目录
[1. 字符串 & 数字相互转换](#1. 字符串 & 数字相互转换)
[1. x的平方根](#1. x的平方根)
[2. 阶乘后的零](#2. 阶乘后的零)
[3. 用rand7实现rand10](#3. 用rand7实现rand10)
[4. 计算质数](#4. 计算质数)
[5. H指数](#5. H指数)
[6. 基本计算器](#6. 基本计算器)
[6.1. 基本计算器](#6.1. 基本计算器)
[6.2. 基本计算器II](#6.2. 基本计算器II)
[7. 逆波兰表达式](#7. 逆波兰表达式)
[8. 小于n的最大数](#8. 小于n的最大数)
[9. 最大矩形](#9. 最大矩形)
[10. 最大正方形](#10. 最大正方形)
[11. 直线上最多的点](#11. 直线上最多的点)
[12. 四数之和](#12. 四数之和)
[13. 3D接雨水](#13. 3D接雨水)
[14. 打家劫舍②](#14. 打家劫舍②)
[15. 使用最小花费爬楼梯](#15. 使用最小花费爬楼梯)
[16. 分发饼干](#16. 分发饼干)
[17. 分发糖果](#17. 分发糖果)
[18. 加油站](#18. 加油站)
[19. 寻找峰值](#19. 寻找峰值)
[20. 用最少数量的箭引爆气球](#20. 用最少数量的箭引爆气球)
[20. 最长递增子序列系列](#20. 最长递增子序列系列)
[20.1 最长递增子序列的个数](#20.1 最长递增子序列的个数)
[20.2. 最长连续递增子序列](#20.2. 最长连续递增子序列)
[21. 买卖股票](#21. 买卖股票)
[21.1. 买卖股票的最佳时机②](#21.1. 买卖股票的最佳时机②)
[21.2. 买卖股票的最佳时期③](#21.2. 买卖股票的最佳时期③)
[21.3. 买卖股票的最佳时期④](#21.3. 买卖股票的最佳时期④)
[21.4. 买卖股票的最佳时期含冷冻期](#21.4. 买卖股票的最佳时期含冷冻期)
[21.5. 买卖股票的最佳时期含手续费](#21.5. 买卖股票的最佳时期含手续费)
[22. 下一个更大元素(下一个更大元素① & ②)](#22. 下一个更大元素(下一个更大元素① & ②))
一、常用知识点
1. 字符串 & 数字相互转换
python
'A'~'Z': 65~90
'a'~'z': 97~122
[ord('A'), ord('Z')] = [65, 90]
[ord('a'), ord('z')] = [97, 122]
chr(65), chr(90) = 'A', 'Z'
chr(97), chr(122) = 'a', 'z'
chr(ord('a')), chr(ord('z')) = 'a', 'z'二、非hot100高频题
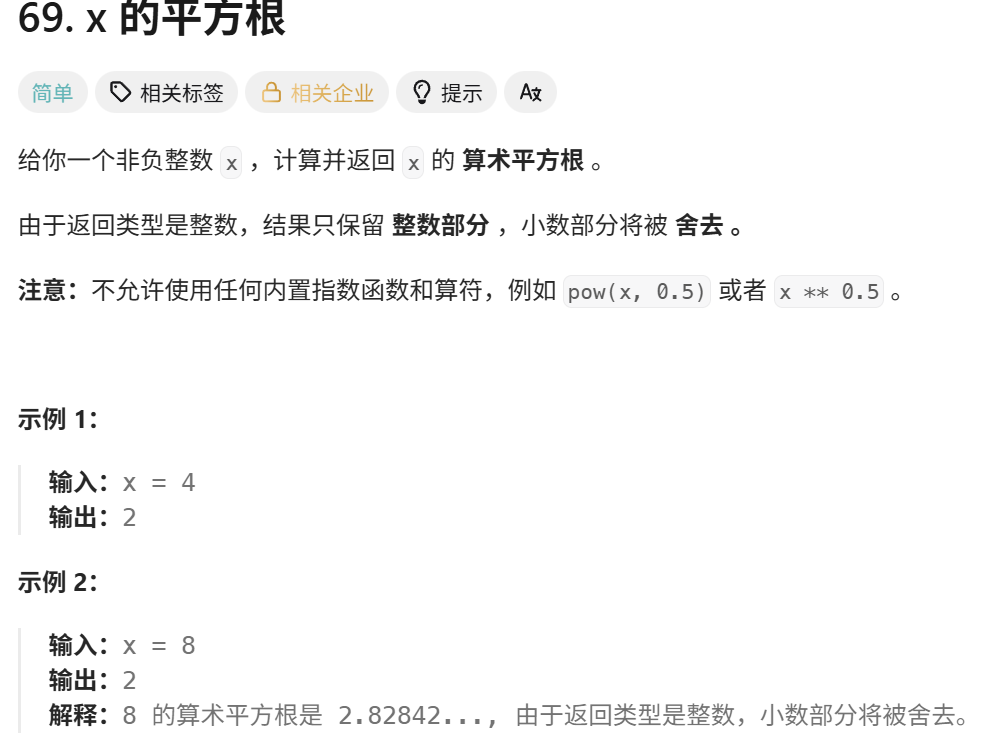
1. x的平方根
python
# 方法(1):牛顿迭代法
class Solution(object):
def mySqrt(self, x):
num = x
while num * num > x:
num = (num + x // num) // 2
return num
# 方法(2):二分查找
class Solution(object):
def mySqrt(self, x):
left, right = 0, x + 1
# [left, right)
while left < right:
mid = left + (right - left) // 2
if mid ** 2 == x:
return mid
if mid ** 2 < x:
left = mid + 1
else:
right = mid
return left - 12. 阶乘后的零

