我们常说的接口超时,主要指 WEB请求超时了,即HTTP请求超时了,HTTP请求对应的接口执行时间过长超时了。那么HTTP请求超时了,是我们理解的那样么?今天和大家一起深入剖析下。
一、分类
首先 HTTP请求超时了,这个超时至少有三个层面的超时:
- 前端请求定义的超时时间到了;
这个层面的超时,通常前端不会收到任何消息。
当然这和前端使用的框架 还有后端对于超时的处理代码 也有关系。
常见有几种情况: a.空消息返回 例如 使用 jquey 或者 axios
b.继续等待接收后端消息,例如 fetch.
- NGINX 或者 其它网关定义的超时时间到了;
这个层面的超时,网关会向接口调用方 发送 HTTP504错误。即前端会收到504的HTTP消息。
- 后端服务定义的超时时间到了,比如 Kestrive、Spring Boot 等等。
这个层面的超时,通常需要向前端发送408错误,但是这个消息需要由后端开发人员处理。
二、做法与影响
三个层面逐一分析他们的做法和影响。
1.前端超时,在使用不同框架的时影响还不一样。
1.1 JQUERY 和 AXIOS 这两个框架,会自动计算超时时间,并在超时的时候,主动向后端发送超时信号。超时时间 通过 timeout 这个参数定义。实现机制 通过调用协议层通用组件(例如 XMLHttpRequest ) 的 abort() 方法。
1.2 Fetch 这个框架没有timeout这个参数,没有超时控制。默认就是一直等待后端接口返回数据;
使用这个框架想要达到超时机制,就得自定行写代码计算超时时间是否到来,并在到来后,自行写代码断开连接,并通知后端已超时。实现机制可实现Fetch的AbortControl,底层也是通过调用协议层通用组件的 abort() 方法。
- 网关超时
网关超时会向前端发送HTTP 504消息,同时会向后端发送超时信号。前端收到504消息。
- 后端超时
此处仅以自己较为熟悉的 ASP.NET 来做分析。
ASP.NET 默认不处理超时机制,即前端调用或者网关定义了超时,且向后端发送了超时信息,我们在代码不做针对性处理的情况,后端代码会继续执行,不受超时信号的影响;
同时,ASP.NET为了后端能够针对超时做出响应,为我们提供了HttpContext.RequestAborted 对象,当前端或者网关发出了超时信号后, HttpContext.RequestAborted 状态值会变化改变,我们通过在接口代码里监听 HttpContext.RequestAborted 状态值 来进行针对性处理,比如 中断代码执行,回滚事务 等等。对于 接口代码里 启用了多线程的情况,多线程的相关方法里 也支持传入此状态值,从而达到控制子线程的目的。这段相对有点抽象,附一段代码给大家参考。
cs
[HttpGet("cycle-delay-with-cancel-check/{seconds}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> CycleDelayWithCancelCheck(int seconds, [FromQuery]string requestId = null)
{
// Generate a unique request ID if not provided
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(requestId))
{
requestId = Guid.NewGuid().ToString();
}
try
{
// 检查请求是否已被取消
if (HttpContext.RequestAborted.IsCancellationRequested)
{
return StatusCode(408, new { error = "Request already cancelled", requestId = requestId });
