文章目录
- [1. Compound协议概述](#1. Compound协议概述)
-
- [1.1 什么是Compound](#1.1 什么是Compound)
- [1.2 Compound发展历程](#1.2 Compound发展历程)
- [1.3 技术栈总览](#1.3 技术栈总览)
- [2. 核⼼业务模型详解](#2. 核⼼业务模型详解)
-
- [2.1 存款业务(Supply)](#2.1 存款业务(Supply))
-
- [2.1.1 cToken机制 - Compound的核⼼创新](#2.1.1 cToken机制 - Compound的核⼼创新)
- [2.1.2 存款流程图](#2.1.2 存款流程图)
- [2.1.3 核⼼知识点:Exchange Rate(汇率)](#2.1.3 核⼼知识点:Exchange Rate(汇率))
- [2.1.4 Solidity核⼼代码实现](#2.1.4 Solidity核⼼代码实现)
- [2.1.5 利息计算机制](#2.1.5 利息计算机制)
- [2.2 借款业务(Borrow)](#2.2 借款业务(Borrow))
-
- [2.2.1 超额抵押机制](#2.2.1 超额抵押机制)
- [2.2.2 借款流程图](#2.2.2 借款流程图)
- [2.2.3 借款核⼼代码](#2.2.3 借款核⼼代码)
- [2.3 清算机制(Liquidation)](#2.3 清算机制(Liquidation))
-
- [2.3.1 清算条件](#2.3.1 清算条件)
- [2.3.2 清算流程图](#2.3.2 清算流程图)
- [2.3.3 清算核⼼代码](#2.3.3 清算核⼼代码)
1. Compound协议概述
1.1 什么是Compound
Compound是以太坊上最早、最具影响⼒的去中⼼化借贷协议之⼀,由Robert Leshner和Geoffrey Hayes于2018年创⽴。作为DeFi领域的先驱,Compound开创性地引⼊了算法货币市场(Algorithmic Money Market)的概念,通过智能合约⾃动化管理借贷市场的供需关系。
核⼼定位:
- 去中⼼化货币市场:⽆需许可的开放式借贷平台,任何⼈都可以参与
- 算法利率协议:基于供需关系⾃动调整利率,⽆需⼈⼯⼲预
- 流动性聚合器:创建共享流动性池,提⾼资⾦使⽤效率
- DeFi基础设施:为其他DeFi协议提供借贷底层服务
关键数据(2024年Q4):
- TVL(总锁仓量):$28亿
- ⽀持资产:20+ 种主流加密货币
- 累计借贷量:$2000亿+
- 活跃⽤户:50万+
- 协议总收⼊:$1.8亿+
- 治理代币:COMP
1.2 Compound发展历程
版本演进
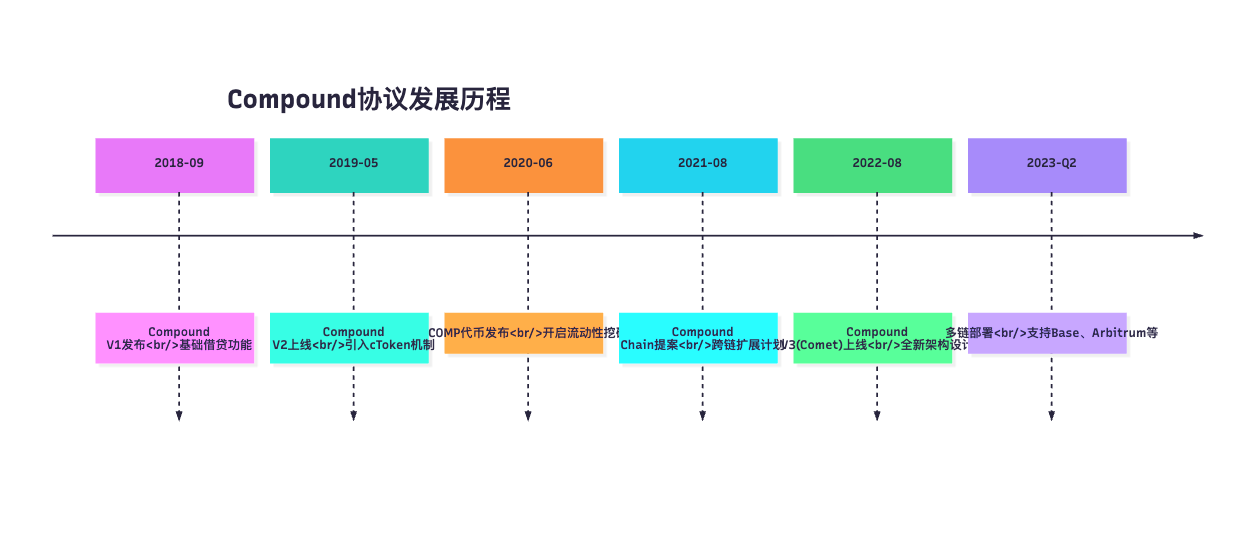
重要⾥程碑:
-
- 2019年5⽉ - Compound V2:引⼊cToken计息模型,成为⾏业标准
-
- 2020年6⽉ - COMP代币:开启"流动性挖矿"热潮,引发DeFi Summer
-
- 2022年8⽉ - Compound V3:推出Comet架构,专注于效率和安全
1.3 技术栈总览
智能合约层(Solidity)
- Solidity 0.8.x: 核⼼合约开发语⾔
- Hardhat: 开发、测试、部署框架
- OpenZeppelin: 安全合约库
- Chainlink: 价格预⾔机
- Ethers.js: 以太坊交互库
后端服务层(Golang)
c
- Go 1.20+: 后端服务开发语⾔
- Gin: HTTP框架
- go-ethereum: 以太坊客户端
- GORM: ORM框架
- PostgreSQL: 数据存储