python
class Solution(object):
def trailingZeroes(self, n):
num = 0
while n > 0:
num += n // 5
n = n // 5
return num3. 用rand7实现rand10

python
class Solution(object):
def rand10(self):
return (rand7()+rand7()+rand7()+rand7()+rand7()+rand7()+rand7()+rand7()+rand7()+rand7())%10+14. 计算质数

python
# 方法(1):时空复杂度分别为:O(nlogn)、O(n)。
class Solution(object):
def countPrimes(self, n):
if n <= 2:
return 0
is_prime = [True] * n
is_prime[0] = is_prime[1] = False # 0和1不是质数
for i in range(2, int(n ** 0.5) + 1):
if is_prime[i]:
# 标记i的所有倍数为非质数
for j in range(i*i, n, i):
is_prime[j] = False
return sum(is_prime)
"""
n = 10:初始化 is_prime = [True] * 10(索引 0-9)。
标记过程:
i=2:标记 4、6、8 为 False。
i=3:标记 9 为 False(i*i=9开始)。
最终 is_prime = [F, F, T, T, F, T, F, T, F, F],统计 True的数量为 4(质数:2, 3, 5, 7)。
"""
# 方法(2):O(n**2)
num=[]
for i in range(2,n):
for j in range(2,i):
if(i%j==0):
break
else:
num.append(i)
print(num)5. H指数

python
# 时空复杂度分别为:O(nlogn)、O(1)
class Solution(object):
def hIndex(self, citations):
citations.sort(reverse=True)
h = 0
for i, citation in enumerate(citations):
if citation > i:
h = i + 1
else:
break
return h
"""
citations=[3,0,6,1,5] --> sorted, [6, 5, 3, 1, 0] --> 3
0:6, 1:5, 2:3, 3:1
"""6. 基本计算器
6.1. 基本计算器

