目录
[0. Preface](#0. Preface)
[1. Nominative Personal Pronouns](#1. Nominative Personal Pronouns)
[2. Present Tense Verb Conjugation](#2. Present Tense Verb Conjugation)
[Regular Verbs (e.g., arbeiten = to work)](#Regular Verbs (e.g., arbeiten = to work))
[Irregular Verbs (Common Examples)](#Irregular Verbs (Common Examples))
[3. Nominative Possessive Adjectives](#3. Nominative Possessive Adjectives)
[4. Sentence Structure (Verb in 2nd Position)](#4. Sentence Structure (Verb in 2nd Position))
[5. Common Question Words](#5. Common Question Words)
专栏前言
考虑到我已经写了2个专栏的中文版德语学习笔记,这个教材的笔记就打算用英文来写,毕竟对于英语基础好的人,用英语学德语效率会更高.
第一课是发音,这里省略,从第二课开始
0. Preface
If you're starting German and prefer learning with English explanations, this post breaks down core Lesson 2 grammar --- personal pronouns, verb conjugation, possessives, and sentence structure.
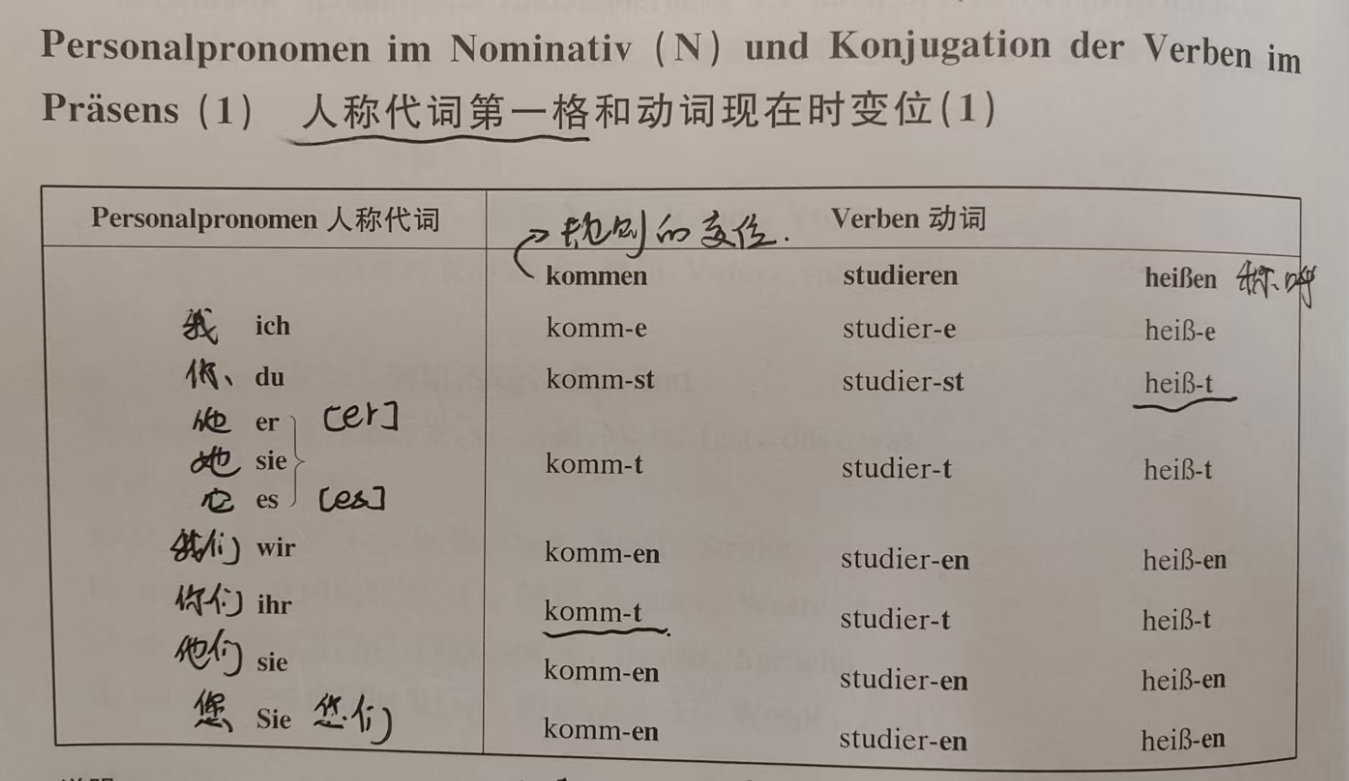
1. Nominative Personal Pronouns
These pronouns act as subjects or predicates in sentences. Use wer (who) for questions about the subject.
