1. 从零开始:如何用 Python 创建你的第一个 MCP(Model Context Protocol)
1.1 什么是 MCP?
Model Context Protocol (MCP) 是一个标准化协议,允许应用程序与大语言模型(LLM)进行安全、结构化的交互。通过 MCP,你可以:
- 为 LLM 提供自定义工具和资源
- 实现 LLM 和外部系统的无缝集成
- 构建可复用的、模块化的 AI 应用
1.2 核心概念
1.2.1 MCP Server(服务器)
定义工具、资源和提示词,通过 stdio 或其他传输方式提供给客户端。
1.2.2 MCP Client(客户端)
连接到 MCP 服务器,获取工具列表,调用工具,并与 LLM 集成。
1.2.3 Tools(工具)
服务器暴露给 LLM 的可调用函数,LLM 可以根据用户需求调用这些工具。
1.3 项目结构
hello-world/
├── server.py # MCP 服务器定义
├── client-deepseek.py # 使用 Deepseek LLM 的客户端
├── client.py # 基础客户端
├── pyproject.toml # 项目配置
└── uv.lock # 依赖锁定文件2. 第一步:创建 MCP 服务器
2.1 安装依赖
0
bash
cd hello-world
UV_INDEX_URL=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ uv sync主要依赖:
mcp[cli]>=1.6.0- MCP 框架openai>=1.75.0- OpenAI 兼容的 LLM 客户端python-dotenv>=1.1.0- 环境变量管理
2.2 编写 Server 端代码
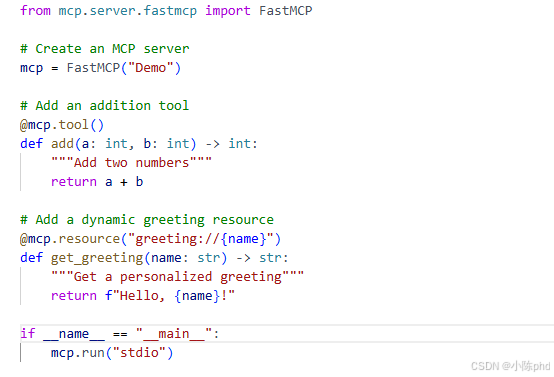
创建 server.py:
python
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
# 创建一个 MCP 服务器实例
mcp = FastMCP("Demo")
# 定义一个工具:两数相加
@mcp.tool()
def add(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Add two numbers"""
return a + b
# 定义一个资源:个性化问候
@mcp.resource("greeting://{name}")
def get_greeting(name: str) -> str:
"""Get a personalized greeting"""
return f"Hello, {name}!"
# 启动服务器
if __name__ == "__main__":
mcp.run("stdio")核心概念解析:
- FastMCP - 简化的 MCP 服务器框架
- @mcp.tool() - 装饰器定义工具函数
- @mcp.resource() - 装饰器定义资源(带 URI 模式)
- mcp.run("stdio") - 通过标准输入输出运行服务器
3. 第二步:创建 MCP 客户端
3.1 基础客户端(无 LLM)
client.py 展示了如何直接调用工具:
python
import sys
import asyncio
from mcp import ClientSession
from mcp.client.stdio import stdio_client, StdioServerParameters
async def main():
# 1. 启动 MCP 服务器进程
server_script = "server.py"
params = StdioServerParameters(
command=sys.executable,
args=[server_script],
)
transport = stdio_client(params)
stdio, write = await transport.__aenter__()
# 2. 建立客户端会话
session = await ClientSession(stdio, write).__aenter__()
await session.initialize()
# 3. 调用工具
result = await session.call_tool("add", {"a": 3, "b": 5})
print(f"3 + 5 = {result}")
# 4. 关闭连接
await session.__aexit__(None, None, None)
await transport.__aexit__(None, None, None)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())3.2 与 LLM 集成的客户端
client-deepseek.py 展示了如何让 LLM 自动调用工具:
python
import sys
import asyncio
import os
import json
from mcp import ClientSession
from mcp.client.stdio import stdio_client, StdioServerParameters
from openai import OpenAI
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
async def main():
# 1. 连接到 MCP 服务器
print(">>> 初始化加法 LLM 工具客户端")
server_script = "server.py"
params = StdioServerParameters(
command=sys.executable,
args=[server_script],
)
transport = stdio_client(params)
stdio, write = await transport.__aenter__()
session = await ClientSession(stdio, write).__aenter__()
await session.initialize()
print(">>> 连接到MCP服务器成功")
