引言
近年来,扩散模型在图像生成领域取得了突破性进展,其中Stable Diffusion系列模型因其出色的生成质量和开源特性而广受欢迎。随着模型规模的扩大,推理速度和显存消耗成为实际部署的关键挑战。Stable Diffusion 3.5 FP8正是在这一背景下推出的优化版本,通过FP8精度量化大幅提升了推理效率。
1. Stable Diffusion 3.5 架构概述
1.1 核心组件
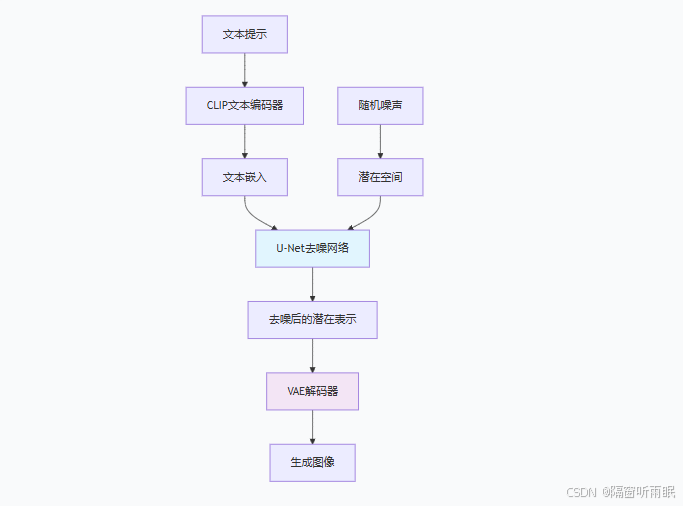
Stable Diffusion 3.5基于Latent Diffusion框架,主要由以下组件构成:
-
变分自编码器(VAE):负责将图像压缩到潜在空间,以及从潜在空间重建图像
-
U-Net网络:在潜在空间执行去噪过程的核心组件
-
文本编码器:将文本提示转换为嵌入向量
-
调度器(Scheduler):控制去噪过程的时间步长
1.2 架构示意图
2. FP8量化技术原理
2.1 FP8格式简介
FP8(8位浮点数)是一种新兴的数值格式,在保持足够精度的同时大幅减少内存占用和计算开销。主要有两种格式:
-
E5M2:5位指数,2位尾数,动态范围大
-
E4M3:4位指数,3位尾数,精度更高
2.2 量化策略
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.cuda.amp import autocast
class FP8Quantizer:
def __init__(self, format='E4M3'):
"""
FP8量化器实现
Args:
format: 量化格式,'E4M3' 或 'E5M2'
"""
self.format = format
self.eps = 1e-8
def quantize(self, tensor):
"""
将FP32张量量化为FP8
"""
if self.format == 'E4M3':
return self._quantize_e4m3(tensor)
else: # E5M2
return self._quantize_e5m2(tensor)
def _quantize_e4m3(self, tensor):
"""E4M3格式量化"""
# 计算缩放因子
max_val = tensor.abs().max()
scale = max_val / (self.eps + 1.75) # E4M3最大值为1.75
# 缩放并四舍五入到8位
scaled = tensor / scale
quantized = torch.clamp(scaled, -1.75, 1.75)
quantized = quantized.to(torch.float8_e4m3fn)
return quantized, scale
def dequantize(self, quantized_tensor, scale):
"""反量化回FP32"""
dequantized = quantized_tensor.float() * scale
return dequantized3. Stable Diffusion 3.5 FP8优化实现
3.1 混合精度推理
import torch
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
import numpy as np
from typing import Optional, Union
class StableDiffusionFP8Optimizer:
def __init__(self,
model_id: str = "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-3.5",
device: str = "cuda",
use_fp8: bool = True):
self.device = device
self.use_fp8 = use_fp8
# 加载原始模型
self.pipeline = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
model_id,
torch_dtype=torch.float16 if not use_fp8 else torch.float32
)
self.pipeline = self.pipeline.to(device)
if use_fp8:
self._convert_to_fp8()
def _convert_to_fp8(self):
"""将关键组件转换为FP8精度"""
# 优化VAE编码器/解码器
self._optimize_vae()
# 优化U-Net
self._optimize_unet()
# 优化注意力机制
self._optimize_attention()
def _optimize_unet(self):
"""优化U-Net为FP8混合精度"""
unet = self.pipeline.unet
# 关键层使用FP8
for name, module in unet.named_modules():
if isinstance(module, nn.Conv2d):
module.weight.data = self._maybe_convert_to_fp8(module.weight.data)
if module.bias is not None:
module.bias.data = self._maybe_convert_to_fp8(module.bias.data)
def _optimize_attention(self):
"""优化注意力计算为FP8"""
from torch.nn import functional as F
def fp8_attention(q, k, v, scale_factor=1.0):
"""FP8优化的注意力计算"""
# 转换为FP8进行计算
with autocast(dtype=torch.float8_e4m3fn):
# QK^T计算
attn_weights = torch.matmul(q, k.transpose(-2, -1))
attn_weights = attn_weights / (q.size(-1) ** 0.5)
# Softmax
attn_weights = F.softmax(attn_weights, dim=-1)
# 注意力输出
output = torch.matmul(attn_weights, v)
return output.float() # 转换回FP16/FP32
# 替换原始的注意力计算
self._replace_attention_forward(fp8_attention)
def _maybe_convert_to_fp8(self, tensor):
"""条件转换为FP8"""
if self.use_fp8 and tensor.is_floating_point():
return tensor.to(torch.float8_e4m3fn)
return tensor
def generate_image(self,