| Person | Singular | Plural | English Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | ich | wir | I / we |
| 2nd (informal) | du | ihr | you (sing./pl.) |
| 2nd (formal) | Sie | Sie | you (polite) |
| 3rd | er/sie/es | sie | he/she/it / they |
2. Present Tense Verb Conjugation
Most verbs follow this stem + ending rule (irregular verbs like sein /wissen have unique forms):
Regular Verbs (e.g., arbeiten = to work)
| Person | Ending | Example (arbeiten) |
|---|---|---|
| ich | -e | ich arbeite |
| du | -st | du arbeitest |
| er/sie/es | -t | er arbeitet |
| wir/sie/Sie | -en | wir arbeiten |
| ihr | -t | ihr arbeitet |
Note: If the verb stem ends in t/d/ffn/chn/gn , add e before -t/ -st* (e.g., öffnen → du öffnest).*
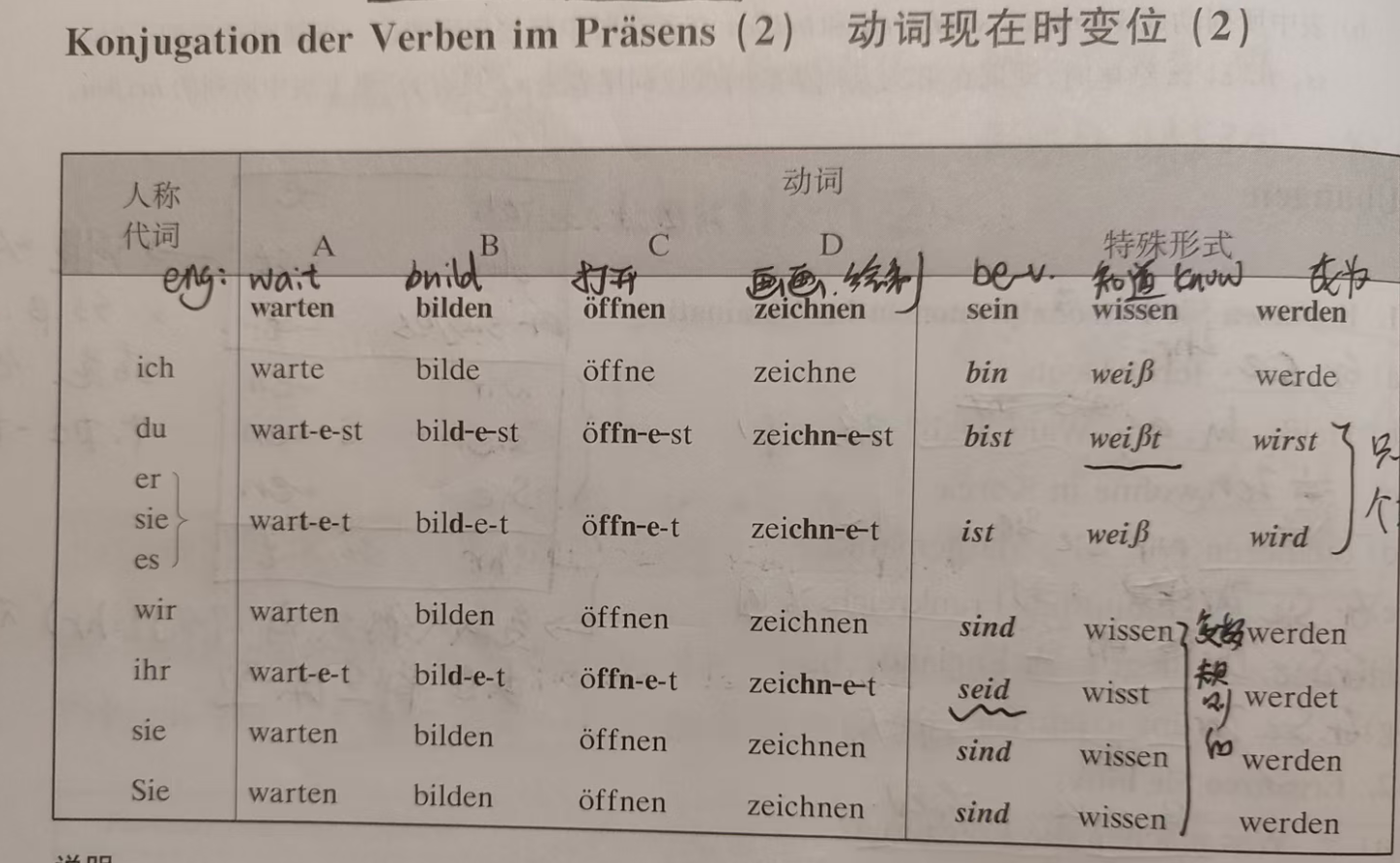
Irregular Verbs (Common Examples)
| Verb | English | ich | du | er/sie/es | wir/sie/Sie | ihr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sein | to be | bin | bist | ist | sind | seid |
| wissen | to know | weiß | weißt | weiß | wissen | wisst |
| werden | to become | werde | wirst | wird | werden | werdet |
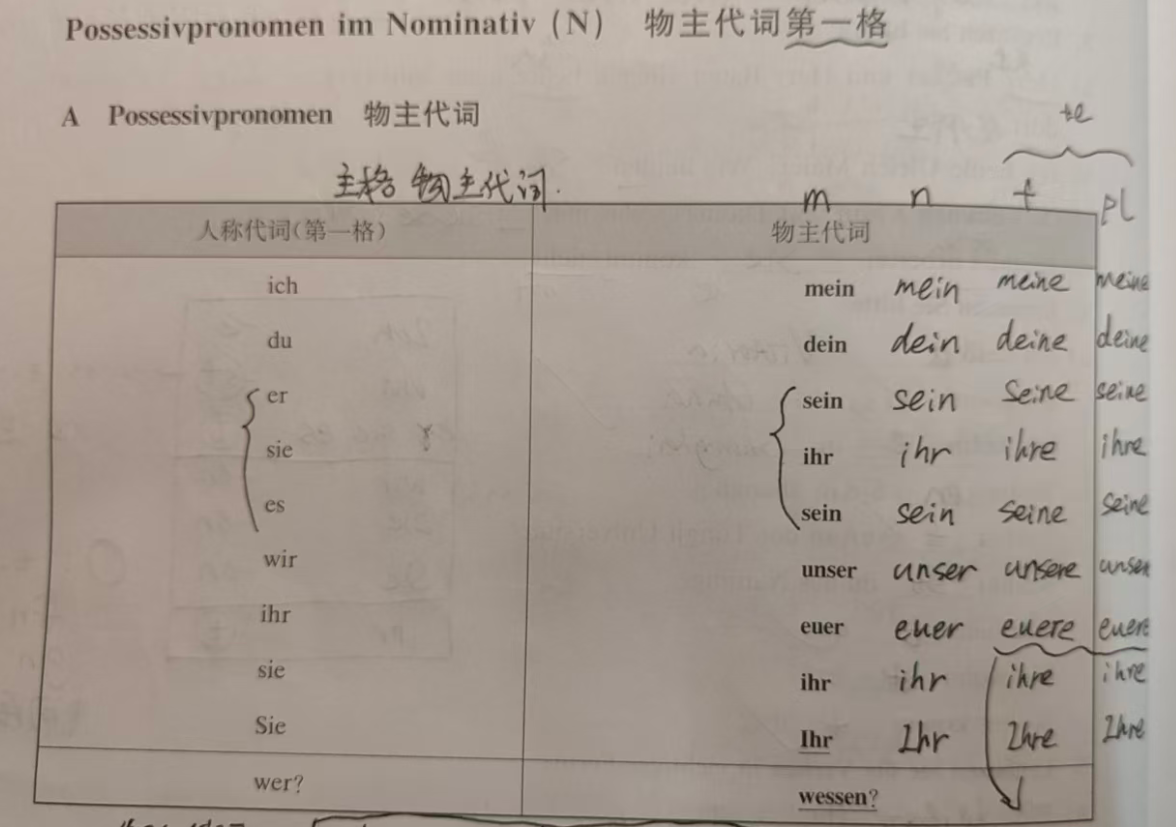
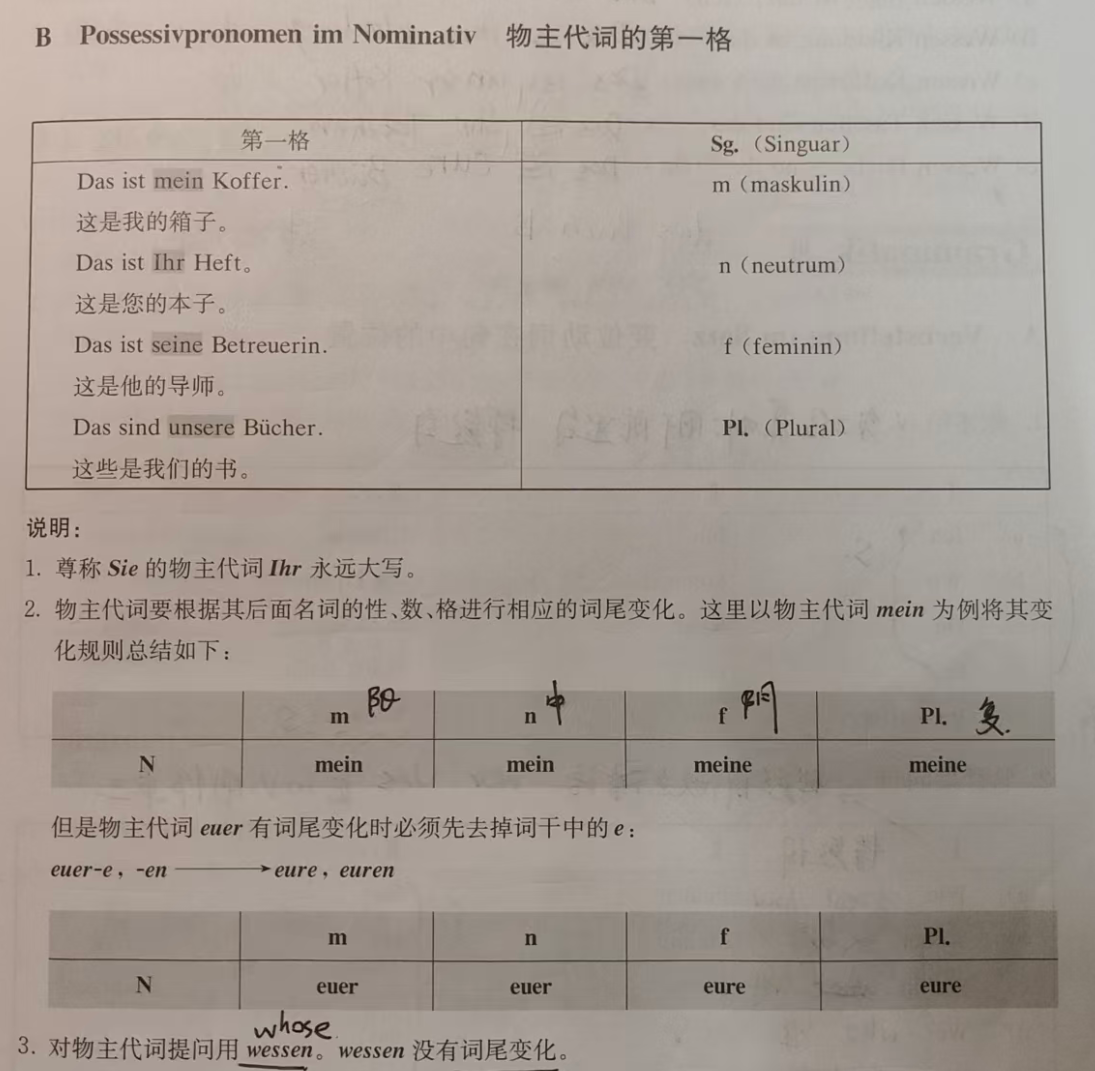
3. Nominative Possessive Adjectives
These describe "who something belongs to." They agree with the gender/number of the noun (add e for feminine/plural):
| Person | Singular | Plural | English Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| ich | mein | unser | my / our |
| du | dein | euer (→ eure) | your (sing./pl.) |
| er/sie/es | sein/ihr/sein | ihr | his/her/its / their |
| Sie | Ihr | Ihr | your (polite) |
4. Sentence Structure (Verb in 2nd Position)
German sentences follow V2 word order (verb is always the 2nd element):
- Statement : Subject + Verb + ... (e.g., Horst liest. = Horst reads.)