- Redis: 缓存层
- Kafka: 消息队列前端层(TypeScript)
- React 18: UI框架
- Compound.js: 官⽅SDK
- Ethers.js: 区块链交互
- Web3-React: 钱包连接
2. 核⼼业务模型详解
2.1 存款业务(Supply)
存款是Compound协议的基础功能。⽤户将资产存⼊Compound,即可开始赚取利息。与传统⾦融不同,Compound的利息是实时累积的,每个以太坊区块(约12秒)都会更新⼀次。
2.1.1 cToken机制 - Compound的核⼼创新
什么是cToken?
cToken(Compound Token)是Compound最重要的创新之⼀。当⽤户存⼊资产时,会收到对应的cToken作为存款凭证:
- 存⼊ETH → 获得cETH
- 存⼊USDC → 获得cUSDC
- 存⼊DAI → 获得cDAI
cToken的三⼤特性:
-
- 计息凭证:cToken代表⽤户在资⾦池中的份额,⾃动累积利息
-
- ERC20代币:可以转账、交易,甚⾄在其他DeFi协议中使⽤
-
- 汇率增⻓:cToken与底层资产的兑换率不断增加,反映利息累积
cToken与底层资产的关系:
c
初始状态:
- 存⼊ 1000 USDC
- 获得 50,000 cUSDC
- 当前汇率:1 cUSDC = 0.02 USDC
30天后:
- cUSDC数量:50,000(不变)
- 新汇率:1 cUSDC = 0.0201 USDC
- 可赎回:50,000 × 0.0201 = 1,005 USDC
- 利息收益:5 USDC2.1.2 存款流程图
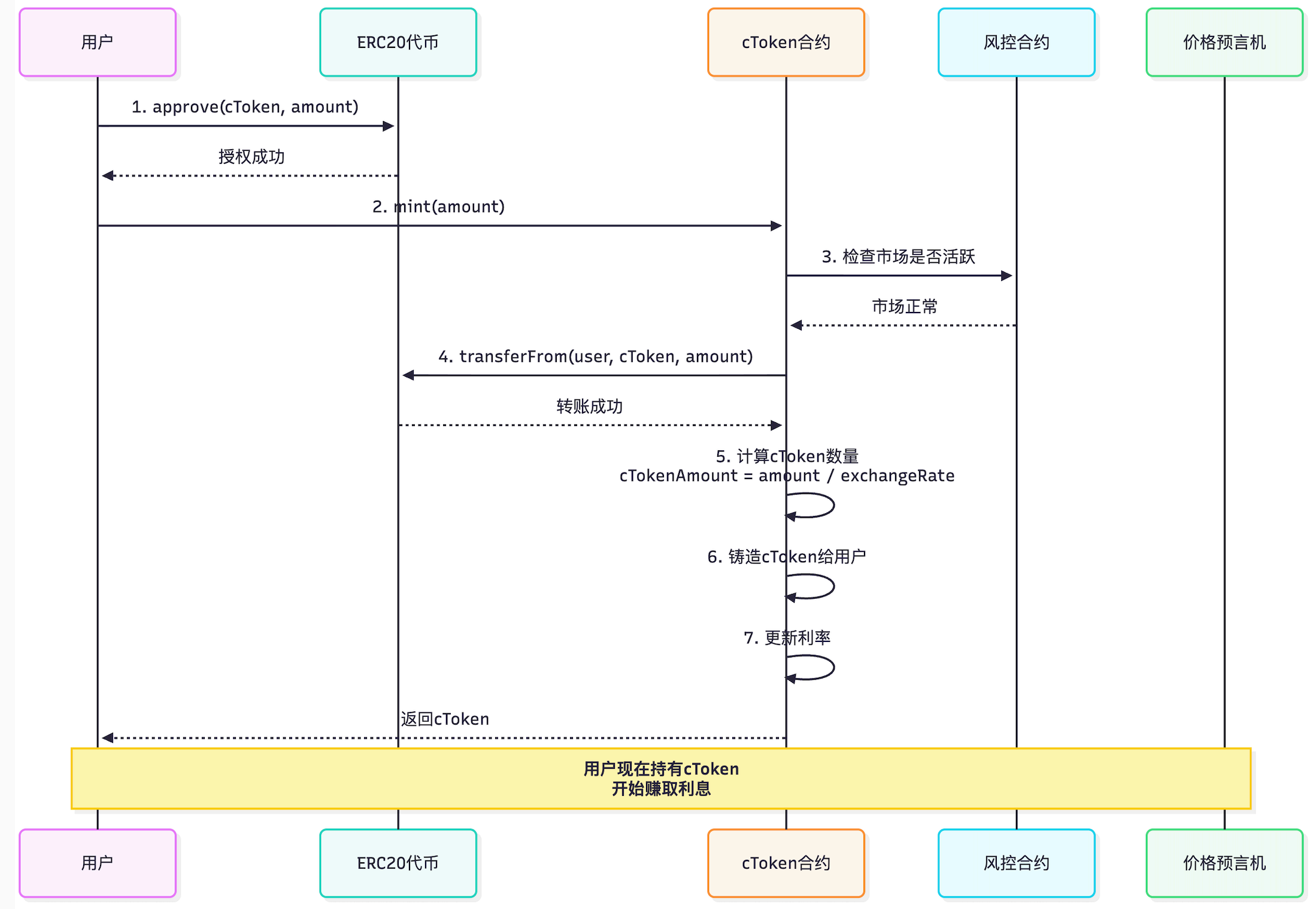
2.1.3 核⼼知识点:Exchange Rate(汇率)
汇率计算公式:
Exchange Rate是cToken机制的核⼼,决定了cToken和底层资产之间的兑换⽐例。
exchangeRate = (totalCash + totalBorrows - totalReserves) / totalSupply
其中:
- totalCash: 资⾦池中的现⾦余额
- totalBorrows: 总借款量(包含累积利息)
- totalReserves: 协议储备⾦
- totalSupply: cToken总供应量
实际计算示例:
c
cUSDC市场状态:
- totalCash: 10,000,000 USDC(池中剩余)
- totalBorrows: 5,000,000 USDC(已被借出)
- totalReserves: 50,000 USDC(协议储备)
- totalSupply: 750,000,000 cUSDC
exchangeRate = (10,000,000 + 5,000,000 - 50,000) / 750,000,000
= 14,950,000 / 750,000,000
= 0.0199333... USDC per cUSDC
⽤户操作:
- Alice存⼊ 1,000 USDC
- 获得cUSDC数量 = 1,000 / 0.0199333 = 50,167 cUSDC
- ⼀个⽉后,exchangeRate增⻓到 0.0201
- Alice赎回:50,167 × 0.0201 = 1,008.36 USDC
- 利息收益:8.36 USDC2.1.4 Solidity核⼼代码实现
c
// CErc20.sol - cToken核⼼实现
pragma solidity ^0.8.10;
contract CErc20 {
// 底层ERC20代币地址
address public underlying;
// cToken总供应量