python
class Solution:
def calculate(self, s: str) -> int:
stack = []
# 当连续数字是追加
tmp_str = ''
for i in s[::-1]:
if i == ' ':
continue
if i.isdigit():
# 追加连续数字
tmp_str += i
continue
# 遇到非数字场景
if tmp_str:
# 先将tmp_str 逆序后添加至stack中
stack.append(int(tmp_str[::-1]))
# 重置
tmp_str = ''
# 遇到-号,取出尾数,添加负号后重新放入
if i == '-':
stack.append(-stack.pop())
# 正常添加
elif i == ')':
stack.append(i)
# 开始合并左括号到右括号之间的数字
elif i == '(':
num = 0
while True:
if stack[-1] == ')':
stack.pop()
break
num += stack.pop()
stack.append(num)
# 未加入的临时数字,进行追加
if tmp_str:
stack.append(int(tmp_str[::-1]))
return sum(stack)6.2. 基本计算器II

python
class Solution:
def calculate(self, s):
stack = []
pre_op = '+'
num = 0
for i, each in enumerate(s):
if each.isdigit():
num = 10 * num + int(each)
if i == len(s) - 1 or each in '+-*/':
if pre_op == '+':
stack.append(num)
elif pre_op == '-':
stack.append(-num)
elif pre_op == '*':
stack.append(stack.pop() * num)
elif pre_op == '/':
top = stack.pop()
if top < 0:
stack.append(int(top / num))
else:
stack.append(top // num)
pre_op = each
num = 0
return sum(stack)7. 逆波兰表达式

python
import operator
class Solution:
def evalRPN(self, tokens: List[str]) -> int:
ops = {'+': operator.add, '-': operator.sub, '*': operator.mul, '/': operator.truediv}
s = []
for x in tokens:
if x not in ops:
s.append(x)
else:
a = s.pop()
b = s.pop()
# 这里使用 truediv 处理类似 6 / -3 的情况
s.append(int(ops[x](int(b), int(a))))
return int(s[0])8. 小于n的最大数

