学习链接
文章目录
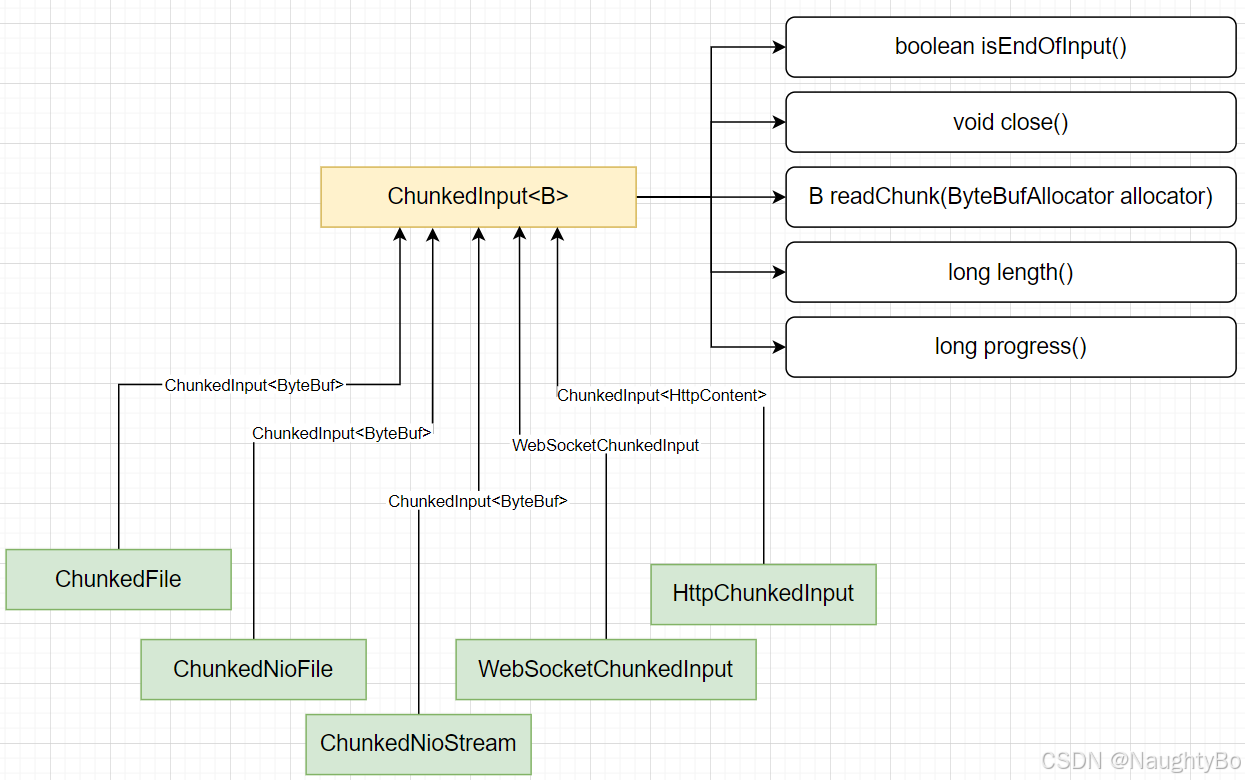
ChunkedInput<B>
先来看下分块读取的ChunkedInput接口
java
// 是否 流中已没有数据, 已经结束了
boolean isEndOfInput() throws Exception;
// 关闭并释放资源
void close() throws Exception;
// 从流中 获取分块数据。
// 一旦这个方法返回最后一块分块数据,就表示这个流已经到末尾了,后面调用isEndOfInput()将会返回true。
// 如果这个方法返回null,并不代表这个流已经到末尾了,在一些ChunkedInput的实现中,只是暂时获取不到分块
B readChunk(ByteBufAllocator allocator) throws Exception;
// 如果总长度已知的话,返回总长度;如果总长度未知的话,返回负数;
long length();
// 返回当前的传输进度
long progress();ChunkedFile
ChunkedFile是ChunkedInput接口的一个实现,它内部使用随机IO读写RandomAccessFile
属性
java
// 支持随机IO读写
private final RandomAccessFile file;
// 起始索引
private final long startOffset
// 结束索引
private final long endOffset;
// 每次读取的块大小
private final int chunkSize;
// 偏移量
private long offset;构造方法
java
public ChunkedFile(File file) throws IOException {
// 默认分块大小是: 8092
this(file, ChunkedStream.DEFAULT_CHUNK_SIZE);
}
public ChunkedFile(File file, int chunkSize) throws IOException {
// 创建随机io读写RandomAccessFile
this(new RandomAccessFile(file, "r"), chunkSize);
}
public ChunkedFile(RandomAccessFile file) throws IOException {
// 默认分块大小是: 8092
this(file, ChunkedStream.DEFAULT_CHUNK_SIZE);
}
public ChunkedFile(RandomAccessFile file, int chunkSize) throws IOException {
// 从偏移量为0开始读,一共读取file.length()个字节, 每次分块读取chunkSize个字节
this(file, 0, file.length(), chunkSize);
}
public ChunkedFile(RandomAccessFile file, long offset, long length, int chunkSize) throws IOException {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(file, "file");
ObjectUtil.checkPositiveOrZero(offset, "offset");
ObjectUtil.checkPositiveOrZero(length, "length");
ObjectUtil.checkPositive(chunkSize, "chunkSize");
// 随机io读写 RandomAccessFile
this.file = file;
// 起始索引和当前索引 赋值
this.offset = startOffset = offset;
// 结束索引赋值
this.endOffset = offset + length;
// 每次分块读取的大小
this.chunkSize = chunkSize;
file.seek(offset);
}isEndOfInput
java
@Override
public boolean isEndOfInput() throws Exception {
// 如果当前的索引 小于 结束索引,并且当前file还是打开状态,就没结束
