=[0,0,0,1,1] , topx = [4,5,6,1,3]
# idx 的值是 0 或 1, 表示这个 token 是作为当前专家的 top1 还是 top2 (0表示top1, 1表示top2)
# top_x 的值是 token 在 batch*seq_len 中的位置索引
# 例如对于 batch_size=2, seq_len=4 的输入:
# top_x 的值范围是 0-7, 表示在展平后的 8 个 token 中的位置
# idx 的值是 0/1, 表示这个 token 把当前专家作为其 top1/top2 专家
# hidden_states 的 shape 是 (b * s, hidden_dim)
# 需要取到 top_x 对应的 hidden_states
current_state = hidden_states.unsqueeze(0)[:, top_x, :].reshape(-1, hidden_dim) # (selected_token_number, hidden_dim)
# router_weight 的 shape 是 (b * s, top_k)
# current_hidden_states = expert_layer(
# current_state
# ) * router_weights[top_x, idx].unsqueeze(-1) # (selected_token_number, 1) 这里有广播
expert_out = expert_layer(current_state) # (selected_token_number, hidden_dim)= 5*16
select_weights = router_weights[top_x, idx].unsqueeze(-1) # (selected_token_number, 1)
current_hidden_states = expert_out * select_weights
# 把当前专家的输出加到 final_hidden_states 中
# 方式1 的写法性能更好,并且方式1容易
final_hidden_states.index_add_(0, top_x, current_hidden_states.to(hidden_states.dtype))
# 方式2
# final_hidden_states[top_x] += current_hidden_states.to(hidden_states.dtype)
# 方式2 的写法性能更差,并且方式2容易出现错误,+= 操作在处理重复索引时需要多次读写内存,可能会导致竞争条件
# 把 final_hidden_states 还原到原来的 shape
final_hidden_states = final_hidden_states.reshape(batch_size, seq_len, hidden_dim)
return final_hidden_states, router_logits # shape 是 (b * s, expert_number)
def test_token_level_moe():
x = torch.rand(2, 4, 16) # bs, seq_len, hidden_dim
config = MOEConfig(16, 4, 2) # hidden_dim, expert_number, top_k
token_level_moe = SparseMOE(config)
out = token_level_moe(x)
print(out[0].shape, out[1].shape)