python
def largest_number_less_than_n(A, n):
s = str(n)
length = len(s)
digits = sorted(map(str, A))
max_digit = max(digits)
# 生成所有位数相同且小于n的数
candidates = []
# 使用DFS生成所有可能
def dfs(index, tight, path):
if index == length:
num_str = ''.join(path)
if int(num_str) < n:
candidates.append(num_str)
return
if tight:
for d in digits:
if d <= s[index]:
new_tight = (d == s[index])
dfs(index+1, new_tight, path+[d])
else:
for d in digits:
dfs(index+1, False, path+[d])
dfs(0, True, [])
if candidates:
return int(max(candidates))
else:
# 构造位数少一位的最大数
if length - 1 == 0:
return 0
return int(max_digit * (length - 1))
print(largest_number_less_than_n(['1','2','4','9'], 2533)) # 2499
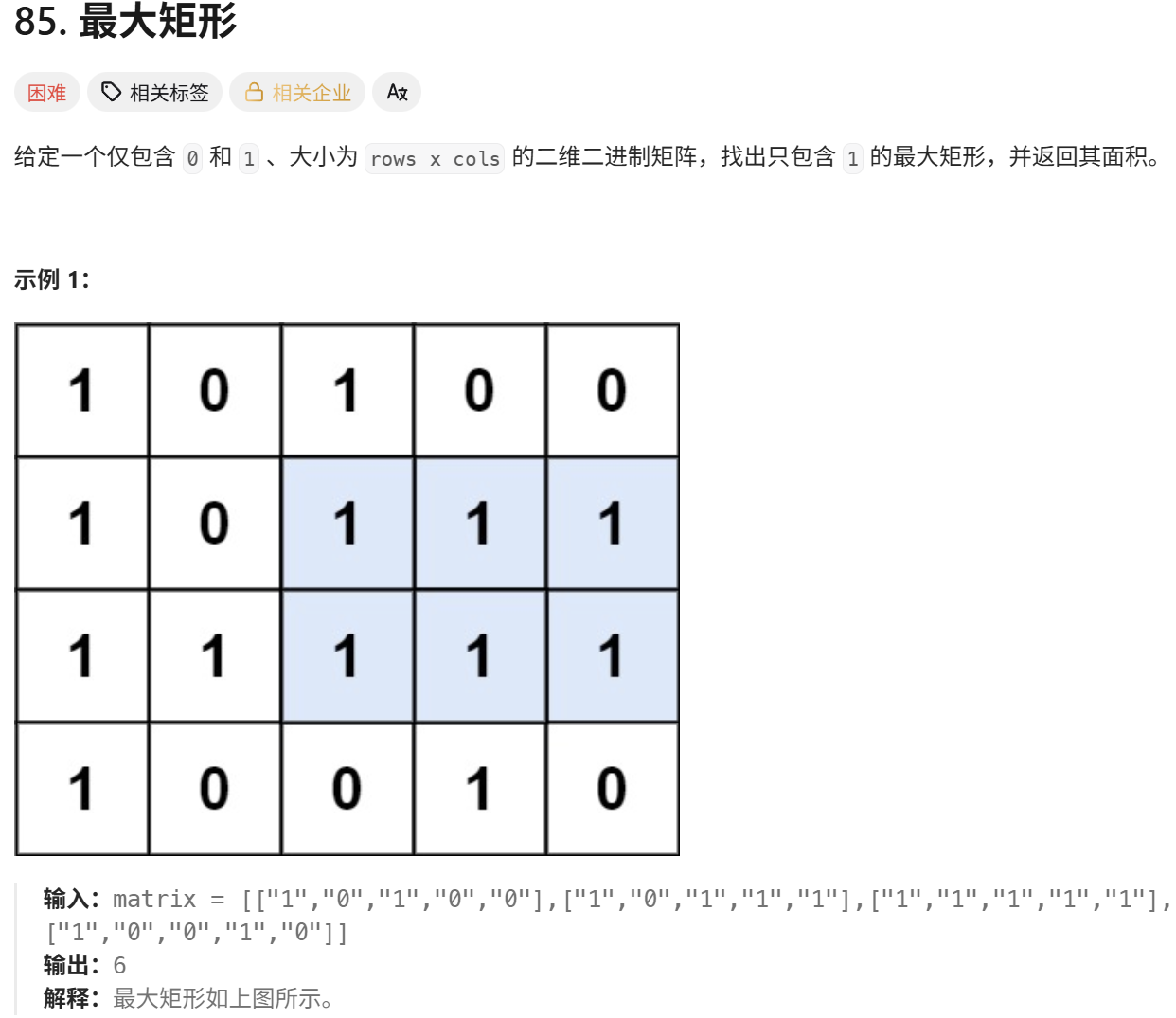
print(largest_number_less_than_n(['9','6','3','5'], 56449)) # 563999. 最大矩形
python
class Solution(object):
def maximalRectangle(self, matrix):
if not matrix:return 0
m,n=len(matrix),len(matrix[0])
# 记录当前位置上方连续"1"的个数
pre=[0]*(n+1)
res=0
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
# 前缀和
pre[j]=pre[j]+1 if matrix[i][j]=="1" else 0
# 单调栈
stack=[-1]
for k,num in enumerate(pre):
while stack and pre[stack[-1]]>num:
index=stack.pop()