- Inverted Statement (emphasize something): Emphasized word + Verb + Subject + ... (e.g., Im Koffer sind Bücher. = In the bag are books.)
- Question : Verb + Subject + ... (e.g., Liest Horst? = Does Horst read?)
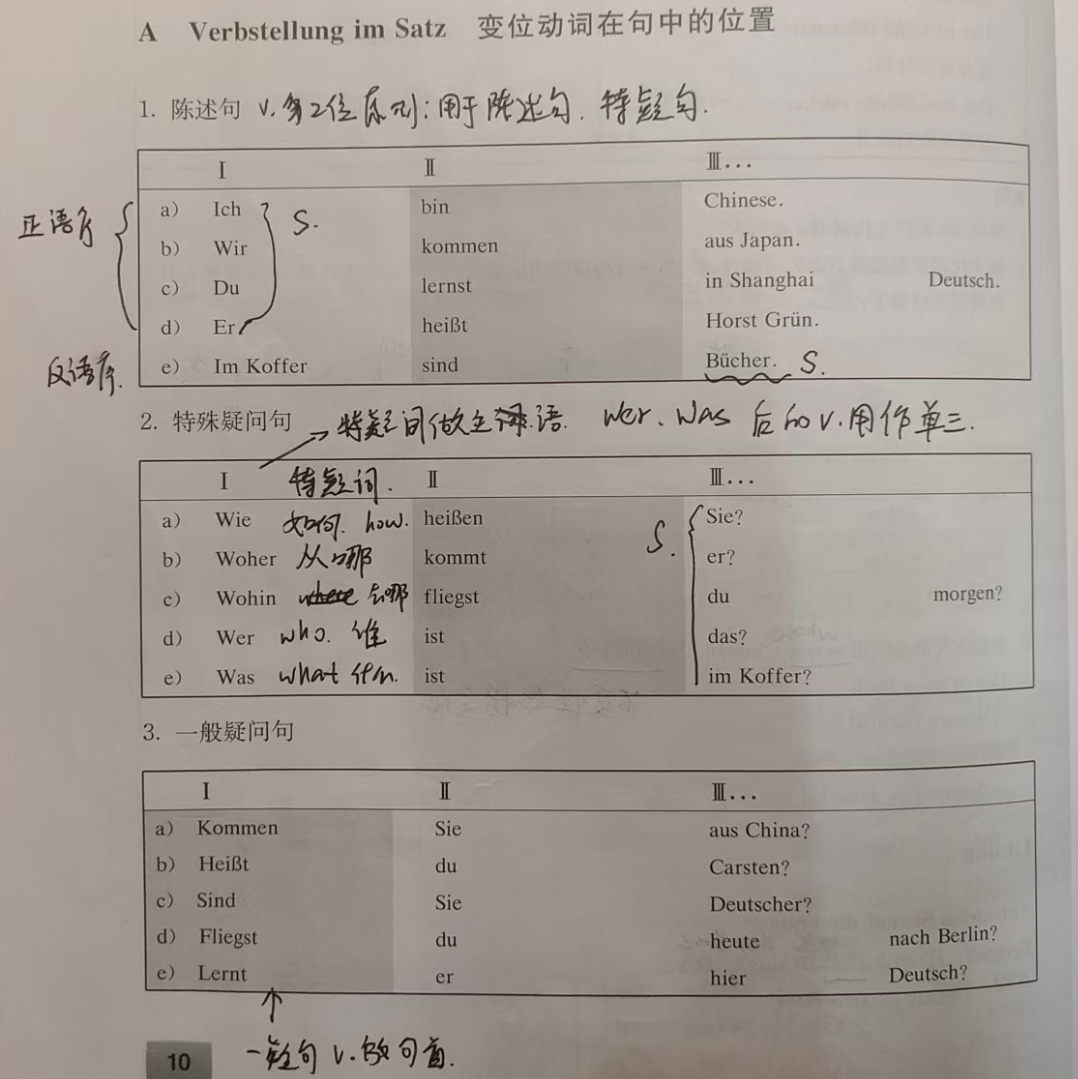
5. Common Question Words
Use these to form questions (pair with V2 order):
| German Word | English | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| wer | who | Wer liest? (Who is reading?) |