uint256 public totalSupply;
// ⽤户cToken余额
mapping(address => uint256) internal accountTokens;
// 借款信息
mapping(address => uint256) internal accountBorrows;
// 利率累积索引
uint256 public borrowIndex;
/**
* @notice 存款函数(铸造cToken)
* @param mintAmount 存⼊的底层资产数量
* @return 0表示成功
*/
function mint(uint256 mintAmount) external returns (uint) {
// 1. 触发利率更新
accrueInterest();
// 2. 计算当前汇率
uint256 exchangeRate = exchangeRateCurrent();
// 3. 计算应铸造的cToken数量
// cTokenAmount = mintAmount / exchangeRate
uint256 mintTokens = (mintAmount * 1e18) / exchangeRate;
// 4. 转移底层资产到合约
require(
doTransferIn(msg.sender, mintAmount) == 0,
"Transfer failed"
);
// 5. 铸造cToken给⽤户
totalSupply += mintTokens;
accountTokens[msg.sender] += mintTokens;
// 6. 触发事件
emit Mint(msg.sender, mintAmount, mintTokens);
return 0;
}
/**
* @notice 计算当前汇率
* @return 当前的cToken汇率(scaled by 1e18)
*/
function exchangeRateCurrent() public returns (uint256) {
// 先累积利息
accrueInterest();
// 如果没有cToken被铸造,返回初始汇率
if (totalSupply == 0) {
return initialExchangeRate; // 通常是 0.02e18
}
// 计算汇率
uint256 cash = getCash();
uint256 borrows = totalBorrows;
uint256 reserves = totalReserves;
// exchangeRate = (cash + borrows - reserves) / totalSupply
return ((cash + borrows - reserves) * 1e18) / totalSupply;
}
/**
* @notice 赎回函数(销毁cToken换回底层资产)
* @param redeemTokens 要赎回的cToken数量
* @return 0表示成功
*/
function redeem(uint256 redeemTokens) external returns (uint) {
// 1. 触发利率更新
accrueInterest();
// 2. 计算当前汇率
uint256 exchangeRate = exchangeRateCurrent();
// 3. 计算可赎回的底层资产数量
uint256 redeemAmount = (redeemTokens * exchangeRate) / 1e18;
// 4. 检查是否有⾜够的现⾦
require(getCash() >= redeemAmount, "Insufficient cash");