res=max(res,pre[index]*(k-stack[-1]-1))
stack.append(k)
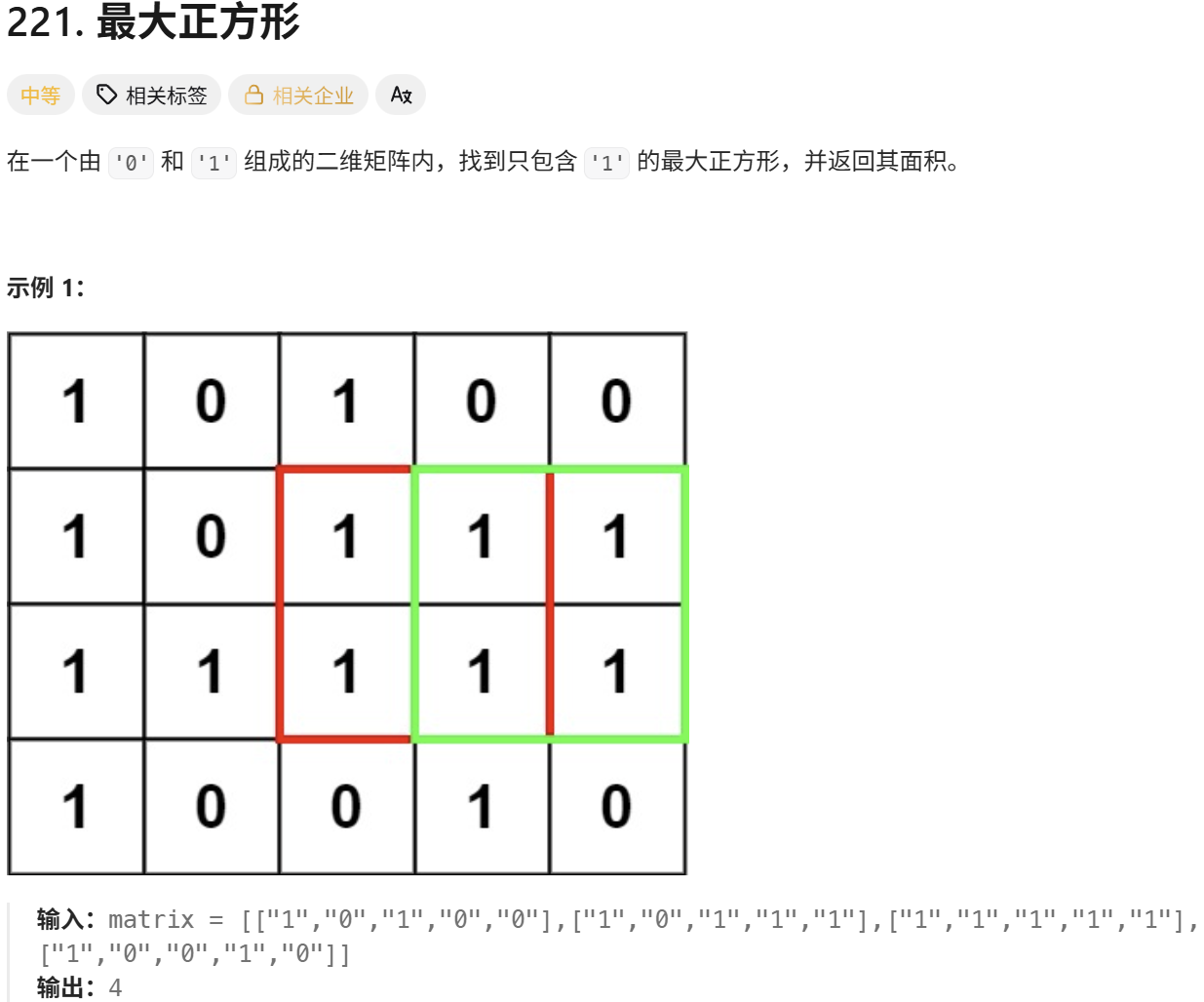
return res10. 最大正方形
python
class Solution(object):
def maximalSquare(self, matrix):
res = 0
m = len(matrix)
if m == 0:
return 0
n = len(matrix[0])
dp = [[0] * (n + 1) for _ in range(m + 1)]
for i in range(1, m + 1):
for j in range(1, n + 1):
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1], dp[i - 1][j - 1]) + 1 if matrix[i - 1][j - 1] == "1" else 0
res = max(res, dp[i][j])
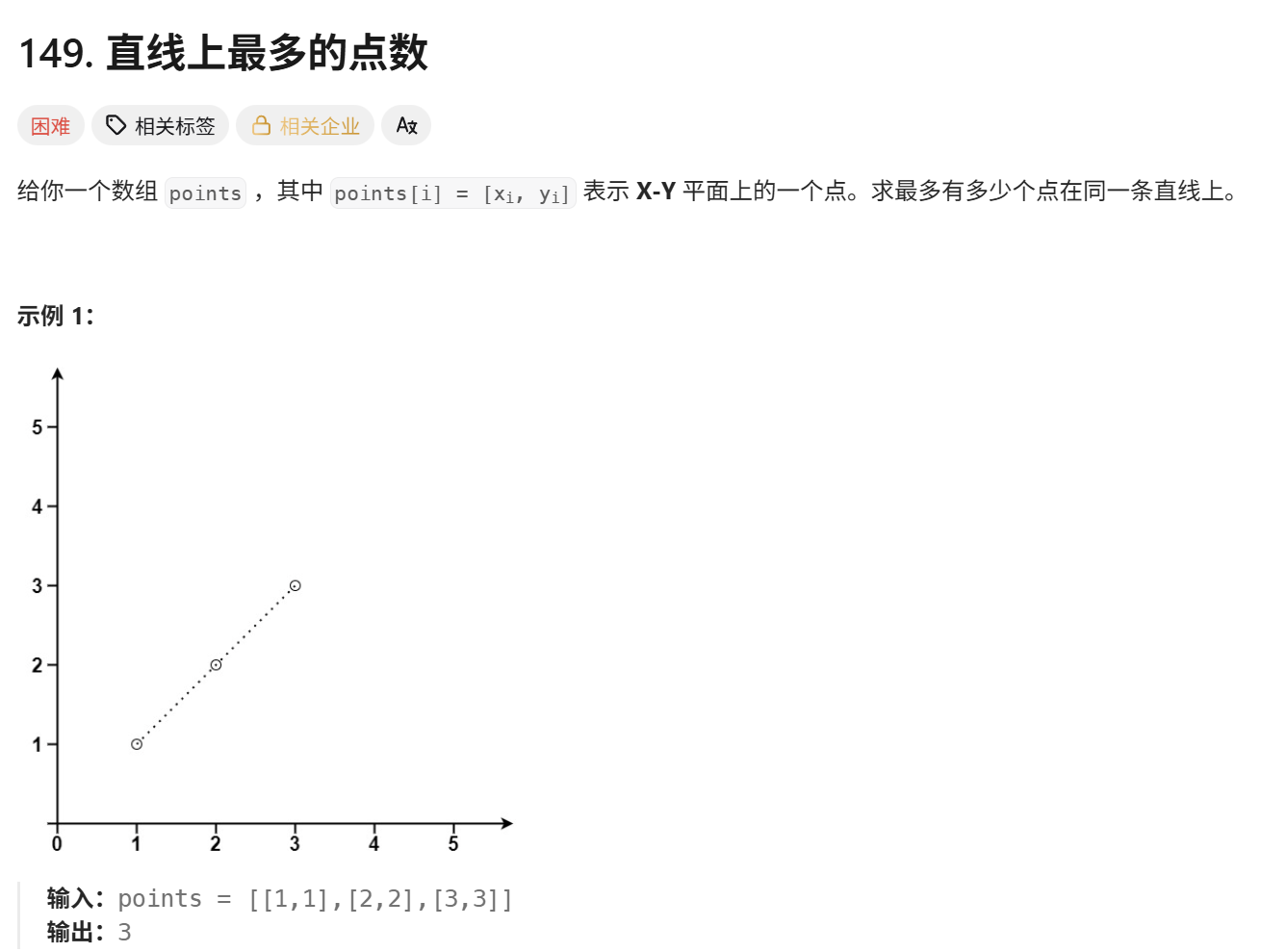
return res ** 211. 直线上最多的点
python
class Solution(object):
def maxPoints(self, points):
"""
通过两点[x1,y1],[x2,y2]可以计算一般式ax+by+c=0中的A,B,C三个参数分别为:
A = y2 - y1
B = x1 - x2
C = x2y1 - x1y2
"""
cnt = {}
n = len(points)
if n < 2:
return 1
m = 1
for i in range(n-1):
for j in range(i+1,n):
x1=points[i][0]
x2=points[j][0]
y1=points[i][1]
y2=points[j][1]
A = float(y2 - y1)
B = float(x1 - x2)
C = float(x2*y1 - x1*y2)
if A != 0:
A, B, C = 1, B/A, C/A
elif B != 0:
A, B, C = A/B, 1, C/B
elif C != 0:
A, B, C = A/C, B/C, 1
f=(A,B,C)
if f not in cnt:
cnt[f]=1
else:
cnt[f]+=1
m=max(m,cnt[f])
return int(ceil(sqrt(m * 2)))12. 四数之和