# 2. 初始化 LLM 客户端(使用通义千问)
client = OpenAI(
api_key=os.getenv("QWEN_API_KEY"),
base_url=os.getenv("QWEN_BASE_URL")
)
# 3. 从 MCP 服务器获取工具列表
resp = await session.list_tools()
tools = [{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": tool.name,
"description": tool.description,
"parameters": tool.inputSchema
}
} for tool in resp.tools]
print("可用工具:", [t["function"]["name"] for t in tools])
# 4. 主交互循环
while True:
print("\n请输入你的加法问题(如:5加7是多少?或'退出'):")
user_input = input("> ")
if user_input.strip().lower() == '退出':
break
print(f"\n📝 用户问题: {user_input}")
# 构造对话
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "你是一个加法助手,遇到加法问题请调用工具add,最后用自然语言回答用户。"},
{"role": "user", "content": user_input}
]
# 5. LLM 与工具调用循环
iteration = 0
while True:
iteration += 1
print(f"\n🔄 第 {iteration} 次 LLM 调用...")
# 调用 LLM
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="qwen-plus",
messages=messages,
tools=tools,
tool_choice="auto"
)
message = response.choices[0].message
messages.append(message)
# 检查是否有工具调用
if not message.tool_calls:
print(f"\n✅ LLM 最终回答:")
print(f"\nAI 回答:\n {message.content}")
break
# 6. 执行工具调用
for tool_call in message.tool_calls:
args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
print(f"\n🔧 调用工具: {tool_call.function.name}")
print(f"📥 工具参数: {args}")
result = await session.call_tool(tool_call.function.name, args)
print(f"📤 工具返回结果: {result}")
# 将工具结果加入对话历史
messages.append({
"role": "tool",
"content": str(result),
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id
})
await session.__aexit__(None, None, None)
await transport.__aexit__(None, None, None)
print(">>> 客户端已关闭")
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())4. 第三步:配置环境变量
创建或修改 .env 文件:
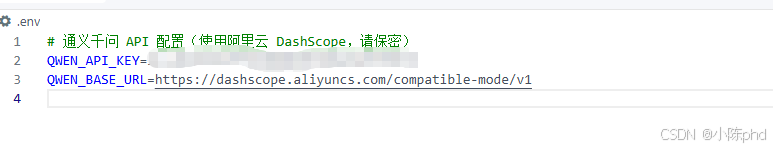
env
# 通义千问 API 配置(使用阿里云 DashScope)
QWEN_API_KEY=your-api-key-here
QWEN_BASE_URL=https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v15. 第四步:运行程序
5.1 方式一:两个终端分别运行
终端 1:启动服务器
bash
cd 01-hello-world
UV_INDEX_URL=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ uv run python server.py终端 2:运行客户端
bash
cd 01-hello-world
UV_INDEX_URL=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ \
QWEN_API_KEY="your-api-key" \
QWEN_BASE_URL="https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1" \
uv run python client-deepseek.py5.2 方式二:非交互式测试
bash
cd 01-hello-world
timeout 60 bash -c 'echo -e "15加8等于多少?\n退出" | \
UV_INDEX_URL=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ \
QWEN_API_KEY="your-api-key" \
QWEN_BASE_URL="https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1" \
uv run python client-deepseek.py'6. 执行流程示例
当用户输入 "15加8等于多少?" 时:
📝 用户问题: 15加8等于多少?
🔄 第 1 次 LLM 调用...
🔧 调用工具: add
📥 工具参数: {'a': 15, 'b': 8}
📤 工具返回结果: meta=None content=[TextContent(type='text', text='23', annotations=None)] isError=False
🔄 第 2 次 LLM 调用...