prompt: str,
height: int = 512,
width: int = 512,
num_inference_steps: int = 30,
guidance_scale: float = 7.5):
"""生成图像"""
with torch.inference_mode():
if self.use_fp8:
# 使用FP8混合精度
with autocast(dtype=torch.float8_e4m3fn):
image = self.pipeline(
prompt=prompt,
height=height,
width=width,
num_inference_steps=num_inference_steps,
guidance_scale=guidance_scale
).images[0]
else:
# 原始精度
image = self.pipeline(
prompt=prompt,
height=height,
width=width,
num_inference_steps=num_inference_steps,
guidance_scale=guidance_scale
).images[0]
return image3.2 内存优化技术
class MemoryOptimizedSD:
def __init__(self, pipeline, chunk_size=2):
self.pipeline = pipeline
self.chunk_size = chunk_size
def chunked_attention(self, query, key, value):
"""
分块注意力计算,减少内存峰值
"""
batch_size, num_heads, seq_len, head_dim = query.shape
output = torch.zeros_like(query)
# 分块处理
for i in range(0, seq_len, self.chunk_size):
end_idx = min(i + self.chunk_size, seq_len)
# 计算当前块的注意力
q_chunk = query[:, :, i:end_idx, :]
attn_weights = torch.matmul(
q_chunk,
key.transpose(-2, -1)
) / (head_dim ** 0.5)
attn_weights = torch.softmax(attn_weights, dim=-1)
chunk_output = torch.matmul(attn_weights, value)
output[:, :, i:end_idx, :] = chunk_output
return output
def gradient_checkpointing(self):
"""启用梯度检查点,训练时节省显存"""
self.pipeline.unet.enable_gradient_checkpointing()
def cpu_offloading(self):
"""将不活跃的模块卸载到CPU"""
from accelerate import cpu_offload
# 将VAE和文本编码器卸载到CPU
cpu_offload(self.pipeline.vae)
cpu_offload(self.pipeline.text_encoder)
# 只保留U-Net在GPU上
self.pipeline.unet.to(self.pipeline.device)4. 性能基准测试
4.1 推理速度对比
import time
from contextlib import contextmanager
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
@contextmanager
def benchmark_context(name):
"""基准测试上下文管理器"""
start_time = time.time()
start_memory = torch.cuda.memory_allocated() if torch.cuda.is_available() else 0
yield
end_time = time.time()
end_memory = torch.cuda.memory_allocated() if torch.cuda.is_available() else 0
elapsed = end_time - start_time
memory_used = (end_memory - start_memory) / (1024 ** 3) # 转换为GB
print(f"{name}:")
print(f" 时间: {elapsed:.2f}秒")
print(f" 显存使用: {memory_used:.2f} GB")
print("-" * 40)
return elapsed, memory_used
def run_benchmark():
"""运行性能基准测试"""
results = []
# 测试不同配置
configs = [
("FP32原始", False, torch.float32),
("FP16混合精度", False, torch.float16),
("FP8优化", True, torch.float8_e4m3fn),
]
for name, use_fp8, dtype in configs:
print(f"\n测试配置: {name}")
# 创建优化器实例
optimizer = StableDiffusionFP8Optimizer(
use_fp8=use_fp8
)
# 预热
_ = optimizer.generate_image("warmup", num_inference_steps=1)
# 正式测试
with benchmark_context(f"生成512x512图像") as (time_taken, memory_used):
image = optimizer.generate_image(
"a beautiful sunset over mountains",
num_inference_steps=30
)
results.append({
"配置": name,
"推理时间(秒)": time_taken,
"显存使用(GB)": memory_used,
"数据类型": str(dtype)
})
# 创建结果表格
df = pd.DataFrame(results)
print("\n性能对比结果:")
print(df.to_string(index=False))
# 可视化结果
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 5))
# 推理时间对比
ax1.bar(df["配置"], df["推理时间(秒)"], color=['#FF6B6B', '#4ECDC4', '#45B7D1'])
ax1.set_title("推理时间对比")
ax1.set_ylabel("时间 (秒)")
