先随便看看吧,暂时没有时间写完整
一、钢笔工具功能分析
先去pixso官网用一下钢笔工具:https://pixso.cn/
本文会先梳理一下绘制逻辑和简单实现,然后再介绍一些具体实现,比如用的是Konva框架。
导入方式:import Konva from 'konva';
1、关键变量定义
java
// 编辑模式 分为"idle"、"creating"、"halfDone"、"finalized"
const editingMode = ref("idle")
// 临时曲线
const tempP1 = ref({ x: 0, y: 0 });
const tempC1 = ref({ x: 0, y: 0 });
const tempC2 = ref({ x: 0, y: 0 });
const tempP2 = ref({ x: 0, y: 0 });
// 鼠标信息
const mousePosition = ref({ x: 0, y: 0 })
//预览线是否开启
const previewLine = ref(false)
//上一个点坐标
const lastPoint = ref(null)
//长按相关
const longPressTimer = ref(null)
const isLongPress = ref(false)
const PRESS_DURATION = 300;
showHandles.value = { // 控制柄显示状态恢复
showBigHandle: false,
showTempBezier: false,
showBothControlPoints: false,
};
const currentPolygon = computed(() => {
if(polygons.value.length === 0) {
startNewPolygon()
}
return polygons.value[currentPolygonIndex.value]
})idle就是普通添加直线点的模式
creating就是长按移动大控制柄的模式(后面有解释)
halfDone是长按移动大控制柄后松开,进入的动态曲线绘制模式
finalized是完成了动态曲线的绘制
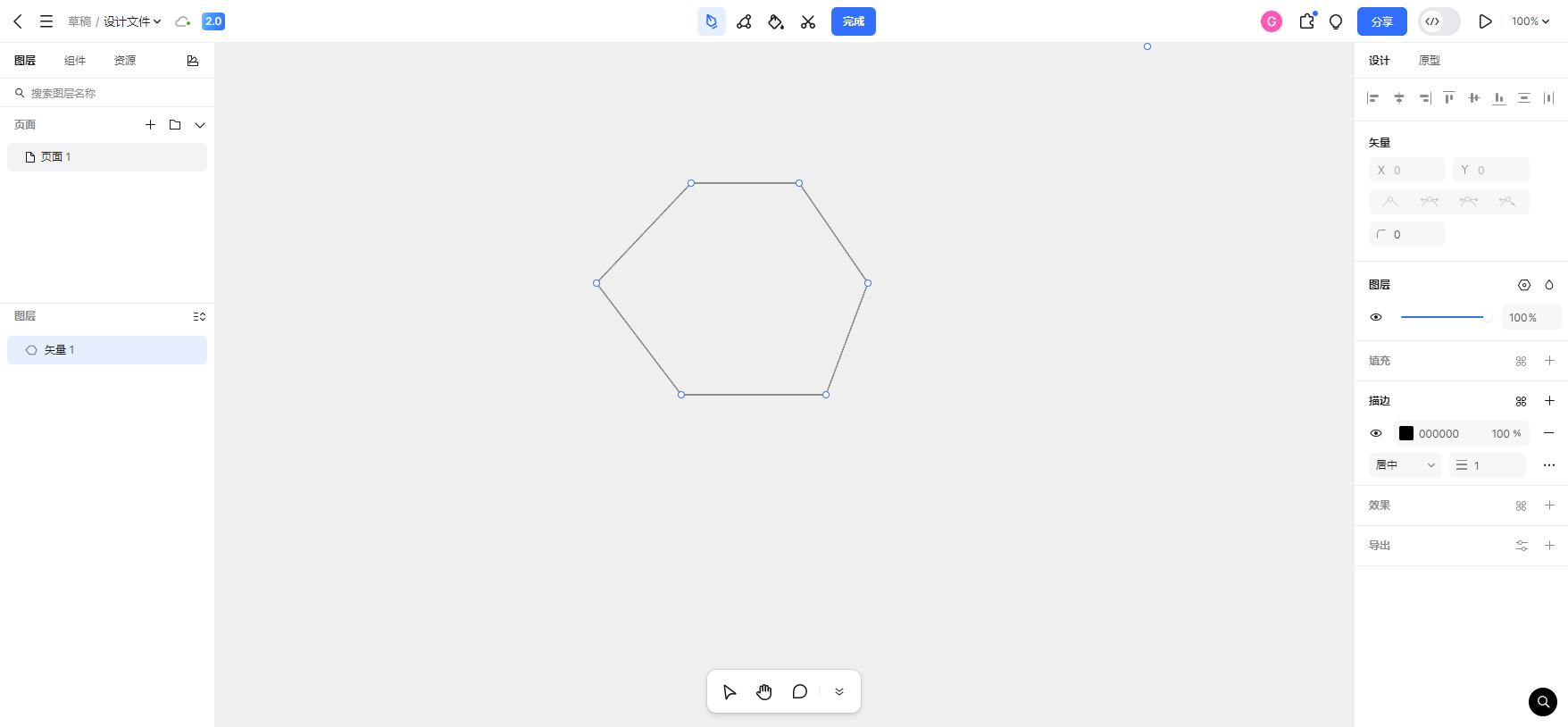
2、点击鼠标左键可在画布上添加一个点,并且这个点会拉出一条预览线,这条预览线的路径是<刚添加的点,鼠标当前的位置>。不断添加点可以绘制直线
//点击画布区域的函数
javascript
const onPenStageClick = (event) => {
// 获取鼠标按钮类型
const button = event.button || (event.evt ? event.evt.button : 0);
const stage = event.target.getStage();
const position = stage.getRelativePointerPosition(
const { x, y } = position;
const target = event.target;
const targetName = target.name ? target.name() : "";
// 普通点击创建直线点逻辑
if(button == 0 || button ==1) normalAddPointLogic(x, y, targetName);
}
//如果形成了封闭区域,则新建一个多边形的函数
javascript
function startNewPolygon() {
const newPolygon = {
points: [],
segments: [],
closed: false,
};
polygons.value.push(newPolygon);
currentPolygonIndex.value = polygons.value.length
}//普通点击创建直线点的函数
javascript
function normalAddPointLogic(x, y, targetName) {
// 保存当前状态到撤销栈
saveState();
const old_polygon = currentPolygon.value;
if (old_polygon?.closed) {
//如果形成了封闭区域,则新建一个多边形
startNewPolygon();
}
const polygon = currentPolygon.value;
const segments = polygon?.segments;
const points = polygon?.points;
if (segments?.length > 0) {
const lastSegment = segments[segments.length - 1];
if (segments?.length >= 3) {