return !(offset < endOffset && file.getChannel().isOpen());
}close()
java
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
file.close();
}readChunk
java
@Override
public ByteBuf readChunk(ByteBufAllocator allocator) throws Exception {
// 获取当前的索引, 如果当前的索引已经 到了 结束索引的未知, 那么返回null
long offset = this.offset;
if (offset >= endOffset) {
return null;
}
// 每次最多读取 chunkSize大小的字节数。最后读取 endoffset-offset 大小的字节数。
int chunkSize = (int) Math.min(this.chunkSize, endOffset - offset);
// 创建chunkSize大小的堆缓冲区
ByteBuf buf = allocator.heapBuffer(chunkSize);
// 如果下面读取发生异常, 则需要释放上面创建的堆缓冲区
boolean release = true;
try {
// 一直到读够chunkSize个字节数据为止
file.readFully(buf.array(), buf.arrayOffset(), chunkSize);
// 写索引向前移动 chunkSize
buf.writerIndex(chunkSize);
// 当前索引往后移动 chunkSize
this.offset = offset + chunkSize;
// 读取数据成功, 不需要释放缓冲区
release = false;
// 读取数据的缓冲区
return buf;
} finally {
// 如果读取发生异常, 则释放缓冲区
if (release) {
buf.release();
}
}
}length()
java
public long length() {
// 返回总长度
return endOffset - startOffset;
}progress()
java
@Override
public long progress() {
// 返回已读取了多个字节
return offset - startOffset;
}HttpChunkedInput
java
public class HttpChunkedInput implements ChunkedInput<HttpContent> {
// 实际操作的ChunkedInput
private final ChunkedInput<ByteBuf> input;
// 最后的内容
private final LastHttpContent lastHttpContent;
// 是否发送了最后的分块
private boolean sentLastChunk;
/* 构造方法, 需要传入实际的 ChunkedInput */
public HttpChunkedInput(ChunkedInput<ByteBuf> input) {
this.input = input;
lastHttpContent = LastHttpContent.EMPTY_LAST_CONTENT;
}
public HttpChunkedInput(ChunkedInput<ByteBuf> input,
LastHttpContent lastHttpContent) {
this.input = input;
this.lastHttpContent = lastHttpContent;
}
@Override
public boolean isEndOfInput() throws Exception {
// 如果input都读完了,还需要看是否发完了最后1个分块
if (input.isEndOfInput()) {
return sentLastChunk;
} else {
return false;
}
}
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
input.close();
}
@Override
public HttpContent readChunk(ByteBufAllocator allocator) throws Exception {