// 5. 检查赎回后的账户健康度
require(
comptroller.redeemAllowed(address(this), msg.sender, redeemTokens) == 0,
"Redemption not allowed"
);
// 6. 销毁cToken
totalSupply -= redeemTokens;
accountTokens[msg.sender] -= redeemTokens;
// 7. 转移底层资产给⽤户
require(
doTransferOut(msg.sender, redeemAmount) == 0,
"Transfer out failed"
);
emit Redeem(msg.sender, redeemAmount, redeemTokens);
return 0;
}
/**
* @notice 累积利息
* @dev 每次状态变更前都要调⽤
*/
function accrueInterest() public returns (uint) {
uint256 currentBlockNumber = block.number;
uint256 accrualBlockNumberPrior = accrualBlockNumber;
// 如果在同⼀区块内,⽆需重复计算
if (accrualBlockNumberPrior == currentBlockNumber) {
return 0;
}
// 计算经过的区块数
uint256 blockDelta = currentBlockNumber - accrualBlockNumberPrior;
// 获取当前借款利率
uint256 borrowRate = interestRateModel.getBorrowRate(
getCash(),
totalBorrows,
totalReserves
);
// 计算利息累积倍数
// simpleInterestFactor = borrowRate * blockDelta
uint256 simpleInterestFactor = borrowRate * blockDelta;
// 计算新增利息
uint256 interestAccumulated = (simpleInterestFactor * totalBorrows) / 1e18;
// 更新总借款(包含新增利息)
totalBorrows += interestAccumulated;
// 更新储备⾦(协议收⼊)
totalReserves += (interestA ccumulated * reserveFactorMantissa) / 1e18;
// 更新借款索引
borrowIndex += (simpleInterestFactor * borrowIndex) / 1e18;
// 更新区块号
accrualBlockNumber = currentBlockNumber;
return 0;
}
/**
* @notice 获取账户当前余额(包含利息)
* @param account 账户地址
* @return cToken余额
*/
function balanceOf(address account) external view returns (uint256) {
return accountTokens[account];
}
/**
* @notice 获取账户可赎回的底层资产数量
* @param account 账户地址
* @return 底层资产数量
*/
function balanceOfUnderlying(address account) external returns (uint256) {
