划到最后,附彩蛋,制作不易,点赏一个赞+关注吧!
++一 更新日志++
++2024.11.12 开始制作谷歌小恐龙游戏++
++2025.7.1 发布这篇文章(今日头条)++
++2025.7.23 改进这篇文章上传至CSDN++
谷歌小恐龙游戏点我下载![]() https://gitee.com/xcpcn/dinosaur-game
https://gitee.com/xcpcn/dinosaur-game
想试玩的话,谷歌浏览器可以直接输入网址打开:谷歌小恐龙![]() http://chrome://dino
http://chrome://dino
其余浏览器可以用这个网址:谷歌小恐龙中文版![]() https://dino.zone/zh-cn/
https://dino.zone/zh-cn/
如果大家对这个游戏感兴趣并且想通过自己的双手编写出来的话那我们就继续往下看吧。同时也推荐看这篇文章并且想学的朋友注意观察前后代码的区别。由于这个游戏我是自己慢慢想的(没有参考任何小恐龙跳跃游戏的代码),我也会在里面加入一些我自己的想法,因此可能我的思路并不适合每一个人,但我也依然希望你能从中学到一些有用的东西。
那么废话不多说我们开始吧。
讲解教程(千字详细)
接下来我将按照步骤一步步来展示我编写这个游戏的过程。
文章中我将采用先将结果用图片显示再解释代码的形式为大家叙述。
此外,推荐在看本文之前应掌握Python这门语言的一些基本的语法,以及对Pygame这个库有一些初步的了解,我本人推荐看这篇博客:Python游戏编程(Pygame)![]() https://weibgg.blog.csdn.net/article/details/82940350
https://weibgg.blog.csdn.net/article/details/82940350
创建窗口
既然要写一个游戏,那我们肯定需要一个窗口显示。
首先通过Pygame内置的函数创建出一个窗口。

python
import pygame
import sys
pygame.init() # 初始化pygame
size = width, height = 734, 286 # 设置窗口大小
screen = pygame.display.set_mode(size) # 显示窗口
while True: # 死循环确保窗口一直显示
for event in pygame.event.get(): # 遍历所有事件
if event.type == pygame.QUIT: # 如果单击关闭窗口,则退出
sys.exit()正文
接下来我将按照步骤一步步来展示我编写这个游戏的过程。
文章中我将采用先将结果用图片显示再解释代码的形式为大家叙述。
此外,推荐在看本文之前应掌握Python这门语言的一些基本的语法,以及对Pygame这个库有一些初步的了解创建窗口
既然要写一个游戏,那我们肯定需要一个窗口显示。
首先通过Pygame内置的函数创建出一个窗口。
python
import pygame
import sys
pygame.init() # 初始化pygame
size = width, height = 734, 286 # 设置窗口大小
screen = pygame.display.set_mode(size) # 显示窗口
background = pygame.image.load('D:/project/Python/PDL_Python/pygame/dragon/picture/background1.png') # 加载图片
backgroundrect = background.get_rect() # 获取矩形区域
while True: # 死循环确保窗口一直显示
for event in pygame.event.get(): # 遍历所有事件
if event.type == pygame.QUIT: # 如果单击关闭窗口,则退出
sys.exit()
screen.blit(background, backgroundrect) # 将图片画到窗口上
pygame.display.flip() # 更新全部显示添加静态小恐龙
接着我们让主角小恐龙登场
python
import pygame
import sys
pygame.init() # 初始化pygame
size = width, height = 734, 286 # 设置窗口大小
screen = pygame.display.set_mode(size) # 显示窗口
background = pygame.image.load('D:/project/Python/PDL_Python/pygame/dragon/picture/background1.png') # 加载图片
backgroundrect = background.get_rect() # 获取矩形区域
dragon = pygame.image.load('D:/project/Python/PDL_Python/pygame/dragon/picture/dragon1.png')
