2025/12/27:
好久没写了,记录一下自己学习agent时遇到和解决的一些问题。
文章目录
- [一、pubMed API 获取](#一、pubMed API 获取)
- 二、通过langchain调用api
- [三、重载 run 函数](#三、重载 run 函数)
- 四、源码
一、pubMed API 获取
What
pubMed是生物医学领域权威的信息检索平台,通过这个平台检索到的内容可以支持agent进行一些医疗知识问答的工作。
Why
如果没有API密钥,任何IP地址每秒服务器发送超过3个请求将收到错误消息。通过包含API密钥,默认情况下,站点每秒最多可以发布10个请求。简单来说该api支持我们更频繁地获取检索信息。
How
想获取api很简单,流程如下:
-
访问站点 pubmed
注册或直接登录,注册账号也很快,我直接用微软账号登录。
-
选择setting进入
-
划到界面最下方直接创建key
二、通过langchain调用api
项目目录需要加入一个名为.env的文件,.env文件中写入获取的api,供dotenv读入,具体为:
PUBMED_API_KEY=获取的api
同时还需要写入一些调用的api信息,这里我用的是qwen(dashScope),因此在.env中加入百炼控制台申请的key:
DASHSCOPE_API_KEY=获取的api
exa.py中的具体代码如下,langchain官方提供的例子实测运行不起来,没传入api_key,且存在ssl证书相关报错:
python
from langchain_community.retrievers import PubMedRetriever
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import certifi
import ssl
from functools import partial
# 避免自签名证书验证失败
ssl._create_default_https_context = partial(ssl.create_default_context, cafile=certifi.where())
load_dotenv()
# 创建PubMed检索器实例
retriever = PubMedRetriever(api_key=os.getenv("PUBMED_API_KEY"))
# 检索与"chatgpt"相关的文献
documents = retriever.invoke("cancer")
# 输出检索结果
for document in documents:
print(f"Title: {document.metadata['Title']}")
print(f"Published: {document.metadata['Published']}")
print(f"Copyright Information: {document.metadata['Copyright Information']}")
print(f"Content: {document.page_content}\n")检索结果如下:
Title: LDAcoop: Integrating non-linear population dynamics into the analysis of clonogenic growth in vitro.
Published: 2025-12-26
Copyright Information: © 2025 The Author(s). Molecular Oncology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Content: The limiting dilution assay (LDA) is a key method to quantify clonogenic cells with self-renewing capacity in vitro, crucial for preclinical cancer research and therapy response assessment. It estimates the frequency of individual clonogenic, stem-like cells within a population based on their ability to form colonies with ≥50 cells at limiting cell numbers. Standard LDA analysis relies on linear, single-hit Poisson models, yet clonogenic growth under single-cell conditions often involves cooperative or competitive dynamics, violating this linearity assumption. Here, we present a modeling framework incorporating non-linear population dynamics into LDA analysis and introduce LDAcoop, an R-based tool for universal quantification of clonogenic cells in LDA formats. Across multiple cancer cell types, we benchmarked LDA against the colony formation assay (CFA) and show that LDA outperforms CFA, especially for patient-derived organoids, suspension cultures, and higher throughput applications. This renders the LDA format particularly suitable for larger-scale pharmacogenomic screening and drug sensitivity testing in complex models. Our results establish LDA and LDAcoop as versatile, scalable tools for robust quantification of clonogenic growth, supporting preclinical drug development and molecular precision oncology research.
Title: Tumor Control After Radiosurgery in Sporadic and Neurofibromatosis Type 2 Vestibular Schwannomas.
Published: --
Copyright Information: © 2025 The Author(s). Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Content: INTRODUCTION: The tumor control rate after stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for neurofibromatosis type 2-associated vestibular schwannomas (NF2-VSs) compared to sporadic vestibular schwannomas (S-VSs) remains unclear. This nationwide, multicenter, retrospective study (KGKRS-21-001) aimed to clarify this issue.
METHODS: A total of 4718 patients treated with SRS for vestibular schwannomas were analyzed from 13 nationwide institutions in Korea. NF2-VS cases were propensity score-matched with S-VS cases at a ratio of 1:1, based on age, tumor volume, and marginal dose, resulting in 122 cases in each group.
RESULTS: No significant differences in age, tumor volume, or marginal dose were observed between the matched cohorts. The overall tumor control rates at 1, 3, and 10 years after SRS were 93.3%, 87.7%, and 80.7%, respectively, with no significant difference between NF2-VS and S-VS groups (p = 0.63). Subgroup analysis showed that age ≤ 19 years was a significant negative prognostic factor for tumor control in NF2-VS patients (p < 0.001), whereas no such correlation was found in the S-VS cohort (p = 0.78).
