今天来梳理一下 Flink 双流操作相关的源码。
写在前面
通过Flink学习笔记:多流 Join一文的介绍,我们知道 Flink 有三种数据关联的方式,分别是 Window Join、Interval Join 和 CoGroup。下面我们分别看下这三种关联方式的源码实现。
Window Join
我们先回顾一下 window join 的使用方法。
java
DataStream<Tuple2<String, Double>> result = source1.join(source2)
.where(record -> record.f0)
.equalTo(record -> record.f0)
.window(TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(2L)))
.apply(new JoinFunction<Tuple2<String, Double>, Tuple2<String, Double>, Tuple2<String, Double>>() {
@Override
public Tuple2<String, Double> join(Tuple2<String, Double> record1, Tuple2<String, Double> record2) throws Exception {
return Tuple2.of(record1.f0, record1.f1);
}
});上述调用链路类的流转如下:
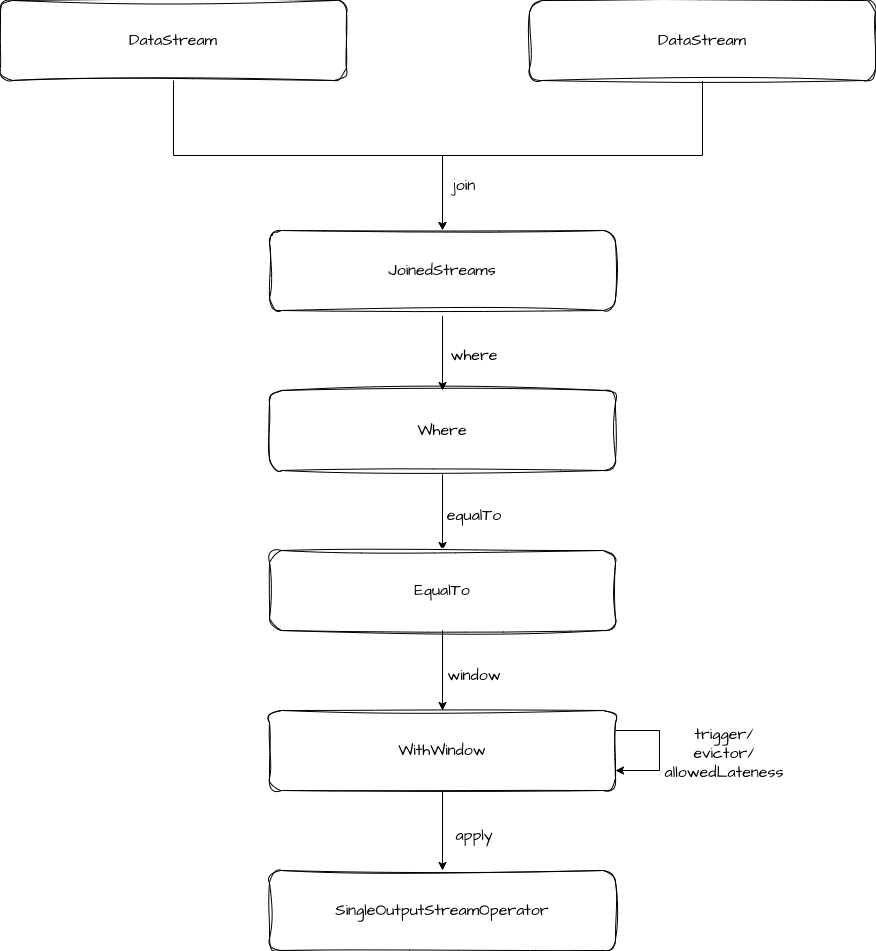
在 WithWindow 的 apply 方法中,是构建了一个 coGroupedWindowedStream,然后调用它的 apply 方法。
java
public <T> SingleOutputStreamOperator<T> apply(
JoinFunction<T1, T2, T> function, TypeInformation<T> resultType) {
// clean the closure
function = input1.getExecutionEnvironment().clean(function);
coGroupedWindowedStream =
input1.coGroup(input2)
.where(keySelector1)
.equalTo(keySelector2)
.window(windowAssigner)
.trigger(trigger)
.evictor(evictor)
.allowedLateness(allowedLateness);
return coGroupedWindowedStream.apply(new JoinCoGroupFunction<>(function), resultType);
}这里可以看出,Window Join 的底层是转换成 coGroup 进行处理的。
在 JoinCoGroupFunction 中,coGroup 方法就是对两个流进行两层遍历,然后将其应用到我们自定义的 JoinFunction 上。
java
private static class JoinCoGroupFunction<T1, T2, T>
extends WrappingFunction<JoinFunction<T1, T2, T>>
implements CoGroupFunction<T1, T2, T> {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public JoinCoGroupFunction(JoinFunction<T1, T2, T> wrappedFunction) {
super(wrappedFunction);
}
@Override
public void coGroup(Iterable<T1> first, Iterable<T2> second, Collector<T> out)
throws Exception {
for (T1 val1 : first) {
for (T2 val2 : second) {
out.collect(wrappedFunction.join(val1, val2));
}
}
}
}CoGroup
CoGroup 的整体用法和流程与 Join 都类似,我们就不逐个介绍了。我们直接来看 apply 方法。
java
public <T> SingleOutputStreamOperator<T> apply(
CoGroupFunction<T1, T2, T> function, TypeInformation<T> resultType) {
// clean the closure
function = input1.getExecutionEnvironment().clean(function);
UnionTypeInfo<T1, T2> unionType =
new UnionTypeInfo<>(input1.getType(), input2.getType());