dragonrect = dragon.get_rect()
dragonrect = dragonrect.move(50,210)
while True: # 死循环确保窗口一直显示
for event in pygame.event.get(): # 遍历所有事件
if event.type == pygame.QUIT: # 如果单击关闭窗口,则退出
sys.exit()
screen.blit(background, backgroundrect) # 将图片画到窗口上
screen.blit(dragon, dragonrect)
pygame.display.flip() # 更新全部显示小恐龙原地踏步的原理是将两张图片在背景中循环播放。
程序小优化(增加小知识)
为了让下载的用户可以下载下来就使用,不需要下载代码后还需要更改地址等操作才能使用,因此特地更新一下代码。更新内容如下:
将注释更加完善。如果看不懂可以私信或者留言,我会持续改善。
使用OS库,读取文件当前目录,并合并成图片所在地址,这样读取图片时无需频繁更改路径,只需保证下载时整个文件夹保持一致就行。
代码如下:
python
import pygame
import sys
import os
#获取当前文件的目录,方便在别的电脑运行时读取相应文件
Current_path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'pygame', 'dragon', 'picture')
Current_path = Current_path.replace('\\', '/')
pygame.init() # 初始化pygame
size = width, height = 734, 286 # 设置窗口大小
screen = pygame.display.set_mode(size) # 显示窗口
clock = pygame.time.Clock() #创建一个时间对象用于控制游戏运作的快慢
background = pygame.image.load(Current_path + '/background1.png') # 加载图片
backgroundrect = background.get_rect() # 获取矩形区域
dragon1 = pygame.image.load(Current_path + '/dragon1.png')
dragon2 = pygame.image.load(Current_path + '/dragon2.png')
dragonrect = dragon1.get_rect()
dragonrect = dragonrect.move(50,210) #将小恐龙移动到"地上"
flag = True #创建一个flag标志用于在循环中判断使用哪张图片
while True: # 死循环确保窗口一直显示
clock.tick(6)
for event in pygame.event.get(): # 遍历所有事件
if event.type == pygame.QUIT: # 如果程序发现单击关闭窗口按钮
sys.exit() #将窗口关闭
screen.blit(background, backgroundrect) # 将背景图片画到窗口上
#根据flag标志确定显示的图片,这样可以造成小恐龙在跑的现象
if flag == True:
screen.blit(dragon1, dragonrect)
else:
screen.blit(dragon2, dragonrect)
flag = not flag
pygame.display.flip() # 更新全部显示背景动起来
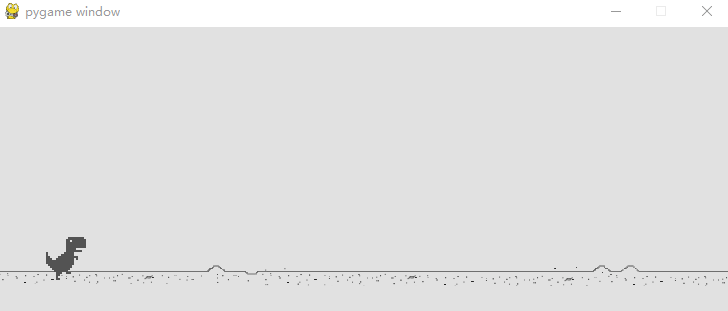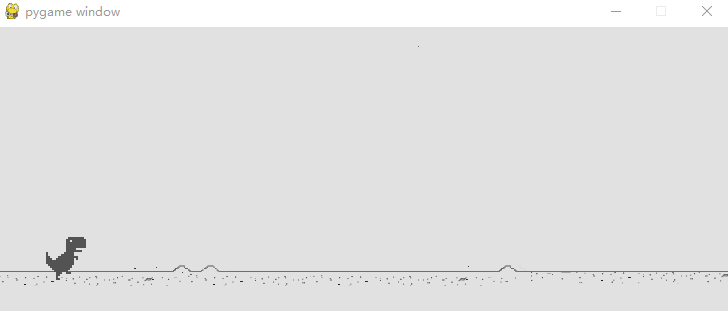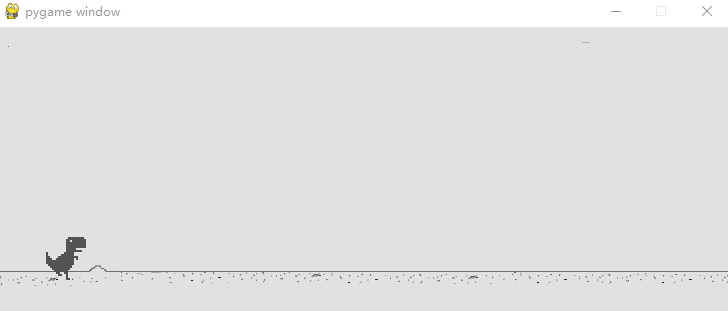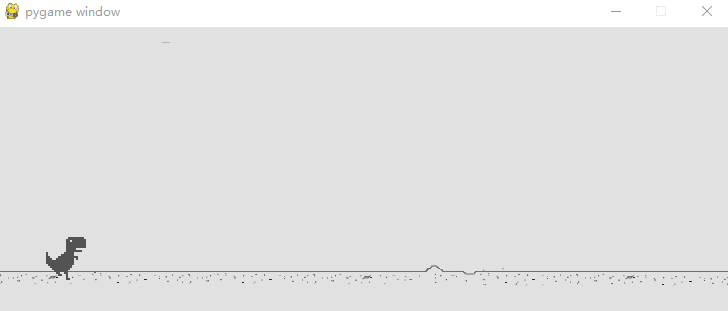
小恐龙原地踏步在加上背景移动是不是就真正让小恐龙跑起来啦!
其实实现这一步的原理很简单,我用 Tkinter(Python自带的用户交互界面设计包)设计了一个动画演示。实际上就是两张背景在后面循环移动。
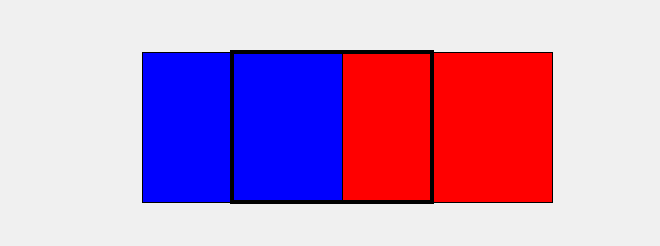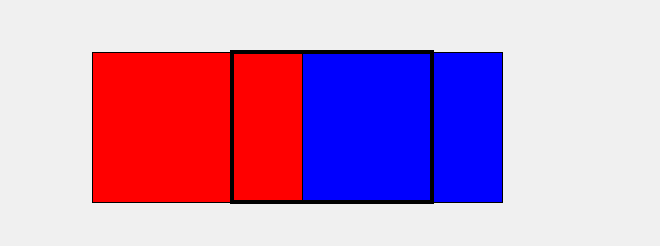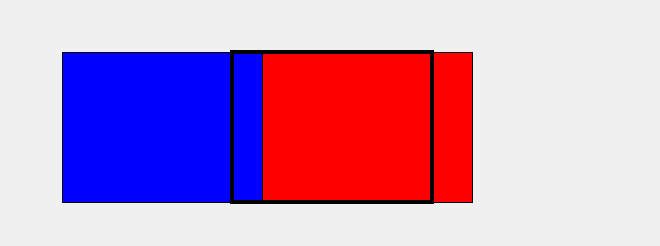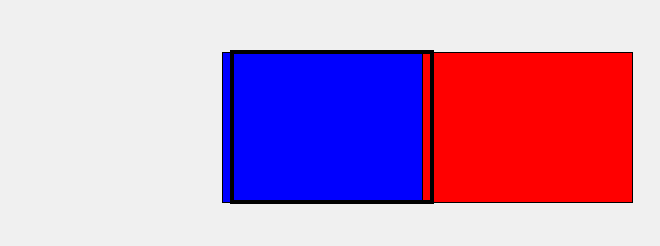
上面的图中,黑色框框代表我们游戏显示的画面,而红色和蓝色就分别是两个背景框,当我们让其"排着队"从程序窗口前滑过时就形成了背景运动的效果。
具体实现的方式是,我们去检测红色框的右边框,当其移出屏幕时,我们就让其瞬移到蓝色框后面,也就是将红色的左边框设置成和此时蓝色的左边框一致,可能有点绕,多看上面的动图就懂啦,当然,蓝色框我们也是如此操作。
下面代码改变内容为:
1.导入多一张背景图片以及设计多一个背景框
2.让背景实现循环移动(42-47行)
python
import pygame
import sys
import os
#获取当前文件的目录,方便在别的电脑运行时读取相应文件
Current_path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'picture')
Current_path = Current_path.replace('\\', '/')
pygame.init() # 初始化pygame
size = width, height = 734, 286 # 设置窗口大小
screen = pygame.display.set_mode(size) # 显示窗口
clock = pygame.time.Clock() #创建一个时间对象用于控制游戏运作的快慢
background1 = pygame.image.load(Current_path + '/background1.png') # 加载图片
background2 = pygame.image.load(Current_path + '/background2.png') # 加载图片
backgroundrect1 = background1.get_rect() # 获取矩形区域
backgroundrect2 = background2.get_rect() # 获取矩形区域
backgroundrect2[0] = backgroundrect1.right
dragon1 = pygame.image.load(Current_path + '/dragon1.png')
dragon2 = pygame.image.load(Current_path + '/dragon2.png')
dragonrect = dragon1.get_rect()
dragonrect = dragonrect.move(50, 210) #将小恐龙移动到"地上"
flag = True #创建一个flag标志用于在循环中判断使用哪张图片
while True: # 死循环确保窗口一直显示
clock.tick(6)
for event in pygame.event.get(): # 遍历所有事件
if event.type == pygame.QUIT: # 如果程序发现单击关闭窗口按钮
sys.exit() #将窗口关闭
screen.blit(background1, backgroundrect1) # 将背景图片画到窗口上
screen.blit(background2, backgroundrect2)
#根据flag标志确定显示的图片,这样可以造成小恐龙在跑的现象
if flag == True:
screen.blit(dragon1, dragonrect)
else:
screen.blit(dragon2, dragonrect)
flag = not flag
backgroundrect1 = backgroundrect1.move(-10, 0) #将背景向左移动
backgroundrect2 = backgroundrect2.move(-10, 0) #将背景向左移动
if backgroundrect1.right < 0: #判断第一个背景框如果移动到了窗口外面
backgroundrect1[0] = backgroundrect2.right #将第一个背景框移动到第二个背景框后面,形成循环
if backgroundrect2.right < 0: #和上面同理,最终实现的效果就是两个图片排着队从窗口前划过
backgroundrect2[0] = backgroundrect1.right
pygame.display.flip() # 更新全部显示小恐龙跳跃(代码大改,做好心理准备)
在做小恐龙跳跃的时候我遇到了一个难题,如何将小恐龙跳跃的速度和背景移动的速度剥离开来,如果我们玩过那个游戏的话,不难发现,随着分数的增加,背景的移动速度会越来越快,但是小恐龙的跳跃速度是不会发生改变的,我们之前小恐龙踏步的速度其实是和背景移动的速度一样的,都由全局游戏速度来控制,当背景移动越来越快,那么小恐龙跳的上下速度也会越来越快。因此我修改了大部分的代码,但我们逻辑始终没有变化,就是增加了定义类,这样更好的管理我们的代码,可以使得代码不在那么臃肿。
先上效果图:
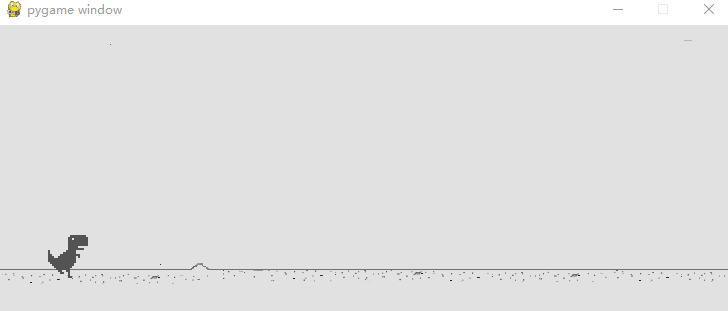
现在的小恐龙已经能检测到按键(空格或者鼠标)按下就跳跃,并且现在地图会移动得越来越快。
更新的内容:
删除了没必要的库(之前添加的又删了,我真的是闲),直接通过间接寻址获取图片,就不需要再用OS库了。换了一种关掉游戏的循环方式,也不需要sys库啦。
删除掉了很多没有必要的全局变量,增加程序的可读性同时增强程序的规范化。
用类的方式分别定义地图与小恐龙,让其分别携带自身属性,方便以后添加代码。这涉及到了类的定义,如果不太懂的同学可以去看看别的python基础教程。其中每个类里有一些默认属性,以及update函数用于更新框的位置与显示图片。