uint256 exchangeRate = exchangeRateCurrent();
uint256 cTokenBalance = accountTokens[account];
return (cTokenBalance * exchangeRate) / 1e18;
}
/**
* @notice 获取资⾦池中的现⾦余额
* @return 现⾦数量
*/
function getCash() public view returns (uint256) {
return ERC20(underlying).balanceOf(address(this));
}
}2.1.5 利息计算机制
区块级利息累积:
Compound的利息计算与Aave不同,采⽤的是区块级累积⽽⾮秒级累积。
利息计算公式:
borrowIndex(n) = borrowIndex(n-1) × (1 + borrowRate × blocks)
⽤户利息 = 本⾦ × (当前borrowIndex / 存款时borrowIndex - 1)
示例:
Alice在区块 #1000 存⼊ 1000 USDC
当时borrowIndex = 1.0
当时exchangeRate = 0.02
区块 #2000(约2⼩时后):borrowIndex = 1.00015
exchangeRate = 0.02003
Alice的cToken: 50,000
可赎回: 50,000 × 0.02003 = 1,001.5 USDC
利息: 1.5 USDC
2.2 借款业务(Borrow)
借款是Compound的核⼼功能,允许⽤户以超额抵押的⽅式借出其他资产。
2.2.1 超额抵押机制
为什么必须超额抵押?
与传统⾦融不同,DeFi借贷⽆法进⾏信⽤评估和法律追索,因此必须要求借款⼈提供价值⾼于借款的抵押品。
Collateral Factor(抵押因⼦):
Compound使⽤Collateral Factor来定义每种资产的借款能⼒:
可借款额度 = Σ(抵押品价值 × Collateral Factor)
示例:
- ETH的Collateral Factor: 75%
- USDC的Collateral Factor: 80%
- LINK的Collateral Factor: 60%
计算:
- Alice抵押 10 ETH @ 3,000 = 30,000
- ETH的CF = 75%
- 最⼤借款额度 = 30,000 × 75% = 22,500
2.2.2 借款流程图
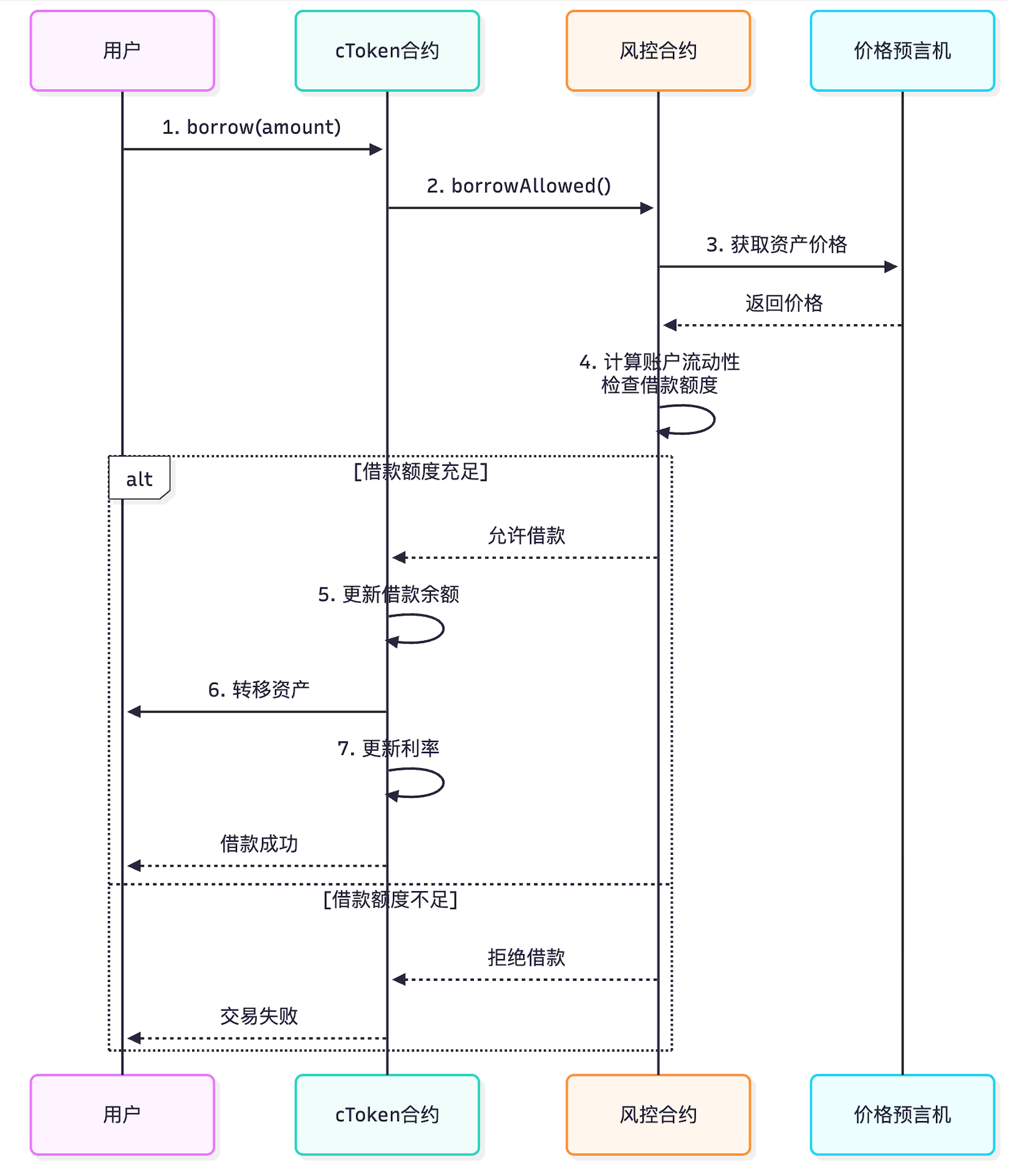
2.2.3 借款核⼼代码
c
/**
* @notice 借款函数
* @param borrowAmount 借款数量
* @return 0表示成功
*/
function borrow(uint256 borrowAmount) external returns (uint) {
// 1. 累积利息
accrueInterest();
// 2. 检查是否允许借款
require(
comptroller.borrowAllowed(address(this), msg.sender, borrowAmount) == 0,
"Borrow not allowed"
);
// 3. 检查资⾦池是否有⾜够现⾦
require(getCash() >= borrowAmount, "Insufficient cash");
// 4. 计算新的借款本⾦
// 需要考虑之前的借款和累积的利息
uint256 accountBorrowsPrev = borrowBalanceStored(msg.sender);