python
class Solution(object):
def fourSum(self, nums, target):
nums.sort()
sets=set()
for i in range(len(nums)-3):
for j in range(i+1,len(nums)-2):#固定两个数
left=j+1#左指针
right=len(nums)-1#右指针
while(right>left):
temp=nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[left]+nums[right]
if temp==target:
sets.add((nums[i],nums[j],nums[left],nums[right]))
left+=1
right-=1
if temp>target:right-=1#太大了,右指针左移
if temp<target:left+=1#反之
#去重
res=[]
for i in sets:
res.append(list(i))
return res13. 3D接雨水

python
import heapq
class Solution(object):
def trapRainWater(self, heightMap):
if not heightMap: return 0
m, n = len(heightMap), len(heightMap[0])
if m < 3 or n < 3: return 0
heap = []
visited = [[False] * n for _ in range(m)]
# 将边界存入堆
for i in range(m):
for j in [0, n-1]:
heapq.heappush(heap, (heightMap[i][j], i, j))
visited[i][j] = True
for j in range(1, n-1):
for i in [0, m-1]:
heapq.heappush(heap, (heightMap[i][j], i, j))
visited[i][j] = True
res = 0
dirs = [(-1,0), (1,0), (0,-1), (0,1)]
while heap:
h, x, y = heapq.heappop(heap)
for dx, dy in dirs:
nx, ny = x+dx, y+dy
if 0<=nx<m and 0<=ny<n and not visited[nx][ny]:
res += max(0, h - heightMap[nx][ny])
heapq.heappush(heap, (max(h, heightMap[nx][ny]), nx, ny))
visited[nx][ny] = True
return res14. 打家劫舍②