const firstSegment = segments[0];
const firstPoint = getPointById(polygon, firstSegment.startPointId);
//已经有点且超过3个点,要判断是否闭合
const dist = calculateDistance({ x, y }, firstPoint);
if (dist < 10) {
//已形成封闭区域
const closingSegment = {
type: "line",
startPointId: lastSegment.endPointId,
endPointId: firstPoint.id,
controlPoints: [],
};
segments.push(closingSegment);
polygon.closed = true;
previewLine.value = false;
return;
}
}
//已经有点,但是没闭合,要添加一段新的点和直线
const newPoint = { id: uuidv4(), x, y };
points.push(newPoint);
const newSegment = {
type: "line",
startPointId: lastSegment.endPointId,
endPointId: newPoint.id,
controlPoints: [],
};
segments.push(newSegment);
}else{
//一个点也没有,添加第一个点
const newPoint = { id: uuidv4(), x, y };
points.push(newPoint);
const newSegment = {
type: "line",
startPointId: newPoint.id,
endPointId: newPoint.id, //第一个点自己指向自己
controlPoints: [],
};
segments.push(newSegment);
}
//更新视图
polygons.value = [...polygons.value];
}辅助函数
javascript
function calculateDistance(p1, p2) {
const dx = p1.x -p2.x
const dy = p1.y - p2.y;
return Math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
}
function getPointById(polygon, pointId) {
return polygon.points.find((p) => p.id === pointI
}
function getLinePoints(polygon, segment) {
const startPt = getPointById(polygon, segment.startPointId);
const endPt = getPointById(polygon, segment.endPoitById(polygon, segment.endPointId);
return [startPt.x, startPt.y, endPt.x, endPt.y];
}
function getBezierPoints(polygon, segment) {
const P0 = getPointById(polygon, segment.startPointId);
const P3 = getPointById(polygon, segment.endPointId);
const C1 = segment.controlPoints[0];
const C2 = segment.controlPoints[1];
return [P0.x, P0.y, C1.x, C1.y, C2.x, C2.y, P3.x,
}3、首先我们整体描述一下绘制曲线的问题。
我们先定义一段曲线的首端是P1,末端是P2,P1的切线是C1,P2的切线是C2。长按可以绘制曲线。假设已经有一个点P1,然后移动鼠标到某个位置P2开始保持长按并移动鼠标到某一位置tempC1,P1和P2之间会形成曲线,P1的切线是C1,P2的切线是C2。
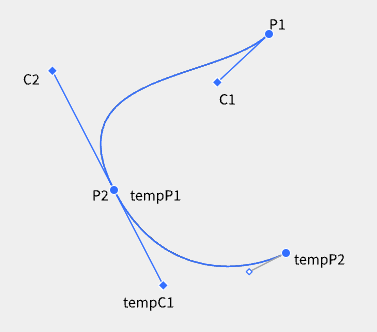
C2-P2-tempC1会形成一个大控制柄,这三个点在一条直线上,鼠标移动tempC1会对整个大控制板进行移动,也就是说C2随着tempC1的移动会跟随移动,移动时保持三点一线。
为什么称为tempC1,我们将大控制板下半段P2-tempC1看做是未来的曲线的首端的切线,也就是说这是未来曲线的C1,我们记作临时点tempC1。