ax1.tick_params(axis='x', rotation=45)
# 显存使用对比
ax2.bar(df["配置"], df["显存使用(GB)"], color=['#FF6B6B', '#4ECDC4', '#45B7D1'])
ax2.set_title("显存使用对比")
ax2.set_ylabel("显存 (GB)")
ax2.tick_params(axis='x', rotation=45)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("performance_comparison.png", dpi=150, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
return df
# 运行基准测试
if __name__ == "__main__":
results_df = run_benchmark()4.2 生成质量评估
from PIL import Image
import lpips
import numpy as np
class QualityEvaluator:
def __init__(self):
self.lpips_loss = lpips.LPIPS(net='alex')
def evaluate_fidelity(self, original_img, quantized_img):
"""
评估量化后的保真度
"""
# 转换为张量
original_tensor = self._to_tensor(original_img)
quantized_tensor = self._to_tensor(quantized_img)
# 计算LPIPS(感知相似度)
lpips_score = self.lpips_loss(original_tensor, quantized_tensor).item()
# 计算PSNR
mse = torch.mean((original_tensor - quantized_tensor) ** 2)
psnr = 20 * torch.log10(1.0 / torch.sqrt(mse))
# 计算SSIM
ssim_score = self._calculate_ssim(original_tensor, quantized_tensor)
return {
"LPIPS": lpips_score,
"PSNR": psnr.item(),
"SSIM": ssim_score
}
def _to_tensor(self, img):
"""图像转换为张量"""
if isinstance(img, Image.Image):
img = np.array(img).astype(np.float32) / 255.0
img = torch.from_numpy(img).permute(2, 0, 1).unsqueeze(0)
return img
def _calculate_ssim(self, img1, img2, window_size=11, size_average=True):
"""计算SSIM"""
from math import exp
# 实现SSIM计算
C1 = (0.01 * 1) ** 2
C2 = (0.03 * 1) ** 2
mu1 = torch.nn.functional.avg_pool2d(img1, window_size, stride=1, padding=window_size//2)
mu2 = torch.nn.functional.avg_pool2d(img2, window_size, stride=1, padding=window_size//2)
mu1_sq = mu1.pow(2)
mu2_sq = mu2.pow(2)
mu1_mu2 = mu1 * mu2
sigma1_sq = torch.nn.functional.avg_pool2d(img1*img1, window_size, stride=1, padding=window_size//2) - mu1_sq
sigma2_sq = torch.nn.functional.avg_pool2d(img2*img2, window_size, stride=1, padding=window_size//2) - mu2_sq
sigma12 = torch.nn.functional.avg_pool2d(img1*img2, window_size, stride=1, padding=window_size//2) - mu1_mu2
ssim_map = ((2*mu1_mu2 + C1)*(2*sigma12 + C2)) / ((mu1_sq + mu2_sq + C1)*(sigma1_sq + sigma2_sq + C2))
if size_average:
return ssim_map.mean().item()
else:
return ssim_map5. 部署优化建议
5.1 TensorRT优化
import tensorrt as trt
import onnx
class TensorRTOptimizer:
def __init__(self):
self.logger = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.WARNING)
def build_engine(self, onnx_path, fp8_mode=True):
"""
构建TensorRT引擎
"""
builder = trt.Builder(self.logger)
network = builder.create_network(1 << int(trt.NetworkDefinitionCreationFlag.EXPLICIT_BATCH))
parser = trt.OnnxParser(network, self.logger)
# 解析ONNX模型
with open(onnx_path, 'rb') as f:
if not parser.parse(f.read()):
for error in range(parser.num_errors):
print(parser.get_error(error))
return None
# 配置优化选项
config = builder.create_builder_config()
config.set_memory_pool_limit(trt.MemoryPoolType.WORKSPACE, 2 << 30) # 2GB
# 启用FP8
if fp8_mode and builder.platform_has_fast_fp8:
config.set_flag(trt.BuilderFlag.FP8)
config.set_flag(trt.BuilderFlag.STRICT_TYPES)
# 优化配置
config.set_flag(trt.BuilderFlag.PREFER_PRECISION_CONSTRAINTS)