UnionKeySelector<T1, T2, KEY> unionKeySelector =
new UnionKeySelector<>(keySelector1, keySelector2);
SingleOutputStreamOperator<TaggedUnion<T1, T2>> taggedInput1 =
input1.map(new Input1Tagger<T1, T2>());
taggedInput1.getTransformation().setParallelism(input1.getParallelism(), false);
taggedInput1.returns(unionType);
SingleOutputStreamOperator<TaggedUnion<T1, T2>> taggedInput2 =
input2.map(new Input2Tagger<T1, T2>());
taggedInput2.getTransformation().setParallelism(input2.getParallelism(), false);
taggedInput2.returns(unionType);
DataStream<TaggedUnion<T1, T2>> unionStream = taggedInput1.union(taggedInput2);
// we explicitly create the keyed stream to manually pass the key type information in
windowedStream =
new KeyedStream<TaggedUnion<T1, T2>, KEY>(
unionStream, unionKeySelector, keyType)
.window(windowAssigner);
if (trigger != null) {
windowedStream.trigger(trigger);
}
if (evictor != null) {
windowedStream.evictor(evictor);
}
if (allowedLateness != null) {
windowedStream.allowedLateness(allowedLateness);
}
return windowedStream.apply(
new CoGroupWindowFunction<T1, T2, T, KEY, W>(function), resultType);
}在 apply 方法中,先把两个流进行合并,然后创建了 windowedStream,并把窗口相关的属性设置好,最后是调用 windowedStream 的 apply 方法。
在调用 windowedStream.apply 方法时,又将 function 包装成了 CoGroupWindowFunction。
java
private static class CoGroupWindowFunction<T1, T2, T, KEY, W extends Window>
extends WrappingFunction<CoGroupFunction<T1, T2, T>>
implements WindowFunction<TaggedUnion<T1, T2>, T, KEY, W> {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public CoGroupWindowFunction(CoGroupFunction<T1, T2, T> userFunction) {
super(userFunction);
}
@Override
public void apply(KEY key, W window, Iterable<TaggedUnion<T1, T2>> values, Collector<T> out)
throws Exception {
List<T1> oneValues = new ArrayList<>();
List<T2> twoValues = new ArrayList<>();
for (TaggedUnion<T1, T2> val : values) {
if (val.isOne()) {
oneValues.add(val.getOne());
} else {
twoValues.add(val.getTwo());
}
}
wrappedFunction.coGroup(oneValues, twoValues, out);
}
}在 CoGroupWindowFunction 的 apply 方法中是将主键为 key 的流分开两个流,再去调用 JoinCoGroupFunction 的 coGroup 方法。这里的 values 都是相同的 key,原因是在 window 中维护的 windowState,它内部是一个 stateTable,窗口的 namespace 和 key 共同维护一个 state,当窗口触发时,就会对相同 key 的数据调用 apply 方法。
Interval Join