CONCLUSIONS: SRS provides comparable tumor control for NF2-VSs and S-VSs. However, among NF2-VS patients, younger age (≤ 19 years) was associated with poorer tumor control, suggesting that age may be a critical factor in treatment decisions.
Title: Adverse Events of EUS-Guided Biliary Drainage for Malignant Biliary Obstruction: A Large Multicenter Study.
Published: 2025-12-26
Copyright Information: © 2025 Japanese Society of Hepato‐Biliary‐Pancreatic Surgery.
Content: BACKGROUND AND AIMS: This study aimed to evaluate adverse events (AEs) for endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage (EUS-BD) and identify risk factors for early AEs and recurrent biliary obstruction (RBO).
METHODS: A multicenter retrospective study was conducted using a common database of 21 Japanese referral centers.
RESULTS: A total of 616 patients who underwent EUS-BD, including endoscopic ultrasound-guided choledochoduodenostomy (n = 107), hepaticogastrostomy (n = 487), and hepaticojejunostomy (n = 22), for malignant biliary obstruction were analyzed. Early AEs occurred in 13.6% of patients. Independent risk factors for all AEs included procedure time ≥ 32 min (odds ratio [OR] 1.82) and antiplatelet/anticoagulant use (OR 2.15). A risk factor for peritonitis included electrocautery use (OR 3.87), while bleeding risk was increased with antiplatelet/anticoagulant use (OR 7.19) and performance status > 2 (OR 5.26). The use of plastic stents was associated with a higher risk of a shorter time to RBO. AE and RBO rates did not significantly differ among the three EUS-BD approaches.
CONCLUSIONS: Patients on antiplatelet and/or anticoagulation therapy should be aware of the increased risk of AEs of EUS-BD. In addition, it is important to minimize procedure time, avoid the use of electrocautery, and use a metal stent to prevent early AEs and RBO.可以看到取得了cancer(癌症)相关的检索信息,另外,可以根据PubMedAPIWrapper的参数进行检索器更加细粒度的配置,比如top_k的大小以及返回文档的最大长度等等。
-
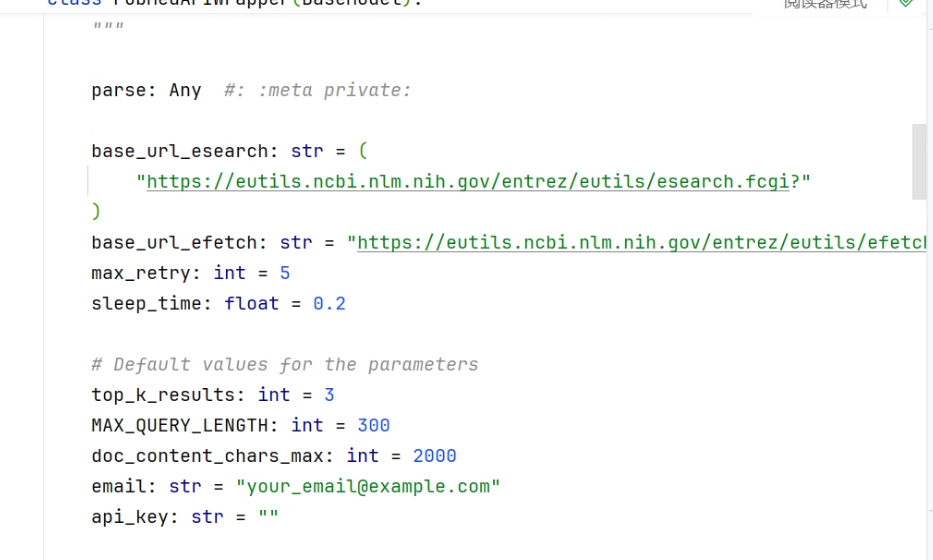
max_retry:最多重试请求的次数,遇到可重试的 HTTP 错误(如 429)时会重试,超过后抛出错误。 -
sleep_time:首次重试前等待的秒数;实现中通常会指数增长(例如每次乘以 2)。 -
top_k_results:每次查询返回的最相关文献条目数(top-K)。 -
MAX_QUERY_LENGTH:对查询字符串的最大允许长度,超过会被截断以避免请求过长。 -
doc_content_chars_max:最终返回文档内容的最大字符数,上限用于截断长文本。
这里同样额外说明一下retriever.invoke返回数据的格式,这在PubMedAPIWrapper.run中有所提及:docs = [
f"Published: {result['Published']}\n"
f"Title: {result['Title']}\n"
f"Copyright Information: {result['Copyright Information']}\n"
f"Summary::\n{result['Summary']}"
for result in self.load(query[: self.MAX_QUERY_LENGTH])
]
三、重载 run 函数
如果retreiver.invoke返回的内容不合你的心意?