}
// 将秒数转换为总毫秒数,分段延迟以检查取消
int totalMilliseconds = seconds * 1000;
int interval = 1000; // 每秒检查一次
for (int i = 0; i < seconds; i++)
{
// 检查请求是否已被取消
if (HttpContext.RequestAborted.IsCancellationRequested)
{
var cancelledResult = StatusCode(408, new { error = "--cancelled", secondsCompleted = i, requestId = requestId });
// 发送SignalR消息,但要处理可能的连接问题
try
{
await _hubContext.Clients.Group($"request-{requestId}").SendAsync("ReceiveStatusUpdate", "cancelled", $"-- cancelled after {i} seconds", requestId);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// 记录错误但不抛出,因为HTTP响应已经发送
Console.WriteLine($"SignalR send failed: {ex.Message}");
}
return cancelledResult;
}
await Task.Delay(interval, HttpContext.RequestAborted);
// Send periodic updates with request ID
try
{
await _hubContext.Clients.Group($"request-{requestId}").SendAsync("ReceiveStatusUpdate", "progress", $"Processing... {i+1}/{seconds} seconds completed", requestId);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"SignalR progress send failed: {ex.Message}");
}
}
// 检查请求是否已被取消
if (HttpContext.RequestAborted.IsCancellationRequested)
{
var cancelledResult = StatusCode(408, new { error = " cancelled ", requestId = requestId });
// 发送SignalR消息,但要处理可能的连接问题
try
{
await _hubContext.Clients.Group($"request-{requestId}").SendAsync("ReceiveStatusUpdate", "cancelled", " -- cancelled ", requestId);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// 记录错误但不抛出,因为HTTP响应已经发送
Console.WriteLine($"SignalR send failed: {ex.Message}");
}
return cancelledResult;
}
var successResult = Ok(new { message = $" -- completed for {seconds} seconds", timestamp = DateTime.Now, requestId = requestId });