| was | what | Was machst du? (What are you doing?) |
| wann | when | Wann kommst du? (When are you coming?) |
| wie | how | Wie geht es dir? (How are you?) |
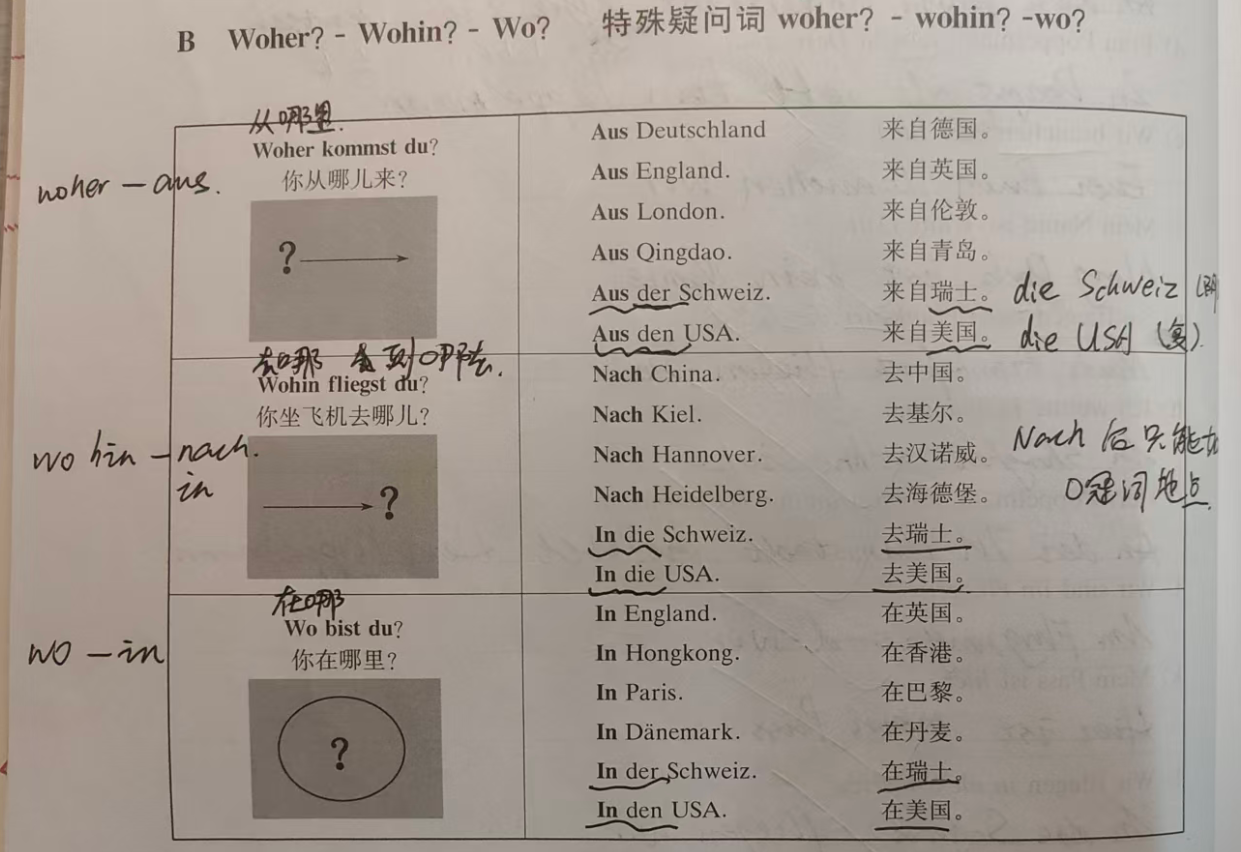
| wo | where | Wo bist du? (Where are you?) |
| woher | where from | Woher kommst du? (Where are you from?) |
| wohin | where to | Wohin fliegst du? (Where are you flying to?) |