鼠标长按后拉动到tempC1之后,就会形成P1和P2的曲线以及C2-P2-tempC1这个大控制柄,为什么叫大控制柄,因为虽然在保持长按的状态下移动tempC1可以控制整个大控制柄的方向,但是其实大控制柄可以看做是两段,第一段P2-C2是曲线P1P2的末端小控制柄(P2的切线),第二段是P2-tempC1是未来曲线tempP1-tempP2的首端小控制板(tempP1的切线),实际上tempP1就是P2。
用户在tempC1松开长按状态后会引出一条动态曲线tempP1-tempP2,tempP2是鼠标位置,如果用户点击了某处,tempP2就固定了;如果用户在tempP2长按了,则会在tempP2形成新的大控制柄,逻辑就跟前面长按是一样的。
对于当前步骤来说,我们只暂时关注鼠标长按拉到tempC1这个阶段,如下图所示。关于用户在tempC1松开长按状态后的逻辑,我们在后面的步骤再细说。
对于用户鼠标长按这个阶段,实际上有两种情况,一种是鼠标在P2点原地长按形成曲线P1-P2,一种是鼠标从P2点长按并移动到tempC1,那么不但形成曲线P1-P2,还形成一个大控制柄C2-P2-tempC1。第二种情况其实就是上图的情况,第一种情况其实是下图的情况,也就是说曲线P1和P2被创建了,但它们看起来还是一条直线,这是因为,直线可以看做是特殊的曲线。我们可以想象一下有一条直线P1-P2,向量P1-P2的方向上有一个P1-C1,向量P2-P1的方向上有一个P2-C2(下图只显示了P1-C1),我们定义了直线的情况下两个控制点的位置,此时直线可以看做是特殊的曲线,具体是为什么直线可以看做是特殊的曲线,要了解二阶贝塞尔曲线公式。

3.1 长按生成曲线P1-P2
//当鼠标点击左键
javascript
function onPenMouseDown(event) {
// 记录"长按起点"------后面要用它判断是否真的移动了
const stage = event.target.getStage();
const startPos = stage.getRelativePointerPosition();
longPressStartPos.value = { x: startPos.x, y: starPos.y };
//将tempC1从(0,0)的初始化位置更新为当前鼠标添加点的位置
if (editingMode.value === "idle" || editingMode.value === "creating"){
tempC1.value = longPressStartPos.value
}
// 重置长按标志
isLongPress.value = false;
pendingBezier.value = false;
hasDraggedDuringLongPress.value = false;
pendingSegmentIdx.value = null;
longPressTimer.value = setTimeout(() => {
const segIdx = createPointAndStraightSegment(event
pendingBezier.value = true; // 表示这条新段 *可能* 要改成贝塞尔
pendingSegmentIdx.value = segIdx;
// 此时不把 editingMode 改成 creating,等到真的拖动时再改
}, PRESS_DURATION);
}
javascript
/**
* ① 长按计时器触发后调用
* 在当前多边形末端 **添加一个新点** 并 **用线段** 把它连起来。
* 返回新段的索引,后面会用它来把段改为贝塞尔(如果用户真的拖动)。
*/
function createPointAndStraightSegment(event) {
saveState(); // 与原来保持一致
const polygon = currentPolygon.value;
const { segments, points } = polygon;
// 取当前多边形最后一段的终点(即前一个点)
const lastSeg = segments[segments.length - 1];
const stage = event.target.getStage();
const { x, y } = stage.getRelativePointerPosition();
// 新点(Pnew)
const newPt = { id: uuidv4(), x, y };
points.push(newPt);
// 用 **直线** 把它接上(暂时不算贝塞尔)
const newSeg = {
type: "line", // 先写成 line,后面如果拖动再改成 bezier
startPointId: lastSeg.endPointId,
endPointId: newPt.id,
};
segments.push(newSeg);
// 更新 UI(预览线等)
previewLine.value = true;
lastPoint.value = newPt;