python
class Solution:
def rob1(self, nums):
f0 = f1 = 0
for x in nums:
f0, f1 = f1, max(f1, f0 + x)
return f1
def rob(self, nums):
return max(nums[0] + self.rob1(nums[2:-1]), self.rob1(nums[1:]))15. 使用最小花费爬楼梯

python
class Solution(object):
def minCostClimbingStairs(self, cost):
n = len(cost)
dp = [0] * (n + 1)
for i in range(2, n + 1):
dp[i] = min(dp[i - 1] + cost[i - 1], dp[i - 2] + cost[i - 2])
return dp[n]16. 分发饼干
python
class Solution(object):
def findContentChildren(self, g, s):
# 将胃口和饼干排序
g.sort()
s.sort()
# 孩子的数量
n = len(g)
# 饼干的数量
m = len(s)
# 记录结果
res = 0
for i in range(m):
# 从胃口小的开始喂
if res < n and g[res] <= s[i]:
res += 1
return res17. 分发糖果

python
class Solution(object):
def candy(self, ratings):
n = len(ratings)
candies = [1] * n
for i in range(1, n):
if ratings[i] > ratings[i - 1]:
candies[i] = candies[i - 1] + 1
for i in range(n - 2, -1, -1):
if ratings[i] > ratings[i + 1]:
candies[i] = max(candies[i], candies[i + 1] + 1)
total = 0
for num in candies:
total += num
return total18. 加油站

python
class Solution(object):
def canCompleteCircuit(self, gas, cost):
start = 0
curSum = 0
totalSum = 0
for i in range(len(gas)):
curSum += gas[i] - cost[i]
totalSum += gas[i] - cost[i]
if curSum < 0:
curSum = 0
start = i + 1
if totalSum < 0: return -1
return start19. 寻找峰值
python
class Solution(object):
def findPeakElement(self, nums):
idx = 0
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
if nums[i] > nums[idx]:
idx = i
return idx20. 用最少数量的箭引爆气球