config.set_flag(trt.BuilderFlag.DIRECT_IO)
# 构建引擎
engine = builder.build_serialized_network(network, config)
return engine
def optimize_inference(self, engine_path):
"""
优化推理流程
"""
runtime = trt.Runtime(self.logger)
with open(engine_path, 'rb') as f:
engine = runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read())
# 创建执行上下文
context = engine.create_execution_context()
# 设置优化参数
context.set_optimization_profile_async(0, torch.cuda.current_stream().cuda_stream)
return context5.2 动态批处理
class DynamicBatchProcessor:
def __init__(self, max_batch_size=4):
self.max_batch_size = max_batch_size
self.batch_cache = []
def process_batch(self, prompts):
"""
动态批处理多个提示
"""
results = []
for i in range(0, len(prompts), self.max_batch_size):
batch_prompts = prompts[i:i + self.max_batch_size]
# 统一批处理
with torch.no_grad():
batch_output = self._process_single_batch(batch_prompts)
results.extend(batch_output)
return results
def _process_single_batch(self, prompts):
"""处理单个批次"""
# 统一文本编码
text_inputs = self.pipeline.tokenizer(
prompts,
padding="max_length",
max_length=self.pipeline.tokenizer.model_max_length,
truncation=True,
return_tensors="pt"
)
# 批量生成
with autocast(dtype=torch.float8_e4m3fn):
latents = self._generate_latents_batch(text_inputs)
images = self.pipeline.vae.decode(latents).sample
return images6. 实际应用示例
6.1 图像生成API
from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException
from pydantic import BaseModel
import base64
from io import BytesIO
app = FastAPI(title="Stable Diffusion 3.5 FP8 API")
class GenerationRequest(BaseModel):
prompt: str
negative_prompt: str = None
width: int = 512
height: int = 512
num_inference_steps: int = 30
guidance_scale: float = 7.5
num_images: int = 1
class StableDiffusionAPI:
def __init__(self):
self.optimizer = StableDiffusionFP8Optimizer(use_fp8=True)
def generate_to_base64(self, request: GenerationRequest):
"""生成图像并转换为base64"""
try:
images = []
for _ in range(request.num_images):
image = self.optimizer.generate_image(
prompt=request.prompt,
height=request.height,
width=request.width,
num_inference_steps=request.num_inference_steps,
guidance_scale=request.guidance_scale
)
# 转换为base64
buffered = BytesIO()
image.save(buffered, format="PNG")
img_str = base64.b64encode(buffered.getvalue()).decode()
images.append(img_str)
return {
"status": "success",
"images": images,
"parameters": request.dict()
}
except Exception as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=str(e))
# 初始化API
sd_api = StableDiffusionAPI()
@app.post("/generate")
async def generate_image(request: GenerationRequest):
"""图像生成端点"""
return sd_api.generate_to_base64(request)
@app.get("/health")
async def health_check():
"""健康检查"""
return {"status": "healthy", "optimization": "FP8"}7. 结论与展望
Stable Diffusion 3.5 FP8通过先进的量化技术,在保持生成质量的同时,显著提升了推理速度和内存效率。关键优化点包括:
-
FP8混合精度推理:减少内存占用,加速计算
-
注意力机制优化:分块处理,降低内存峰值
-
动态批处理:提升吞吐量
-
硬件加速:利用TensorRT等推理引擎
随着硬件对低精度计算支持的不断完善,FP8及更低位宽的量化技术将在生成式AI部署中发挥越来越重要的作用。未来可进一步探索:
-
自适应量化策略:根据不同层的重要性动态调整精度
-
训练后量化校准:提高量化模型的生成质量
-
多模态扩展:将FP8优化应用到视频、3D生成等领域
通过持续优化,Stable Diffusion等大型生成模型将能够在更广泛的设备和场景中部署应用,推动AIGC技术的普及和发展。
注意:本文代码为示例实现,实际部署时需根据具体硬件和需求进行调整。建议在生产环境中进行充分的测试和验证。