polygons.value = [...polygons.value]; // 响应式更新
// 返回新段的索引,后面会用它来改成贝塞尔
return segments.length - 1;
}3.2 保持长按状态下移动鼠标能够移动大控制柄
javascript
function onPenMouseMove(event) {
const stage = event.target.getStage();
const position = stage.getRelativePointerPosition()
if (
isLongPress.value &&
editingMode.value == "creating" &&
currentSegmentIndex.value != null
) {
updateC1C2WhileCreating(position);
}
// 长按后但还没有确认是否要画贝塞尔的阶段
if (pendingBezier.value && !hasDraggedDuringLongPress.value) {
// 计算从长按起点到当前指针的位移
const moved = dist(position, longPressStartPos.value);
if (moved >= MOVE_THRESHOLD) {
// 用户真的拖动了就把那条直线段改为贝塞尔段
const segIdx = pendingSegmentIdx.value;
const seg = polygon.segments[segIdx];
const startPt = getPointById(polygon, seg.startPointId);
const endPt = getPointById(polygon, seg.endPointId);
//控制点C1的位置是向量P1-P2的方向上的点
const dx = x - lastPt.x;
//控制点C2的位置是向量P2-P1的方向上的与P1-C1等距的点
const dy = y - lastPt.y;
//取控制点C1的位置为向量P1-P2的方向上四分之一位置的点
const cp1 = { x: lastPt.x + dx * 0.25, y: lastPt.y + dy * 0.25 };
//取控制点C2的位置为向量P1-P2的方向上四分之三位置的点,其实相当于向量P2-P1的方向上四分之一位置的点
const cp2 = { x: lastPt.x + dx * 0.75, y: lastPt.y: lastPt.y + dy * 0.75 };
seg.type = "bezier";
seg.controlPoints = [cp1, cp2];
// 进入正式的贝塞尔创建状态
editingMode.value = "creating";
currentSegmentIndex.value = segIdx; // 让后面的updateC1C2WhileCreating能找到它
isLongPress.value = true; // 真正的长按标记
previewLine.value = false; //预览线条
showHandles.value.showBigHandle = true; // 显示大控制柄
// 标记已经拖动过,后面的 mouseup 不会再走 "直线回退" 分支
hasDraggedDuringLongPress.value = true;
}
}
if (editingMode.value === "halfDone" && currentSegmentIndex.value !== null) {
// 仅在鼠标不在控制点上时显示动态贝塞尔曲线
if (!isMouseOverControlPoint.value) {
showHandles.value.showTempBezier = true;
}
}
//更新动态曲线的tempP2为当前鼠标位置
tempP2.value = { x: mousePosition.value.x, y: mousePosition.value.y };
//预览直线
if (currentPolygon.value?.segments?.length && previewLine.value) {
const lastSegment = currentPolygon.value.segments[currentPolygon.value.segments.length - 1];
if (lastSegment) {
const lastPointObj = getPointById(
currentPolygon.value,
lastSegment.endPointId
);
lastPoint.value = lastPointObj;
}
}
}
//当用户添加了P1之后,在P2处长按,就会在P1-P2形成新的曲线。