代码目录
Main.py(主文件)
python
# 导入所需的模块
import pygame
import os
import random
pygame.init()
# 全局常量
SCREEN_HEIGHT = 600
SCREEN_WIDTH = 1100
SCREEN = pygame.display.set_mode((SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_HEIGHT))
# 加载游戏中使用的图像资源
RUNNING = [pygame.image.load(os.path.join("Assets/Dino", "DinoRun1.png")),
pygame.image.load(os.path.join("Assets/Dino", "DinoRun2.png"))]
JUMPING = pygame.image.load(os.path.join("Assets/Dino", "DinoJump.png"))
DUCKING = [pygame.image.load(os.path.join("Assets/Dino", "DinoDuck1.png")),
pygame.image.load(os.path.join("Assets/Dino", "DinoDuck2.png"))]
SMALL_CACTUS = [pygame.image.load(os.path.join("Assets/Cactus", "SmallCactus1.png")),
pygame.image.load(os.path.join("Assets/Cactus", "SmallCactus2.png")),
pygame.image.load(os.path.join("Assets/Cactus", "SmallCactus3.png"))]
LARGE_CACTUS = [pygame.image.load(os.path.join("Assets/Cactus", "LargeCactus1.png")),
pygame.image.load(os.path.join("Assets/Cactus", "LargeCactus2.png")),
pygame.image.load(os.path.join("Assets/Cactus", "LargeCactus3.png"))]
BIRD = [pygame.image.load(os.path.join("Assets/Bird", "Bird1.png")),
pygame.image.load(os.path.join("Assets/Bird", "Bird2.png"))]
CLOUD = pygame.image.load(os.path.join("Assets/Other", "Cloud.png"))
BG = pygame.image.load(os.path.join("Assets/Other", "Track.png"))
# 定义小恐龙类
class Dinosaur:
X_POS = 80
Y_POS = 310
Y_POS_DUCK = 340
JUMP_VEL = 8.5
def __init__(self):
self.duck_img = DUCKING
self.run_img = RUNNING
self.jump_img = JUMPING
self.dino_duck = False
self.dino_run = True
self.dino_jump = False
self.step_index = 0
self.jump_vel = self.JUMP_VEL
self.image = self.run_img[0]
self.dino_rect = self.image.get_rect()
self.dino_rect.x = self.X_POS
self.dino_rect.y = self.Y_POS
def update(self, userInput):
# 处理小恐龙的动作状态
if self.dino_duck:
self.duck()
if self.dino_run:
self.run()
if self.dino_jump:
self.jump()
if self.step_index >= 10:
self.step_index = 0
# 根据用户输入更新小恐龙的状态
if userInput[pygame.K_UP] and not self.dino_jump:
self.dino_duck = False
self.dino_run = False
self.dino_jump = True
elif userInput[pygame.K_DOWN] and not self.dino_jump:
self.dino_duck = True
self.dino_run = False
self.dino_jump = False
elif not (self.dino_jump or userInput[pygame.K_DOWN]):