test_token_level_moe()debug过程
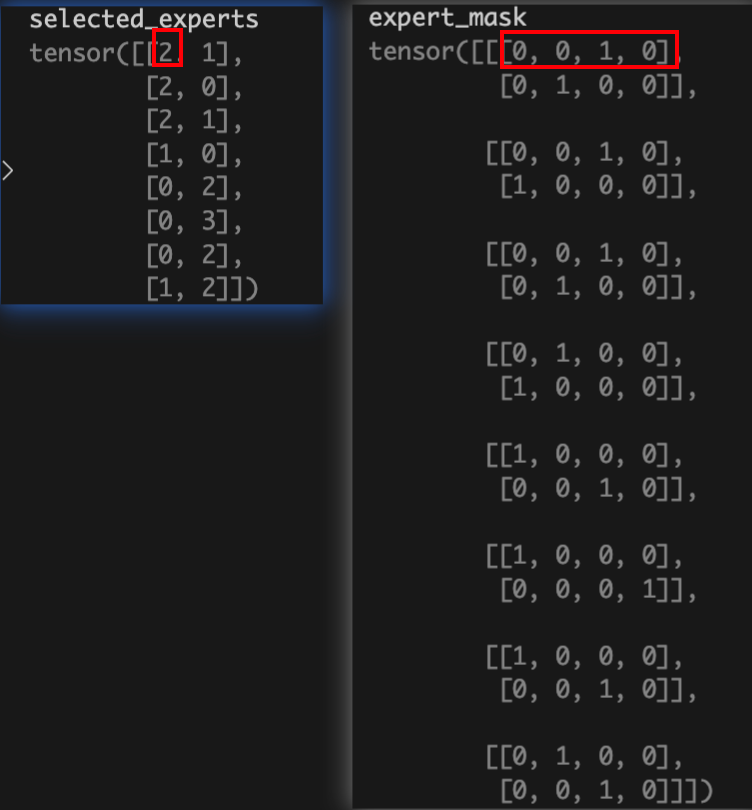
routing_probs:8 * 4 ,表示8个token, 4个专家的概率
routing_weights: 8 * 2, 表示8个token,每个token选择top2的专家

select_experts表示每个token选择的top2的专家的index;
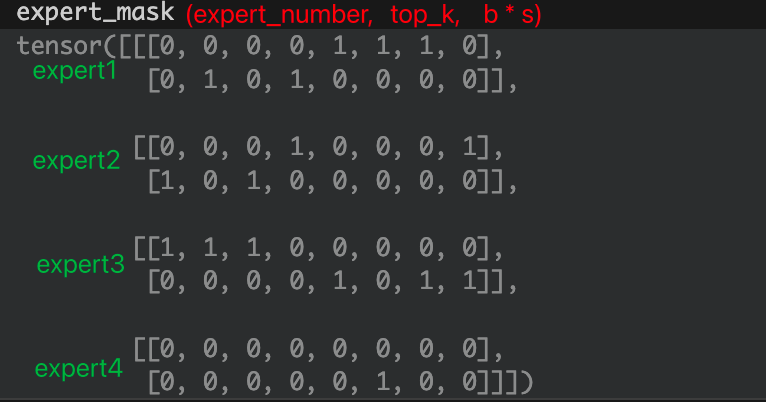
expert_mask : 把select_experts用one_hot表示;如2表示为[0,0,1,0]; 所以其shape为(b * s, top_k, expert_number)
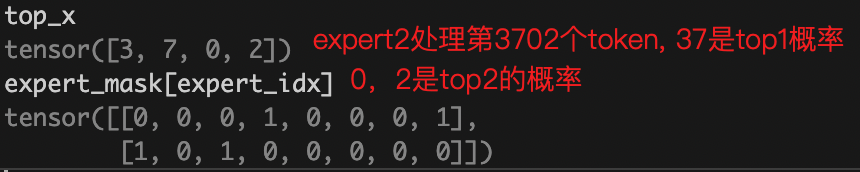
转置后的expert_mask, 表示共有4个expert,以 第一个expert 为例,第一行[0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0]表示专家1处理4,5,6 token, 且处理完后乘以top1的概率; 第二行[0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0]表示专家1处理1,3 token, 且处理完后乘以top2的概率;
DeepSeek MoE
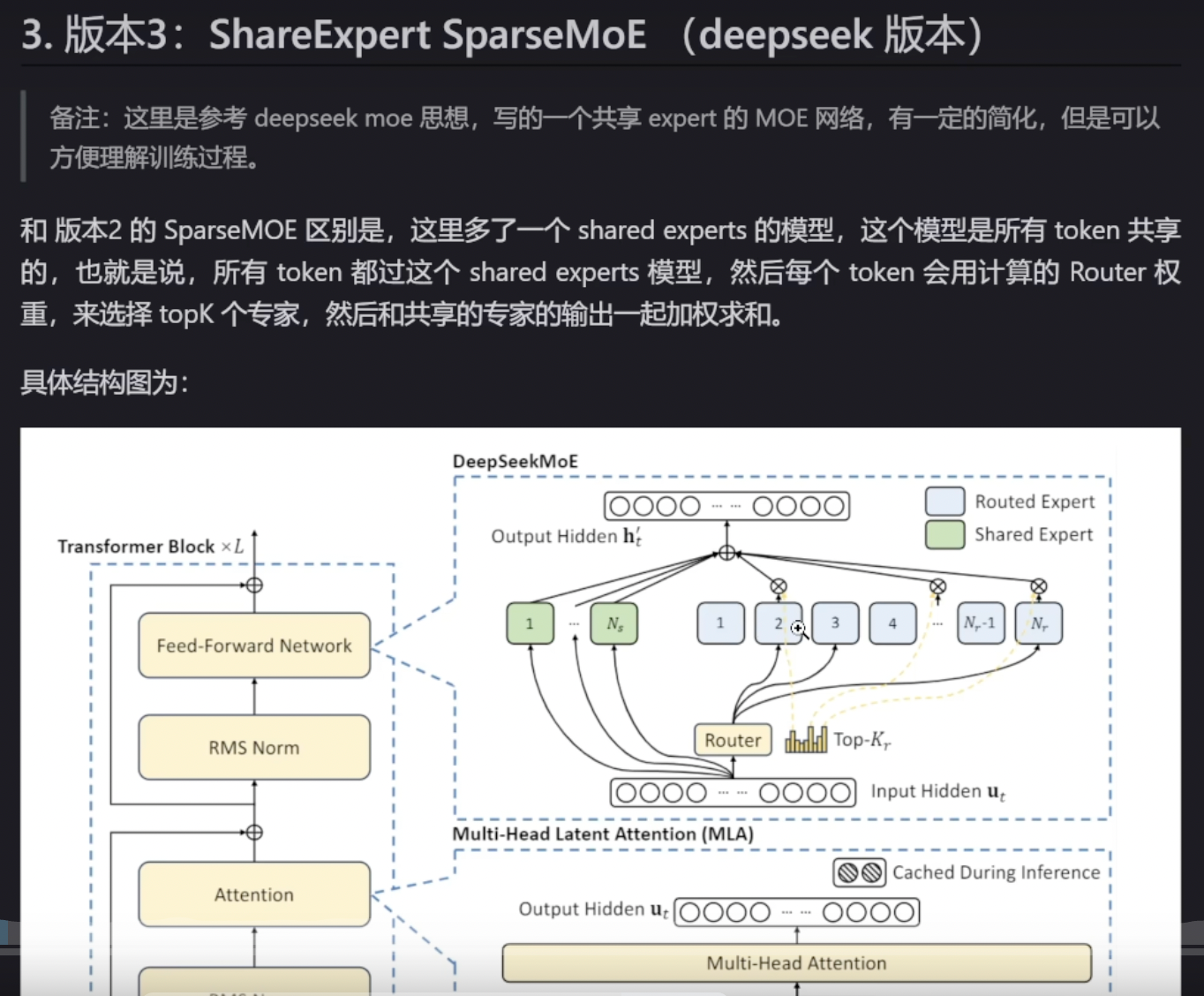
原理
代码
python
class ShareExpertMOE(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.moe_model = SparseMOE(config)
self.shared_experts = nn.ModuleList(
[
BasicExpert(
config.hidden_dim, config.hidden_dim
) for _ in range(config.shared_experts_number)
]
)
def forward(self, x):
# x shape 是 (b, s, hidden_dim)
# 首先过 moe 模型
sparse_moe_out, router_logits = self.moe_model(x)
# 针对的还是 x 的每一个
# 然后过 shared experts
shared_experts_out = [
expert(x) for expert in self.shared_experts
] # 每一个 expert 的输出 shape 是 (b, s, hidden_dim)
shared_experts_out = torch.stack(
shared_experts_out, dim=0
).sum(dim=0)
# 把 sparse_moe_out 和 shared_experts_out 加起来
return sparse_moe_out + shared_experts_out, router_logits
def test_share_expert_moe():
x = torch.rand(2, 4, 16)
config = MOEConfig(16, 2, 2)
share_expert_moe = ShareExpertMOE(config)
out = share_expert_moe(x)
print(out[0].shape, out[1].shape)
test_share_expert_moe()