function startCreatingBezierSegment(event) {
const polygon = currentPolygon.value;
const segments = polygon.segments;
const points = polygon.points;
if (segments.length > 0) {
const lastSegment = segments[segments.length - 1];
//上一个点其实就是P1
const lastPt = getPointById(polygon, lastSegment.endPointId);
const stage = event.target.getStage();
const pos = stage.getRelativePointerPosition();
const { x, y } = pos; //当前鼠标位置是我们即将要创建的P2
const newPoint = { id: uuidv4(), x, y };
points.push(newPoint); //添加一个P2
const dx = x - lastPt.x; //控制点C1的位置是向量P1-P2的方向上的点
const dy = y - lastPt.y; //控制点C2的位置是向量P2-P1的方向上的与P1-C1等距的点
//取控制点C1的位置为向量P1-P2的方向上四分之一位置的点
const cp1 = { x: lastPt.x + dx * 0.25, y: lastPt.y + dy * 0.25 };
//取控制点C2的位置为向量P1-P2的方向上四分之三位置的点,其实相当于向量P2-P1的方向上四分之一位置的点
const cp2 = { x: lastPt.x + dx * 0.75, y: lastPt.y: lastPt.y + dy * 0.75 };
//新建曲线P1-P2
const newSegment = {
type: "bezier",
startPointId: lastSegment.endPointId,
endPointId: newPoint.id,
controlPoints: [cp1, cp2],
};
segments.push(newSegment);
// 此时显示大控制柄(上一段C2 + 本段tempC1),初始tempC1与鼠标一致
showHandles.value.showBigHandle = true;
polygons.value = [...polygons.value];
}
}
javascript
// 计算两点欧氏距离
function dist(a, b) {
const dx = a.x - b.x;
const dy = a.y - b.y;
return Math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
}
javascript
function updateC1C2WhileCreating(pos) {
const polygon = currentPolygon.value;
const segments = polygon.segments;
const segment = segments[currentSegmentIndex.value
if (segment && segment.type === "bezier") {
tempC1.value = { x: pos.x, y: pos.y }; //当前鼠标位置
const P1 = getPointById(polygon, segment.startPointId);
const P2 = getPointById(polygon, segment.endPointId);
const C1 = segment.controlPoints[0];
const C2 = segment.controlPoints[1];
const ratio = -0.7;
C2.x = P2.x + (pos.x - P2.x) * ratio; //C2是P2-tempC1反方向,就是tempC1-P2
C2.y = P2.y + (pos.y - P2.y) * ratio; //C2是P2-tempC1反方向,就是tempC1-P2
const tangentRatio = 0.4;
const tangentDX = C2.x - P1.x;
const tangentDY = C2.y - P1.y;
C1.x = P1.x + tangentDX * tangentRatio; //C1是P1-C2的方向上的点
C1.y = P1.y + tangentDY * tangentRatio; //C1是P1-C2的方向上的点
polygons.value = [...polygons.value];
}