✅ LLM 最终回答:
AI 回答:
15加8等于23。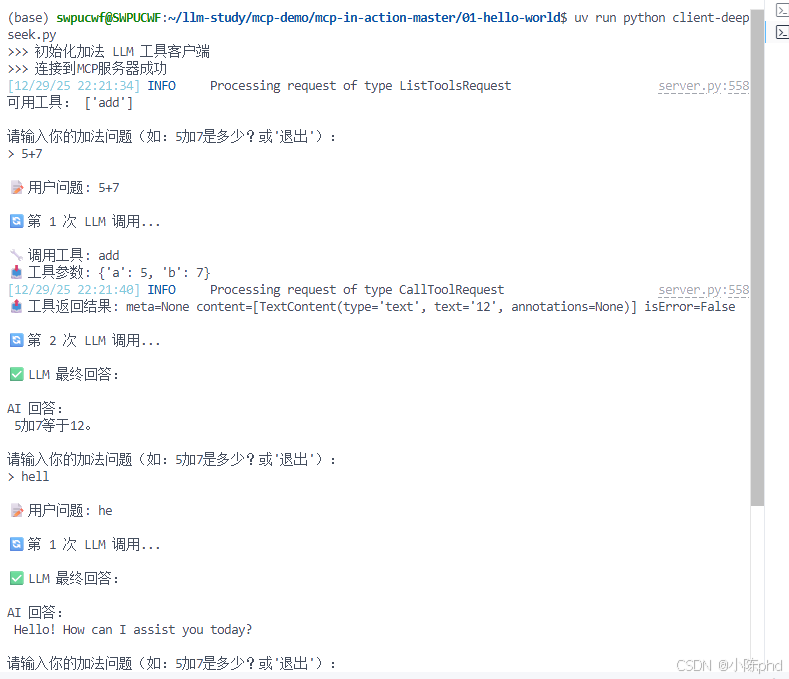
7. 关键要点
7.1 异步编程
MCP 使用 asyncio,所有网络操作都是异步的:
python
async def main():
# 异步操作
await session.initialize()
result = await session.call_tool(...)7.2 工具定义
简单易用的装饰器风格:
python
@mcp.tool()
def my_tool(param1: int, param2: str) -> str:
"""Tool description"""
return f"Result: {param1} {param2}"7.3 工具调用链
LLM 根据需要多次调用工具,直到得到最终答案:
用户输入 → LLM 分析 → 调用工具 → 获得结果 → LLM 再次分析 → 最终回答7.4 消息历史
保持对话历史以便 LLM 理解上下文:
python
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "..."},
{"role": "user", "content": "..."},
{"role": "assistant", "content": "..."},
{"role": "tool", "content": "..."},
]8. 扩展应用
8.1 添加更多工具
python
@mcp.tool()
def multiply(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Multiply two numbers"""
return a * b
@mcp.tool()
def divide(a: float, b: float) -> float:
"""Divide two numbers"""
if b == 0:
raise ValueError("Cannot divide by zero")
return a / b8.2 添加资源
python
@mcp.resource("user://{user_id}")
def get_user_info(user_id: str) -> str:
"""Get user information"""
return f"User {user_id} information"8.2.1 什么是资源(Resource)?
@mcp.resource() 装饰器用于定义一个可以根据参数返回不同数据的接口。资源是不同于工具的数据取...