梳理完了 Window Join 和 CoGroup 之后,我们再接着看 Interval Join。还是先来回顾一下用法。
java
DataStream<Tuple2<String, Double>> intervalJoinResult = source1.keyBy(record -> record.f0)
.intervalJoin(source2.keyBy(record -> record.f0))
.between(Time.seconds(-2), Time.seconds(2))
.process(new ProcessJoinFunction<Tuple2<String, Double>, Tuple2<String, Double>, Tuple2<String, Double>>() {
@Override
public void processElement(Tuple2<String, Double> record1, Tuple2<String, Double> record2, ProcessJoinFunction<Tuple2<String, Double>, Tuple2<String, Double>, Tuple2<String, Double>>.Context context, Collector<Tuple2<String, Double>> out) throws Exception {
out.collect(Tuple2.of(record1.f0, record1.f1 + record2.f1));
}
});通过用法可以看出,interval join 传入的对象是两个 KeyedStream,接着使用 between 方法定义 interval join 的上下边界,最后调用 process 方法执行计算逻辑。
在调用过程中,类型的转换如下图。
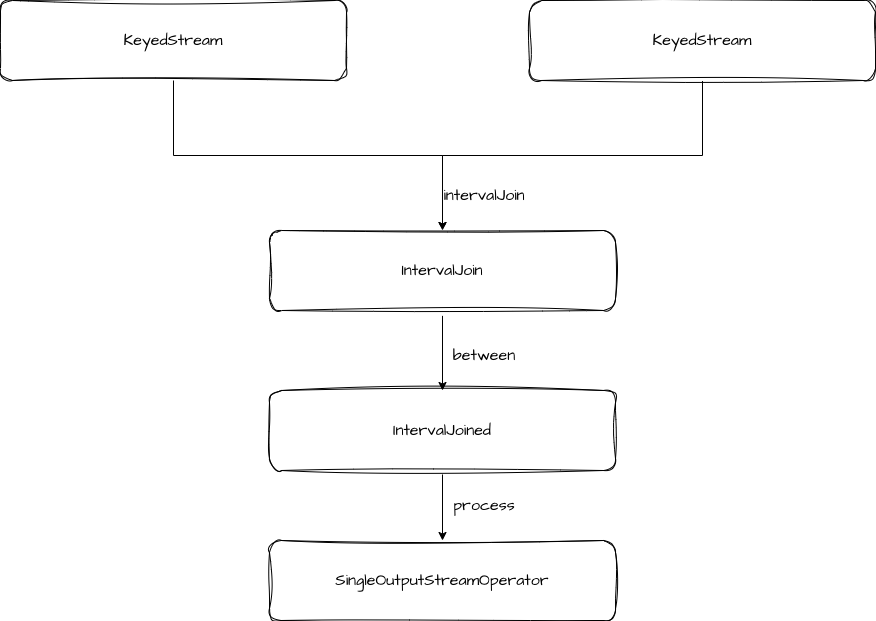
我们主要关注 process 的逻辑。
java
public <OUT> SingleOutputStreamOperator<OUT> process(
ProcessJoinFunction<IN1, IN2, OUT> processJoinFunction,
TypeInformation<OUT> outputType) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(processJoinFunction);
Preconditions.checkNotNull(outputType);
final ProcessJoinFunction<IN1, IN2, OUT> cleanedUdf =
left.getExecutionEnvironment().clean(processJoinFunction);
if (isEnableAsyncState) {
final AsyncIntervalJoinOperator<KEY, IN1, IN2, OUT> operator =
new AsyncIntervalJoinOperator<>(
lowerBound,
upperBound,
lowerBoundInclusive,
upperBoundInclusive,
leftLateDataOutputTag,
rightLateDataOutputTag,
left.getType()
.createSerializer(
left.getExecutionConfig().getSerializerConfig()),
right.getType()
.createSerializer(
right.getExecutionConfig().getSerializerConfig()),
cleanedUdf);
return left.connect(right)
.keyBy(keySelector1, keySelector2)
.transform("Interval Join [Async]", outputType, operator);
} else {
final IntervalJoinOperator<KEY, IN1, IN2, OUT> operator =
new IntervalJoinOperator<>(
lowerBound,
upperBound,
lowerBoundInclusive,
upperBoundInclusive,
leftLateDataOutputTag,
rightLateDataOutputTag,
left.getType()
.createSerializer(
left.getExecutionConfig().getSerializerConfig()),
right.getType()
.createSerializer(
right.getExecutionConfig().getSerializerConfig()),
cleanedUdf);
return left.connect(right)
.keyBy(keySelector1, keySelector2)