}4、在tempC1处松开以后,会出现一段曲线,这段曲线会跟随鼠标的位置进行实时绘制,即实时绘制<P2-当前鼠标位置>的曲线

javascript
function onPenMouseUp(event) {
clearTimeout(longPressTimer.value);
// 长按后没有真正拖动(hasDraggedDuringLongPress === false)
// 已经在长按计时器里创建了一条直线段,直接保留它
if (pendingBezier.value && !hasDraggedDuringLongPress.value) {
// 退出 creating 状态,恢复到普通 idle
editingMode.value = "idle";
isLongPress.value = false;
pendingBezier.value = null;
hasDraggedDuringLongPress.value = false;
// 隐藏所有贝塞尔相关的 UI(大柄、绿色临时曲线)
showHandles.value.showBigHandle = false;
showHandles.value.showTempBezier = false;
tempC1.value = null;
tempP2.value = null;
previewLine.value = true; // 仍然显示普通的预览直线
return;
}
// 进入正式的贝塞尔创建(已经改成 bezier 且 isLongPress 为 true)
// 按原来的流程进入 halfDone / finalize
if (isLongPress.value) {
if (editingMode.value === "creating") {
editingMode.value = "halfDone";
updateLastPointFromCurrentSegment();
tempC1.value = { x: mousePosition.value.x, y: mousePosition.value.y };
showHandles.value.showTempBezier = true;
}
// 重置长按标记,防止后续误判
isLongPress.value = false;
pendingBezier.value = false;
pendingSegmentIdx.value = null;
hasDraggedDuringLongPress.value = false;
previewLine.value = true;
return;
}else{
// 完全没有触发长按(普通短点)
if (editingMode.value === "halfDone") {
//半完成状态下没有触发长按,直接在tempP2短按,需要固定动态曲线
previewLine.value = false;
finalizeBezierSegment();
}
}
previewLine.value = true;
}5、
(1)在第4步之后,用户有可能鼠标点击某个空白位置以确定这条曲线。在某个位置单击与在某个位置长按但鼠标不移动,两者都是下图的效果。
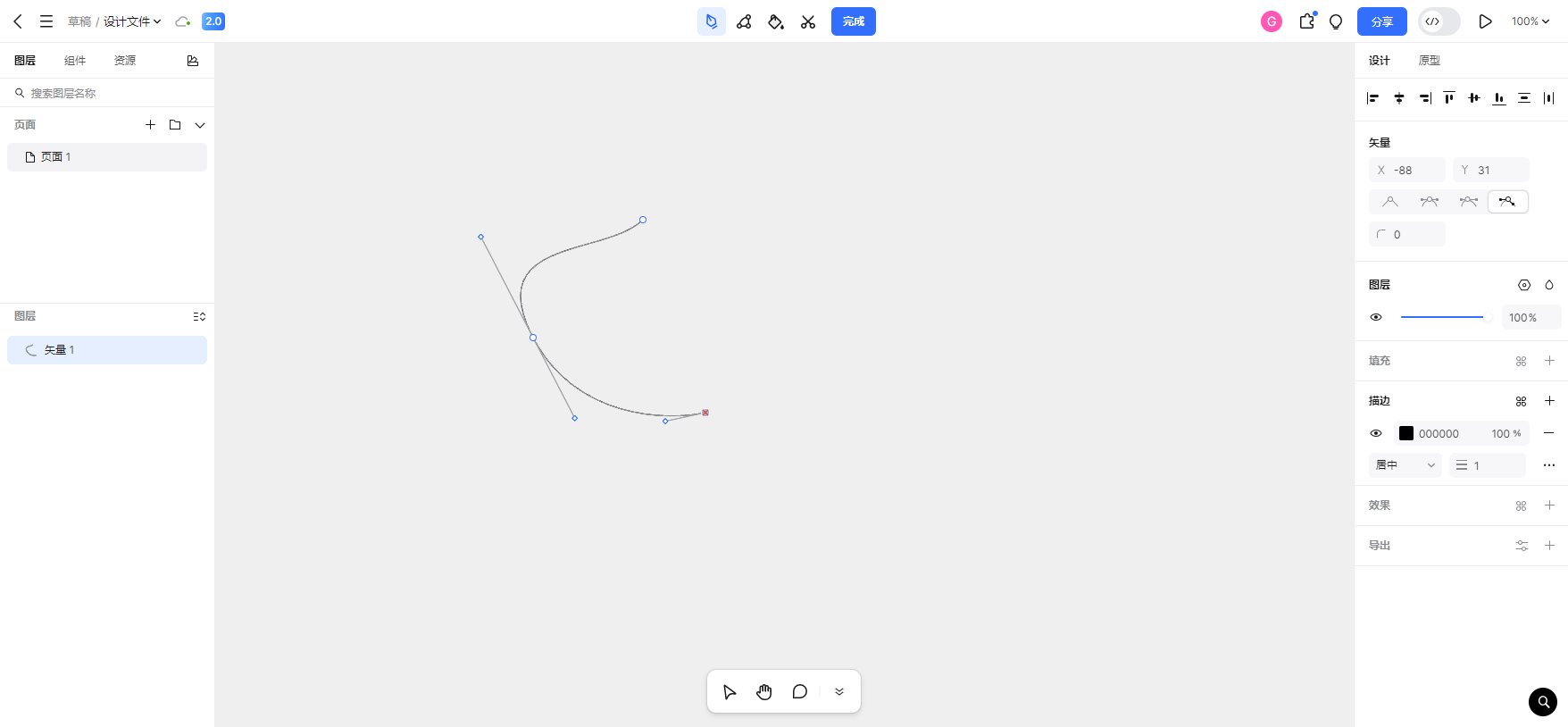
javascript
function finalizeBezierSegment() {
editingMode.value = "finalized";
const polygon = currentPolygon.value;
const P1 = tempP1.value;
const endPoint = { id: uuidv4(), x: tempP2.value.x, y: tempP2.value.y };
polygon.points.push(endPoint);
const newSegment = {
type: "bezier",
startPointId: P1.id,
endPointId: endPoint.id,
controlPoints: [
{ x: tempC1.value.x, y: tempC1.value.y },
{ x: tempC2.value.x, y: tempC2.value.y },
],
};
polygon.segments.push(newSegment);
currentSegmentIndex.value = polygon.segments.length - 1;
showHandles.showTempBezier = false;
showHandles.value.showBigHandle = true;
polygons.value = [...polygons.value];
} (2)在第4步之后,用户有可能还可能在某个空白位置进行长按并且发生移动,会出现下面的画面。那这个长按然后移动鼠标松开的操作,其实前面已经介绍过了。