uint256 accountBorrowsNew = accountBorrowsPrev + borrowAmount;
// 5. 更新⽤户借款记录
accountBorrows[msg.sender] = BorrowSnapshot({
principal: accountBorrowsNew,
interestIndex: borrowIndex
});
// 6. 更新总借款量
totalBorrows += borrowAmount;
// 7. 转移资产给借款⼈
require(
doTransferOut(msg.sender, borrowAmount) == 0,
"Transfer out failed"
);
emit Borrow(msg.sender, borrowAmount, accountBorrowsNew, totalBorrows);
return 0;
}
/**
* @notice 计算账户当前借款余额(包含利息)
* @param account 账户地址
* @return 借款余额
*/
function borrowBalanceCurrent(address account) external returns (uint256) {
accrueInterest();
return borrowBalanceStored(account);
}
/**
* @notice 获取存储的借款余额(内部函数)
*/
function borrowBalanceStored(address account) internal view returns (uint256) {
BorrowSnapshot storage borrowSnapshot = accountBorrows[account];
// 如果没有借款,返回0
if (borrowSnapshot.principal == 0) {
return 0;
}
// 计算累积利息
// currentBalance = principal × (currentIndex / borrowSnapshotIndex)
uint256 principalTimesIndex = borrowSnapshot.principal * borrowIndex;
return principalTimesIndex / borrowSnapshot.interestIndex;
}2.3 清算机制(Liquidation)
清算是Compound⻛险管理的核⼼机制,确保协议的偿付能⼒。
核心是当借款人抵押资产价值不足以覆盖债务时,允许第三方(清算人)代借款人偿还债务,同时清算人获取借款人抵押资产作为回报,以此规避坏账风险
2.3.1 清算条件
Shortfall(资⾦缺⼝):
Compound使⽤"Shortfall"概念判断是否可以清算:
c
账户流动性 = Σ(抵押品价值 × CF) - Σ(借款价值)
Shortfall = max(0, -账户流动性)
清算条件:
- Shortfall > 0:可以被清算
- Shortfall = 0:临界状态
- Shortfall < 0(即流动性 > 0):安全清算示例:
初始状态:
- 抵押:10 ETH @ 3,000 = 30,000
- CF:75%
- 借款:$22,000 USDC
- 账户流动性 = 30,000 × 0.75 - 22,000 = $500(安全)
ETH价格下跌到$2,900:
- 抵押价值:$29,000
- 账户流动性 = 29,000 × 0.75 - 22,000 = -$250
- Shortfall = $250 > 0(可以清算!)