举个例子,接下来确定一下我们新数据结构的需求:
# 之前
docs = [
f"Published: {result['Published']}\n"
f"Title: {result['Title']}\n"
f"Copyright Information: {result['Copyright Information']}\n"
f"Summary::\n{result['Summary']}"
for result in self.load(query[: self.MAX_QUERY_LENGTH])
]
# 新数据结构(仅示意)
info = {
'id': id + 1, # Increment id for easier subsequent operations
'title': 网页title
'url': 网页url
'date': result.get('publishedDate', '').split('T')[0],
'snippet': 摘要
'context': '待填充上下文
}可以看到新增了一个url字段。
接下来我们需要对run函数做一个重载,改变一下原函数返回的数据结构:
看代码可知:
invoke -调用-> 父类PubMedAPIWrapper.run() -调用-> load() -调用-> lazy_load() -调用-> retrieve_article() -调用-> _parse_article()
retrieve_article 和_parse_article 的具体代码如下:
python
def retrieve_article(self, uid: str, webenv: str) -> dict:
url = (
self.base_url_efetch
+ "db=pubmed&retmode=xml&id="
+ uid
+ "&webenv="
+ webenv
)
if self.api_key != "":
url += f"&api_key={self.api_key}"
retry = 0
while True:
try:
result = urllib.request.urlopen(url)
break
except urllib.error.HTTPError as e:
if e.code == 429 and retry < self.max_retry:
# Too Many Requests errors
# wait for an exponentially increasing amount of time
print( # noqa: T201
f"Too Many Requests, "
f"waiting for {self.sleep_time:.2f} seconds..."
)
time.sleep(self.sleep_time)
self.sleep_time *= 2
retry += 1
else:
raise e
xml_text = result.read().decode("utf-8")
text_dict = self.parse(xml_text)
return self._parse_article(uid, text_dict)
def _parse_article(self, uid: str, text_dict: dict) -> dict:
try:
ar = text_dict["PubmedArticleSet"]["PubmedArticle"]["MedlineCitation"][
"Article"
]
except KeyError:
ar = text_dict["PubmedArticleSet"]["PubmedBookArticle"]["BookDocument"]
abstract_text = ar.get("Abstract", {}).get("AbstractText", [])
summaries = [
f"{txt['@Label']}: {txt['#text']}"
for txt in abstract_text
if "#text" in txt and "@Label" in txt
]
summary = (
"\n".join(summaries)
if summaries
else (
abstract_text
if isinstance(abstract_text, str)
else (
"\n".join(str(value) for value in abstract_text.values())
if isinstance(abstract_text, dict)
else "No abstract available"
)
)
)
a_d = ar.get("ArticleDate", {})
pub_date = "-".join(
[
a_d.get("Year", ""),
a_d.get("Month", ""),
a_d.get("Day", ""),
]
)
return {
"uid": uid,
"Title": ar.get("ArticleTitle", ""),
"Published": pub_date,
"Copyright Information": ar.get("Abstract", {}).get(
"CopyrightInformation", ""
),
"Summary": summary,
}run里直接使用了该函数的返回值,所以直接对这个数据结构进行增减即可。由于除了在retrieve_article中组装、但在_parse_article未出现的url字段,其他字段均可由原返回结果得到,因此现在我们需要重载的类函数为 retrieve_article。不过需要注意的是,这里有个大坑:
python
def _dict2document(self, doc: dict) -> Document:
"""
ATTENTION:
旧写法:summary = doc.pop("Summary"),所以metadata中缺少Summary字段
"""
summary = doc["Summary"]
return Document(page_content=summary, metadata=doc)在父类的该函数中去掉了result包含的summary字段,直接将该字段作为content输出,所以在result中找了很久这个字段没找到,如果我们需要从result中获取该字段,该方法也需要重载 (不重载也行,直接从document获取content即可)。
另外,如果需要关于文献的其他字段信息,可以通过进一步修改parse函数解析xml文件来获取,这里是xml文件的部分信息:
四、源码
blog中涉及的部分源码如下:
python
import os
import ssl
import certifi
import urllib.error
import urllib.parse
import urllib.request
from functools import partial
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from langchain_community.retrievers import PubMedRetriever
from langchain_core.documents import Document
import re
import string
import time
import jieba
import requests
import concurrent.futures