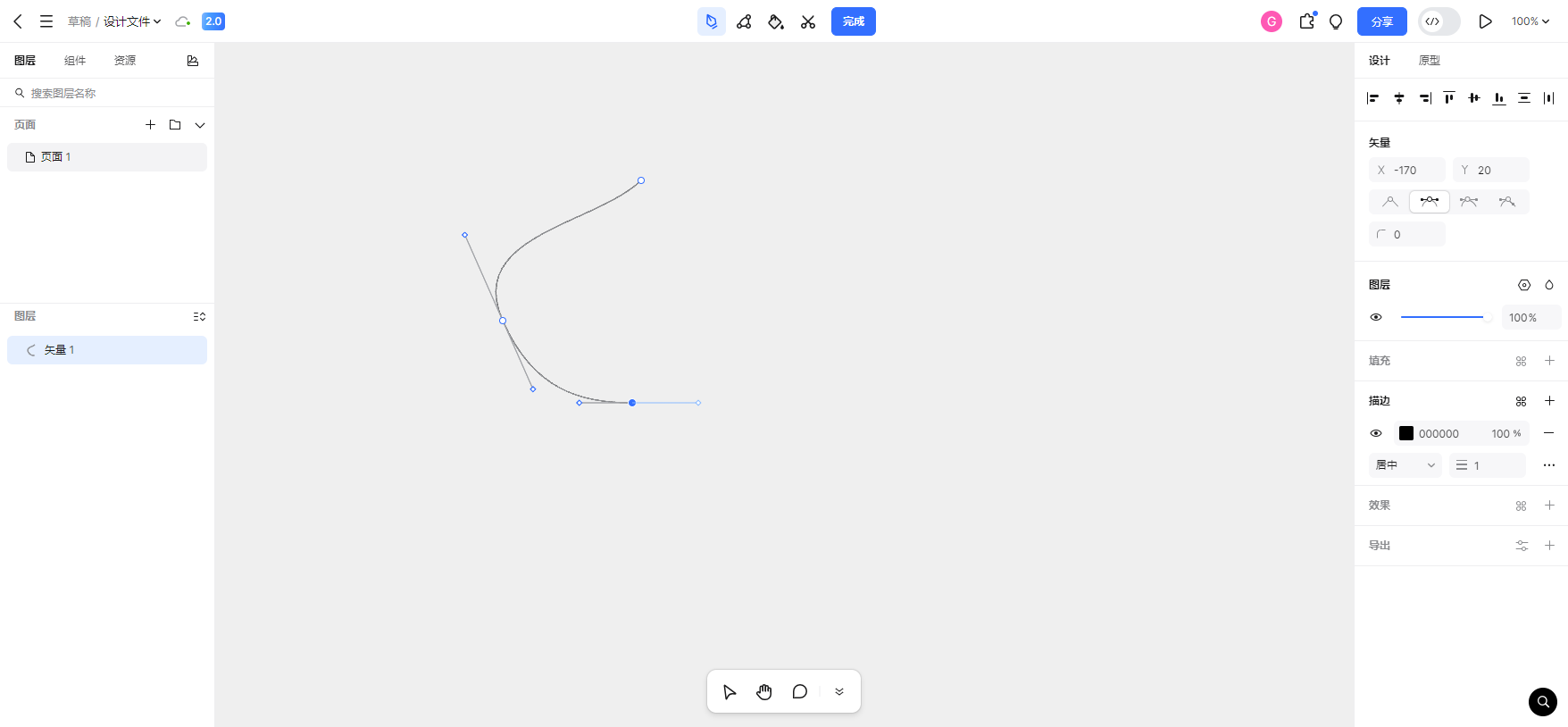
6、重做
javascript
const clearCanvas = () => {
polygons.value = []
// 清空撤销栈和重做栈
undoStack.value = []
redoStack.value = []
// 清空预览线条
previewLine.value = false
lastPoint.value = null;
mousePosition.value = { x: 0, y: 0 }; // 鼠标位置恢复
editingMode.value = "idle"; // 编辑模式恢复
showHandles.value = { // 控制柄显示状态恢复
showBigHandle: false,
showTempBezier: false,
showBothControlPoints: false,
};
currentSegmentIndex.value = null; // 当前段索引清空
currentPolygonIndex.value = -1; // 没有正在编辑的
// 临时贝塞尔点/控制点全部归零
tempP1.value = { x: 0, y: 0 }
tempC1.value = { x: 0, y: 0 }
tempC2.value = { x: 0, y: 0 }
tempP2.value = { x: 0, y: 0 }
//如果还有显示尺寸/光标等 UI 也同步关闭
cursorLayerConfig.visible = false;
}
javascript
// 执行绘制操作,将当前状态存入撤销栈
const saveState = () => {
const currentState = cloneFullState()
undoStack.value.push(currentState)
redoStack.value = []
}
// 保存画布状态
const cloneFullState = () => {
return JSON.parse(JSON.stringify({
polygons: : polygons.value,
brushStrokes: brushStrokes.value
}))
}
// 撤销操作二、模板实现(并不完整)
javascript
<template>
<div class="right-wrapper">
<div v-if="!isBatch" ref="konvaContentRef" :class="['konva-content', headerActiveTool === 'move' && 'konva-content-cursor']">
<div v-if="!['extend'].includes(firstTool)" class="canvas-wrapper" :style="{width: stageSize.width || 1500, height: stageSize.height || 900,}">
<v-stage
ref="stageRef"
:config="stageSize"
@mousedown="handleStageMouseDown"
@mousemove="onMouseMove"
@mouseup="onMouseUp"
@click="onStageClick"
:style="{zIndex: 1001, cursor: isHideStagePointer ? 'none' : 'default'}"
@wheel="handleDrawStageWheel"
>
<v-layer ref="penLayer">
<!-- 渲染多边形的线 -->
<template
v-for="(polygon, polygonIndex) in polygons"
:key="'polygon-' + polygonIndex"
>
<template
v-for="(segment, segmntIndex) in polygon.segments"
:key="'segment-' + polygonIndex + '-' + segmentIndex"
>
<!-- 直线段 -->
<v-line
v-if="segment.type === 'line'"
:points="getLinePoints(polygon, segment)"
@click="onLineSegmentClick(polygonIndex, segmentIndex, $event)
/>
<!-- 贝塞尔段 -->
<v-line
v-if="segment.type === 'line'"
:points="getBezierPoints(polygon, segment)"
@click="onBezierSegmentClick(polygonIndex, segmentIndex, $event)