2.3.2 清算流程图
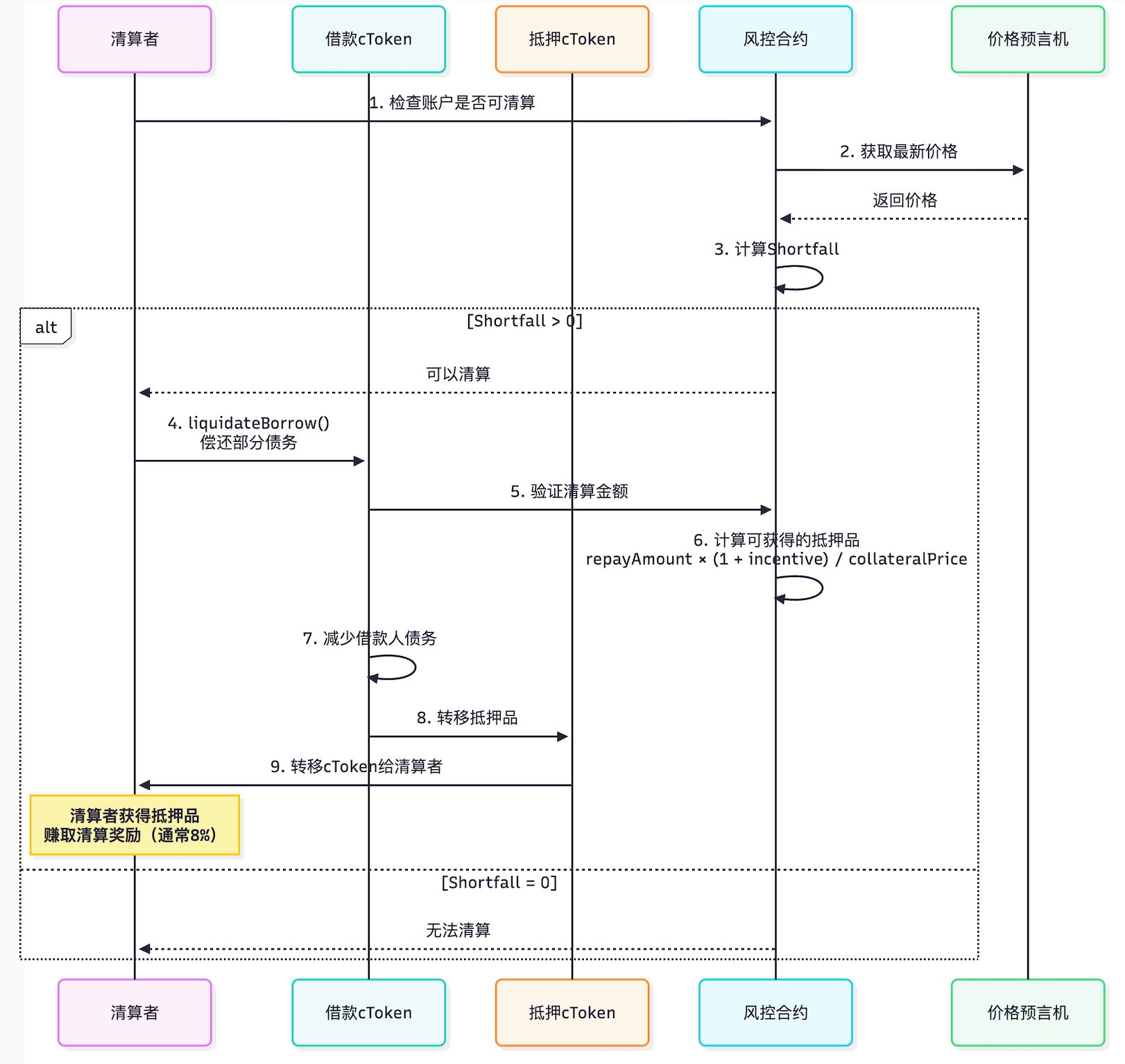
2.3.3 清算核⼼代码
c
/**
* @notice 清算函数
* @param borrower 被清算的借款⼈地址
* @param repayAmount 偿还的债务数量
* @param cTokenCollateral 要获得的抵押品cToken地址
* @return 0表示成功
*/
function liquidateBorrow(
address borrower,
uint256 repayAmount,
CToken cTokenCollateral
) external returns (uint) {
// 1. 累积双⽅的利息
accrueInterest();
cTokenCollateral.accrueInterest();
// 2. 检查是否允许清算
require(
comptroller.liquidateBorrowAllowed(
address(this),
address(cTokenCollateral),
msg.sender,
borrower,
repayAmount
) == 0,
"Liquidation not allowed"
);
// 3. 检查清算者⾃身账户健康
require(
msg.sender != borrower,
"Cannot liquidate self"
);
// 4. 计算实际偿还⾦额(不能超过50%)
uint256 borrowBalance = borrowBalanceStored(borrower);
uint256 maxClose = (borrowBalance * closeFactorMantissa) / 1e18;
uint256 actualRepayAmount = repayAmount;
if (repayAmount == type(uint256).max) {
actualRepayAmount = maxClose;
}
require(actualRepayAmount <= maxClose, "Too much repay");
// 5. 从清算者转⼊偿还资产
require(
doTransferIn(msg.sender, actualRepayAmount) == 0,
"Transfer in failed"
);
// 6. 减少借款⼈的债务
uint256 accountBorrowsPrev = borrowBalanceStored(borrower);
uint256 accountBorrowsNew = accountBorrowsPrev - actualRepayAmount;
accountBorrows[borrower] = BorrowSnapshot({
principal: accountBorrowsNew,
interestIndex: borrowIndex
});
totalBorrows -= actualRepayAmount;