from typing import Tuple, Optional
from tqdm import tqdm
from concurrent.futures.thread import ThreadPoolExecutor
class customRetriever(PubMedRetriever):
def _dict2document(self, doc: dict) -> Document:
"""
ATTENTION:
旧写法:summary = doc.pop("Summary"),所以metadata中缺少Summary字段
"""
summary = doc["Summary"]
return Document(page_content=summary, metadata=doc)
def _parse_article(self, uid: str, text_dict: dict) -> dict:
try:
ar = text_dict["PubmedArticleSet"]["PubmedArticle"]["MedlineCitation"][
"Article"
]
except KeyError:
ar = text_dict["PubmedArticleSet"]["PubmedBookArticle"]["BookDocument"]
abstract_text = ar.get("Abstract", {}).get("AbstractText", [])
summaries = [
f"{txt['@Label']}: {txt['#text']}"
for txt in abstract_text
if "#text" in txt and "@Label" in txt
]
summary = (
"\n".join(summaries)
if summaries
else (
abstract_text
if isinstance(abstract_text, str)
else (
"\n".join(str(value) for value in abstract_text.values())
if isinstance(abstract_text, dict)
else "No abstract available"
)
)
)
a_d = ar.get("ArticleDate", {})
pub_date = "-".join(
[
a_d.get("Year", ""),
a_d.get("Month", ""),
a_d.get("Day", ""),
]
)
return {
"uid": uid,
"Title": ar.get("ArticleTitle", ""),
"Published": pub_date,
"Copyright Information": ar.get("Abstract", {}).get(
"CopyrightInformation", ""
),
"Summary": summary,
}
def retrieve_article(self, uid: str, webenv: str) -> dict:
"""
获取文章的详细信息
通过efetch接口获取文章的详细信息,包括标题、摘要、出版日期等
:param uid:
:param webenv:
:return:
"""
url = (
self.base_url_efetch
+ "db=pubmed&retmode=xml&id="
+ uid
+ "&webenv="
+ webenv
)
if self.api_key != "":
url += f"&api_key={self.api_key}"
retry = 0
while True:
try:
result = urllib.request.urlopen(url)
break
except urllib.error.HTTPError as e:
if e.code == 429 and retry < self.max_retry:
# Too Many Requests errors
# wait for an exponentially increasing amount of time
print( # noqa: T201
f"Too Many Requests, "
f"waiting for {self.sleep_time:.2f} seconds..."
)
time.sleep(self.sleep_time)
self.sleep_time *= 2
retry += 1
else:
raise e
xml_text = result.read().decode("utf-8")
text_dict = self.parse(xml_text)
ret_dict = self._parse_article(uid, text_dict)
# 加入url字段
ret_dict["url"] = url
return ret_dict
class NCBIRetriever():
def __init__(self):
# 创建PubMed检索器实例
# 如果取不到环境变量则报错
if os.getenv("PUBMED_API_KEY") is None:
raise ValueError("PUBMED_API_KEY environment variable not set")
self.retriever = customRetriever(api_key=os.getenv("PUBMED_API_KEY"))
def web_search(self, query: str, top_k_results: int = 3, MAX_QUERY_LENGTH: int = 2000) -> list[Document]:
"""
发送查询请求,获取相关文献
这里可以根据需要调整top_k_results参数
例如:top_k_results=5表示获取前5条相关文献
:param query: 查询关键词
:param top_k_results: 获取的文献数量
:return: 文献列表
"""
self.retriever.top_k_results = top_k_results
self.retriever.MAX_QUERY_LENGTH = MAX_QUERY_LENGTH
results = self.retriever.invoke(query)
return results
# 避免自签名证书验证失败
ssl._create_default_https_context = partial(ssl.create_default_context, cafile=certifi.where())
load_dotenv()
# 创建PubMed检索器实例
retrieverManager = NCBIRetriever()
# 检索与"chatgpt"相关的文献
documents = retrieverManager.web_search("cancer", top_k_results=3)
useful_info = extract_relevant_info(documents)
# 输出检索结果
for info in useful_info:
print(f"Title: {info['title']}")
print(f"Published: {info['date']}")
print(f"URL: {info['url']}")
print(f"Date: {info['date']}")
print(f"Snippet: {info['snippet']}")