python
class Solution(object):
def findMinArrowShots(self, points):
if len(points) == 0: return 0
points.sort(key=lambda x: x[0])
result = 1
for i in range(1, len(points)):
if points[i][0] > points[i - 1][1]: # 气球i和气球i-1不挨着,注意这里不是>=
result += 1
else:
points[i][1] = min(points[i - 1][1], points[i][1]) # 更新重叠气球最小右边界
return result20. 最长递增子序列系列
20.1 最长递增子序列的个数

python
class Solution(object):
def findNumberOfLIS(self, nums):
n = len(nums)
if n == 1:
return l
max_l = 0
dp = [1]*n
count = [1]*n
for i in range(1,n):
for j in range(i):
if nums[i]>nums[j]:
if dp[j] + 1 > dp[i]:
count[i] = count[j]
dp[i] = dp[j]+1
elif dp[j]+1 == dp[i]:
count[i] += count[j]
max_l = max(max_l, dp[i])
res = 0
for i in range(n):
if dp[i]==max_l:
res += count[i]
return res20.2. 最长连续递增子序列

python
class Solution(object):
def findLengthOfLCIS(self, nums):
res = 0
n = len(nums)
start = 0
for i in range(n):
if i > 0 and nums[i] <= nums[i - 1]:
start = i
res = max(res, i - start + 1)
return res21. 买卖股票
21.1. 买卖股票的最佳时机②
python
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices):
max_profit = 0
for i in range(1, len(prices)):
if prices[i] > prices[i-1]:
max_profit += prices[i] - prices[i-1]
return max_profit21.2. 买卖股票的最佳时期③
python
class Solution(object):
def maxProfit(self, prices):
b1, b2, s1, s2 = -float("inf"), -float("inf"), 0, 0
for p in prices:
b1 = max(b1, 0 - p)
s1 = max(s1, b1 + p)
b2 = max(b2, s1 - p)
s2 = max(s2, b2 + p)
return s221.3. 买卖股票的最佳时期④
python
class Solution(object):
def maxProfit(self, k, prices):
k = min(k, len(prices) // 2)
buy = [-float("inf")] * (k+1)
sell = [0] * (k+1)
for p in prices:
for i in range(1, k+1):
buy[i] = max(buy[i], sell[i-1] - p)
sell[i] = max(sell[i], buy[i] + p)
return sell[-1]21.4. 买卖股票的最佳时期含冷冻期
python
class Solution(object):
def maxProfit(self, prices):
buy, sell_pre, sell = -float("inf"), 0, 0
for p in prices:
buy = max(buy, sell_pre - p)
sell_pre, sell = sell, max(sell, buy + p)
return sell21.5. 买卖股票的最佳时期含手续费
python
class Solution(object):
def maxProfit(self, prices, fee):
buy, sell = -float("inf"), 0
for p in prices:
buy = max(buy, sell - p - fee)
sell = max(sell, buy + p)
return sell22. 下一个更大元素(下一个更大元素① & ②)
|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---|
| 
 | |
| |
python
# 下一个更大元素①
class Solution(object):
def nextGreaterElement(self, nums1, nums2):
m, n = len(nums1), len(nums2)
res = [0] * m
for i in range(m):
j = nums2.index(nums1[i])
k = j + 1
while k < n and nums2[k] < nums2[j]:
k += 1
res[i] = nums2[k] if k < n else -1
return res
# 下一个更大元素②
class Solution(object):
def nextGreaterElements(self, nums):
n = len(nums)
res = [-1] * n
stk = list()
for i in range(n * 2 - 1):
while stk and nums[stk[-1]] < nums[i % n]:
res[stk.pop()] = nums[i % n]
stk.append(i % n)
resurn res