资源 vs 工具的对比:
| 特性 | Resource(资源) | Tool(工具) |
|---|---|---|
| 用途 | 提供只读或结构化的数据 | 执行操作或计算 |
| 调用方式 | read_resource("uri://path") |
call_tool("name", args) |
| 参数传递 | URI 路径参数 | 函数参数 |
| 使用场景 | 获取文件、查询数据库 | 计算、修改数据 |
8.2.2 URI 模式详解
python
@mcp.resource("greeting://{name}")
def get_greeting(name: str) -> str:
"""Get a personalized greeting"""
return f"Hello, {name}!"语法分解:
| 部分 | 含义 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
@mcp.resource() |
资源装饰器 | 定义资源的标记 |
"greeting://" |
资源协议(Scheme) | user://、file://、api:// |
{name} |
动态参数占位符 | 类似路由参数,接收不同值 |
get_greeting(name: str) |
处理函数 | 参数名必须与 URI 占位符一致 |
工作流程:
客户端请求 greeting://Alice
↓
MCP 框架识别 URI 模式
↓
提取参数 name = "Alice"
↓
调用函数 get_greeting("Alice")
↓
返回 "Hello, Alice!" 给客户端8.2.3 常见资源示例
示例 1:用户信息资源
python
@mcp.resource("user://{user_id}")
def get_user_info(user_id: str) -> str:
users = {"1": "Alice", "2": "Bob"}
return users.get(user_id, "Not found")
# 客户端调用:await session.read_resource("user://1")
# 返回:Alice示例 2:文件资源(多参数)
python
@mcp.resource("file://{folder}/{filename}")
def read_file(folder: str, filename: str) -> str:
# 注意:参数名必须与 URI 中的占位符一致
path = f"{folder}/{filename}"
try:
with open(path, 'r') as f:
return f.read()
except FileNotFoundError:
return "File not found"
# 客户端调用:await session.read_resource("file://docs/readme.txt")
# 返回:文件内容示例 3:API 文档资源
python
@mcp.resource("docs://api/{version}")
def get_api_docs(version: str) -> str:
docs = {
"v1": "API v1: 支持基础功能",
"v2": "API v2: 新增高级功能"
}
return docs.get(version, "Version not found")示例 4:多参数资源
python
@mcp.resource("product://{category}/{product_id}")
def get_product(category: str, product_id: str) -> str:
# 访问歩骤:product://electronics/12345
return f"Product {product_id} from {category}"8.2.4 客户端中使用资源
python
# 方法 1:直接读取资源
result = await session.read_resource("greeting://Alice")
print(result) # 输出: Hello, Alice!
# 方法 2:列出所有资源
resources = await session.list_resources()
for resource in resources.resources:
print(f"Resource: {resource.uri} - {resource.description}")8.2.5 资源 URI 命名最佳实践
✅ 好的设计:
python
@mcp.resource("user://{user_id}") # 清晨的协议名
@mcp.resource("file://{path}/{filename}") # 多参数路径
@mcp.resource("docs://api/{version}") # 泊根路径❌ 避免的做法:
python
@mcp.resource("res://{id}") # ❌ 不清楚的协议名
@mcp.resource("user://{user_id}")
def get_user(uid: str): # ❌ 参数名不匹配!
pass8.3 自定义 System Prompt
python
system_prompt = """
你是一个数学助手。
当用户问到加法、减法、乘法、除法时,请调用相应的工具。
最后用清晰的中文回答用户的问题。
"""
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": user_input}
]9. 常见问题
9.1 Q1: 如何调试 MCP 服务器?
使用日志输出:
python
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
@mcp.tool()
def my_tool(x: int):
logger.info(f"Tool called with x={x}")
return x * 29.2 Q2: 如何处理工具调用错误?
python
try:
result = await session.call_tool(tool_name, args)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Tool call failed: {e}")
# 错误恢复逻辑9.3 Q3: 如何支持多轮对话?
保持 messages 列表,每次交互都添加新消息:
python
while True:
user_input = input("> ")
messages.append({"role": "user", "content": user_input})
# ... 处理响应,添加到 messages ...10. 性能优化建议
- 连接复用 - 不要频繁创建/销毁连接
- 超时设置 - 为 LLM 调用设置合理超时
- 错误重试 - 实现指数退避重试机制
- 日志级别 - 生产环境减少日志输出
11. 总结
通过 MCP,你可以轻松构建强大的 AI 应用,让 LLM 能够访问和使用自定义工具。核心步骤是:
- 定义工具(Server)
- 连接到服务器(Client)
- 让 LLM 自动调用工具
- 处理工具结果并返回给用户
希望这个教程能帮助你开始 MCP 的学习之旅!