/>
</template>
</template>
<!-- 渲染多边形的点 -->
<template
v-for="(polygon, polygonIndex) in polygons"
:key="'points-polygon-' + polygonIndex"
>
<template
v-for="point in polygon.points"
:key="'point-' + polygonIndex + '-' + point.id"
>
<v-circle
:config="{
x: point.x,
y: point.y,
}
@contextmenu="onRightClick(polygonIndex, point.id,, $event)"
@contextmenu="onDragMove(polygonIndex, point.id,, $event)"
@mouseenter="onPolygonPointMouseEnter"
@mouseenter="onPolygonPointMouseLeave"
/>
</template>
</template>
<!-- 预览线条 -->
<!-- 临时贝塞尔曲线显示(半完成状态下) -->
<v-line
v-if="
editingMode === 'halfDone' &&
showHandles.showTempBezier &&
currentSegmentIndex !== null
"
:points="getTempBezierPoints()"
/>
</v-layer>
<v-layer ref="controlLayer">
<template
v-for="(polygon, polygonIndex) in polygons"
:key="'control-polygon-' + polygonIndex"
>
<template v-if="polygonIndex === currentPolygonIndex">
<template
v-for="(segment, segmntIndex) in polygon.segments"
:key="'control-segment-' + polygonIndex + '-' + segmentIndex"
>
<!-- 如果是贝塞尔段,就渲染两条参考线 -->
<template
v-if="
segment.type === 'bezier' &&
(segmentIndex === currentSegmentIndex || segmentIndex === currentSegmentIndex - 1)
"
>
<template
v-for="(cp, cpIndex) in segment.controlPoints"
:key="'cp-' + segmentIndex + '-' + cpIndex"
>
<!-- 1) 画控制线 -->
<v-line
v-if="shouldRenderLine(segmentIndex, cpIndex)"
:points="
getControlLinePoints(
polygon,
segment,
segmentIndex
)
"
/>
<!-- 2) 画控制点 -->
<v-rect
v-if="shouldRenderControlPoint(segmentIndex, cpIndex)"
:config="{
}
:key="'cprect-' + segmentIndex + '-' + cpIndex"
@dragmove="
onControlPointDrag(
)
"
@mouseenter="onControlPointMouseEnter"
@mouseleave="onControlPointMouseLeave"
/>
</template>
</template>
</template>
</template>
<!-- 显示大控制柄(tempC1与上一段C2的连线)和对应的参考线条 -->
<template
v-if="showHandles.showBigHandle && currentSegmentIndex !== null"
>
<v-line
:points="getP2toTempC1Line()"
/>
<v-rect :x="tempC1.x - 5" :y="tempC1.y - 5" width="10" height="10"
fill="#1984ec" stroke="#1984ec" :strokeWidth="1"
name="tempC1-handle" draggable="true" dragOnTop: true,
@dragmove="onTempC1Drag" />
</template>
</v-layer>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>