// 7. 计算清算者应得的抵押品
// seizeTokens = repayAmount × liquidationIncentive / collateralPrice
uint256 seizeTokens = comptroller.liquidateCalculateSeizeTokens(
address(this),
address(cTokenCollateral),
actualRepayAmount
);
// 8. 转移抵押品给清算者
require(
cTokenCollateral.seize(msg.sender, borrower, seizeTokens) == 0,
"Seize failed"
);
emit LiquidateBorrow(
msg.sender,
borrower,
actualRepayAmount,
address(cTokenCollateral),
seizeTokens
);
return 0;
}
/**
* @notice 扣押抵押品(由借款cToken调⽤)
* @param liquidator 清算者地址
* @param borrower 借款⼈地址
* @param seizeTokens 扣押的cToken数量
*/
function seize(
address liquidator,
address borrower,
uint256 seizeTokens
) external returns (uint) {
// 只能由Comptroller授权的cToken调⽤
require(
comptroller.seizeAllowed(
address(this),
msg.sender,
liquidator,
borrower,
seizeTokens
) == 0,
"Seize not allowed"
);
// 检查借款⼈是否有⾜够的cToken
require(
accountTokens[borrower] >= seizeTokens,
"Insufficient collateral"
);
// 转移cToken
accountTokens[borrower] -= seizeTokens;
accountTokens[liquidator] += seizeTokens;
emit Transfer(borrower, liquidator, seizeTokens);
return 0;
}清算参数说明:
Close Factor(清算因⼦):
定义:单次最多可清算的债务⽐例
通常值:50%
作⽤:防⽌过度清算,保护借款⼈
Liquidation Incentive(清算激励):定义:清算者获得的折扣奖励
通常值:108%(即8%奖励)
作⽤:激励清算者维护协议安全
计算示例:借款⼈债务:$10,000 USDC
可清算:10,000 × 50% = 5,000
清算者偿还:$5,000 USDC
获得抵押品价值:5,000 × 1.08 = 5,400
清算者利润:$400(8%)