// 发送SignalR消息,但要处理可能的连接问题
try
{
await _hubContext.Clients.Group($"request-{requestId}").SendAsync("ReceiveStatusUpdate", "success", $" -- completed for {seconds} seconds", requestId);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// 记录错误但不抛出,因为HTTP响应已经发送
Console.WriteLine($"SignalR send failed: {ex.Message}");
}
return successResult;
}
catch (OperationCanceledException)
{
var exceptionResult = StatusCode(408, new { error = "-- cancelled", requestId = requestId });
// 发送SignalR消息,但要处理可能的连接问题
try
{
await _hubContext.Clients.Group($"request-{requestId}").SendAsync("ReceiveStatusUpdate", "cancelled", "--Task.Delay cancelled", requestId);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// 记录错误但不抛出,因为HTTP响应已经发送
Console.WriteLine($"SignalR send failed: {ex.Message}");
}
return exceptionResult;
}
}好了,超时这块就先分析到这里,如果需要对应的测试代码可以联系我。 Q304418200
三、IIS 、Kestrive和AI 吐槽点
末了,吐槽一下分析原理和写测试代码时遇到的几个坑点
-
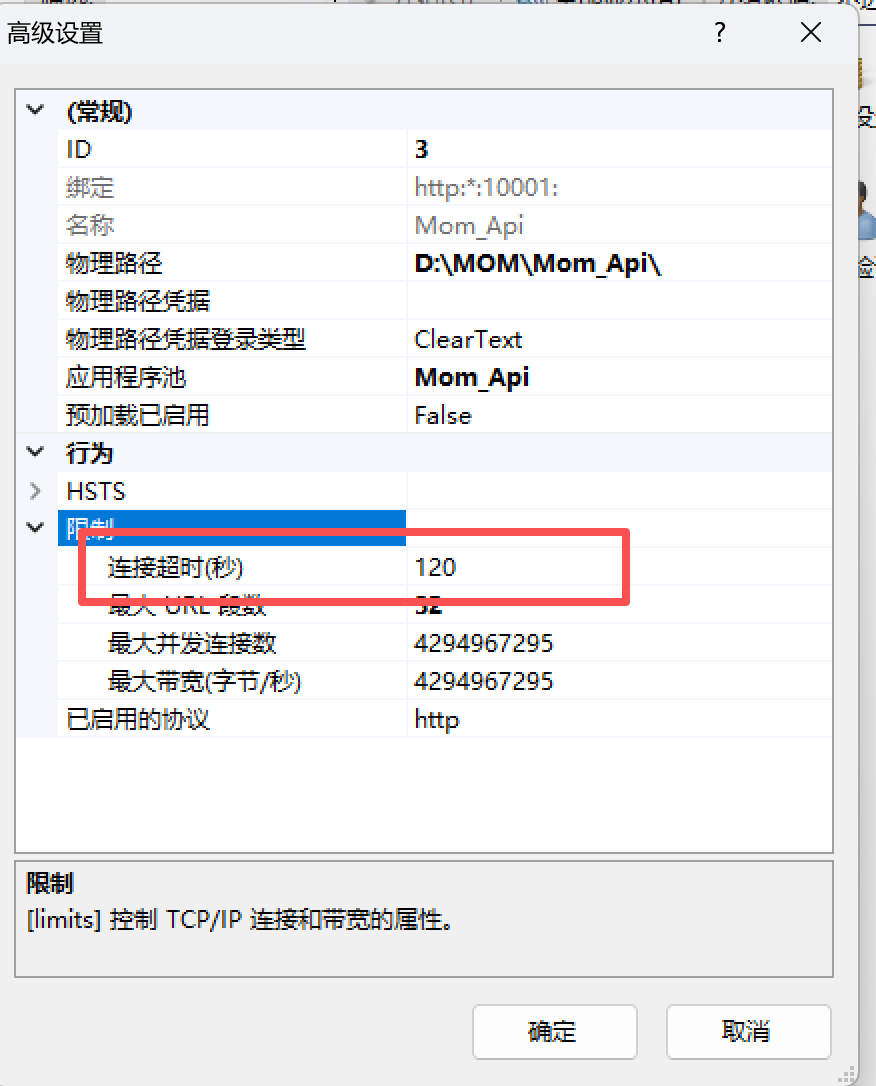
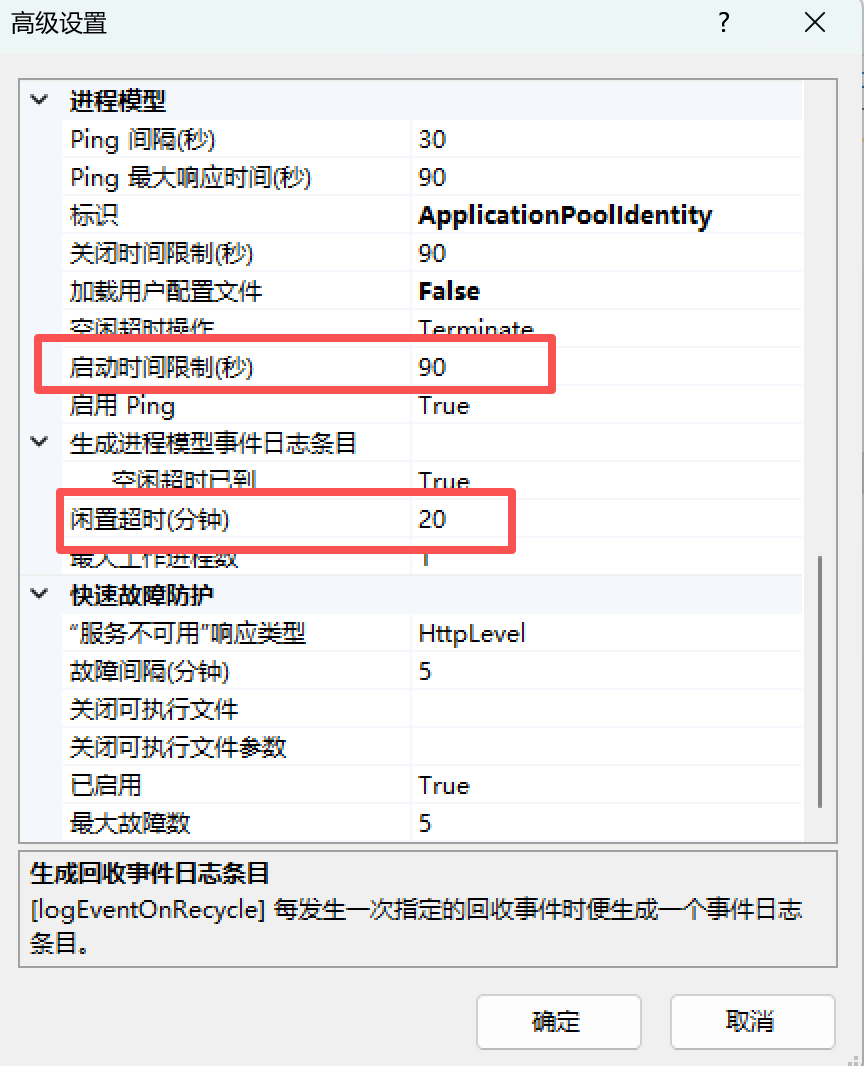
IIS设置界面上的超时的超时设置都不是我们想要的接口运行超时时间。见文末附图。
-
Kestrive 提供了对应IIS图上几个超时设置的方法,但是没有提供运行超时的设置属性(因为它想让我们通过 监听 HttpContext.RequestAborted 来实现 )。
-
AI 一个劲的给出错误解释 和 错误代码, 先后试过 豆包、文心一言、DEEPSEEK、通义灵码包括微软自家的Copilot , 都给出了无效代码和 根本不存在的错误代码
cs
//无效代码==>设置的不是运行时间超时
builder.WebHost.ConfigureKestrel(options =>
{
options.Limits.RequestHeadersTimeout = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(20);
options.Limits.KeepAliveTimeout = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(20);
});
//错误代码==>根本不存在 DefautRequestTimeout 属性。
builder.WebHost.ConfigureKestrel(options =>
{
options.DefautRequestTimeout = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(20);
});