self.dino_duck = False
self.dino_run = True
self.dino_jump = False
def duck(self):
# 处理小恐龙蹲下动作
self.image = self.duck_img[self.step_index // 5]
self.dino_rect = self.image.get_rect()
self.dino_rect.x = self.X_POS
self.dino_rect.y = self.Y_POS_DUCK
self.step_index += 1
def run(self):
# 处理小恐龙奔跑动作
self.image = self.run_img[self.step_index // 5]
self.dino_rect = self.image.get_rect()
self.dino_rect.x = self.X_POS
self.dino_rect.y = self.Y_POS
self.step_index += 1
def jump(self):
# 处理小恐龙跳跃动作
self.image = self.jump_img
if self.dino_jump:
self.dino_rect.y -= self.jump_vel * 4
self.jump_vel -= 0.8
if self.jump_vel < - self.JUMP_VEL:
self.dino_jump = False
self.jump_vel = self.JUMP_VEL
def draw(self, SCREEN):
# 在屏幕上绘制小恐龙
SCREEN.blit(self.image, (self.dino_rect.x, self.dino_rect.y))
# 定义云类
class Cloud:
def __init__(self):
self.x = SCREEN_WIDTH + random.randint(800, 1000)
self.y = random.randint(50, 100)
self.image = CLOUD
self.width = self.image.get_width()
def update(self):
# 更新云的位置
self.x -= game_speed
if self.x < -self.width:
self.x = SCREEN_WIDTH + random.randint(2500, 3000)
self.y = random.randint(50, 100)
def draw(self, SCREEN):
# 在屏幕上绘制云
SCREEN.blit(self.image, (self.x, self.y))
# 定义障碍物基类
class Obstacle:
def __init__(self, image, type):
self.image = image
self.type = type
self.rect = self.image[self.type].get_rect()
self.rect.x = SCREEN_WIDTH
def update(self):
# 更新障碍物的位置
self.rect.x -= game_speed
if self.rect.x < -self.rect.width:
obstacles.pop()
def draw(self, SCREEN):
# 在屏幕上绘制障碍物
SCREEN.blit(self.image[self.type], self.rect)
# 定义小仙人掌类
class SmallCactus(Obstacle):
def __init__(self, image):
self.type = random.randint(0, 2)
super().__init__(image, self.type)
self.rect.y = 325
# 定义大仙人掌类
class LargeCactus(Obstacle):
def __init__(self, image):
self.type = random.randint(0, 2)
super().__init__(image, self.type)
self.rect.y = 300
# 定义鸟类
class Bird(Obstacle):
def __init__(self, image):
self.type = 0
super().__init__(image, self.type)
self.rect.y = 250
self.index = 0
def draw(self, SCREEN):
# 在屏幕上绘制鸟
if self.index >= 9:
self.index = 0
SCREEN.blit(self.image[self.index//5], self.rect)
self.index += 1
# 游戏主函数
def main():
global game_speed, x_pos_bg, y_pos_bg, points, obstacles
