这两个类在功能上几乎完全一样 (都是将聊天记录存储在程序的内存 RAM 中),它们的核心区别在于所属的代码库 和LangChain 的发展趋势。
简而言之:InMemoryChatMessageHistory 是新版推荐用法,ChatMessageHistory 是旧版遗留用法。
详细对比表
| 特性 | ChatMessageHistory |
InMemoryChatMessageHistory |
|---|---|---|
| 所属库 | langchain_community |
langchain_core |
| 存储位置 | 内存 | 内存 |
| 持久化 | 不支持(程序结束数据丢失) | 不支持(程序结束数据丢失) |
| 导入路径 | from langchain_community.chat_message_histories import ChatMessageHistory |
from langchain_core.chat_history import InMemoryChatMessageHistory |
| API 接口 | .add_message(), .messages |
.add_message(), .messages |
| 推荐程度 | 较低(逐渐被替代) | 高(LangChain 官方推荐) |
1. ChatMessageHistory (旧版/社区版)
- 来源 :属于
langchain_community包。 - 背景 :这是 LangChain 早期版本中广泛使用的类。LangChain 以前把很多通用实现放在
community里。 - 缺点 :为了使用这一个简单的内存存储功能,你可能需要安装整个
langchain-community库(虽然你通常已经安装了),这在架构上不够轻量。
2. InMemoryChatMessageHistory (新版/核心版)
- 来源 :属于
langchain_core包。 - 背景 :随着 LangChain 架构的升级,官方将最核心、最基础的接口和实现移动到了
langchain-core中。 - 优点 :
- 更加轻量,不依赖社区包。
- 命名更清晰(
InMemory明确表示是在内存中)。 - 官方现在的文档和教程主要推荐使用这个。
代码替换演示
如果你现在的代码是这样的(旧写法):
from langchain_community.chat_message_histories import ChatMessageHistory
store = {}
def get_session_history(session_id: str):
if session_id not in store:
store[session_id] = ChatMessageHistory() # 旧版
return store[session_id]建议修改为(新写法):
from langchain_core.chat_history import InMemoryChatMessageHistory # 注意引入的变化
store = {}
def get_session_history(session_id: str):
if session_id not in store:
# 使用新版,功能完全一样
store[session_id] = InMemoryChatMessageHistory()
return store[session_id]什么时候用哪个?
- 在新项目中 :直接使用
InMemoryChatMessageHistory。这是未来的标准。 - 在旧项目维护中 :如果你的代码已经在用
ChatMessageHistory并且工作正常,不需要急着改。两者在功能上没有区别,不会影响运行结果。 - 关于持久化 :
- 如果你需要聊天记录保存到数据库(如 Redis, PostgreSQL, SQLLite),这两个类都不能用。
- 你需要使用
langchain_community中的具体实现,例如RedisChatMessageHistory或PostgresChatMessageHistory。
总结
- 功能:没区别。
- 趋势 :用
InMemoryChatMessageHistory(fromlangchain_core)。
示例:
from langchain_ollama import ChatOllama
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langchain.agents import create_tool_calling_agent, AgentExecutor
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
from langchain_core.runnables.history import RunnableWithMessageHistory
from langchain_core.chat_history import InMemoryChatMessageHistory
# ================== 工具定义 ==================
@tool
def get_weather(city: str):
"""获取指定城市的天气。输入必须是城市名称(如 "北京")。"""
weather = {"北京": "晴天30度", "成都": "晴天32度"}
return weather.get(city.strip(), f"{city}天气未知")
@tool
def calculate_expression(expression: str):
"""计算数学表达式,例如 '30 * 9 / 5 + 32'。仅支持基本算术运算。"""
try:
# 注意:eval 有安全风险,生产环境请用 simpleeval
result = eval(expression)
return str(result)
except Exception as e:
return f"计算错误: {e}"
# ================== LLM 与 Agent ==================
# 使用支持 function calling 的模型
model = ChatOllama(model="qwen3:8b", base_url="http://localhost:11434", temperature=0.2)
tools = [get_weather, calculate_expression]
# 构建 prompt(必须包含 agent_scratchpad)
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "你是一个智能助手,可以调用工具回答问题。请利用对话历史理解上下文。"),
MessagesPlaceholder("chat_history"),
("human", "{input}"),
MessagesPlaceholder("agent_scratchpad") # 必需:记录工具调用过程
])
# 创建 Tool-Calling Agent
agent = create_tool_calling_agent(model, tools, prompt)
# 创建执行器(不传 memory!)
agent_executor = AgentExecutor(
agent=agent,
tools=tools,
verbose=True,
handle_parsing_errors=True,
max_iterations=3
)
# ================== 添加会话记忆 ==================
store = {}
def get_session_history(session_id: str):
if session_id not in store:
store[session_id] = InMemoryChatMessageHistory()
return store[session_id]
# 包装成带历史的 Runnable
agent_with_memory = RunnableWithMessageHistory(
runnable=agent_executor,
get_session_history=get_session_history,
input_messages_key="input",
history_messages_key="chat_history",
# 注意:Tool-Calling Agent 不直接使用 chat_history,但 RunnableWithMessageHistory 会自动注入 Human/AI 消息
)
# ================== 测试多轮对话 ==================
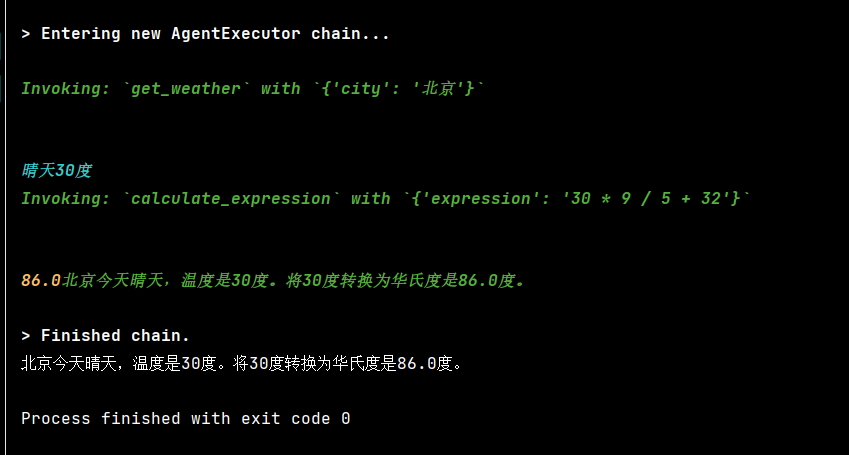
if __name__ == "__main__":
session_id = "user_abc"
result0 = agent_with_memory.invoke(
{"input": "北京天气如何?如果温度是30度,转成华氏度是多少?"},
# {"input": "北京天气如何?"},
config={"configurable": {"session_id": session_id}}
)
print(result0["output"])
# # 第一轮:问天气
# result1 = agent_with_memory.invoke(
# {"input": "北京天气怎么样?"},
# config={"configurable": {"session_id": session_id}}
# )
# print("第一轮:", result1["output"])
#
# # 第二轮:基于上文问温度转换(依赖"30度"来自上文)
# result2 = agent_with_memory.invoke(
# {"input": "那30摄氏度等于多少华氏度?"},
# config={"configurable": {"session_id": session_id}}
# )
# print("第二轮:", result2["output"])