// 如果 input结束了
if (input.isEndOfInput()) {
// 如果最后的分块发出去了,则返回null
if (sentLastChunk) {
return null;
} else {
// 如果最后的分块没有发出去, 则此时将sendLastChunk置为true, 并返回lastHttpContent
sentLastChunk = true;
return lastHttpContent;
}
} else {
// 如果input未结束, 则调用input的读取分块的方法
ByteBuf buf = input.readChunk(allocator);
if (buf == null) {
return null;
}
// 分块内容封装为 DefaultHttpContent
return new DefaultHttpContent(buf);
}
}
@Override
public long length() {
// 返回input的总长度
return input.length();
}
@Override
public long progress() {
// 返回input读取的字节数
return input.progress();
}
}PendingWrite
PendingWrite是ChunkedWriteHandler中的一个静态内部类
java
private static final class PendingWrite {
// 待写入的消息内容对象
final Object msg;
// 写入结束后通过promise去通知
final ChannelPromise promise;
PendingWrite(Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) {
this.msg = msg;
this.promise = promise;
}
// 写入失败,通知写入失败
void fail(Throwable cause) {
// 释放msg
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
// 通知失败
promise.tryFailure(cause);
}
// 写入成功,通知成功
void success(long total) {
// 如果promise已经完成了,直接结束
if (promise.isDone()) {
return;
}
// 通知写入完成进度 100%
progress(total, total);
// 通知成功
promise.trySuccess();
}
// 通知写入进度
void progress(long progress, long total) {
if (promise instanceof ChannelProgressivePromise) {
((ChannelProgressivePromise) promise).tryProgress(progress, total);
}
}
}ChunkedWriteHandler的属性
java
// 基于数组实现的 双端队列
final Queue<PendingWrite> queue = new ArrayDeque<PendingWrite>();
// 当前handler添加到pipeline后的 上下文
volatile ChannelHandlerContext ctx;ChunkedWriteHandler的方法
handlerAdded
java
@Override
public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 当handler添加到pipeline后,将ctx保存到当前handler中
this.ctx = ctx;
}resumeTransfer
java
public void resumeTransfer() {
// 如果当前handler还没挂载到pipeline上,则直接返回
final ChannelHandlerContext ctx = this.ctx;
if (ctx == null) {
return;
}
// 当前代码执行时所在的线程与 ctx的eventLoop线程是否是同一个线程
if (ctx.executor().inEventLoop()) {
// 如果是同一个线程, 则直接在当前线程上执行 恢复传输
resumeTransfer0(ctx);
} else {