run = True
clock = pygame.time.Clock()
player = Dinosaur()
cloud = Cloud()
game_speed = 20
x_pos_bg = 0
y_pos_bg = 380
points = 0
font = pygame.font.Font('freesansbold.ttf', 20)
obstacles = []
death_count = 0
# 得分函数
def score():
global points, game_speed
points += 1
if points % 100 == 0:
game_speed += 1
text = font.render("Points: " + str(points), True, (0, 0, 0))
textRect = text.get_rect()
textRect.center = (1000, 40)
SCREEN.blit(text, textRect)
# 背景滚动函数
def background():
global x_pos_bg, y_pos_bg
image_width = BG.get_width()
SCREEN.blit(BG, (x_pos_bg, y_pos_bg))
SCREEN.blit(BG, (image_width + x_pos_bg, y_pos_bg))
if x_pos_bg <= -image_width:
SCREEN.blit(BG, (image_width + x_pos_bg, y_pos_bg))
x_pos_bg = 0
x_pos_bg -= game_speed
while run:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
run = False # 处理退出事件
SCREEN.fill((255, 255, 255))
userInput = pygame.key.get_pressed()
player.draw(SCREEN)
player.update(userInput)
if len(obstacles) == 0:
# 随机生成障碍物
if random.randint(0, 2) == 0:
obstacles.append(SmallCactus(SMALL_CACTUS))
elif random.randint(0, 2) == 1:
obstacles.append(LargeCactus(LARGE_CACTUS))
elif random.randint(0, 2) == 2:
obstacles.append(Bird(BIRD))
for obstacle in obstacles:
obstacle.draw(SCREEN)
obstacle.update()
if player.dino_rect.colliderect(obstacle.rect):
pygame.time.delay(2000)
death_count += 1
menu(death_count)
background()
cloud.draw(SCREEN)
cloud.update()
score()
clock.tick(30)
pygame.display.update()
# 菜单函数
def menu(death_count):
global points
run = True
while run:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT: # 检测窗口关闭事件
exit()
elif event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN:
main()
SCREEN.fill((255, 255, 255))
font = pygame.font.Font('freesansbold.ttf', 30)
if death_count == 0:
text = font.render("Press any Key to start", True, (0, 0, 0))
elif death_count > 0:
text = font.render("Press any Key to Restart", True, (0, 0, 0))
score = font.render("Your Score: " + str(points), True, (0, 0, 0))
scoreRect = score.get_rect()
scoreRect.center = (SCREEN_WIDTH // 2, SCREEN_HEIGHT // 2 + 50)
SCREEN.blit(score, scoreRect)
textRect = text.get_rect()
textRect.center = (SCREEN_WIDTH // 2, SCREEN_HEIGHT // 2)
SCREEN.blit(text, textRect)