.transform("Interval Join", outputType, operator);
}
}Interval join 是基于 ConnectedStream 实现的,ConnectedStream 提供了更加通用的双流操作,它将两个流组合成一个 TwoInputTransformation,然后加入执行图中。
具体的 Operator 是 IntervalJoinOperator 或 AsyncIntervalJoinOperator,它们都是 TwoInputStreamOperator 的实现类,提供 processElement1 和 processElement2 两个方法分别处理两个输入源的数据,最终都调用的是 processElement。
java
private <THIS, OTHER> void processElement(
final StreamRecord<THIS> record,
final MapState<Long, List<IntervalJoinOperator.BufferEntry<THIS>>> ourBuffer,
final MapState<Long, List<IntervalJoinOperator.BufferEntry<OTHER>>> otherBuffer,
final long relativeLowerBound,
final long relativeUpperBound,
final boolean isLeft)
throws Exception {
final THIS ourValue = record.getValue();
final long ourTimestamp = record.getTimestamp();
if (ourTimestamp == Long.MIN_VALUE) {
throw new FlinkException(
"Long.MIN_VALUE timestamp: Elements used in "
+ "interval stream joins need to have timestamps meaningful timestamps.");
}
if (isLate(ourTimestamp)) {
sideOutput(ourValue, ourTimestamp, isLeft);
return;
}
addToBuffer(ourBuffer, ourValue, ourTimestamp);
for (Map.Entry<Long, List<BufferEntry<OTHER>>> bucket : otherBuffer.entries()) {
final long timestamp = bucket.getKey();
if (timestamp < ourTimestamp + relativeLowerBound
|| timestamp > ourTimestamp + relativeUpperBound) {
continue;
}
for (BufferEntry<OTHER> entry : bucket.getValue()) {
if (isLeft) {
collect((T1) ourValue, (T2) entry.element, ourTimestamp, timestamp);
} else {
collect((T1) entry.element, (T2) ourValue, timestamp, ourTimestamp);
}
}
}
long cleanupTime =
(relativeUpperBound > 0L) ? ourTimestamp + relativeUpperBound : ourTimestamp;
if (isLeft) {
internalTimerService.registerEventTimeTimer(CLEANUP_NAMESPACE_LEFT, cleanupTime);
} else {
internalTimerService.registerEventTimeTimer(CLEANUP_NAMESPACE_RIGHT, cleanupTime);
}
}在 IntervalJoinOperator 中维护了两个 MapState,每个消息进来的时候,都会加入到 MapState 中,key 是 timestamp,value 是一个元素的列表。然后遍历另一个 MapState,得到符合条件的数据。最后是为每条数据注册一个定时器,当时间超过有效范围后,会从 MapState 中清除这个时间戳的数据。
总结
本文我们梳理了 Flink 的三种双流操作的源码,我们了解到 Window Join 底层是通过 CoGroup 实现的。CoGroup 本身是将两个流合并成 WindowedStream 并依赖于 WindowState 进行数据 join。最后 Interval Join 是通过 ConnectedStreams 实现的,内部的 IntervalJoinOperator 会维护两个 MapState,通过 MapState 进行数据关联。