// 如果不是同一个线程, 则等待eventloop线程下一次循环时再执行 恢复传输
ctx.executor().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
resumeTransfer0(ctx);
}
});
}
}resumeTransfer0
java
private void resumeTransfer0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
try {
// 只是调用doFlush, 并忽略其中所发生的所有异常
doFlush(ctx);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("Unexpected exception while sending chunks.", e);
}
}write
java
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx,
Object msg,
ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
// 将待写入的msg消息对象封装到PendingWrite中,添加到 queue双端队列 中
queue.add(new PendingWrite(msg, promise));
}flush
java
@Override
public void flush(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 调用doFlush
doFlush(ctx);
}channelInactive
当channel处于inactive状态时的回调
java
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 调用doFlush
doFlush(ctx);
// 向后面的入站处理器继续传播channelInactive事件
ctx.fireChannelInactive();
}channelWritabilityChanged
当channel的写状态(可写/不可写 切换)发生变化时
java
@Override
public void channelWritabilityChanged(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 当channel切换为可写状态时
if (ctx.channel().isWritable()) {
// 调用doFlush
doFlush(ctx);
}
// 向后面的入站处理器继续传播fireChannelWritabilityChanged事件
ctx.fireChannelWritabilityChanged();
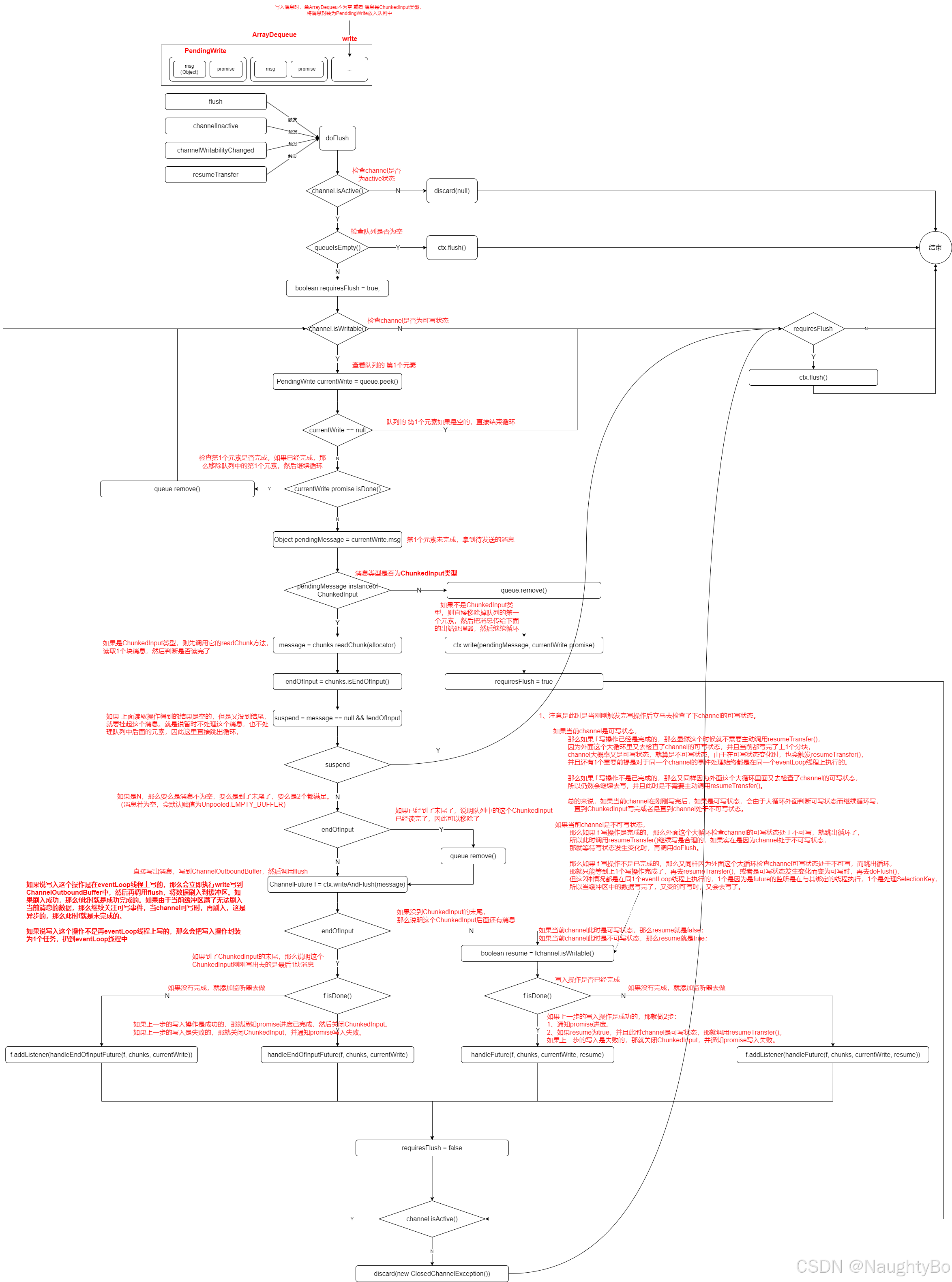
}doFlush
java
private void doFlush(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
//
final Channel channel = ctx.channel();
if (!channel.isActive()) {
discard(null);
return;
}
boolean requiresFlush = true;
ByteBufAllocator allocator = ctx.alloc();
while (channel.isWritable()) {
final PendingWrite currentWrite = queue.peek();
if (currentWrite == null) {
break;
}
if (currentWrite.promise.isDone()) {
// This might happen e.g. in the case when a write operation
// failed, but there're still unconsumed chunks left.
// Most chunked input sources would stop generating chunks
// and report end of input, but this doesn't work with any
// source wrapped in HttpChunkedInput.