SCREEN.blit(RUNNING[0], (SCREEN_WIDTH // 2 - 20, SCREEN_HEIGHT // 2 - 140))
pygame.display.update()
menu(death_count=0)添加障碍物
接下来还要填了坑有:
1、加入障碍物,鸟类
2、加入分数以及让分数和背景运动速度成正相关
图片文件如下(下载吧):











好吧,图片目录

彩蛋(划走你就后悔了)打开浏览器吧
谷歌Chrome小恐龙代码(自动跳,高跳,无敌,加速)
大多数浏览器都有自己的彩蛋,而今天我们分享的是谷歌Chrome
谷歌小恐龙游戏是一个浏览器自带的小游戏。
断网联网状态都是可以玩的
那么如何在联网的状态下进行游戏呢?
首先打开谷歌Chrome,在地址栏输入:chrome://dino/
开头写的网址终于有帮助了!
开整
自动跳代码:
html
function TrexRunnerBot() {
const makeKeyArgs = (keyCode) => {
const preventDefault = () => void 0; return {keyCode, preventDefault}; };
const upKeyArgs = makeKeyArgs(38); const downKeyArgs = makeKeyArgs(40); const startArgs = makeKeyArgs(32);
if (!Runner().playing) {
Runner().onKeyDown(startArgs); setTimeout(() => {
Runner().onKeyUp(startArgs); }, 500); }
function conquerTheGame() {
if (!Runner || !Runner().horizon.obstacles[0]) return;
const obstacle = Runner().horizon.obstacles[0];
if (obstacle.typeConfig && obstacle.typeConfig.type === 'SNACK') return;
if (needsToTackle(obstacle) && closeEnoughToTackle(obstacle)) tackle(obstacle); }
function needsToTackle(obstacle) {
return obstacle.yPos !== 50; }
function closeEnoughToTackle(obstacle) {
return obstacle.xPos <= Runner().currentSpeed * 18; }
function tackle(obstacle) {
if (isDuckable(obstacle)) {
duck(); } else {
jumpOver(obstacle); }
}
function isDuckable(obstacle) {
return obstacle.yPos == 75; }
function duck() {
drop(); Runner().onKeyDown(downKeyArgs);
setTimeout(() => {
Runner().onKeyUp(downKeyArgs); }, 500); }
function drop() {
Runner().onKeyDown(downKeyArgs);
Runner().onKeyUp(downKeyArgs); }
function jumpOver(obstacle) {
if (isNextObstacleCloseTo(obstacle))
jumpFast(); else
Runner().onKeyDown(upKeyArgs); }
function isNextObstacleCloseTo(currentObstacle) {
const nextObstacle = Runner().horizon.obstacles[1];
return nextObstacle && nextObstacle.xPos - currentObstacle.xPos <=
Runner().currentSpeed * 42; }
function jumpFast() {
Runner().onKeyDown(upKeyArgs); Runner().onKeyUp(upKeyArgs); }
return {conquerTheGame: conquerTheGame}; }
let bot = TrexRunnerBot(); let botInterval = setInterval(bot.conquerTheGame, 2);无敌代码:
html
Runner.instance_.gameOver=function(){} 疾跑代码(可以改括号内参数):
html
Runner.instance_.setSpeed(50) 大家都明白了吗,有问题到评论区评论哦~
快在信息课的时候给别人炫耀炫耀吧