// Note, that we're not trying to release the message/chunks
// as this had to be done already by someone who resolved the
// promise (using ChunkedInput.close method).
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/8700.
queue.remove();
continue;
}
final Object pendingMessage = currentWrite.msg;
if (pendingMessage instanceof ChunkedInput) {
final ChunkedInput<?> chunks = (ChunkedInput<?>) pendingMessage;
boolean endOfInput;
boolean suspend;
Object message = null;
try {
message = chunks.readChunk(allocator);
endOfInput = chunks.isEndOfInput();
if (message == null) {
// No need to suspend when reached at the end.
suspend = !endOfInput;
} else {
suspend = false;
}
} catch (final Throwable t) {
queue.remove();
if (message != null) {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(message);
}
closeInput(chunks);
currentWrite.fail(t);
break;
}
if (suspend) {
// ChunkedInput.nextChunk() returned null and it has
// not reached at the end of input. Let's wait until
// more chunks arrive. Nothing to write or notify.
break;
}
if (message == null) {
// If message is null write an empty ByteBuf.
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/1671
message = Unpooled.EMPTY_BUFFER;
}
if (endOfInput) {
// We need to remove the element from the queue before we call writeAndFlush() as this operation
// may cause an action that also touches the queue.
queue.remove();
}
// Flush each chunk to conserve memory
ChannelFuture f = ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
if (endOfInput) {
if (f.isDone()) {
handleEndOfInputFuture(f, currentWrite);
} else {
// Register a listener which will close the input once the write is complete.
// This is needed because the Chunk may have some resource bound that can not
// be closed before its not written.
//
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/303
f.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) {
handleEndOfInputFuture(future, currentWrite);
}
});
}
} else {
final boolean resume = !channel.isWritable();
if (f.isDone()) {
handleFuture(f, currentWrite, resume);
} else {
f.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) {
handleFuture(future, currentWrite, resume);
}
});
}
}
requiresFlush = false;
} else {
queue.remove();
ctx.write(pendingMessage, currentWrite.promise);
requiresFlush = true;
}
if (!channel.isActive()) {
discard(new ClosedChannelException());
break;
}
}
if (requiresFlush) {
ctx.flush();
}
}
java
private void resumeTransfer0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
try {
// 只调用doFlush, 并忽略其中发生的所有的异常
doFlush(ctx);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("Unexpected exception while sending chunks.", e);
}
}discard
java
private void discard(Throwable cause) {
for (;;) {
PendingWrite currentWrite = queue.poll();
if (currentWrite == null) {
break;
}
Object message = currentWrite.msg;
if (message instanceof ChunkedInput) {
ChunkedInput<?> in = (ChunkedInput<?>) message;
boolean endOfInput;
long inputLength;
try {
endOfInput = in.isEndOfInput();
inputLength = in.length();
closeInput(in);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeInput(in);
currentWrite.fail(e);
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn(ChunkedInput.class.getSimpleName() + " failed", e);
}
continue;
}
if (!endOfInput) {
if (cause == null) {
cause = new ClosedChannelException();
}
currentWrite.fail(cause);
} else {
currentWrite.success(inputLength);
}
} else {
if (cause == null) {
cause = new ClosedChannelException();
}
currentWrite.fail(cause);
}
}
}handleEndOfInputFuture
java
private static void handleEndOfInputFuture(ChannelFuture future, PendingWrite currentWrite) {
ChunkedInput<?> input = (ChunkedInput<?>) currentWrite.msg;
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
closeInput(input);
currentWrite.fail(future.cause());
} else {
// read state of the input in local variables before closing it
long inputProgress = input.progress();
long inputLength = input.length();
closeInput(input);
currentWrite.progress(inputProgress, inputLength);
currentWrite.success(inputLength);
}
}handleFuture
java
private void handleFuture(ChannelFuture future,
PendingWrite currentWrite,
boolean resume) {
ChunkedInput<?> input = (ChunkedInput<?>) currentWrite.msg;
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
closeInput(input);
currentWrite.fail(future.cause());
} else {
currentWrite.progress(input.progress(), input.length());
if (resume && future.channel().isWritable()) {
resumeTransfer();
}
}
}